Sallie Mae Bundle
How has Sallie Mae Transformed Over the Years?
Ever wondered about the journey of a leading student loan company? Sallie Mae, a name synonymous with education finance, boasts a rich and complex Sallie Mae SWOT Analysis that has significantly shaped the landscape of higher education funding. From its roots as a government-sponsored enterprise to its current status as a private entity, the Sallie Mae history reveals a fascinating evolution.

This brief history of Sallie Mae highlights the company's pivotal role in the evolution of federal student loans and private student loans. Understanding the Sallie Mae origin story is crucial for grasping its impact on education and its current market position. Explore the Sallie Mae timeline to see how this institution adapted to the changing financial environment, becoming a key player in the education finance sector.
What is the Sallie Mae Founding Story?
The Sallie Mae story begins on June 23, 1972, when it was officially established as the Student Loan Marketing Association. This marked a pivotal moment in the Sallie Mae history, designed to reshape the landscape of education finance.
Created by Congress, Sallie Mae emerged as a government-sponsored enterprise (GSE). Its primary mission was to tackle the liquidity challenges that banks faced when providing federal student loans. The creation of Sallie Mae aimed to encourage private investment in student loans, converting them into bonds backed by the U.S. government.
The initial operations of Sallie Mae involved purchasing federally guaranteed student loans from banks. This action freed up capital, allowing banks to issue more loans. The company, benefiting from advantages like tax exemptions and favorable borrowing terms, quickly gained a competitive edge. The first office opened on May 14, 1973, in Washington, D.C. The name 'Sallie Mae' became a widely recognized term, derived from its original, more formal name.
Here are the key facts about the founding of Sallie Mae.
- Founded: June 23, 1972, as the Student Loan Marketing Association.
- Purpose: To address the lack of liquidity in the student loan market, encouraging private investment.
- Business Model: Purchasing federally guaranteed student loans to free up capital for banks.
- Government Support: Benefited from tax exemptions and favorable borrowing terms as a GSE.
For a deeper dive into the strategic moves that shaped the company, explore the Growth Strategy of Sallie Mae.
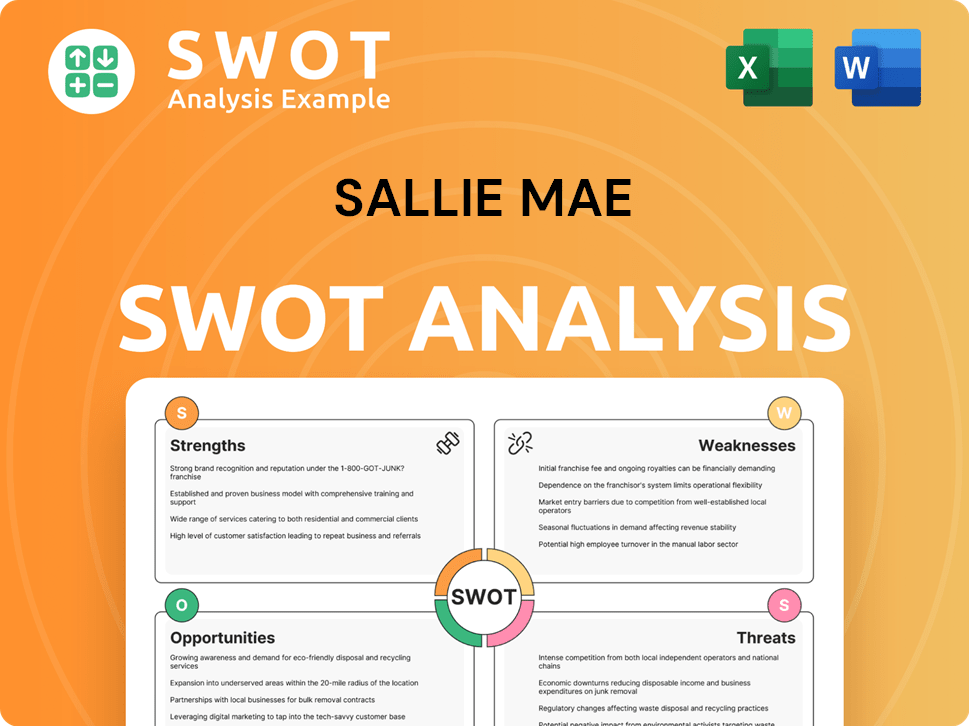
Sallie Mae SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Sallie Mae?
