Icahn Enterprises Bundle
Can Carl Icahn's Icahn Enterprises Outmaneuver Its Rivals?
Icahn Enterprises, spearheaded by the legendary Carl Icahn, operates in a dynamic arena where strategic prowess and market acumen are paramount. This diversified holding company, known for its activist investment approach, constantly reshapes industries through its significant stakes and interventions. Understanding the Icahn Enterprises SWOT Analysis is crucial to grasping its competitive positioning and future prospects.
The competitive landscape surrounding Icahn Enterprises is complex, shaped by its diverse investment portfolio and the ever-changing dynamics of its business segments. Analyzing the Icahn Enterprises SWOT Analysis helps to identify its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, providing a comprehensive view of its market position. Examining the company's corporate structure and business strategy is vital to understanding how it navigates its industry rivals and maintains its competitive advantages. This exploration provides insights into Carl Icahn's investment philosophy and the impact of Icahn Enterprises on the market.
Where Does Icahn Enterprises’ Stand in the Current Market?
Icahn Enterprises L.P. (IELP) operates as a diversified holding company, setting it apart from direct competitors within specific industries. Its market position is defined by its ownership and active management of a diverse portfolio of businesses spanning sectors like investment, energy, automotive, food packaging, real estate, and home fashion. This structure allows IELP to navigate various market conditions and opportunities.
As of early 2024, IELP reported a net asset value of $5.3 billion, with its investment segment being a significant contributor to its overall financial health. The company's financial results for the first quarter of 2024 showed a net loss attributable to IEP common unitholders of $105 million, or $0.28 per depositary unit, compared to a net loss of $263 million, or $0.74 per depositary unit, in the prior year period, indicating some improvement in performance.
IELP's approach involves acquiring significant stakes in companies, often with the intent of influencing management and strategic direction to enhance value. This activist investment model means its 'customer segments' are often the shareholders of the companies it targets, seeking to realize value for them. This strategy is a core element of its competitive positioning, distinguishing it from typical industry players. For a deeper dive into their strategic approach, consider reading about the Growth Strategy of Icahn Enterprises.
IELP's market presence is primarily concentrated in North America, although its investment activities can have a global reach. The company's diverse portfolio includes operations in sectors such as automotive aftermarket, energy, and investment management. This broad scope allows IELP to capitalize on various market opportunities.
IELP differentiates itself through its activist investment model, acquiring significant stakes in companies to influence management and strategic direction. This approach contrasts with traditional industry players. The company's focus on value creation for shareholders is a key element of its strategy.
The financial performance of IELP is influenced by its diverse business segments. The company's financial results for the first quarter of 2024 showed a net loss attributable to IEP common unitholders of $105 million, or $0.28 per depositary unit. This indicates a focus on improving financial outcomes across its portfolio.
IELP's key strategies involve active management and strategic direction of its portfolio companies. The company focuses on acquiring stakes in companies with the intent of influencing management. This approach is a core element of its competitive positioning.
Within its diverse portfolio, IELP faces varying degrees of competition. In the automotive aftermarket, it competes with established players. In the energy sector, its refining operations compete with major oil and gas companies. Its investment segment competes with large hedge funds and institutional investors.
- Automotive aftermarket competitors include established parts distributors and service providers.
- Energy sector rivals include major oil and gas companies.
- Investment segment competitors include large hedge funds and institutional investors.
- The company's activist investment strategy sets it apart from typical industry players.
Icahn Enterprises SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
Who Are the Main Competitors Challenging Icahn Enterprises?
Understanding the competitive landscape of Icahn Enterprises (IEP) requires recognizing its highly diversified structure. The company operates across various sectors, each with its own set of competitors. This diversification means that IEP faces a wide array of rivals, making a comprehensive competitive analysis complex.
The investment segment, a core part of IEP's business, competes with other activist hedge funds. The industrial segments, including energy, automotive, and food packaging, have their own unique competitive environments. The company's performance and strategic decisions are significantly influenced by these varied competitive pressures.
The competitive landscape for IEP is dynamic, with rivals constantly evolving. This article will provide a detailed overview of the key competitors across IEP's main business segments, offering insights into the challenges and opportunities the company faces.
In the investment arena, IEP's investment arm, Icahn Capital LP, competes with other prominent activist hedge funds. These funds often take significant stakes in companies, advocating for changes to boost shareholder value. This competitive environment is marked by high-profile battles and proxy contests.
Key competitors include Elliott Management, known for its activist campaigns and significant assets under management. Starboard Value is another major player, focusing on improving corporate performance through strategic changes. Pershing Square Capital Management, led by Bill Ackman, also engages in activist investing.
