Iron Mountain Bundle
How did Iron Mountain rise from Cold War fears to a global data giant?
In a world awash in data, Iron Mountain's story is a fascinating tale of adaptation and foresight. Founded in 1951 with a unique mission, the company's origins are rooted in the Cold War era, offering a secure haven for vital corporate records. From storing documents in repurposed mines to becoming a leader in information management, Iron Mountain's journey is a testament to its resilience.

Iron Mountain's Iron Mountain SWOT Analysis reveals the strategic moves that propelled it forward. Originally conceived to protect against nuclear threats, the company has consistently evolved to meet the changing needs of businesses. Today, it offers comprehensive records management and data storage solutions worldwide, solidifying its position as a critical player in the information age. This brief history of Iron Mountain company highlights its remarkable transformation.
What is the Iron Mountain Founding Story?
The Iron Mountain story is rooted in the vision of Herman Knaust, a man who made his mark in the mushroom industry. In 1936, Knaust made a significant investment, purchasing an old iron ore mine in Kingston, New York. This purchase set the stage for what would become a leading player in the records management and data storage sectors.
Initially, Knaust intended to use the mine to expand his mushroom cultivation operations. However, market changes led him to explore other uses for the property. The mine, which he had already named 'Iron Mountain,' would soon become the foundation of a pioneering business model.
The Cold War era provided the perfect backdrop for Knaust's innovative idea. He recognized the need for secure, off-site storage to protect vital corporate information from potential threats. This insight, combined with his personal experiences, led to the founding of Iron Mountain Atomic Storage Corporation in 1951.
Iron Mountain's early days were marked by a focus on providing secure storage for critical corporate records, a service driven by the anxieties of the Cold War. The company's first customer was East River Savings Bank.
- In 1951, Iron Mountain opened its first underground 'vaults'.
- The first sales office was in the Empire State Building.
- The initial business model focused on bomb-resistant storage for vital corporate records.
- Knaust's initial investment likely came from his mushroom business.
The company's early commitment to security was evident from the start. Knaust's purchase of a 28-ton bank vault door, despite the high shipping costs, highlighted the importance of safeguarding sensitive information. The cultural and economic context of the Cold War played a significant role in Iron Mountain's creation. Businesses sought to protect their critical information assets from the widespread anxieties of the time.
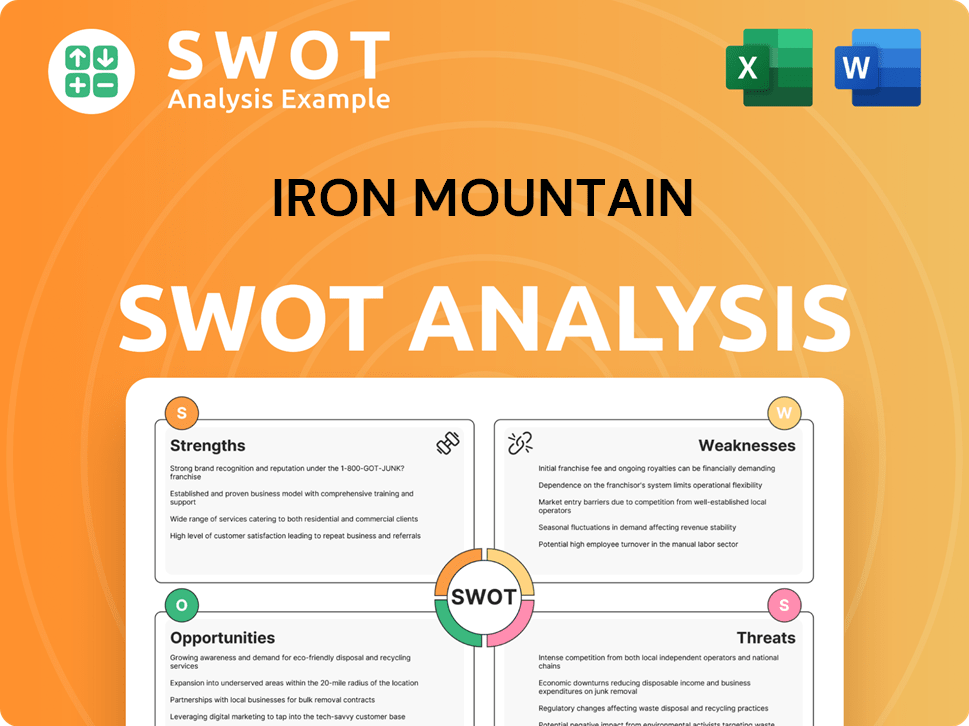
Iron Mountain SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Iron Mountain?
