Nissan Motor Bundle
How did Nissan Motor Company become a global automotive giant?
Journey back in time to explore the fascinating Nissan Motor SWOT Analysis and the evolution of a Japanese car manufacturer. From its humble beginnings in 1911 as Kaishinsha Motor Car Works, producing the DAT, to its official establishment in 1933, Nissan's history is a testament to innovation and resilience. Discover the key milestones and pivotal moments that shaped this automotive powerhouse.
This brief history of Nissan cars reveals a company that has weathered significant market challenges, including a net loss in fiscal year 2024, yet maintains a strong financial position. Explore the Nissan timeline, from the early Nissan models to its global expansion, and understand the impact of key figures like Nissan founder Yoshisuke Aikawa. Learn how Nissan's commitment to innovation, particularly in electric vehicles, positions it for the future.
What is the Nissan Motor Founding Story?
The story of the Owners & Shareholders of Nissan Motor begins in early 20th-century Japan. It's a tale of ambition, innovation, and the transformation of a nation's industrial landscape. The journey of this Japanese car manufacturer started with a small workshop and evolved into a global automotive powerhouse.
The roots of the company can be traced back to March 1914, with the establishment of Kwaishinsha Motor Car Works, founded by Masujiro Hashimoto in Tokyo. This marked Japan's initial steps into automobile manufacturing. The first vehicle, named DAT, was an acronym derived from the surnames of its three initial investors: Kenjiro Den, Rokuro Aoyama, and Meitaro Takeuchi.
The official establishment of Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. occurred on December 26, 1933, in Yokohama. Jidosha Seizou KK (Automobile Manufacturing Co.) was jointly founded by Nihon Sangyo and Tobata Imono. Yoshisuke Aikawa, who became president of Nihon Sangyo in 1928, was instrumental in this formation. The name 'Nissan' itself originated in the 1930s as an abbreviation used on the Tokyo Stock Exchange for Nihon Sangyo, a holding company founded by Aikawa. The company officially became Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. on May 30, 1934, when Jidosha Seizou KK was renamed and became a wholly owned subsidiary of Nihon Sangyo.
Here are some of the key milestones in the Nissan history.
- 1914: Kwaishinsha Motor Car Works founded.
- 1933: Jidosha Seizou KK established.
- 1934: Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. officially formed.
- 1930s-1940s: Early models and wartime production.
- Post-WWII: Rebuilding and expansion.
Aikawa's vision was to build a robust automobile manufacturing industry in Japan. The initial capital for Jidosha Seizou KK was 10 million yen, with Nihon Sangyo contributing six million yen and Tobata Imono contributing four million yen. Despite challenges, these foundational efforts laid the groundwork for Nissan to become one of the world's leading automobile manufacturers. The company's early focus was on producing vehicles for the domestic market, gradually expanding its reach. By the late 1950s and early 1960s, Nissan began exporting its vehicles, marking the start of its global expansion. This period saw the introduction of iconic models and strategic partnerships that propelled Nissan's growth.
