Japan Airlines Bundle
Who Really Controls Japan Airlines?
Unraveling the complex web of Japan Airlines SWOT Analysis and its ownership is key to understanding its future. From its humble beginnings to its current status as a global airline, JAL's journey has been marked by significant shifts in its ownership structure. Discover the key players shaping the destiny of this aviation giant and how they influence its strategic decisions.

Understanding JAL ownership is crucial for anyone interested in the airline industry Japan. The company's resurgence after bankruptcy and its subsequent re-listing provide a fascinating case study in corporate restructuring and shareholder influence. This analysis will explore the Japan Airlines stock dynamics and identify who owns Japan Airlines today, shedding light on the Japan Airlines company structure and the forces driving its financial performance.
Who Founded Japan Airlines?
Japan Airlines (JAL) was established in 1951, marking its beginning as the first private aviation company in Japan. The early stages of JAL's formation and ownership structure are not extensively detailed in the available information. Understanding the initial ownership dynamics is crucial for grasping the airline's subsequent development and its place within the Airline industry Japan.
Details regarding the specific equity split among the founders, their backgrounds, or the initial shareholding percentages at the company's inception are not readily available in the provided search results. Similarly, information on notable early backers, angel investors, or family members who acquired stakes during the initial phase is not detailed in the provided context. The early agreements, such as vesting schedules or founder exits, and initial ownership disputes, are also not detailed.
The absence of comprehensive data on the founders and early ownership of Japan Airlines highlights the challenges in tracing the complete history of the airline's ownership structure. This lack of information makes it difficult to fully understand the early influences and decisions that shaped the company's trajectory.
Japan Airlines was founded in 1951, marking the beginning of commercial aviation in post-war Japan.
It was established as Japan's first private aviation company, setting the stage for the airline's future.
Specific details about the founders, their backgrounds, and initial shareholdings are not readily available.
Information on early backers and angel investors is also not detailed in the available resources.
Details on early agreements, such as vesting schedules, are not readily available.
The context does not provide information about initial ownership disputes or buyouts.
The early ownership structure of Japan Airlines remains somewhat obscure, with limited information available regarding the founders, initial shareholders, and early agreements. This lack of detailed information makes it challenging to fully understand the initial influences and decisions that shaped the company's trajectory. Understanding the history of JAL ownership is important. The Japan Airlines stock symbol is 9201.T. As of May 2024, the company's market capitalization is approximately $6.3 billion USD. The Japan Airlines share price fluctuates, reflecting the airline's financial performance and market conditions. The Japan Airlines financial performance in recent years has been impacted by global events, including the COVID-19 pandemic. The Japan Airlines investor relations department provides updates on the company's financial results and strategic initiatives.
- The company was founded in 1951.
- Specific details about the founders and initial shareholders are not readily available.
- Information on early backers and agreements is also limited.
- The current market capitalization is around $6.3 billion USD (May 2024).