CVR Energy, Inc., a subsidiary of IEP, competes in the energy sector, particularly in refining. This segment faces competition from major independent refiners and integrated oil companies. These rivals often have larger refining capacities and extensive distribution networks.
Major competitors in the energy sector include Valero Energy Corporation, a leading independent refiner with a significant market share. Marathon Petroleum Corporation is another key player, known for its refining capacity and retail network. Phillips 66 also poses a challenge, with its integrated operations and global presence.
Icahn Automotive Group faces competition from large national chains and regional service providers. This segment is characterized by intense competition and the need for efficient operations and customer service. The automotive aftermarket is a large and competitive market.
Key competitors in the automotive aftermarket include AutoZone, a major player with a vast network of stores and strong brand recognition. Advance Auto Parts is another significant rival, competing on a national scale. O'Reilly Auto Parts also presents a challenge, with its expanding presence and focus on customer service.
In the food packaging segment, Viskase Companies, Inc. competes with global players in the casings market. Real estate holdings compete with other large property owners and developers. WestPoint Home, in the home fashion segment, faces competition from other textile manufacturers and distributors. These segments have their own unique competitive dynamics.
- Food Packaging: Viskase Companies, Inc. competes with global players in the casings market.
- Real Estate: Real estate holdings compete with other large property owners and developers.
- Home Fashion: WestPoint Home competes with other textile manufacturers and distributors.
- Emerging Challenges: Emerging players, particularly those leveraging new technologies, pose indirect competitive challenges.
IEP's subsidiaries must adapt and innovate to maintain their competitive positions. Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial for assessing IEP's Growth Strategy of Icahn Enterprises and its future prospects. The company's ability to navigate these diverse competitive environments will significantly impact its financial performance and strategic success.
Icahn Enterprises PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What Gives Icahn Enterprises a Competitive Edge Over Its Rivals?
The competitive advantages of Icahn Enterprises (IEP) are deeply rooted in its activist investment model and the strategic acumen of Carl Icahn. This approach allows IEP to acquire stakes in undervalued companies, then drive operational improvements and strategic shifts to unlock shareholder value. This hands-on involvement distinguishes IEP from passive investment firms, offering a unique value proposition in the market. The strong brand equity associated with Carl Icahn's name provides significant credibility and leverage in corporate engagements.
IEP's diversified portfolio across various industries provides a significant advantage. This diversification helps mitigate risks associated with downturns in any single sector, offering a more stable revenue base compared to companies focused on one industry. For instance, while the energy segment might face headwinds, the real estate or automotive segments could be performing strongly. Furthermore, IEP's ability to identify and acquire distressed or undervalued assets at opportune times, and then implement turnarounds, represents a significant operational advantage. The company's access to substantial capital also allows it to make large-scale investments and acquisitions that many smaller firms cannot.
These advantages have evolved from Icahn's early days of corporate raiding to a more sophisticated approach of long-term value creation through active ownership. However, these advantages can face threats from increased regulatory scrutiny on activist investing, heightened competition from other activist funds, or shifts in market sentiment that favor passive investment strategies.
IEP's core strategy centers on activist investing, where it takes significant stakes in companies and actively influences management. This approach allows IEP to drive operational improvements, strategic shifts, and corporate governance changes. The firm's ability to identify undervalued companies and unlock shareholder value is a key competitive advantage. This strategy is a cornerstone of understanding the competitive landscape of IEP.
IEP's diversified portfolio across various industries mitigates risks associated with sector-specific downturns. This diversification provides a more stable revenue base compared to companies focused on a single industry. For example, in 2023, IEP's investment portfolio included interests in automotive, energy, food packaging, real estate, and other sectors, demonstrating its broad diversification strategy.
The strong brand equity associated with Carl Icahn and his long track record of successful activist campaigns provides IEP with significant credibility and leverage. Icahn's reputation for identifying undervalued assets and driving value creation is a key differentiator. His expertise and influence are critical to IEP's success in corporate engagements.
IEP's access to substantial capital allows it to make large-scale investments and acquisitions. The company's ability to identify and acquire distressed or undervalued assets and implement turnarounds represents a significant operational advantage. This combination of financial resources and operational expertise sets IEP apart in the competitive landscape.
IEP's primary competitive advantages include its activist investment strategy, diversified portfolio, and the brand equity associated with Carl Icahn. These factors enable IEP to identify undervalued assets, drive operational improvements, and mitigate risks. The company's access to substantial capital and turnaround capabilities further enhance its competitive positioning.
- Activist Investing: IEP's active involvement in portfolio companies drives value creation through strategic changes.
- Diversification: A diversified portfolio across various sectors reduces risk and provides stability.
- Brand Recognition: Carl Icahn's reputation and expertise provide credibility and leverage.
- Capital and Turnaround Expertise: Access to substantial capital and the ability to execute turnarounds are key strengths.