The early years of Sallie Mae saw its establishment as a key player in the student loan company landscape. Initially focused on facilitating bank participation in the guaranteed student loan program, Sallie Mae provided crucial financing. This set the stage for its expansion and evolution within the education finance sector.
During the 1970s, Sallie Mae primarily supported the guaranteed student loan program. Its main function was to ensure banks could participate by offering financing and liquidity. This helped establish the guaranteed student loan program as a significant part of America's higher education system, influencing the early Sallie Mae history.
In the 1980s, Sallie Mae broadened its operations, directly servicing loans and introducing new products. This included technological advancements aimed at improving financial aid delivery. The company also went public, marking a blend of public-sector mission and private-sector capital, shaping the Sallie Mae origin story.
The 1990s saw a significant strategic shift as Sallie Mae transitioned from a limited-purpose GSE to a private holding company. This allowed the company to enter the loan origination business. The privatization process, starting in 1997, enabled Sallie Mae to pursue opportunities beyond its original charter.
Key acquisitions, like Nellie Mae in 1999 and USA Group in 2000, expanded Sallie Mae's reach. USA Group was the largest guaranty agency at the time. By 2004, the full privatization of Sallie Mae was complete, allowing it to operate more freely, including entering the private student loans market.
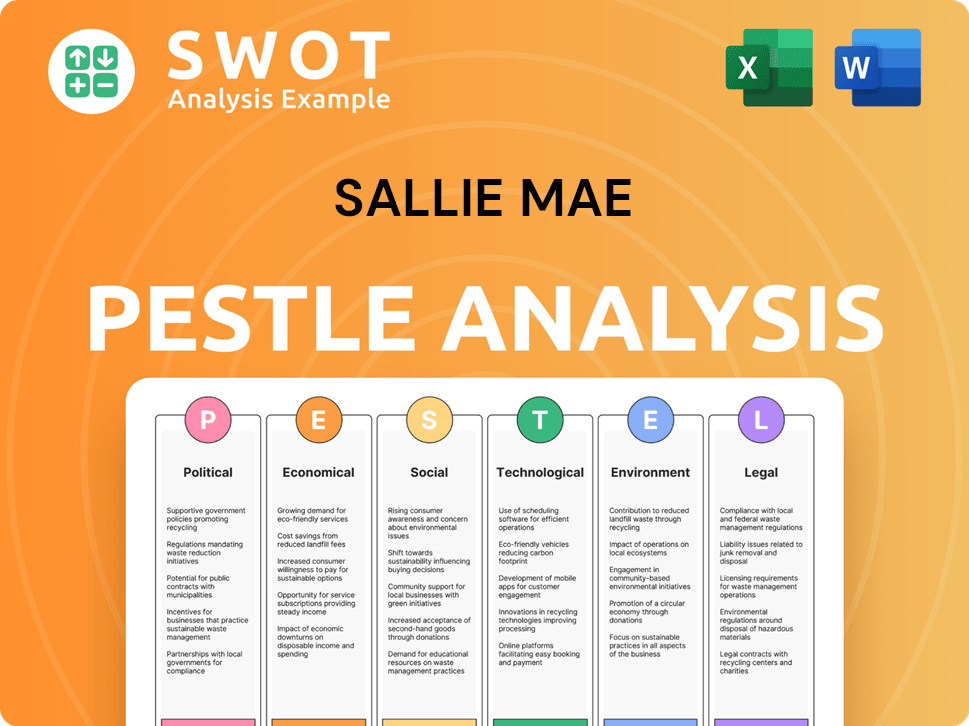
Sallie Mae PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Sallie Mae history?
The brief history of Sallie Mae is marked by significant milestones, starting with its inception and evolving through strategic shifts and market adjustments. The student loan company has played a pivotal role in the landscape of education finance, adapting to both regulatory changes and economic fluctuations.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1972 | Established as the Student Loan Marketing Association, creating a secondary market for student loans. |
| 2004 | Completed transition from a government-sponsored enterprise to a fully private company. |
| 2014 | Spun off its loan servicing operation and most of its loan portfolio into Navient Corporation. |
| 2024 | Recognized as one of the 2024-25 Best Companies to Work For by U.S. News and World Report. |
Sallie Mae pioneered the secondary market for student loans, providing crucial liquidity to lenders, which was innovative for its time. The company's shift to a private entity allowed it to broaden its financial product offerings, including private student loans and other banking services.