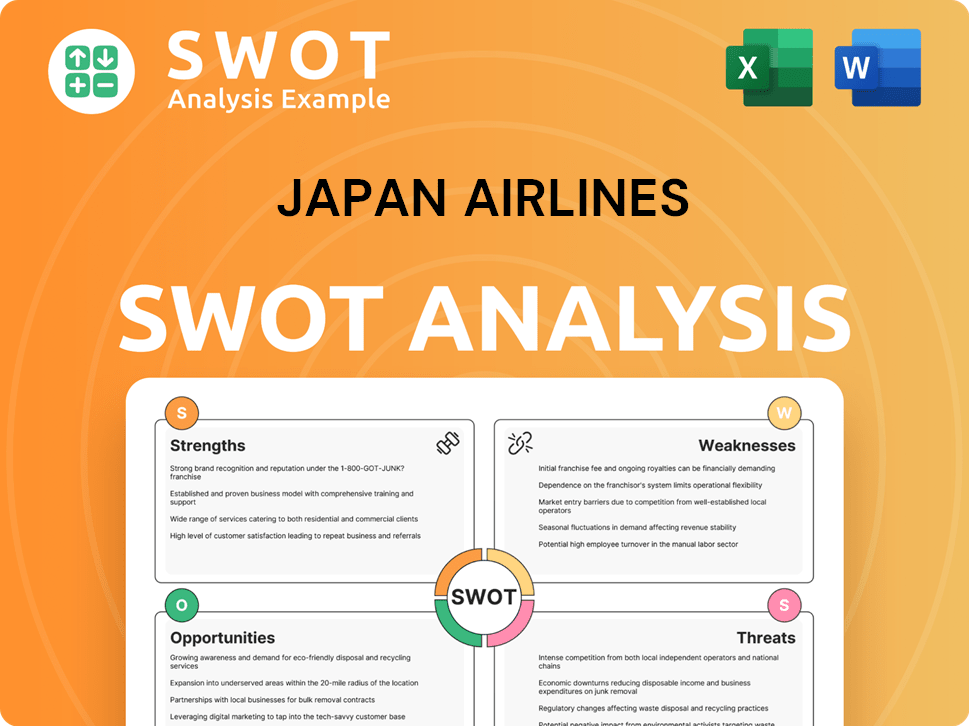
Japan Airlines SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Japan Airlines’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The Marketing Strategy of Japan Airlines has been significantly shaped by its ownership evolution. Following a bankruptcy filing in early 2010, the company underwent a major restructuring. During this period, the Enterprise Turnaround Initiative Corporation of Japan (ETIC), a government-affiliated agency, held approximately 97% of JAL's voting rights, marking a pivotal shift in the company's control.
JAL emerged from bankruptcy in March 2011 and completed its initial public offering (IPO) on the Tokyo Stock Exchange on September 19, 2012. This re-listing, which raised ¥663 billion (US$8.5 billion), was the world's second-largest IPO that year. The government-backed owner sold 175 million shares, using the proceeds to return funds to the state-backed turnaround body and the government.
| Event | Date | Impact on Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| Bankruptcy Filing | Early 2010 | Government control through ETIC (97% voting rights) |
| Emergence from Bankruptcy | March 2011 | Restructuring completed |
| IPO on Tokyo Stock Exchange | September 19, 2012 | Public offering; government stake reduced; increased public ownership |
As of late 2024 and early 2025, several institutional investors hold significant stakes in Japan Airlines. Nomura Asset Management Co., Ltd. held 6.20% as of September 29, 2024. BlackRock, Inc. held 3.76% as of September 29, 2024. Other major shareholders include Nikko Asset Management Co., Ltd. (2.88% as of September 29, 2024), Sumitomo Mitsui Trust Asset Management Co., Ltd. (2.57% as of September 29, 2024), The Vanguard Group, Inc. (1.34% as of April 29, 2025), Mitsubishi UFJ Asset Management Co., Ltd. (1.24% as of May 28, 2025), and Daiwa Asset Management Co., Ltd. (1.15% as of September 29, 2024). JALUX, a core company within the JAL Group, is a subsidiary with Japan Airlines Corporation as its parent company, holding 51.9% of its voting rights.
The ownership of Japan Airlines has evolved significantly from government control to a mix of public and institutional ownership.
- The IPO in 2012 marked a crucial shift, reducing government influence.
- Major institutional investors now hold substantial stakes in the company.
- JALUX, a key part of the JAL Group, is majority-owned by Japan Airlines Corporation.
- Understanding the current ownership structure is vital for assessing the company's stability and strategic direction.
