Japan Airlines Bundle
How has Japan Airlines Navigated the Skies of Global Aviation?
From its humble beginnings in post-war Japan, Japan Airlines (JAL) has soared to become a global aviation giant, embodying the nation's dedication to excellence. Established to rebuild and connect Japan, the airline quickly expanded beyond domestic routes, becoming a symbol of innovation and reliability. Discover the captivating Japan Airlines SWOT Analysis to get a comprehensive overview.

This exploration into JAL history will uncover the pivotal moments that shaped its trajectory, from its early days as a domestic carrier to its international expansion, including its first flights and the challenges it overcame. We'll delve into the airline's strategic adaptations, its financial performance, and its enduring impact on the airline industry Japan, examining its role in Japanese aviation and its future plans. The journey of Japan Airlines company is a testament to resilience and strategic foresight.
What is the Japan Airlines Founding Story?
The story of Japan Airlines (JAL) began on August 1, 1951. The company was established with an initial capital of ¥100 million, marking the start of a journey that would transform the Japanese aviation industry. The founding was a direct response to the Japanese government's vision for a strong air transport system, essential for rebuilding and fostering growth after World War II.
Initially, JAL relied on leased aircraft and outsourced operations to get off the ground. This strategic approach allowed the fledgling airline to navigate the complexities of post-war Japan. The company's focus was on establishing a reliable domestic air network, connecting key cities and supporting the nation's recovery.
The early days of Japan Airlines saw significant milestones. The first post-war domestic flight took off on October 25, 1951, using a Martin 2-0-2 aircraft named 'Mokusei'. Before this, invitational flights were conducted between August 27 and 29, 1951, using a Douglas DC-3 'Kinsei'. These initial flights were crucial in setting the stage for JAL's future. The government's support was critical to the airline's early success, as was the strategic decision to lease aircraft and outsource operations.
The establishment of Japan Airlines was a pivotal moment in the Japanese aviation industry. JAL's early operations involved leased aircraft and outsourced services, allowing it to quickly establish a presence in the market. The Japan Airlines Company Act of 1953 transformed JAL into a state-owned enterprise, enabling significant growth.
- August 1, 1951: Japan Airlines Co., Ltd. was founded with ¥100 million in capital.
- October 25, 1951: First post-war domestic airline service commenced.
- August 1, 1953: The Japan Airlines Company Act was passed.
- October 1, 1953: JAL became a state-owned enterprise with ¥2 billion in capital.
The transition to a state-owned enterprise on October 1, 1953, marked a turning point for JAL. The Japan Airlines Company Act of 1953 provided the framework for this transformation. With a capital of ¥2 billion, JAL took over all assets and liabilities from its private predecessor, setting the stage for rapid expansion. This transition was critical for JAL's ability to grow and become Japan's flag carrier. This strategic move allowed the airline to secure necessary resources and support for its expansion.
JAL's early business model centered on providing scheduled domestic air transportation services, linking major Japanese cities. The airline's focus on domestic routes was a strategic move, supporting the nation's recovery and growth. The company's early operations set the stage for its future growth and international expansion. For more details on the company's financial aspects, you can read about the Revenue Streams & Business Model of Japan Airlines.
