AGC Bundle
How did a Japanese glassmaker become a global materials powerhouse?
Journey back in time to uncover the remarkable AGC SWOT Analysis, a company that began its journey in early 20th century Japan, driven by a vision to revolutionize glass manufacturing. From its humble beginnings as Asahi Glass Co., Ltd., AGC's story is one of relentless innovation and strategic expansion. Discover how this enterprise navigated the ever-changing industrial landscape to become a global leader.
This exploration into the AGC history reveals how the company, initially focused on glass manufacturing, expanded into chemicals, ceramics, and electronics. The early days of AGC were marked by a commitment to meet critical industrial needs, laying the foundation for its current global presence. Learn about the key milestones and strategic decisions that propelled AGC from a domestic manufacturer to a world-leading supplier, impacting sectors like automotive, construction, and electronics.
What is the AGC Founding Story?
The story of the AGC Company, formerly known as Asahi Glass Co., Ltd., began on September 8, 1907. This marked the inception of Japan's first domestic flat glass manufacturer, a vision brought to life by Toshiya Iwasaki, part of the Mitsubishi zaibatsu.
The primary goal was to eliminate Japan's dependence on imported glass, vital for construction and industry. This move was part of a larger strategy to bolster key industries within Japan and reduce reliance on foreign imports. The establishment of the company was a response to the absence of domestic flat glass production capabilities.
The initial business model focused on producing and selling flat glass. The first plant was built in Amagasaki, Hyogo Prefecture, signifying the start of domestic glass manufacturing in Japan. The substantial resources of the Mitsubishi group were crucial in establishing the company. One of the main challenges was overcoming the technical complexities of glass manufacturing, a process needing significant expertise and investment. The cultural and economic environment of the Meiji era, characterized by swift industrialization and a strong push for self-sufficiency, significantly influenced the company's formation and its strategic importance to national development.
The early days of AGC were characterized by overcoming technical hurdles in glass manufacturing and establishing a foothold in a market dominated by imports. The company's founding was a strategic move to support Japan's industrial growth.
- The company's founding date was September 8, 1907.
- Toshiya Iwasaki, the second son of Yataro Iwasaki, founder of Mitsubishi, established the company.
- The primary aim was to create Japan's first domestic flat glass manufacturer.
- The initial plant was located in Amagasaki, Hyogo Prefecture.
The Marketing Strategy of AGC has evolved significantly since its inception. The company's early focus was on establishing a reliable supply of flat glass for the Japanese market. The company's evolution over time has seen it expand its product range and global presence.
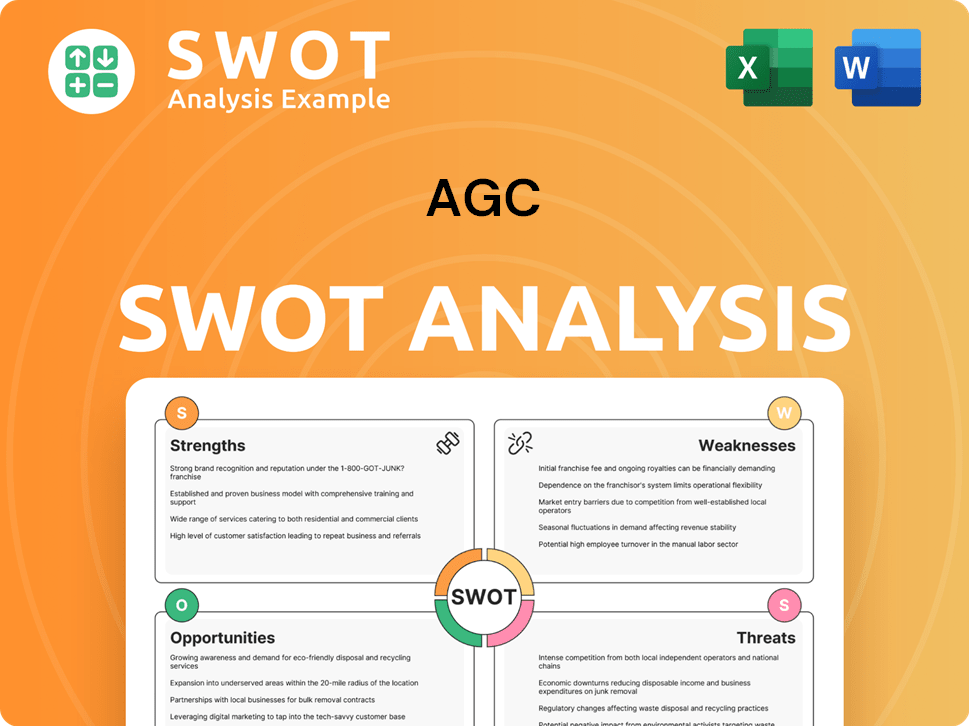
AGC SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of AGC?
