BlackRock Bundle
How Did BlackRock Become a Financial Titan?
Dive into the captivating BlackRock SWOT Analysis to understand the company's strategic moves. BlackRock's story is a testament to how innovation and strategic vision can reshape the financial world. From its inception, the company has redefined investment management, evolving from a specialized firm to a global powerhouse. This journey offers invaluable lessons for investors and business strategists alike.
The brief history of BlackRock company reveals a remarkable growth trajectory, driven by a commitment to superior risk management and a keen understanding of market dynamics. Founded in 1988, BlackRock's early years were marked by a focus on fixed income and institutional clients, setting the stage for its future dominance. Understanding BlackRock's history provides critical insights into its investment strategies, global presence, and the impact it has on the financial services industry. The company, led by its CEO, Larry Fink, has consistently adapted to market changes, solidifying its position as the world's largest asset manager.
What is the BlackRock Founding Story?
The story of BlackRock begins on March 7, 1988. It was founded by a team of eight individuals, a group that would change the face of the investment management industry. This team, which included Laurence Fink, Robert S. Kapito, and Susan Wagner, saw an opportunity to revolutionize how risk was understood and managed in the financial world.
The founders, many of whom had experience at First Boston, recognized a significant gap in the market. They aimed to provide sophisticated risk management tools, a necessity highlighted by the 1987 stock market crash. Their approach was innovative, focusing on quantitative analysis and actively managed fixed income portfolios. This marked the beginning of what would become one of the world's largest investment management firms.
The name 'BlackRock' was chosen to convey strength and stability. Initial funding came from a $5 million loan from Blackstone Group, which received a 50% stake in return. This early partnership was crucial in establishing the firm's credibility and providing the necessary capital for its launch. This brief history of BlackRock reveals the firm's origins in addressing critical market needs.
BlackRock's early focus was on sophisticated risk management and fixed income asset management.
- Founding Date: March 7, 1988.
- Founders: Laurence Fink, Robert S. Kapito, Susan Wagner, and others.
- Initial Problem: Inadequate risk management in the investment community.
- First Product: Actively managed fixed income portfolios.
- Initial Funding: $5 million loan from Blackstone Group.
The early focus on risk management and fixed income positioned BlackRock to capitalize on market needs. The firm's ability to provide comprehensive services quickly attracted institutional clients. This early success set the stage for its future expansion and its global presence. To understand more about how BlackRock has grown, you can explore the Marketing Strategy of BlackRock.
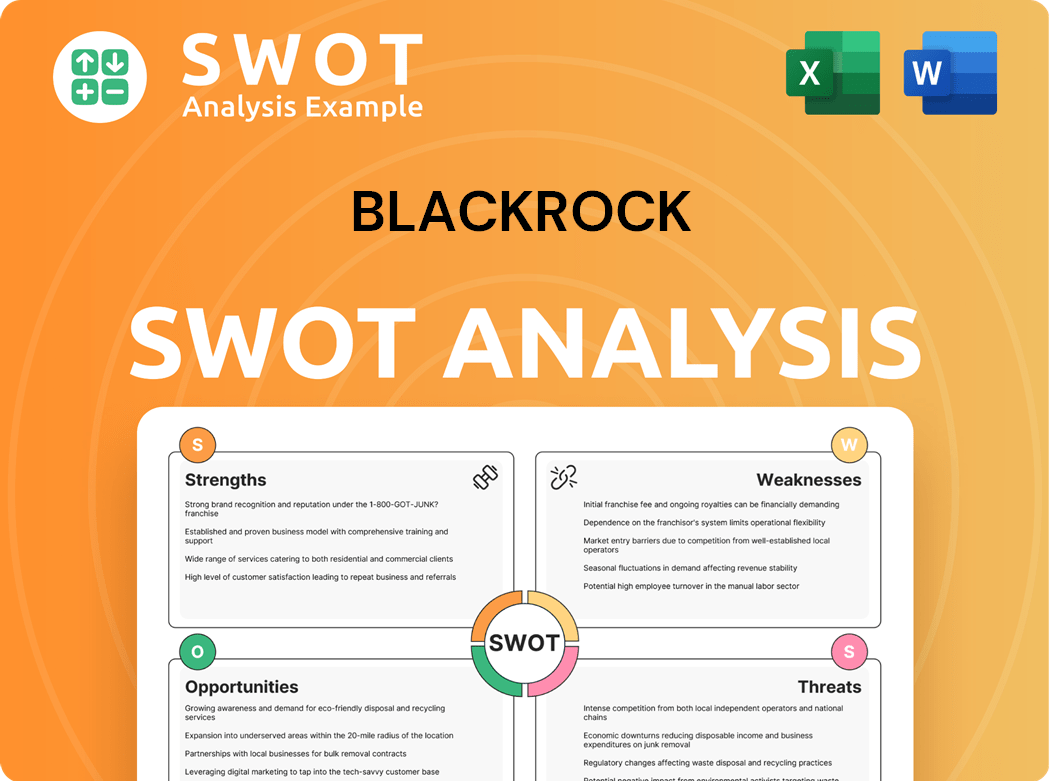
BlackRock SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of BlackRock?
The early growth of BlackRock was marked by a strategic focus on institutional clients and a strong emphasis on risk management. During its initial years, the BlackRock company quickly gained momentum by providing tailored fixed income solutions. By 1992, the firm had already reached $10 billion in assets under management, demonstrating its early success in the investment management sector. This period laid the groundwork for its future expansion and dominance in financial services.
In its early years, BlackRock concentrated on providing specialized fixed income solutions to institutional clients. This strategic focus allowed the company to establish a strong reputation and build a solid client base. The emphasis on fixed income was a key factor in the company's initial growth and success, setting the stage for future diversification. This early specialization helped BlackRock differentiate itself in the competitive market.