The early growth of the company, now known as Iron Mountain, was marked by strategic expansion beyond its initial base, driven by the increasing need for secure information management. This expansion involved significant acquisitions and a shift towards digital asset management. The company's growth trajectory is a key part of the brief history of Iron Mountain company, reflecting its adaptation to evolving market demands.
After establishing its first above-ground records-storage facility, the company expanded to Rhode Island in 1980 by acquiring a former Industrial National Bank cold site and data tape repository. This move marked its entry into New England. Boston eventually became its world headquarters. By the early 1980s, the company was generating around $6 million in revenue and serving numerous Fortune 500 clients.
A major expansion occurred in 1988 with the acquisition of Bell & Howell Records Management, Inc., extending its presence into 12 additional U.S. markets. The company went public on January 31, 1996, after reaching an annual revenue of $100 million. In 1997, the company became a leading software escrow company through the acquisition of Data Securities International (DSI).
The company made its first overseas acquisition in 1998, buying British Data Management, Ltd., and reported $423 million in revenue by the end of that fiscal year. The early 2000s saw continued aggressive growth through acquisitions. In February 2000, the company acquired Pierce Leahy Corp. for approximately $1.1 billion, further consolidating its market position.
In 2004, the company formed 'Iron Mountain Digital' after acquiring Connected Corporation, a developer of online PC backup software, and a year later, it acquired LiveVault, an online backup software provider for server data. By 2007, the company's revenue had surged to $2.7 billion from $3 million in 1981, largely due to these expansion efforts. In 2012, the company expanded its high-security storage facilities and began operating as a REIT on January 1, 2014. For more information, you can check out the Competitors Landscape of Iron Mountain.
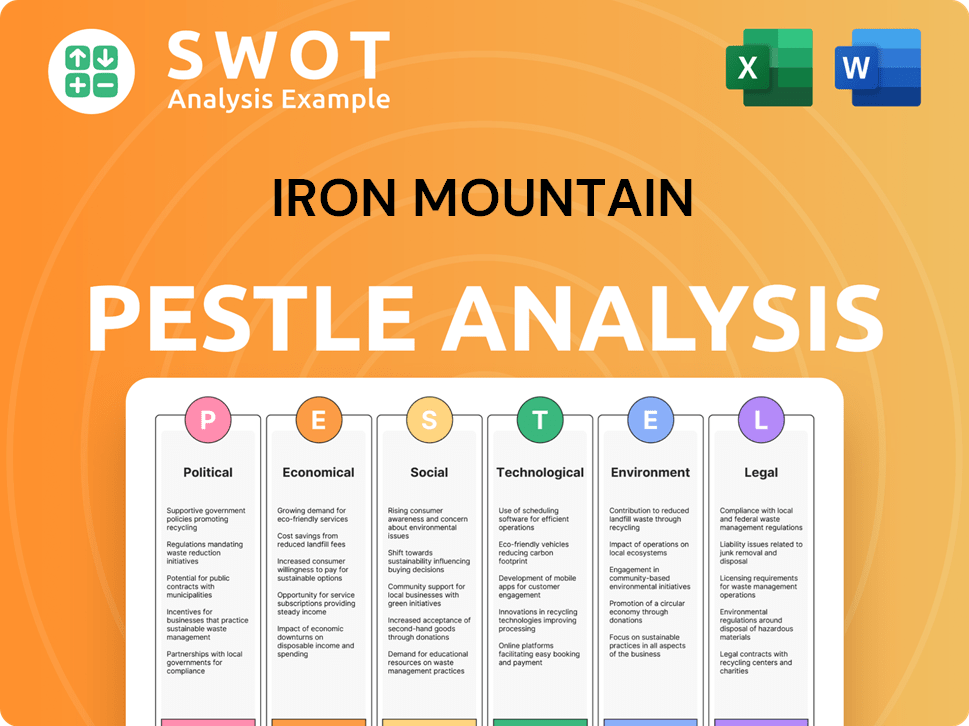
Iron Mountain PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Iron Mountain history?
The Iron Mountain company's journey is marked by significant milestones that have shaped its evolution in the records management and data storage industry. From its humble beginnings to its current status as a global leader, the company has consistently adapted and innovated to meet the changing needs of its clients.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| Mid-1980s | Became the first records management company to use UPC bar codes for real-time access to shipped boxes and documents, improving efficiency. |
| 1999 | Expanded Records Management and Data Security services to include records, film, and sound archive storage, diversifying offerings. |
| 2001 | Selected by ICANN to protect registry data via escrow agreements, demonstrating its trusted position in information protection. |
| 2004 | Formed Iron Mountain Digital, expanding into online data backup and recovery. |
| August 2024 | Launched the InSight Digital Experience Platform (DXP), integrating physical and digital data and automating workflows. |
Iron Mountain has consistently embraced innovation to stay ahead in the data storage and archiving services market. A key move was the adoption of UPC bar codes in the mid-1980s, revolutionizing access to documents. More recently, the company has integrated artificial intelligence (AI) into its operations, particularly with the InSight DXP, to streamline processes and enhance data security.