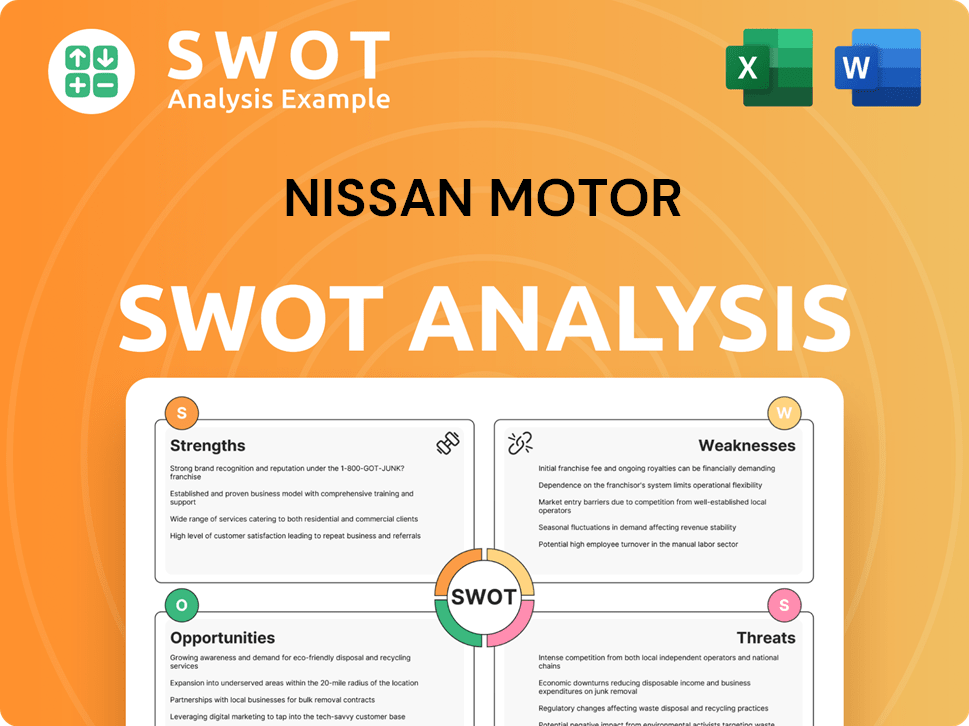
Nissan Motor SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Nissan Motor?
Following its establishment in 1933, Nissan Motor Company experienced significant early growth and expansion, evolving from its foundational efforts to a more prominent role in the automotive industry. This period saw the introduction of key models and the beginning of international ventures. These strategic moves were crucial in shaping Nissan's trajectory and securing its position in the global automotive landscape.
A pivotal early product was the Datsun Type 15, launched in 1937, marking Japan's first mass-produced vehicle. This model was available in various forms, including phaeton, mini pick-up, and delivery van, showcasing Nissan's early diversification in vehicle types. The company continually expanded its product offerings.
Nissan began its international expansion, notably entering the U.S. market in 1958 with the Datsun 1000. This was followed by the Datsun 1200 in 1961 and a compact pickup truck in 1959. These early models helped establish its reputation in America.
In the early 1980s, Nissan, like other Japanese car manufacturers, started establishing manufacturing plants in the United States. Nissan Motor Company USA was founded in 1980. The Smyrna assembly plant initially produced trucks.
The Smyrna facility has since expanded to produce a wider range of vehicles, including popular models like the Nissan Altima, Maxima, Rogue, Pathfinder, Infiniti QX60, and the Nissan Leaf electric car. The Nissan timeline shows that this was a crucial step. For more insights, explore the Marketing Strategy of Nissan Motor.
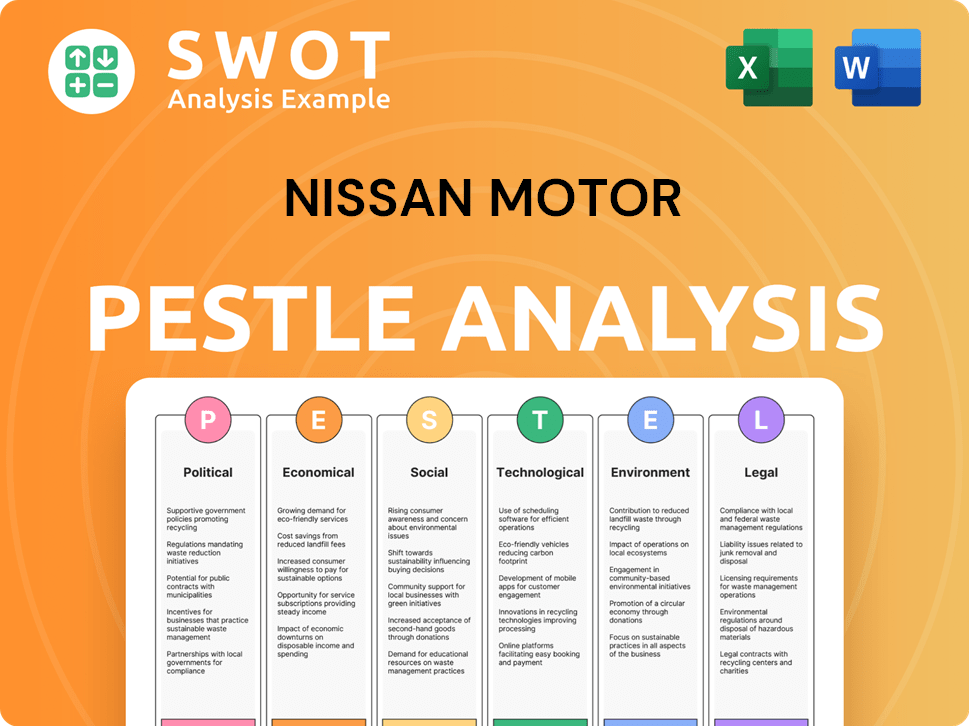
Nissan Motor PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Nissan Motor history?