Sallie Mae established a secondary market for student loans, which was a groundbreaking innovation in education finance. This market provided liquidity to lenders, facilitating the availability of federal student loans and other educational funding options.
The transition to a private entity allowed Sallie Mae to diversify its products beyond federal student loans. This included the introduction of private student loans, credit cards, and other financial services tailored for students and their families.
The 2014 spinoff of Navient Corporation was a strategic move to focus on originating new private student loans. This restructuring allowed Sallie Mae to streamline its operations and adapt to changing market conditions.
Sallie Mae expanded its reach through acquisitions of debt management and collection companies. These acquisitions, such as General Revenue Corporation, Pioneer Credit Recovery, and Arrow Financial Services, broadened its service offerings.
The company faced scrutiny over its lending practices, particularly regarding subprime private student loans, leading to legal challenges. The 2007 financial crisis and subsequent tightening of credit markets also presented significant hurdles, including a failed acquisition attempt.
Sallie Mae faced scrutiny and legal challenges related to its lending practices, particularly concerning subprime private student loans. Accusations included manipulating default rates and improper handling of loan subsidies.
The 2007-2008 financial crisis significantly impacted Sallie Mae, leading to a failed acquisition attempt. The tightening of credit markets created challenges for the student loan company.
Increased regulatory scrutiny prompted Sallie Mae to restructure its operations. The spinoff of Navient was a direct response to evolving market conditions and regulatory demands.
Market volatility and economic downturns posed challenges to Sallie Mae's strategic plans. These factors influenced the company's ability to secure acquisitions and maintain financial stability.
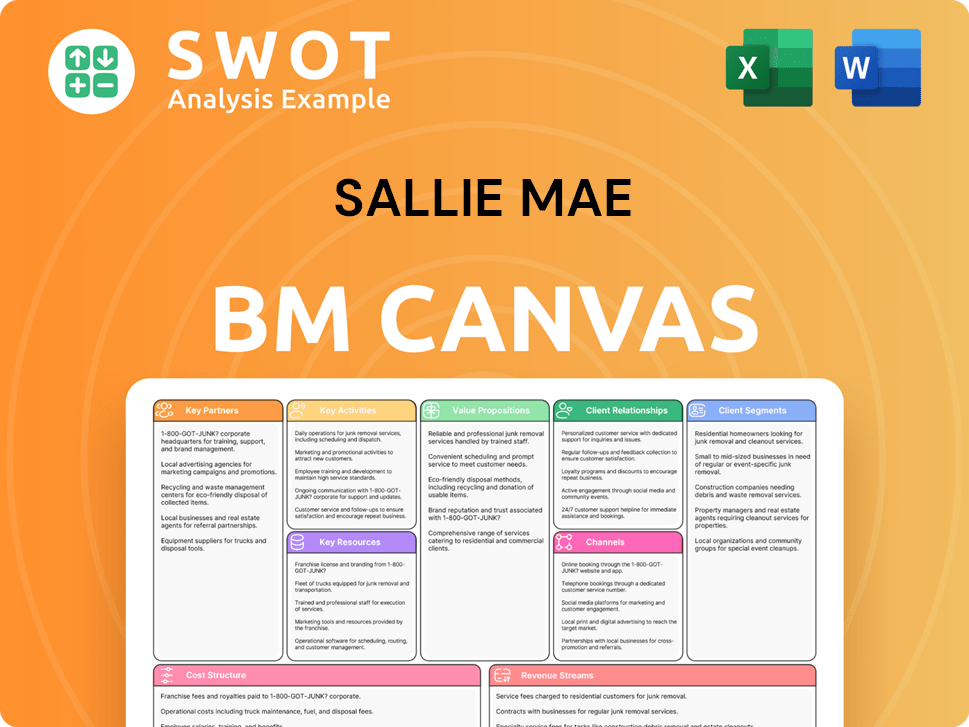
Sallie Mae Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Sallie Mae?
