NEC Bundle
Who Really Controls NEC Corporation?
Unraveling the NEC SWOT Analysis is essential for any investor or strategist. Understanding NEC ownership is paramount for assessing its future prospects and strategic direction. This deep dive into "Who owns NEC" unveils the key players shaping this global technology giant.

Tracing NEC Corporation's ownership history reveals fascinating shifts, from its roots in Japan to its current global footprint. Knowing the NEC parent company and its major stakeholders provides critical insights into its decision-making processes. This exploration of NEC Corporation owner details, including its stock ownership and company structure, is vital for anyone seeking to understand this influential player in the IT and electronics sectors, and for those asking "Is NEC a public company?".
Who Founded NEC?
The origins of NEC Corporation, a prominent player in the technology sector, trace back to July 17, 1899. It began as a joint venture, a strategic alliance between Kunihiko Iwadare, a Japanese engineer, and the Western Electric Company of Illinois, USA. This partnership was pivotal in introducing advanced telecommunications technology to Japan, setting the stage for the company's future endeavors.
Kunihiko Iwadare, with his experience at the Edison Telephone Company of Japan, was instrumental in establishing the company. His vision was to bring cutting-edge technology to the nation. The initial ownership structure reflected this international collaboration, with Western Electric holding a significant stake, providing both capital and technological expertise. The partnership underscored a reliance on foreign investment and technology transfer.
Early agreements between the partners likely included provisions for technology licensing and market distribution, typical of international joint ventures at the time. The early history of NEC is closely tied to the introduction of advanced electrical and communications technology to Japan. The initial ownership structure was designed to facilitate this by leveraging Western Electric's established position in the field.
NEC Corporation was founded on July 17, 1899, as a joint venture. Kunihiko Iwadare, a Japanese engineer, and Western Electric Company of Illinois, USA, were the key players.
The initial ownership structure involved Western Electric, providing capital and technology. This partnership facilitated the introduction of advanced telecommunications to Japan.
Early agreements likely included technology licensing and market distribution. This was a common practice in international joint ventures during that era.
Over time, the ownership dynamics evolved with Japan's industrial growth. The shift towards more independent Japanese control was a typical trend.
The founding team aimed to bring cutting-edge electrical and communications technology to Japan. The initial structure supported this vision.
The collaboration with Western Electric was key. It leveraged their expertise in the field.
Understanding the early ownership of NEC Corporation provides insights into its foundational strategy and its evolution. The initial joint venture was a strategic move to introduce advanced technology to Japan, setting the stage for NEC's future growth. For more details, you can explore the Competitors Landscape of NEC.
- NEC Corporation started as a joint venture with Western Electric.
- Who owns NEC was initially a partnership, with Western Electric holding a significant stake.
- NEC headquarters is currently located in Tokyo, Japan.
- NEC history demonstrates a shift from foreign collaboration to more independent Japanese control.
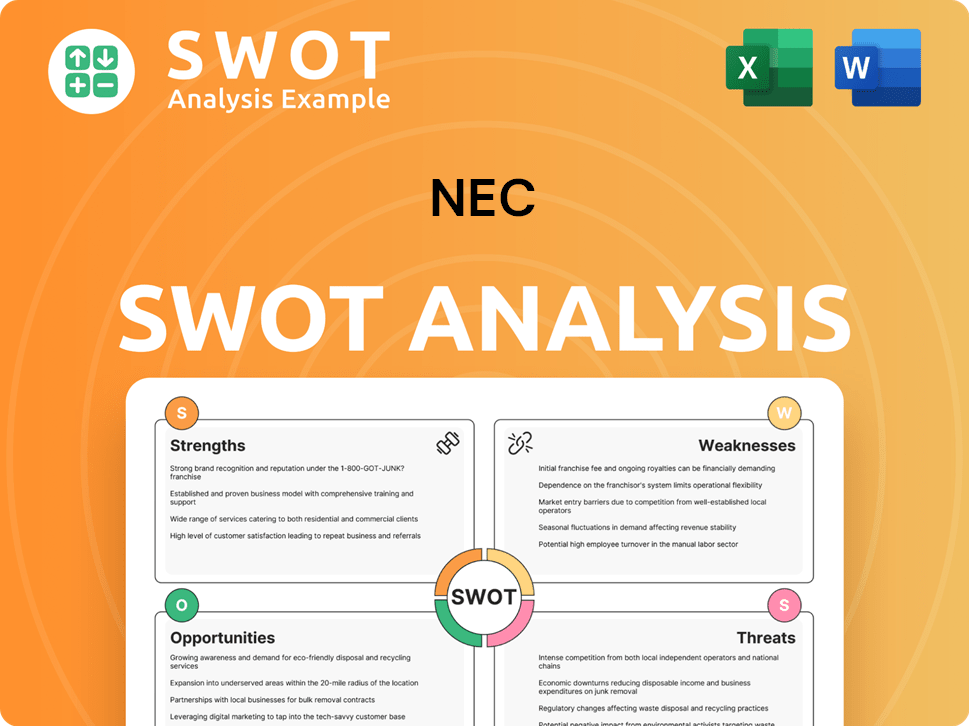
NEC SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has NEC’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of NEC Corporation's ownership reflects its journey from a joint venture to a publicly traded entity. Initially, the company's ownership structure involved a significant stake from Western Electric. This changed over time, with a shift towards increased Japanese ownership. The transition to a publicly listed company on the Tokyo Stock Exchange marked a pivotal moment, diversifying its shareholder base significantly.