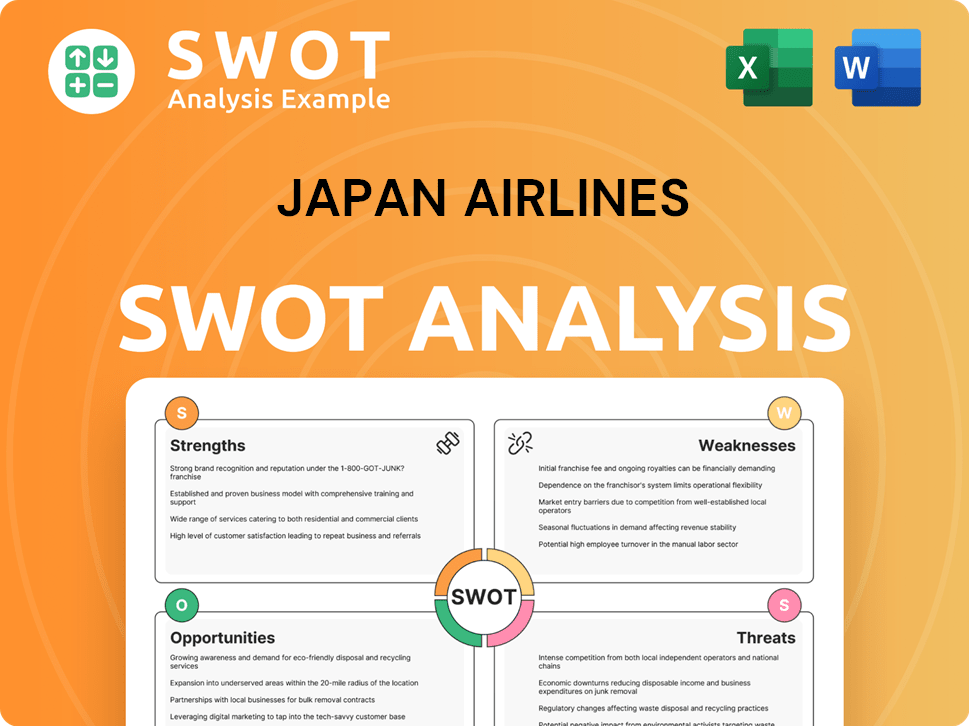
Japan Airlines SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Japan Airlines?
The early years of Japan Airlines, or JAL, were marked by rapid expansion and the establishment of its presence in the global airline industry. The company quickly grew its domestic network, connecting major Japanese cities. This period also saw the launch of its first international flights, setting the stage for future global operations.
In the early days, Japan Airlines focused on building a strong domestic network. By 1953, JAL connected Tokyo with cities like Sapporo, Nagoya, and Fukuoka. This expansion was crucial for establishing a solid foundation in the Japanese aviation market. This growth set the stage for its later international ambitions.
A significant milestone was achieved on February 2, 1954, with JAL's inaugural international flight. The flight carried 18 passengers from Tokyo to San Francisco via Wake Island and Honolulu. The one-way fare for this service was ¥234,000. The aircraft, a Douglas DC-6B, was named 'City of Tokyo'.
The 1960s were a period of significant modernization and global expansion for JAL. The airline introduced jet aircraft, such as the Douglas DC-8, which enabled faster and longer flights. International routes expanded to Europe, Asia, and Oceania, including cities like Moscow and New York. In 1967, JAL became the first airline to offer non-stop flights between Tokyo and New York.
The 'Tsurumaru' (crane motif) logo was introduced during the 1960s. This logo, a symbol of longevity and good fortune in Japanese culture, became a key element of JAL's branding. The logo helped create a recognizable identity for the airline as it expanded its global presence. The branding was crucial for establishing a strong identity.
During the 1970s and 1980s, JAL continued its growth, adding new aircraft, such as the Boeing 747 and McDonnell Douglas DC-10. In 1983, JAL ranked first in international scheduled flight traffic, with a 5.6% year-on-year increase to 4,559 million ton/kilometers. This period also saw the airline's full privatization in 1987.
By 1995, JAL's network included 99 domestic routes and numerous international routes. The airline had 64 offices in Japan and international offices in Seoul and Guangzhou. The establishment of a mileage program during this time further enhanced customer loyalty. This strategic shift was crucial for the airline's long-term success.
