Nissan Motor Bundle
Who Really Controls Nissan Motor Company?
Unraveling the ownership of Nissan Motor Company is key to understanding its strategic moves and future trajectory. The 2018 Carlos Ghosn saga highlighted the critical importance of knowing who holds the reins of power within a global automotive giant. This exploration dives deep into the Nissan Motor SWOT Analysis, examining the company's ownership structure, from its founders to its current stakeholders.
Understanding the Nissan ownership structure is crucial, especially given its complex relationship with the Nissan parent company, Renault. This analysis will dissect the roles of major Nissan shareholders, the influence of the Nissan and Renault alliance, and how these factors shape Nissan's strategic direction. We'll explore the history of Nissan's ownership, the current ownership percentages, and the impact on the company's future in the competitive automotive market.
Who Founded Nissan Motor?
The story of Nissan Motor Company begins with two early automotive ventures: Jitsuyo Jidosha Co., Ltd., established in 1919, and Kwaishinsha Motor Car Works, founded in 1911. Kwaishinsha's DAT car, named after its founders Kenjiro Den, Rokuro Aoyama, and Meitaro Takeuchi, laid some of the earliest groundwork. The formal establishment of Nissan Motor Company as it is known today, however, is primarily attributed to Yoshisuke Aikawa.
In 1933, Aikawa's holding company, Nihon Sangyo (also known as Nissan Konzern), took control of Jidosha Seizo Co., Ltd. The company's name was officially changed to Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. in June 1934. This acquisition and restructuring by Aikawa marked a pivotal moment, consolidating various automotive interests under the Nissan umbrella.
Therefore, while Den, Aoyama, and Takeuchi were crucial in the early stages, Yoshisuke Aikawa is considered the de facto founder of Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. because of his significant investment and consolidation efforts. This consolidation formed the foundation for Nissan's growth into a major automotive manufacturer.
Nihon Sangyo, Yoshisuke Aikawa's zaibatsu, held the controlling stake in the early years.
Specific equity splits and individual shareholdings from 1933-1934 are not available in public historical records.
The formation was largely an internal restructuring and expansion within Aikawa's industrial conglomerate.
Corporate governance structures differed significantly from modern practices during this period.
Aikawa's vision was to create a self-sufficient Japanese automotive industry.
The concentrated control under Nihon Sangyo enabled rapid industrialization and expansion.
The initial ownership of Nissan Motor Company was primarily concentrated under Nihon Sangyo, Yoshisuke Aikawa's holding company. This structure facilitated rapid industrialization and expansion, reflecting Aikawa's vision for a self-sufficient Japanese automotive industry. For further insights into the company's strategic direction, consider reading about the Growth Strategy of Nissan Motor.
Nissan Motor SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Nissan Motor’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The ownership structure of Nissan Motor Company has been significantly shaped by its alliance with Renault. The most critical event was the formation of the Renault-Nissan Alliance in 1999. Before this alliance, Nissan faced financial difficulties, which led to a capital injection and a strategic partnership with the French automaker. This collaboration fundamentally changed Nissan's ownership dynamics.
In early 2024, the primary major stakeholder in Nissan is Renault S.A., holding approximately 15% of Nissan's shares. This is a notable shift from the past, where Renault had a much larger stake, around 43.4%. This reduction was part of a rebalancing agreement within the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance, finalized in late 2023 and early 2024. Under the new agreement, Nissan also holds a 15% stake in Renault, aiming for a more balanced relationship between the two companies.
| Event | Date | Impact on Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| Formation of Renault-Nissan Alliance | 1999 | Renault acquired a controlling stake, reshaping Nissan's ownership. |
| Rebalancing of Alliance | Late 2023-Early 2024 | Renault's stake in Nissan reduced to 15%; Nissan acquired a 15% stake in Renault. |
| Initial Public Offering (IPO) | Earlier in Nissan's History | Nissan became a publicly traded company, increasing the number of shareholders. |
Beyond Renault, Nissan's shares are widely held by institutional investors, mutual funds, index funds, and individual shareholders. Major institutional holders typically include large asset management firms and investment banks. As of March 31, 2024, top institutional investors might include Vanguard Group and BlackRock, holding varying percentages of the publicly traded shares. This shift in the Renault-Nissan alliance is expected to influence future product development and market strategies. To understand more about how Nissan approaches its market, you can read about the Marketing Strategy of Nissan Motor.
Nissan's ownership has evolved significantly, primarily due to the Renault-Nissan Alliance.
- Renault remains a major shareholder, but with a reduced stake.
- Nissan is a publicly traded company with shares held by various institutional and individual investors.
- The rebalancing of the alliance aims for a more equitable partnership.
- The ownership structure influences Nissan's strategic decisions and future direction.
Nissan Motor PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Nissan Motor’s Board?
As of April 2025, the Board of Directors at Nissan Motor Company comprises both internal executives and external independent directors. This structure is designed to ensure robust corporate governance. The board includes leaders from within the company and independent members who bring a variety of expertise. The composition of the board is influenced by the company's ownership structure, even though specific representatives of major shareholders are not always explicitly identified.