As a public company, NEC's ownership structure is now characterized by a mix of institutional investors, mutual funds, index funds, and individual shareholders. This diversification has shaped the company's governance and strategic direction, making it a key player in the global technology market. The shift in ownership also reflects broader trends in corporate governance and investment strategies.
| Event | Impact on Ownership | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Western Electric Divestiture | Increased Japanese Ownership | Early Years |
| Initial Public Offering (IPO) | Transition to Publicly Traded Company | Mid-20th Century |
| Growth of Institutional Investment | Diversification of Shareholders | Ongoing |
As of March 31, 2024, major institutional investors, including Nippon Life Insurance Company, hold substantial stakes in NEC. These investors, along with various trust banks and asset management firms, collectively represent a significant portion of NEC's ownership. The influence of these institutional investors extends to company strategy, with active engagement on financial performance and ESG factors. For example, the top institutional holders collectively own a substantial percentage of outstanding shares, influencing strategic decisions.
NEC's ownership has evolved significantly, transitioning from a joint venture to a publicly traded company.
- Institutional investors like Nippon Life Insurance Company hold significant stakes.
- The ownership structure influences company strategy and governance.
- The company's history includes changes in major shareholding.
- NEC's ownership reflects broader trends in corporate governance.
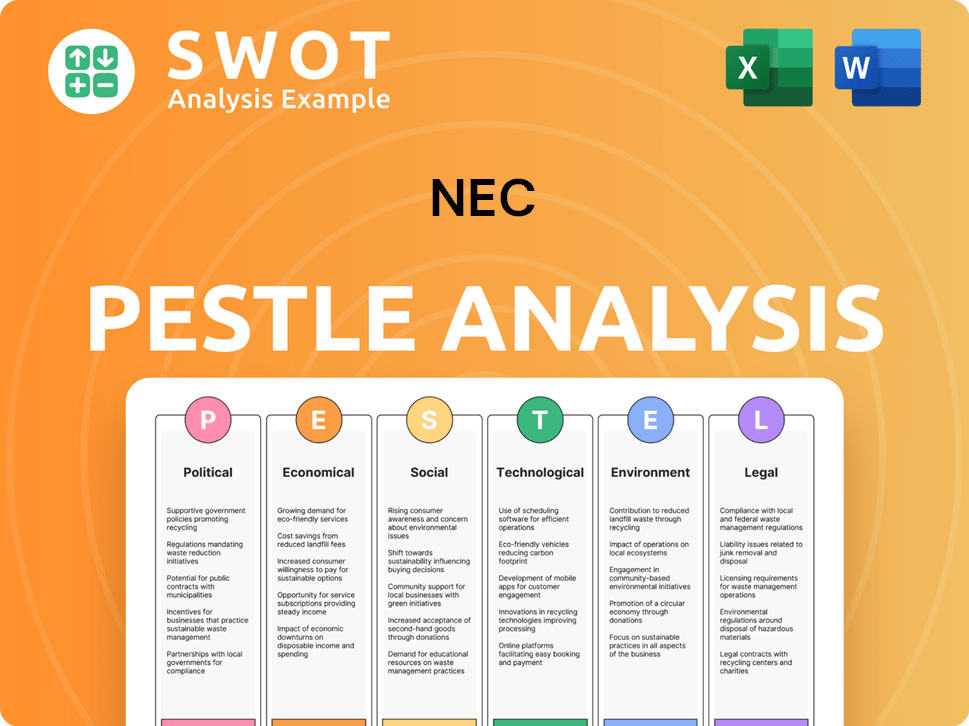
NEC PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on NEC’s Board?