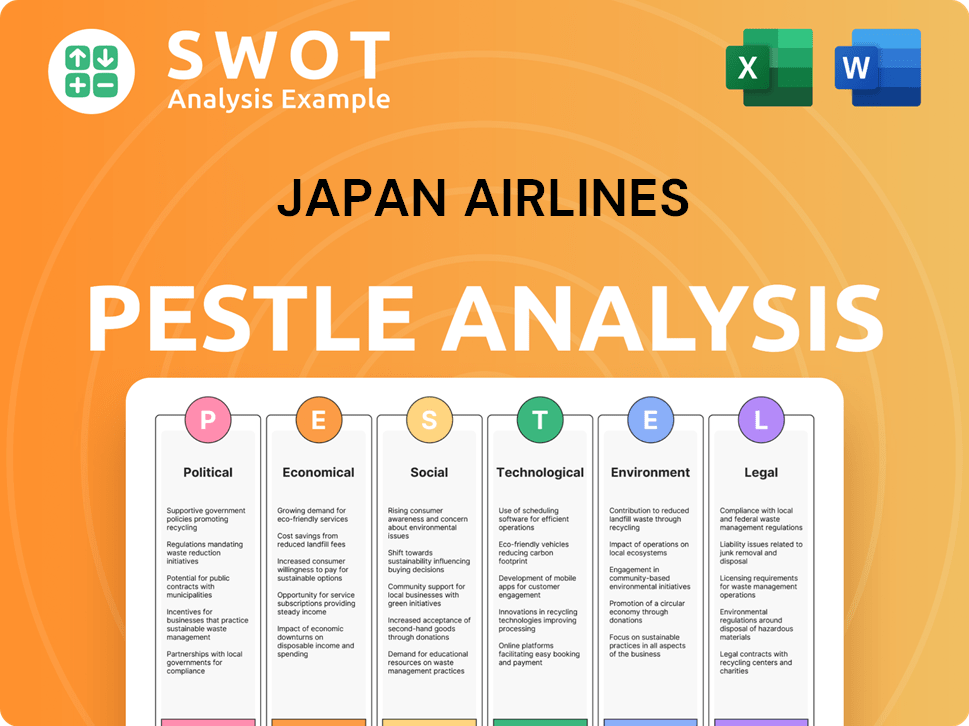
Japan Airlines PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Japan Airlines’s Board?
As of April 1, 2025, the Board of Directors of Japan Airlines (JAL) is led by Yuji Akasaka as Director - Chairperson and Mitsuko Tottori as Representative Director - President. Mitsuko Tottori's appointment in April 2024 marked a significant milestone as the first female president in the company's history. Key figures on the board include Yuji Saito as Representative Director - Executive Vice President, Noriyuki Aoki as Director - Executive Vice President, Yoriyuki Kashiwagi as Director - Senior Managing Executive Officer, and Ryo Tamura as Director. The board also includes outside directors like Eizo Kobayashi, Hiroyuki Yanagi, and Yuko Mitsuya. Following the General Meeting of Shareholders in June 2025, the board will see new appointments, including Yukio Nakagawa as Director - Managing Executive Officer and Masanobu Komoda as an Outside Director.
The executive officers manage day-to-day operations but typically do not have voting rights. The Japan Airlines operates under a one-share-one-vote structure. There is no information available on dual-class shares, special voting rights, or founder shares that would give specific entities or individuals outsized control. This structure ensures that voting power is directly proportional to the number of shares held.
| Board Member | Title | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Yuji Akasaka | Director - Chairperson | Leads the Board |
| Mitsuko Tottori | Representative Director - President | Oversees the company's operations. |
| Yuji Saito | Representative Director - Executive Vice President | Key executive role. |
| Noriyuki Aoki | Director - Executive Vice President | Key executive role. |
| Yoriyuki Kashiwagi | Director - Senior Managing Executive Officer | Senior management role. |
| Ryo Tamura | Director | Board member. |
| Eizo Kobayashi | Outside Director | Independent board member. |
| Hiroyuki Yanagi | Outside Director | Independent board member. |
| Yuko Mitsuya | Outside Director | Independent board member. |
Recent developments highlight a focus on governance and accountability within JAL. Following a pilot drinking incident in December 2024, President Mitsuko Tottori and Chairperson Yuji Akasaka faced a 30% salary reduction for two months in January 2025. Akasaka also relinquished his role as Chief Safety Officer, concentrating on chairing board meetings. The company announced changes to its Board of Directors and Executive Officers effective February 5, 2025, and further changes effective April 1, 2025. The JAL Group's Board of Directors confirmed its overall effectiveness in a FY2023 assessment, acknowledging strengths in authority delegation and constructive feedback from outside directors while also identifying areas for improvement in information sharing, particularly concerning Nominating Committee activities.