The Nissan Motor Company, a prominent Japanese car manufacturer, has a rich history marked by significant milestones. From its origins in Japan to its global expansion, the company has navigated numerous challenges and celebrated key achievements, shaping its trajectory over time.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| Early 1900s | The origins of the company trace back to the Kwaishinsha Motor Car Works, which produced its first car in 1911. |
| 1930s | The company adopted the name Nissan and began producing vehicles under that brand. |
| Post-World War II | Nissan rebuilt its operations and expanded, eventually acquiring Datsun. |
| 1980s-1990s | Nissan expanded globally, establishing a strong presence in various markets. |
| 2010s | The introduction of the Nissan Leaf marked a significant step in electric vehicle (EV) technology. |
| 2024 | Nissan continues to innovate and adapt to the changing automotive landscape, focusing on electrification and global market strategies. |
Nissan has consistently pushed boundaries in automotive innovation, particularly in electric vehicles. The introduction of the Nissan Leaf, one of the first mass-market EVs, showcased the company's early commitment to electrification and innovation in the automotive sector.
Nissan was an early leader in electric vehicles with the launch of the Leaf, demonstrating a forward-thinking approach to sustainable mobility. In 2024, Nissan sold 20,616 EVs in the U.S., highlighting its continued focus on this technology.
The company plans to launch 34 electrified models worldwide from fiscal year 2024 through 2030, aiming for electrified models to account for 40% of global sales by FY2026 and 60% by the end of the decade.
Nissan aims to achieve cost parity between EVs and internal combustion engine vehicles by 2030. They plan to reduce EV costs by 30%, making electric vehicles more accessible to consumers.
Despite its successes, Nissan has faced considerable challenges, particularly in recent years. In fiscal year 2024 (ending March 31, 2025), the company reported a net loss of 670.9 billion yen, reflecting decreased sales volume and increased sales incentives.
Nissan reported a net loss of 670.9 billion yen in fiscal year 2024 due to decreased sales and increased incentives. Global sales in FY2024 remained at 3.346 million units, impacted by intensified sales competition.
The company's market share decreased by 0.2 percentage points to 3.8%. In China, retail sales volume decreased by 12.2% in FY2024, reflecting struggles in the competitive new energy vehicle market.
Nissan has implemented a recovery plan called 'Re:Nissan' to enhance performance and create a leaner business. This plan aims to restore profitability by FY2026, primarily by slashing fixed and variable costs.
The company aims to reduce costs by 500 billion yen compared to FY2024 levels. This includes reducing its workforce by 20,000 employees globally between FY2024 and FY2027 and consolidating vehicle production plants from 17 to 10 by fiscal year 2027.
Nissan is revamping its development processes to reduce engineering costs and complexity. The company aims to decrease platform architectures from 13 to 7 by 2035 and shorten development lead times.
Nissan is actively seeking new partnerships to offset development costs and bring new vehicles to market faster, especially for EV technology. This strategic approach is critical for its future success.