The Board of Directors of NEC Corporation oversees the company's strategic direction. As of the fiscal year ending March 2024, the board includes internal executive directors and independent outside directors. Independent directors are appointed to ensure objectivity and strengthen corporate governance. Major institutional investors, such as Nippon Life Insurance Company, influence the company through engagement and voting at shareholder meetings.
The composition of the board reflects a commitment to diverse expertise and perspectives, crucial for navigating the complexities of the technology sector. The board's structure and the influence of major shareholders are key aspects of understanding NEC ownership and its corporate governance framework. The presence of independent directors is a direct response to the evolving corporate governance landscape in Japan, which emphasizes transparency and accountability.
| Director Category | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Executive Directors | Members of the company's management team | Typically, the CEO and other senior executives |
| Independent Outside Directors | Directors without ties to the company's management, ensuring objectivity | Individuals with experience in finance, technology, or other relevant fields |
| Major Shareholders' Influence | Institutional investors' impact through voting and engagement | Nippon Life Insurance Company |
NEC operates under a one-share-one-vote structure. This means that each share of common stock generally carries one vote, ensuring that voting power is directly proportional to the number of shares held. Japanese corporate governance reforms have emphasized increasing the number of independent directors and enhancing board oversight. While proxy battles or activist investor campaigns against NEC have not been highly prominent in recent public disclosures, the general trend in Japan is towards greater shareholder activism, which could influence decision-making within the company in the future.
The Board of Directors at NEC Corporation plays a vital role in overseeing the company. The board is composed of both internal executive directors and independent outside directors. This structure aims to ensure effective governance and represent shareholder interests.
- The board includes both executive and independent directors.
- Major shareholders influence through voting.
- One-share-one-vote structure is in place.
- Shareholder activism is on the rise.
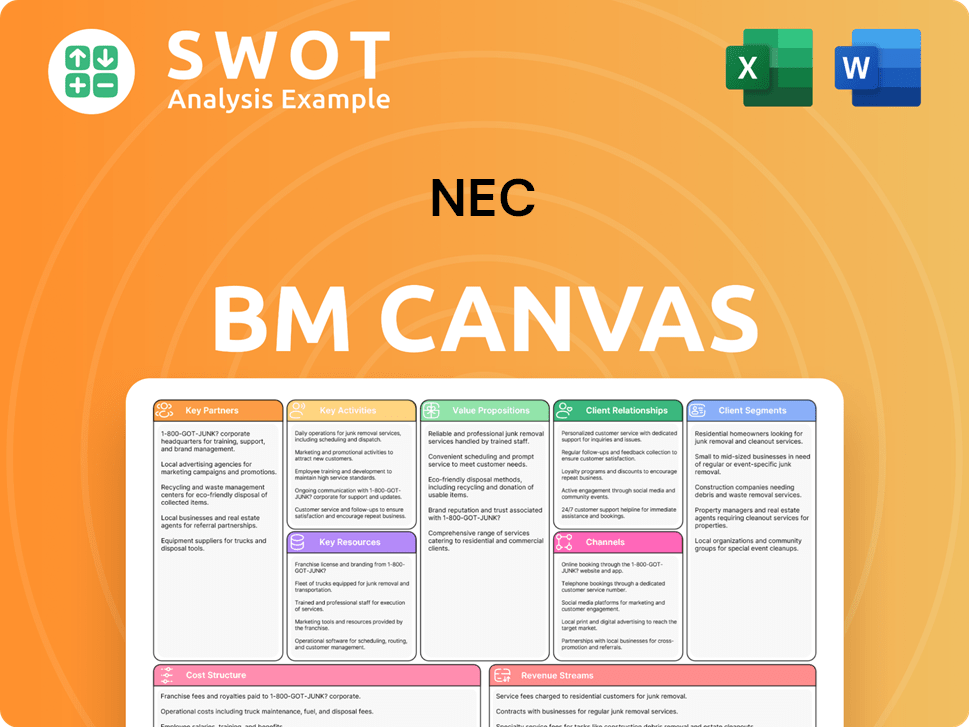
NEC Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped NEC’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, NEC's Brief History has seen its ownership landscape evolve in response to market demands and strategic goals. While there haven't been any huge, publicly announced shifts in its major institutional shareholders, the company has been active in strategic initiatives that can indirectly affect ownership. For instance, acquisitions such as Avaloq Group AG in 2020 and a majority stake in Aspire Technology in 2024, haven’t directly altered the foundational ownership structure, but could lead to capital raises or share issuances.