The early growth of the AGC Company, formerly known as Asahi Glass Company, centered on establishing and expanding its flat glass production capabilities within Japan. Since its inception in 1907, the company focused on increasing its output and refining its manufacturing processes. A primary goal was to reduce Japan's reliance on imported glass through mass production. The company's early focus was on meeting the growing domestic demand for glass in construction and other industrial sectors.
As the company built its expertise in glassmaking, the initial team expanded. The main facility in Amagasaki served as the core of its operations. AGC began to explore new product categories, utilizing its fundamental glass technology. This included ventures into other types of glass and eventually into chemicals, which was a natural extension given the raw materials and processes involved in glass manufacturing.
In the post-World War II period, AGC embarked on significant geographical expansion, establishing production bases and sales networks overseas. This marked a pivotal shift from a domestic supplier to an international player. Key strategic decisions during this period included investments in research and development to improve glass quality and introduce new products, as well as the adoption of advanced manufacturing techniques.
The market reception for AGC's products was generally positive, driven by the increasing demand for construction materials and later, specialized glass products. The competitive landscape, initially dominated by imports, gradually shifted as AGC established its domestic dominance and subsequently expanded globally. This shaped its trajectory towards becoming a diversified materials company, with a focus on innovation and global presence.
Key strategic decisions during this period included investments in research and development to improve glass quality and introduce new products. The company also underwent leadership transitions that guided its expansion efforts. The evolution of AGC involved adapting to changing market demands. The company's focus on innovation and global expansion has been crucial for its growth.
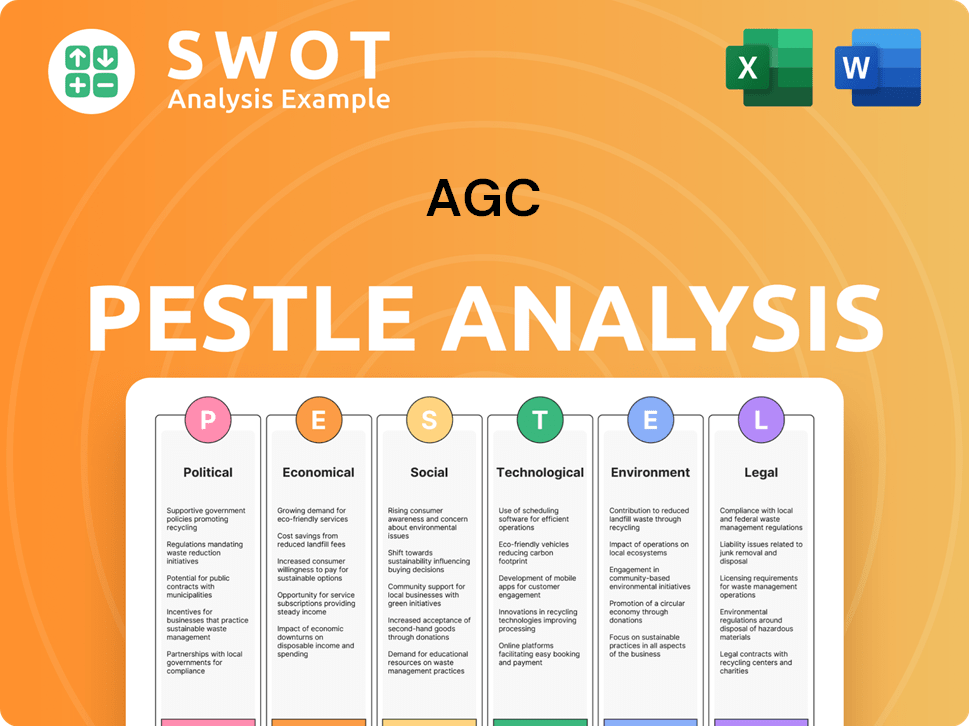
AGC PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in AGC history?