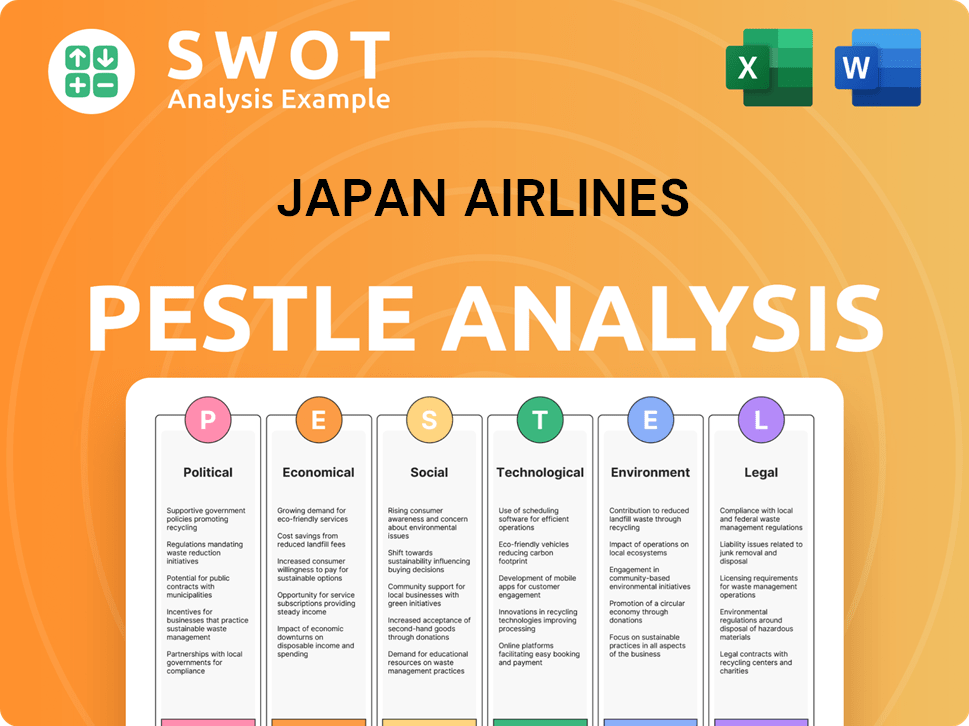
Japan Airlines PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Japan Airlines history?
Throughout its history, Japan Airlines has achieved numerous milestones, solidifying its place in the Japanese aviation industry. From its early beginnings to its current standing, the JAL history is marked by significant achievements in a competitive market. The airline has consistently adapted to changing market conditions and technological advancements, shaping its legacy.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1951 | Japan Airlines was re-established as the national flag carrier after World War II, marking the beginning of its post-war development. |
| 1960s | Introduction of jet aircraft like the Douglas DC-8, which enabled faster and longer international flights, including the pioneering non-stop service between Tokyo and New York in 1967. |
| 1960s | Adoption of the iconic 'Tsurumaru' crane logo, becoming a lasting symbol of the airline's identity and Japanese hospitality. |
| 2007 | Japan Airlines joined the Oneworld alliance, enhancing its global network and partnerships, expanding its international expansion. |
| 2010 | Filed for bankruptcy protection and underwent a comprehensive restructuring plan. |
| 2024 | Recognized as the top airline in the Asia-Pacific region for On-time Performance with 80.90% punctuality. |
Japan Airlines has consistently embraced innovation to enhance its services and operational efficiency. The airline's early adoption of jet aircraft revolutionized international travel, significantly reducing flight times and improving passenger experience. Furthermore, Japan Airlines continually invests in its fleet and technology to maintain its competitive edge in the airline industry Japan.
The introduction of jet aircraft, such as the Douglas DC-8, marked a significant technological advancement, enabling faster and longer international flights.
The adoption of the 'Tsurumaru' crane logo in the 1960s became a lasting symbol of the airline's identity and Japanese hospitality, enhancing brand recognition.
Japan Airlines has continuously modernized its fleet with fuel-efficient aircraft to reduce operating costs and environmental impact.
The airline has consistently focused on improving operational efficiency, as demonstrated by its top ranking in the Asia-Pacific region for on-time performance in 2024.
Japan Airlines aims to substitute 1% of total onboard fuel with Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) by 2025, increasing to 10% by 2030, reflecting its commitment to environmental sustainability.
Japan Airlines consistently receives recognition for its service quality, earning a '5 Star' certification from Skytrax for seven consecutive years.
Throughout its history, Japan Airlines has faced and overcome numerous challenges. The 1990s and early 2000s saw increased competition and economic downturns, leading to financial losses. More recently, the airline has had to adapt to challenges such as pilot shortages and the closure of Russian airspace, which has impacted flight routes.
The airline faced significant financial struggles, culminating in bankruptcy protection in 2010, requiring extensive restructuring to regain stability.