In the mid-1980s, Iron Mountain became the first records management company to use UPC bar codes. This innovation significantly improved the efficiency of accessing and managing shipped boxes and documents.
The formation of Iron Mountain Digital in 2004 marked a strategic move into online data backup and recovery. This expansion positioned the company to meet the growing demand for digital storage solutions.
Launched in August 2024, the InSight DXP integrates physical and digital data. This platform automates workflows and makes data AI-ready for actionable insights, streamlining processes.
Despite its successes, Iron Mountain faces several challenges in the dynamic business environment. Adapting to rapid technological advancements, maintaining customer trust in data security amidst rising cyber threats, and navigating a competitive landscape are key areas of focus. The company's ability to address these challenges will be crucial for its continued growth and success.
Cybercrime is forecasted to reach $10.5 trillion in 2025, highlighting the need for robust cybersecurity solutions. Iron Mountain must continuously enhance its security measures to protect sensitive data.
Dealing with sensitive information across various geographies leads to complex regulatory compliance requirements. Iron Mountain needs to adapt to evolving data protection laws.
Environmental sustainability is a growing challenge, requiring Iron Mountain to address its carbon footprint. Implementing sustainable practices is essential for long-term viability.
The records management and data storage market is competitive with new market entrants. Iron Mountain must differentiate its services to maintain its market share.
Rapid technological advancements require continuous adaptation and investment. Iron Mountain must stay at the forefront of technology to remain competitive.
Maintaining customer trust in data security is paramount, especially with increasing cyber threats. Iron Mountain must ensure robust cybersecurity measures to protect client data.
Iron Mountain has responded to these challenges through strategic pivots and investments. The 'Matterhorn growth strategy' focuses on expanding high-margin digital and data center services. This strategy has led to significant growth in these segments, with data center revenue climbing by 25% in 2024 to a record $620 million, and digital solutions also reaching record revenue levels in 2024, driven by SaaS-based platforms and AI adoption. For more details on the company's financial performance and ownership structure, you can read more about the Owners & Shareholders of Iron Mountain.
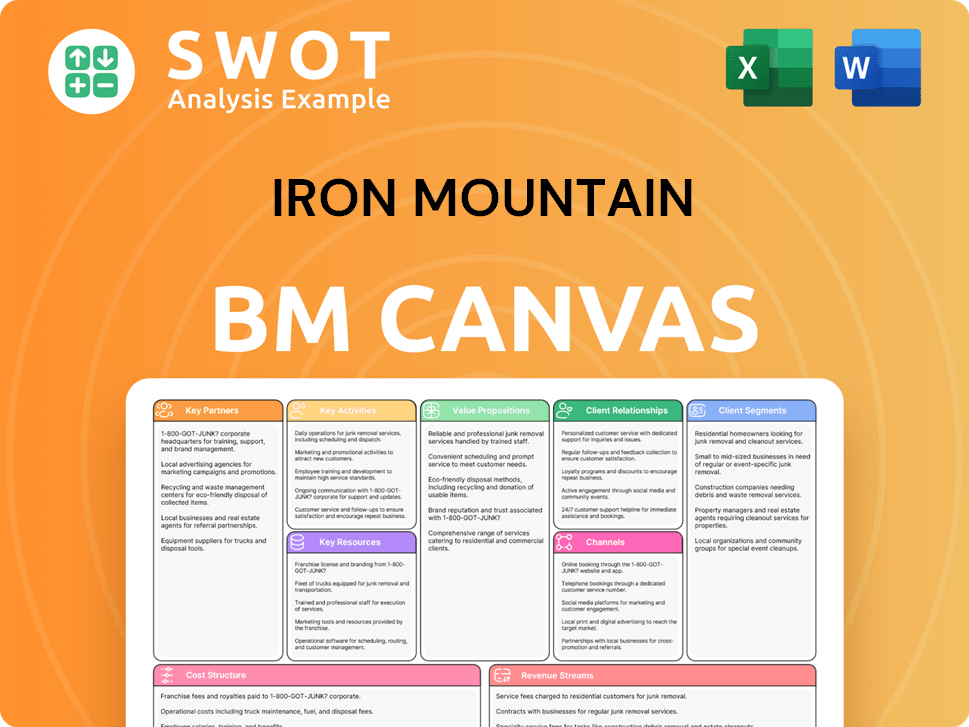
Iron Mountain Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Iron Mountain?