The board structure and voting mechanisms at Japan Airlines are designed to ensure accountability and transparency. The one-share-one-vote system provides a clear and equitable distribution of voting rights among shareholders. The company's commitment to strong governance is evident in its responses to incidents and its ongoing efforts to improve board effectiveness.
- One-share-one-vote structure.
- Focus on governance and accountability.
- Emphasis on board effectiveness.
- Independent directors provide oversight.
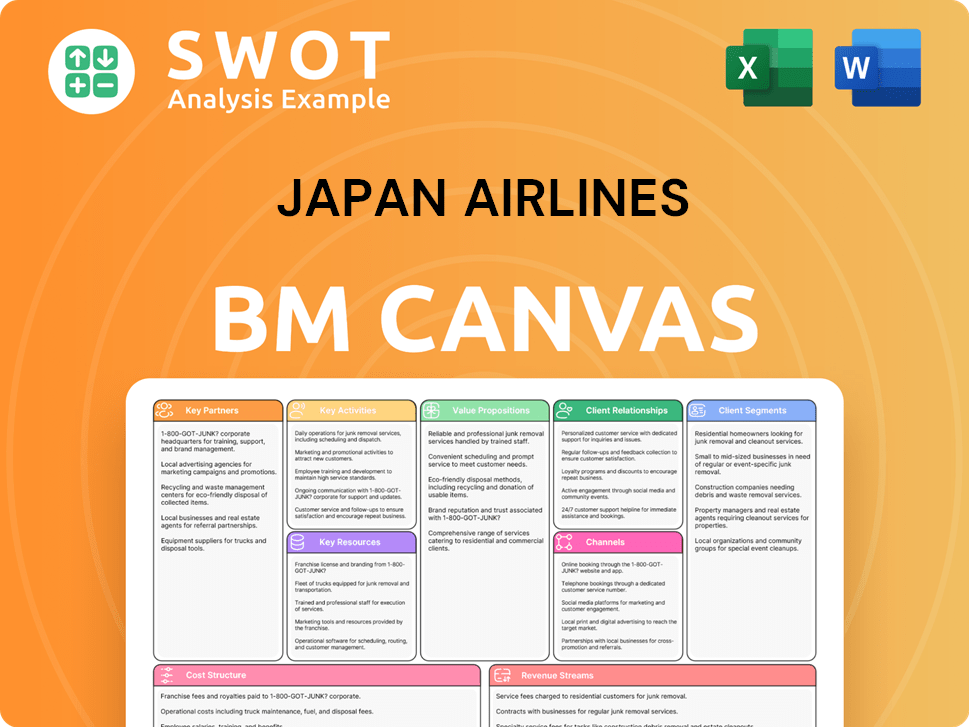
Japan Airlines Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Japan Airlines’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, Japan Airlines has seen significant developments in its ownership and operational strategies. The airline reported strong financial results for the third quarter of fiscal year 2024-2025, with revenues reaching JPY 1,385.9 billion, an 11% year-on-year increase, and EBIT at JPY 144.2 billion, a 12% increase year-on-year. For the full fiscal year 2024-2025, JAL achieved consolidated revenues of JPY 1,844 billion, an 11.6% year-on-year increase, marking its highest performance since re-listing. Furthermore, the company forecasts total revenues of JPY 1,977.0 billion for fiscal year 2025-2026. These figures demonstrate JAL's strong financial health and its ability to navigate the complexities of the airline industry in Japan.