The crash of Japan Airlines Flight 123 on August 12, 1985, resulted in the loss of 520 lives, a tragic event that profoundly impacted the company and its safety record.
Rising competition, particularly from low-cost carriers, has put pressure on Japan Airlines to maintain its market share and profitability.
The airline industry Japan, including Japan Airlines, has been facing pilot shortages, affecting operational capacity and flight schedules.
The closure of Russian airspace has led to longer flight times and increased fuel consumption on certain routes, impacting operational costs.
With foreign visitors now constituting 70% of its travelers, Japan Airlines has had to adapt its onboard experience and marketing to cater to a growing international audience.
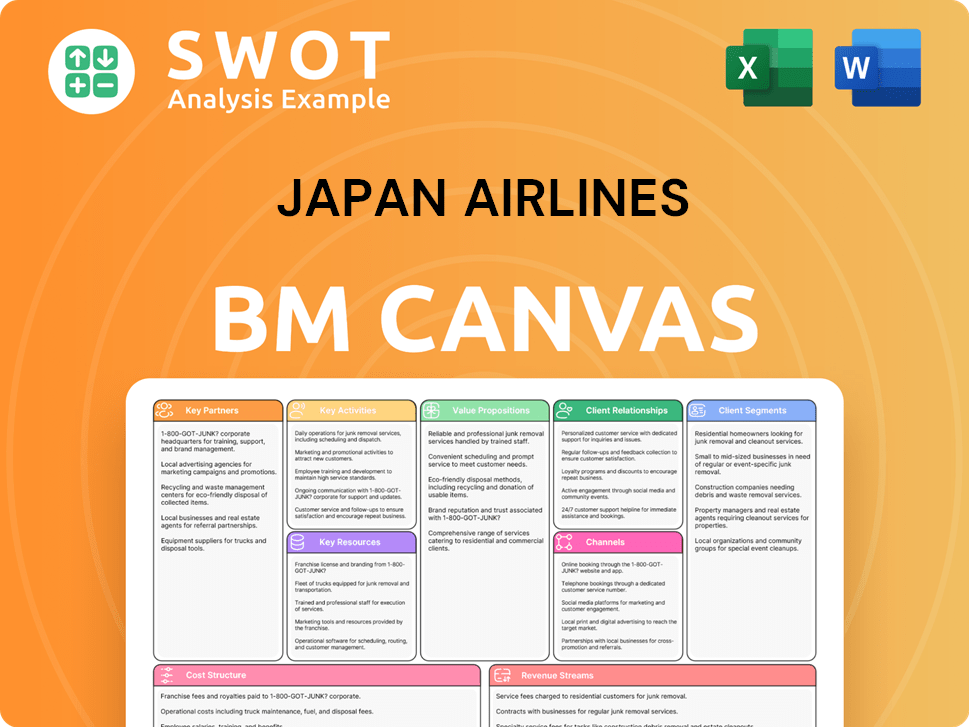
Japan Airlines Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Japan Airlines?
The JAL history is marked by significant milestones, from its post-war beginnings to its current status as a leading global airline. Established in 1951, it quickly became a key player in Japanese aviation, expanding internationally and adapting to technological advancements. The airline has faced challenges, including major accidents and financial difficulties, but has consistently evolved, integrating with other airlines and embracing new technologies and sustainability initiatives to remain competitive in the airline industry Japan.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| August 1, 1951 | Japan Airlines (original company) was established with ¥100 million capital in Ginza, Chūō, Tokyo. |
| October 25, 1951 | Japan's first post-war domestic airline service was inaugurated. |
| February 2, 1954 | First international flights were launched, connecting Tokyo to San Francisco via Wake Island and Honolulu. |
| 1967 | First airline to offer non-stop flights between Tokyo and New York. |
| 1970 | Introduction of the Boeing 747, a significant advancement in aviation. |
| 1983 | Ranked first globally in international scheduled flight traffic by IATA. |
| August 12, 1985 | Japan Airlines Flight 123 accident, a tragic event in JAL history. |
| 1987 | The company completed full privatization. |
| 2002 | Business integration with Japan Air System (JAS) occurred. |
| March 1, 2007 | Joined the Oneworld alliance, expanding its global network. |
| January 19, 2010 | Filed for reorganization proceedings under the Corporate Reorganization Act. |
| 2012 | Achieved peak profitability, becoming one of the most profitable airlines globally. |
| 2020 | Became the first Japanese airline to set a target of achieving net-zero CO2 emissions by 2050. |
| 2024 | Recognized as the top airline in the Asia-Pacific region for On-time Performance. |
| May 2025 | First passenger flight from KIX supplied with commercialized domestic SAF. |
The JAL Group aims for an EBIT of JPY 200 billion for fiscal year 2025, driven by growth in international flights and other revenue streams. For FY2025-26, JAL forecasts revenue of JPY 1,977.0 billion and a net profit of JPY 115.0 billion, reflecting a strong recovery and strategic financial planning.