The Iron Mountain history is marked by significant milestones that have shaped its evolution from a secure storage provider to a comprehensive information management company. Initially founded in 1951, the company has expanded its services and global presence through strategic acquisitions and innovative solutions.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1951 | Founded as Iron Mountain Atomic Storage Corporation in Livingston, NY, offering bomb-resistant underground storage. |
| 1978 | Opened its first above-ground records-storage facility. |
| 1988 | Acquired Bell & Howell Records Management, Inc., expanding its reach to 12 more U.S. markets. |
| 1996 | Went public on January 31, reaching $100 million in annual revenue. |
| 2000 | Acquired Pierce Leahy Corp. for approximately $1.1 billion. |
| 2004 | Formed 'Iron Mountain Digital' after acquiring Connected Corporation, expanding into online PC backup. |
| 2014 | Began operating as a REIT. |
| 2017 | Acquired FORTRUST and IO Data Centers, significantly expanding its data center footprint. |
| 2024 | Achieved record revenue of $6.15 billion, up 12.2% from 2023, and adjusted EBITDA reached an all-time high of $2.24 billion. |
| 2025 (Q1) | Reported record quarterly revenue of $1.6 billion, up 7.8% year-over-year. Data center revenue grew 20.3%, and digital services and asset lifecycle management (ALM) collectively grew over 20% organically. |
In 2024, the company achieved record revenue of $6.15 billion, marking a 12.2% increase from the previous year. Adjusted EBITDA reached an all-time high of $2.24 billion. The first quarter of 2025 saw record quarterly revenue of $1.6 billion, a 7.8% increase year-over-year.
The 'Matterhorn growth strategy' focuses on data centers, digital services, and asset lifecycle management. The company plans to lease 125 megawatts in its data center segment for 2025. Digital services and asset lifecycle management (ALM) collectively grew over 20% organically in Q1 2025.
The company anticipates 2025 revenue to be between $6.74 billion and $6.89 billion, representing approximately 11% growth. Adjusted EBITDA is projected to rise by 13%, reaching between $2.505 billion and $2.555 billion. The focus remains on expanding its global presence and offering innovative data management solutions.
Increasing data regulations and the shift towards digital storage are influencing the company's future. AI is being leveraged to revolutionize information lifecycle management. The InSight Digital Experience Platform enables organizations to unlock insights from both physical and digital data, positioning the company for sustained growth.
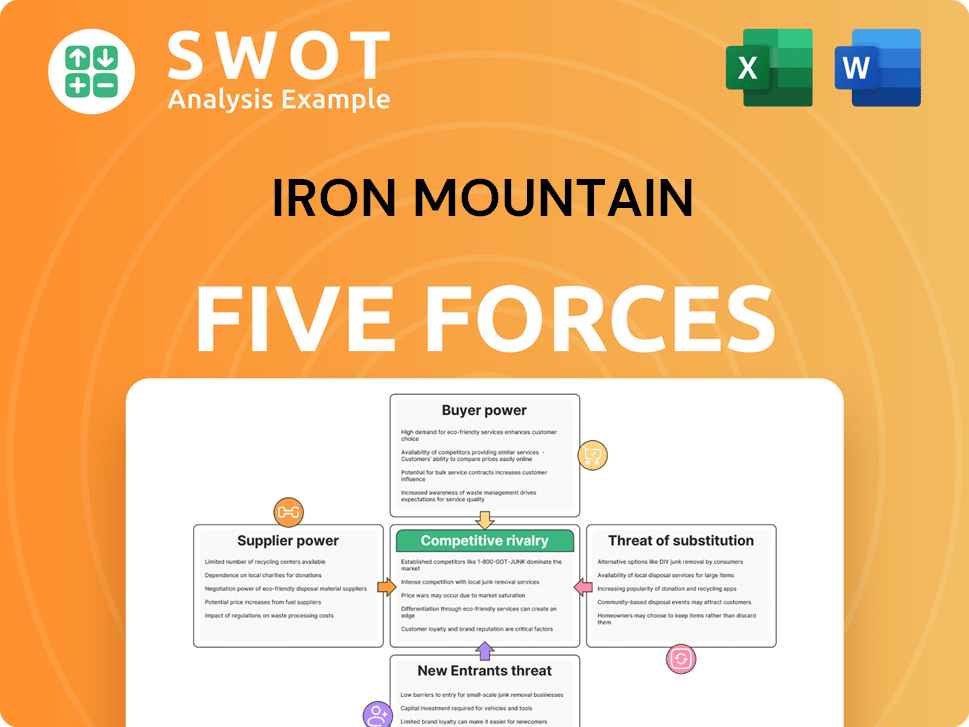
Iron Mountain Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Iron Mountain Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Iron Mountain Company?
- How Does Iron Mountain Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Iron Mountain Company?
- What is Brief History of Iron Mountain Company?
- Who Owns Iron Mountain Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Iron Mountain Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.