The Sallie Mae history is marked by significant shifts and developments. From its inception as a government-sponsored enterprise to its current status as a leading student loan company, the organization has adapted to the evolving landscape of education finance. This evolution showcases its enduring commitment to supporting students and families in achieving their educational goals.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1972 | Congress established the Student Loan Marketing Association, known as Sallie Mae, to create a secondary market for student loans. |
| 1973 | Sallie Mae officially opened its doors in Washington, D.C., marking the beginning of its operations. |
| 1980s | Sallie Mae began direct loan servicing and introduced new products and technology, including going public. |
| 1997 | Sallie Mae began the process of privatization. |
| 1999 | Sallie Mae acquired Nellie Mae, a nonprofit student lending corporation. |
| 2000 | Sallie Mae acquired USA Group, the largest guaranty agency in the U.S., for $770 million. |
| 2004 | Sallie Mae completed its privatization, ending its ties to the government. |
| 2005 | Sallie Mae Bank was established as an industrial bank in Utah. |
| 2006 | Sallie Mae acquired Upromise, a college savings rewards program. |
| 2007 | An investor group attempted to purchase Sallie Mae for approximately $25 billion, but the deal fell through. |
| 2010 | Sallie Mae acquired federally insured loans from Citigroup-owned Student Loan Corporation worth $28 billion. |
| 2014 | Sallie Mae spun off its loan servicing and a majority of its loan portfolio into Navient Corporation. |
| 2020 | Jonathan Witter was appointed as the new CEO of Sallie Mae. |
| 2021 | Sallie Mae partnered with MPOWER Financing to expand access to higher education for international and DACA students. |
| 2024-2025 | U.S. News and World Report named Sallie Mae as one of the Best Companies to Work For. |
Sallie Mae is a leading provider of private student loans, offering financing options for undergraduate, graduate, and professional programs. The company's focus on private student loans is a key component of its business strategy. They provide flexible loan options to meet the needs of students and families.
Sallie Mae continues to invest in digital platforms and online services to enhance the customer experience. This includes streamlining the application process, providing online account management tools, and offering mobile-friendly services. Digital innovation is crucial for attracting and retaining customers.
The company actively seeks strategic partnerships to expand its reach and offer a broader range of services. Collaborations with educational institutions, fintech companies, and other financial institutions are common. These partnerships help Sallie Mae reach new markets.
Sallie Mae emphasizes responsible lending practices and providing excellent customer service. This includes offering clear and transparent loan terms, providing financial literacy resources, and supporting borrowers throughout the repayment process. These practices build trust.
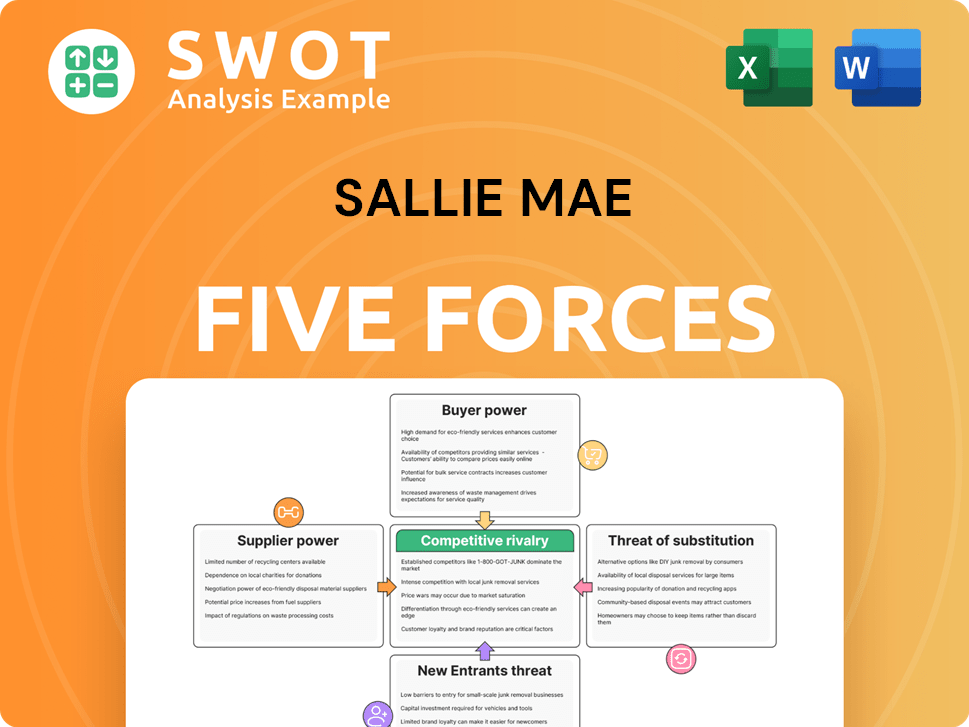
Sallie Mae Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Sallie Mae Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Sallie Mae Company?
- How Does Sallie Mae Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Sallie Mae Company?
- What is Brief History of Sallie Mae Company?
- Who Owns Sallie Mae Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Sallie Mae Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.