JAL plans to modernize its fleet significantly, including the addition of 17 Boeing 737-8 aircraft and 11 Airbus A321neo aircraft, primarily for domestic routes. International operations will see the introduction of ten Boeing 787-9 aircraft and 20 Airbus A350-900s, enhancing operational efficiency and passenger experience.
By fiscal year 2030, JAL expects its international business to grow by approximately 1.5 times compared to 2023 levels. A particular focus will be on expanding services to North America and Asia, capitalizing on growing travel demands in these regions.
JAL is committed to sustainable aviation, aiming to substitute 1% of its total onboard fuel with Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) by 2025 and 10% by 2030. The airline has a long-term goal of virtually zero CO2 emissions by 2050 and is actively pursuing partnerships for SAF production.
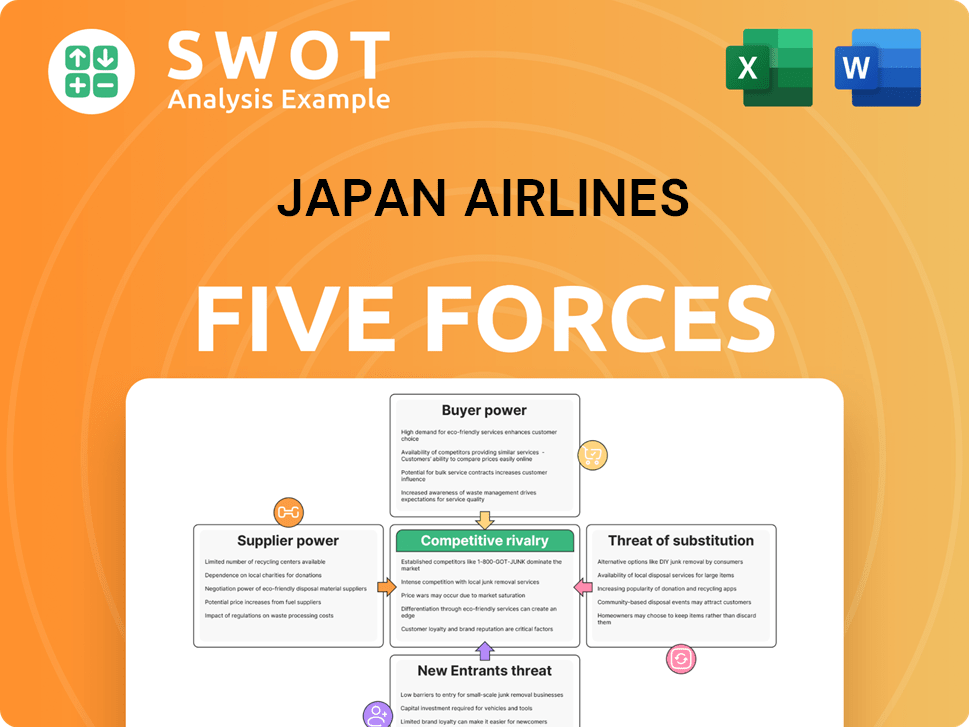
Japan Airlines Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Japan Airlines Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Japan Airlines Company?
- How Does Japan Airlines Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Japan Airlines Company?
- What is Brief History of Japan Airlines Company?
- Who Owns Japan Airlines Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Japan Airlines Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.