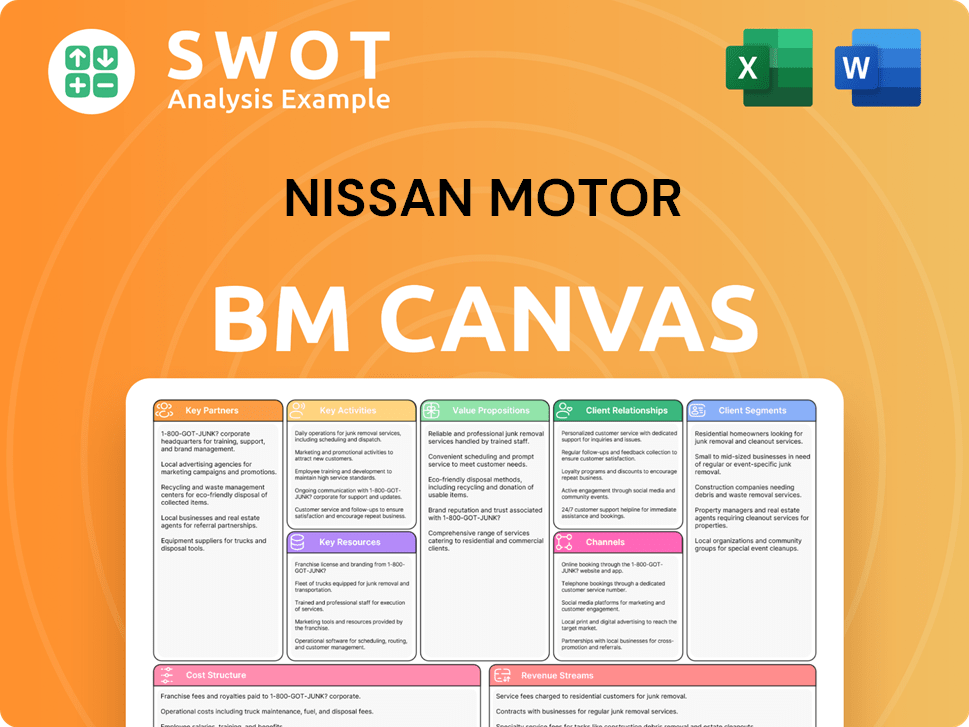
Nissan Motor Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Nissan Motor?
The Nissan timeline showcases a remarkable journey from its origins as a Japanese car manufacturer to a global automotive leader. The story of Nissan Motor Company is marked by innovation, strategic partnerships, and a commitment to sustainable mobility. From producing the first DAT car in 1914 to the launch of the pioneering Nissan Leaf electric vehicle, the company has consistently adapted to market demands while pushing technological boundaries. The formation of the Renault-Nissan Alliance and the subsequent inclusion of Mitsubishi Motors further strengthened its global presence and diversified its offerings. Despite facing challenges, including a net loss in FY2024, Nissan's strategic initiatives, particularly 'The Arc' business plan, signal a clear vision for future growth, focusing on electrification and market expansion.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1911 | Kaishinsha Motor Car Works, the precursor to Nissan, is founded by Masujiro Hashimoto. |
| 1914 | The first DAT car is produced. |
| 1933 | Jidosha Seizou KK is established in Yokohama, the direct predecessor to Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. |
| 1934 | Jidosha Seizou KK is renamed Nissan Motor Co., Ltd., becoming a wholly owned subsidiary of Nihon Sangyo. |
| 1937 | The Datsun Type 15 becomes Japan's first mass-produced vehicle. |
| 1957 | The Nissan Skyline debuts. |
| 1958 | Datsun vehicles are introduced to the U.S. market. |
| 1980 | Nissan Motor Manufacturing Corporation USA is established, breaking ground on its Smyrna assembly plant. |
| 1999 | The Renault-Nissan Alliance is formed. |
| 2010 | The Nissan Leaf, one of the first mass-market electric vehicles, is launched. |
| 2016 | Mitsubishi Motors joins the Renault-Nissan Alliance. |
| 2021 | Nissan unveils 'Nissan Ambition 2030,' its long-term vision focusing on electrification and technological innovation. |
| FY2024 (ending March 31, 2025) | Nissan reports a net loss of 670.9 billion yen. |
| March 2024 | Nissan announces 'The Arc' business plan, outlining the launch of 30 new models, with 16 being EVs or plug-in hybrids, by FY2026. |
| December 2024 | Nissan, Honda, and Mitsubishi Motors sign an MOU to explore potential business integration, though merger talks with Honda later end in February 2025 due to disagreements over structure. |
Nissan's 'The Arc' plan bridges its 'Nissan NEXT' transformation plan and 'Nissan Ambition 2030' vision. It aims to drive value and strengthen competitiveness, focusing on strategic initiatives. This plan includes the launch of 30 new models by the end of fiscal year 2026.