In March 2025, JAL announced strategic fleet renewals, including the introduction of 17 additional Boeing 737-8 aircraft, following a March 2023 order for 21 Boeing 737-8 aircraft. The airline also plans to introduce 11 Airbus A321neo aircraft, 10 Boeing 787-9 aircraft, and 20 Airbus A350-900 aircraft. These investments are geared towards enhancing profitability and expanding international operations, especially in North America and Asia. Regarding strategic investments, Japan Airlines made a strategic investment in Episode Six (E6), a global provider of ledger and cards infrastructure, in March 2025. This investment aims to advance JAL's financial services initiatives, including JAL Pay, which serves its approximately 30 million customers.
| Metric | Fiscal Year 2024-2025 (Actual) | Fiscal Year 2025-2026 (Forecast) |
|---|---|---|
| Consolidated Revenues (JPY Billion) | 1,844 | 1,977.0 |
| Year-on-Year Revenue Growth | 11.6% | N/A |
| EBIT (JPY Billion) | 144.2 (Q3) | N/A |
Regarding JAL ownership, the company is considering a partial reduction of its shareholdings in listed companies, a policy confirmed by the Board of Directors in January 2024. In April 2025, JAL announced its proposal to privatize the shares of AGP, a company in which JAL is the largest shareholder with a 30.47% ownership ratio as of December 31, 2024. This move, supported by Japan Airport Terminal and ANA Holdings, aims to facilitate better dialogue and improve AGP's corporate value. This reflects a strategic focus on consolidating control over key affiliates.
Strong revenue growth in fiscal year 2024-2025, with consolidated revenues reaching JPY 1,844 billion, an 11.6% increase year-on-year.
Investment in Episode Six (E6) to advance financial services, particularly JAL Pay, serving approximately 30 million customers.
Introduction of new aircraft, including Boeing 737-8s, Airbus A321neos, Boeing 787-9s, and Airbus A350-900s, to enhance profitability and expand international routes.
Considering partial reduction of shareholdings and the privatization of AGP, indicating a focus on strategic alignment and value creation.
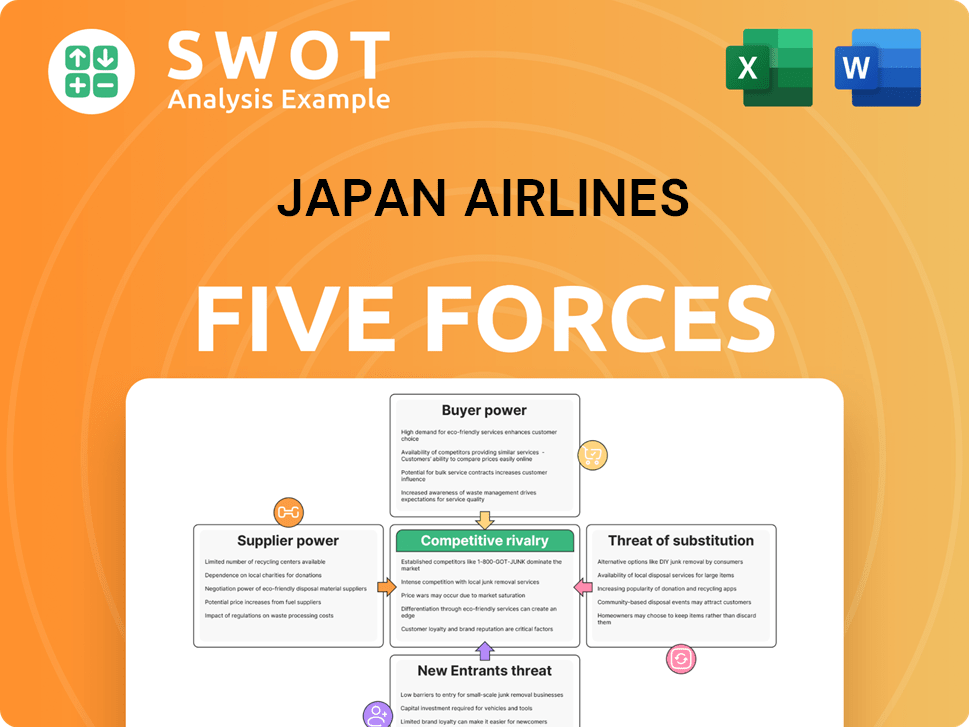
Japan Airlines Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Japan Airlines Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Japan Airlines Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Japan Airlines Company?
- How Does Japan Airlines Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Japan Airlines Company?
- What is Brief History of Japan Airlines Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Japan Airlines Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.