Industry trends show a rise in institutional ownership globally, and NEC is no exception, with large asset managers and pension funds maintaining significant stakes. The focus on digital transformation, 5G, and AI solutions has positioned NEC in high-growth sectors, potentially attracting growth-oriented investors. The company consistently communicates its long-term vision and financial performance, which are key factors for current and prospective shareholders. NEC's recent financial results for the fiscal year ending March 2024 show strong performance in its IT services and network businesses, solidifying its market position and attractiveness to investors.
Institutional investors continue to hold significant stakes in NEC, reflecting confidence in the company's strategic direction. Acquisitions and strategic initiatives, such as the purchase of Aspire Technology in 2024, can influence the shareholder base. The company's focus on high-growth sectors like 5G and AI is attracting growth-oriented investors.
Strong financial results, particularly in IT services and network businesses, bolster NEC's market position. These results enhance the company's attractiveness to current and prospective investors. The fiscal year ending March 2024 showed positive performance, reinforcing investor confidence.
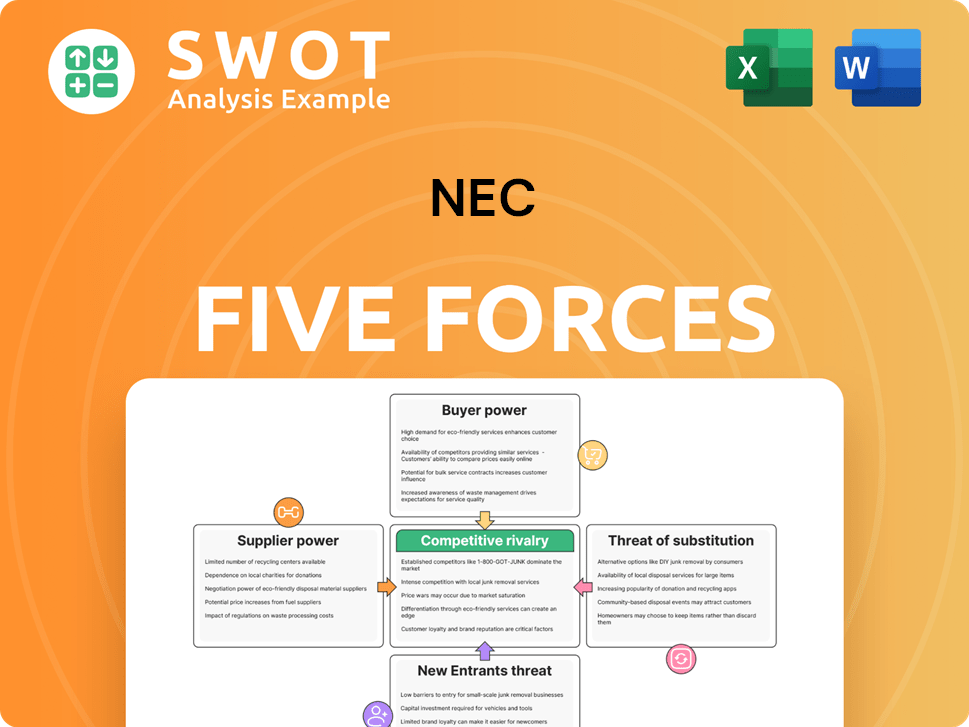
NEC Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of NEC Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of NEC Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of NEC Company?
- How Does NEC Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of NEC Company?
- What is Brief History of NEC Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of NEC Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.