Icahn Enterprises Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Industry Trends Are Reshaping Icahn Enterprises’s Competitive Landscape?
The competitive landscape for Icahn Enterprises (IEP) is shaped by diverse industry trends reflecting its multi-sector operations. The company, led by Carl Icahn, navigates a complex environment, adapting to shifts in energy, automotive, and other sectors. Understanding the competitive dynamics and market analysis is crucial for assessing IEP's future performance.
IEP faces evolving challenges and opportunities, including technological advancements, regulatory changes, and global economic shifts. Its ability to adapt its business strategy and investment portfolio will determine its success. The company's corporate structure and investment philosophy are key factors in its competitive positioning.
In the energy sector, the push towards renewable energy and stricter environmental regulations presents challenges and opportunities for CVR Energy, a subsidiary of IEP. The automotive aftermarket is undergoing a transformation due to the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving technology. Technological advancements like AI and automation offer operational efficiencies across all segments.
Potential threats include increased competition from new market entrants leveraging disruptive technologies. A sustained decline in demand for products in legacy industries poses a risk. Regulatory changes, particularly in environmental and financial sectors, could impact IEP's portfolio companies, requiring adaptation and investment in compliance.
Growth opportunities lie in strategic acquisitions in emerging industries and product innovations within existing segments. Expanding into new geographic markets could boost revenue. IEP can leverage its financial strength and strategic expertise to navigate dynamic trends and capitalize on growth sectors.
IEP's competitive position will likely evolve with its continued focus on activist investing. The company aims to adapt its portfolio to capitalize on growth sectors and mitigate risks in declining ones. IEP's ability to adapt its business strategy is critical for long-term success.
IEP's success depends on its ability to navigate industry shifts and capitalize on opportunities. The company's investment portfolio and business strategy must be agile to respond to changes in the market. IEP's recent acquisitions and activist investing strategies will continue to shape its competitive landscape.
- Technological Advancements: Embrace AI and automation for operational efficiency.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adapt to environmental and financial regulations.
- Strategic Acquisitions: Explore growth opportunities in emerging industries.
- Market Adaptation: Adjust to the rise of EVs and renewable energy.
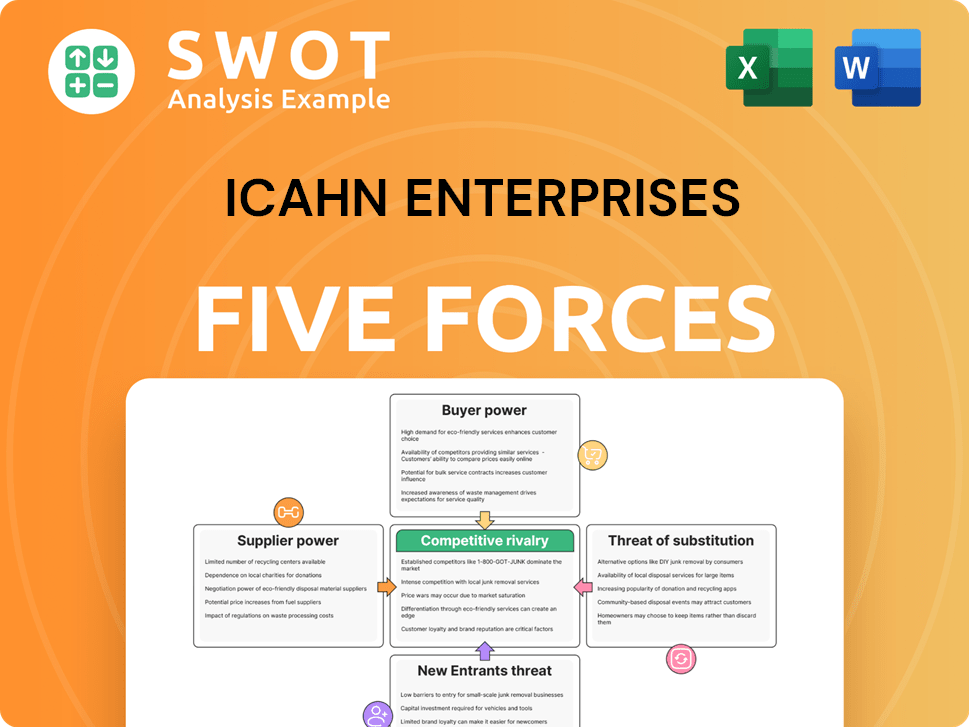
Icahn Enterprises Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Icahn Enterprises Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Icahn Enterprises Company?
- How Does Icahn Enterprises Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Icahn Enterprises Company?
- What is Brief History of Icahn Enterprises Company?
- Who Owns Icahn Enterprises Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Icahn Enterprises Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.