Although Renault no longer holds a controlling stake, its significant 15% ownership still has the potential to influence board appointments or strategic discussions. This influence has been a key factor, especially after the alliance rebalancing in late 2023 and early 2024. The board's role is critical in guiding the company's strategic direction and ensuring accountability to all shareholders. Understanding the Brief History of Nissan Motor helps provide context to the current ownership dynamics.
| Board Member | Title | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Makoto Uchida | President and CEO | Oversees the company's global operations. |
| Ashwani Gupta | Chief Operating Officer | Responsible for operational efficiency and strategy. |
| Jean-Dominique Senard | Chairman | Represents Renault, a major shareholder. |
The voting structure at Nissan generally follows a one-share-one-vote principle for common shares. There are no known dual-class shares or special voting rights that would give outsized control to specific entities. Major decisions, including the election of board members, are typically determined by the collective voting power of all shareholders. This structure ensures that all shareholders have a proportional say in the company's direction. The company is a publicly traded entity, and its shares are available on major stock exchanges.
Nissan's board includes internal and independent directors to ensure good governance. The voting structure is based on a one-share-one-vote principle, ensuring fair representation for all shareholders.
- Renault's influence, despite not having a controlling stake, remains significant with a 15% ownership.
- The board's composition reflects the company's ownership structure, influencing strategic decisions.
- Governance controversies in the past have led to a focus on strengthening independent oversight.
- Activist investor campaigns are always a possibility for publicly traded companies.
Nissan Motor Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Nissan Motor’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the most significant development in Nissan Motor Company's ownership has been the restructuring of its alliance with Renault. This rebalancing, finalized in late 2023 and early 2024, saw Renault reduce its stake in Nissan to 15%, transferring 28.4% of its shares to a French trust. In return, Nissan maintained its 15% stake in Renault. This shift aims to establish a more equitable relationship, fostering greater autonomy for Nissan while preserving the operational benefits of the alliance.
Beyond the Renault alliance adjustments, the trend of increasing institutional ownership is evident. Large asset managers and index funds continue to hold substantial shares of Nissan, reflecting broader market trends. While major share buybacks or secondary offerings have not significantly altered the overall ownership structure in the last 3-5 years, the focus has been on strategic alliance adjustments. The impact of leadership changes, such as the departure of Carlos Ghosn, has indirectly influenced investor perception, though not the direct ownership percentages of major shareholders. The company remains publicly traded, with recent emphasis on leveraging the rebalanced alliance for future growth, especially in electric vehicles and advanced technologies.
| Ownership Aspect | Details | Data (2024/2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Renault's Stake | Percentage of shares held by Renault in Nissan | Reduced to 15% |
| Nissan's Stake in Renault | Percentage of shares held by Nissan in Renault | Remained at 15% |
| Shares in French Trust | Percentage of Nissan shares transferred to a French trust | 28.4% |
| Institutional Ownership | Influence of asset managers and index funds | Significant, reflecting broader market trends |
The rebalancing of the Renault-Nissan alliance is the most significant recent development. Renault reduced its stake to 15%, while Nissan maintained its stake in Renault. This shift promotes greater autonomy and a more balanced partnership.
Institutional investors, including large asset managers and index funds, hold substantial shares. This reflects the broader trend of passive investing in major corporations. The ownership structure is evolving.
Leadership changes, such as executive departures, indirectly influence investor perception. These changes do not directly alter major shareholder percentages. Corporate governance remains a key focus.
The rebalanced alliance is key for future growth, especially in EVs and advanced tech. The company is focusing on improving profitability and leveraging strategic partnerships. The company is publicly traded.
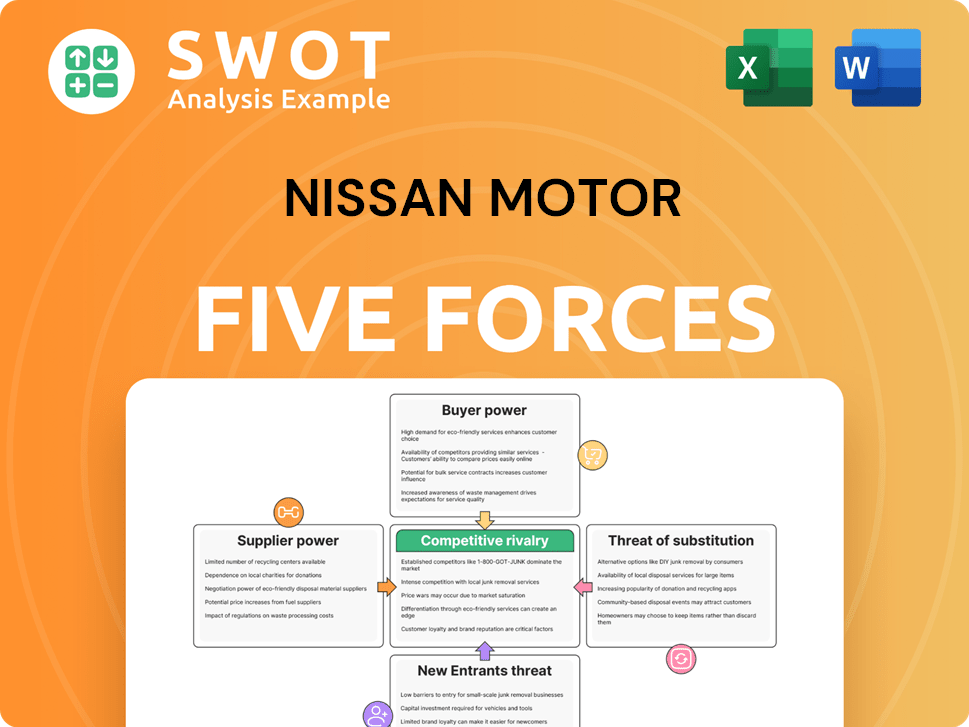
Nissan Motor Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Nissan Motor Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Nissan Motor Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Nissan Motor Company?
- How Does Nissan Motor Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Nissan Motor Company?
- What is Brief History of Nissan Motor Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Nissan Motor Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.