The AGC Company, formerly known as Asahi Glass Company, has a rich history marked by significant milestones in the glass manufacturing industry. A key aspect of the AGC history is its early success in producing flat glass domestically in Japan, a feat that set the stage for its future growth and global expansion. Over the years, the company has consistently demonstrated its ability to innovate and adapt, solidifying its position as a leader in the industry.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| Early 20th Century | Successful domestic production of flat glass in Japan, establishing a foundation for future growth. |
| 1950s-1960s | Introduction of float glass technology, revolutionizing glass production globally. |
| Ongoing | Securing numerous patents across diverse product portfolios, including architectural, automotive, and electronic materials. |
| Ongoing | Establishing major partnerships with global companies, expanding reach and product applications. |
Throughout its history, AGC has been at the forefront of innovation in the glass industry. The company's advancements in float glass technology were groundbreaking, changing how glass is produced worldwide. Furthermore, AGC has consistently developed new materials and technologies to meet evolving market demands, particularly in the electronics and automotive sectors.
Revolutionized glass production, leading to higher quality and more efficient manufacturing processes.
Developed advanced automotive glass products, including lightweight and energy-efficient options.
Introduced high-performance architectural glass, focusing on energy efficiency and aesthetics.
Created specialized glass and materials for displays and other electronic applications, adapting to the rapidly changing tech landscape.
Continuous investment in R&D has been a cornerstone of AGC's innovation strategy, driving the development of new products and technologies.
AGC holds a significant number of patents globally, showcasing its commitment to innovation across various product lines.
The AGC Group has faced numerous challenges throughout its history, including economic downturns and intense competition. The company has had to adapt to volatile raw material prices and shifting market demands, such as those in the electronics industry.
The 2008 financial crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted the company, requiring strategic restructuring and a focus on high-value products.
Competition from other glass manufacturers has driven AGC to continuously innovate and improve its products and processes to maintain its market position.
Fluctuations in the cost of raw materials have required AGC to implement efficient cost management strategies and seek alternative sourcing options.
Changes in the electronics industry have pushed AGC to develop new display glass technologies and adapt to evolving consumer needs.
Rapid technological progress in the automotive sector has driven the need for lighter, more durable, and energy-efficient glass solutions.
Global events, such as trade disputes and political instability, have created uncertainties and impacted AGC's operations and supply chains.
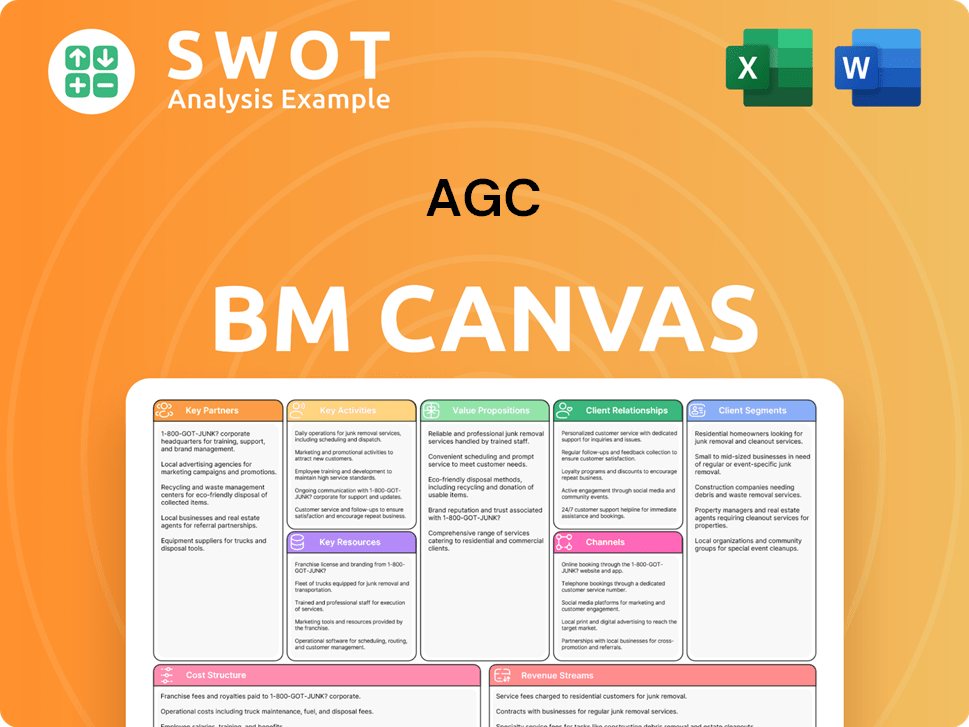
AGC Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for AGC?