Nissan plans to launch 16 electrified vehicles (EVs and plug-in hybrids) out of the 30 new models. The company expects electrified models to constitute 40% of its global sales by FY2026 and 60% by 2030. Nissan aims to reduce EV costs by 30% by 2030.
The company will focus on key markets, including the U.S., Japan, China, Europe, the Middle East, and Mexico, with tailored approaches. Partnerships with the Renault Group and Mitsubishi Motors will be leveraged. Nissan plans to reduce parts complexity by 70% by 2035.
Despite a challenging fiscal year 2024, Nissan remains in a solid cash position with 1.498 trillion yen in automotive net cash. The company is committed to innovation, sustainable growth, and a return to profitability by fiscal year 2026.
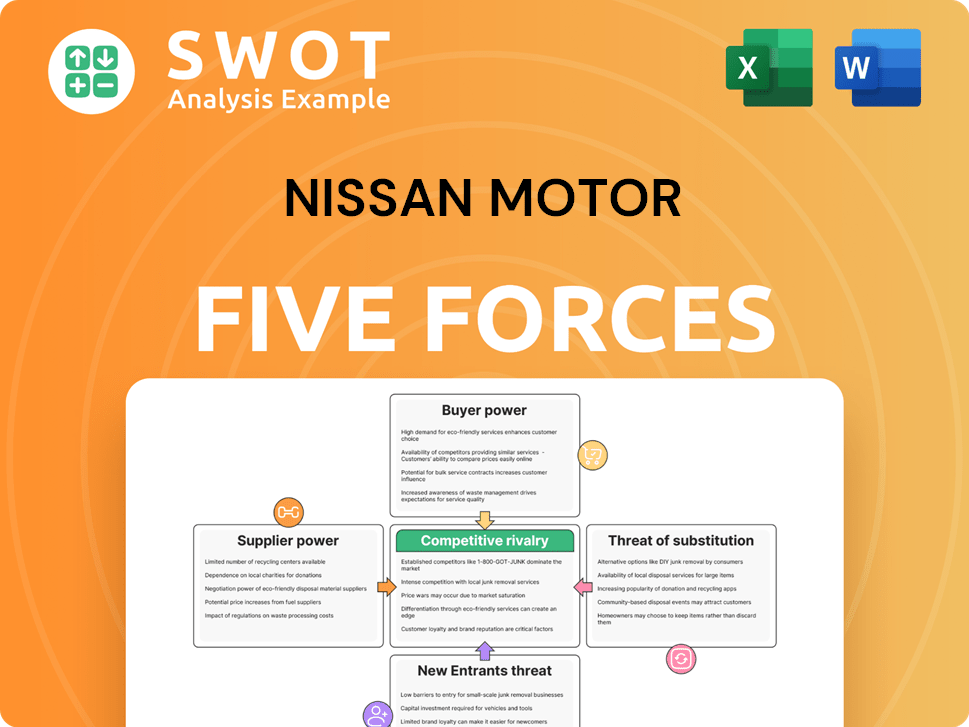
Nissan Motor Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Nissan Motor Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Nissan Motor Company?
- How Does Nissan Motor Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Nissan Motor Company?
- What is Brief History of Nissan Motor Company?
- Who Owns Nissan Motor Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Nissan Motor Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.