The AGC Company, formerly known as Asahi Glass Co., Ltd., has a rich history. It began in 1907 in Amagasaki, Japan. Over the years, it evolved from a glass manufacturer to a diversified global company. Key milestones include early mass production of flat glass, international expansion, and significant diversification into chemicals and electronics materials. The company's name changed to AGC Inc. in 2002, reflecting its broader scope.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1907 | Founded as Asahi Glass Co., Ltd. in Amagasaki, Japan. |
| 1914 | Successfully establishes mass production technology for flat glass. |
| 1920s-1930s | Expands production capacity and diversifies into other glass products. |
| 1950s | Begins international expansion, establishing overseas operations. |
| 1960s | Adopts the float glass process, revolutionizing glass manufacturing. |
| 1980s | Diversifies significantly into chemicals and electronics materials. |
| 1990s | Continues global expansion and strengthens R&D for high-tech materials. |
| 2002 | Changes corporate name to AGC Inc. to reflect its broader business scope. |
| 2010s | Focuses on sustainability initiatives and advanced materials for emerging technologies. |
| 2020s | Accelerates digital transformation and invests in next-generation technologies like bio-pharmaceuticals and advanced mobility solutions. |
AGC is expanding its high-performance materials business, particularly in areas like 5G infrastructure, advanced displays, and life sciences. This strategic move aligns with growing demand in these sectors. The company is investing in R&D to develop cutting-edge technologies and materials. This expansion is a key element of their future growth strategy.
The company aims to enhance its market position in mobility by developing innovative glass solutions for autonomous vehicles and electric vehicles. This includes lightweight and energy-efficient glass. The focus on mobility solutions reflects the shift towards sustainable transportation. This is a significant area of investment and innovation for the company.
In the construction sector, AGC is focusing on sustainable and energy-saving glass products. This commitment addresses the growing demand for environmentally friendly building materials. The company's innovation roadmap includes continued investment in R&D to develop cutting-edge technologies and materials. These products contribute to reducing carbon emissions.
AGC is accelerating its digital transformation across all operations to improve efficiency and foster new business models. The company is also investing in R&D to address global challenges. This includes climate change and an aging society. These efforts are crucial for future growth and sustainability.
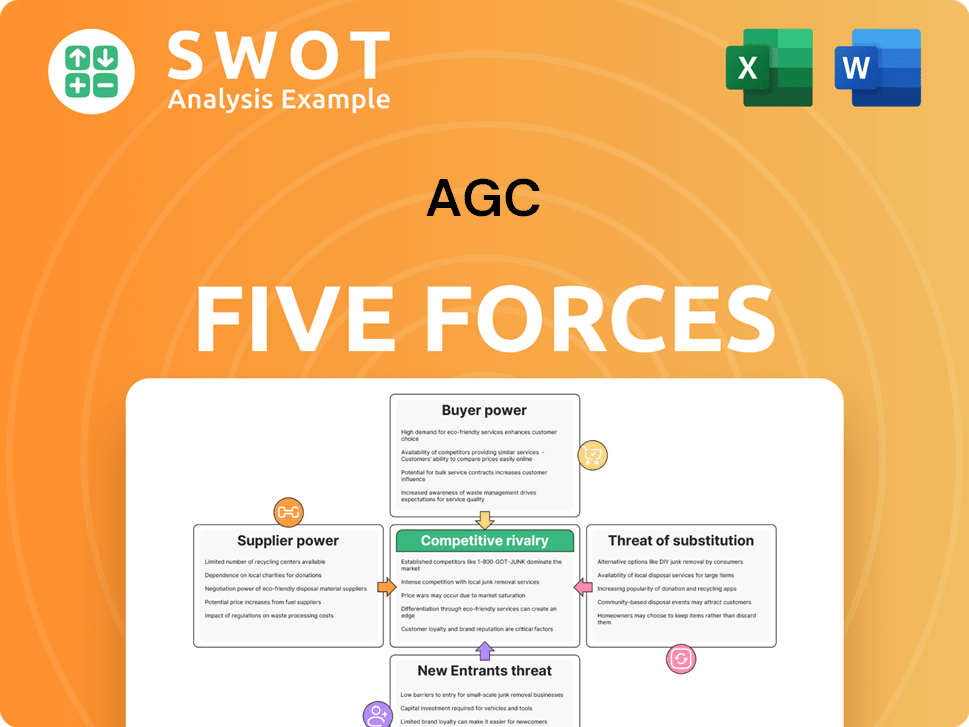
AGC Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of AGC Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of AGC Company?
- How Does AGC Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of AGC Company?
- What is Brief History of AGC Company?
- Who Owns AGC Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of AGC Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.