A critical element of BlackRock's early success was the development of its proprietary risk analytics platform, Aladdin. This technology offered clients unparalleled insights into their portfolio risk exposures, providing a significant competitive advantage. Aladdin evolved into a comprehensive platform, becoming a key differentiator in the market and supporting the company's growth trajectory. The platform's capabilities enhanced BlackRock's ability to serve its clients effectively.
In 1995, BlackRock separated from the Blackstone Group, gaining greater strategic autonomy. This pivotal moment allowed the company to expand its offerings beyond fixed income. Early acquisitions, such as State Street Research & Management in 2005, significantly bolstered its investment capabilities and client base. This period saw the firm make critical decisions to diversify its product offerings and expand its geographical footprint.
The firm began its global expansion, establishing offices in Europe and Asia to serve a growing international clientele. Strategic acquisitions, such as the purchase of Barclays Global Investors in 2009, further amplified its assets under management and market presence. By the mid-2000s, BlackRock had established itself as a major player in the asset management industry. For more information on the company's ownership structure, you can read about the Owners & Shareholders of BlackRock.
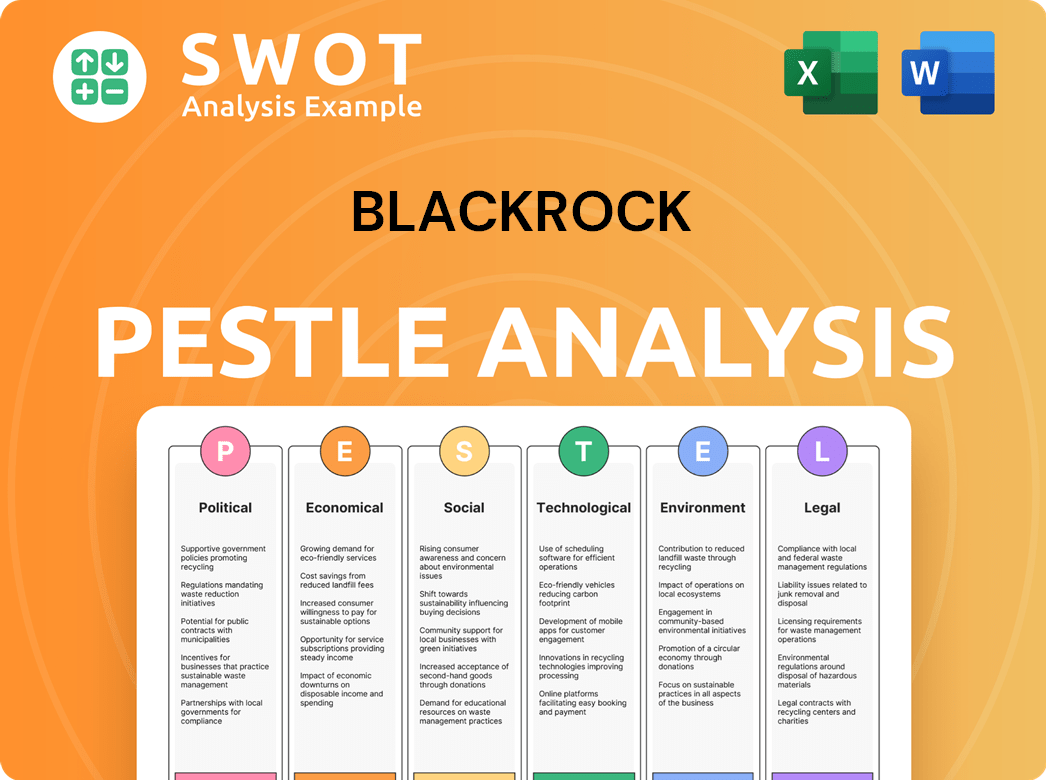
BlackRock PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in BlackRock history?
The BlackRock company's journey is marked by key milestones that have solidified its position in the financial services industry. From its inception to its current status as a global leader in investment management, BlackRock's history is a testament to strategic vision and adaptability.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1988 | BlackRock was founded by Larry Fink and a team of partners. |
| 1999 | BlackRock went public, marking a significant step in its growth trajectory. |
| 2006 | BlackRock acquired Merrill Lynch Investment Managers, expanding its global reach. |
| 2009 | BlackRock acquired Barclays Global Investors (BGI), including iShares, becoming the world's largest asset manager. |
| 2024 | BlackRock continues to innovate and adapt to the evolving financial landscape, with a focus on sustainable investing and technological advancements. |
BlackRock has consistently pioneered innovations in the financial services sector. A notable innovation is Aladdin, its proprietary risk management and trading platform, which has become an industry standard.
Aladdin is BlackRock's proprietary risk management and trading platform, a cornerstone of its operations. It provides sophisticated analytics and risk management tools, used by institutions globally.
The acquisition of Barclays Global Investors (BGI) in 2009, which included iShares, was a pivotal move. This acquisition significantly boosted BlackRock's presence in the ETF market.
BlackRock has integrated ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) factors into its investment processes. This reflects a commitment to sustainable investing and responsible corporate citizenship.
Despite its successes, BlackRock has faced several challenges. The firm has navigated scrutiny related to its stance on ESG investing, and has also encountered competitive pressures from other large asset managers.
BlackRock has faced scrutiny regarding its ESG investing approach, particularly from political factions. The firm has adapted its communication and strategy in response to market and stakeholder feedback.
The company faces intense competition from other large asset managers and the rise of passive investing. BlackRock continues to innovate and adapt to maintain its leadership position.
Market volatility and economic downturns pose ongoing challenges. BlackRock's robust risk management framework helps it navigate these uncertainties.
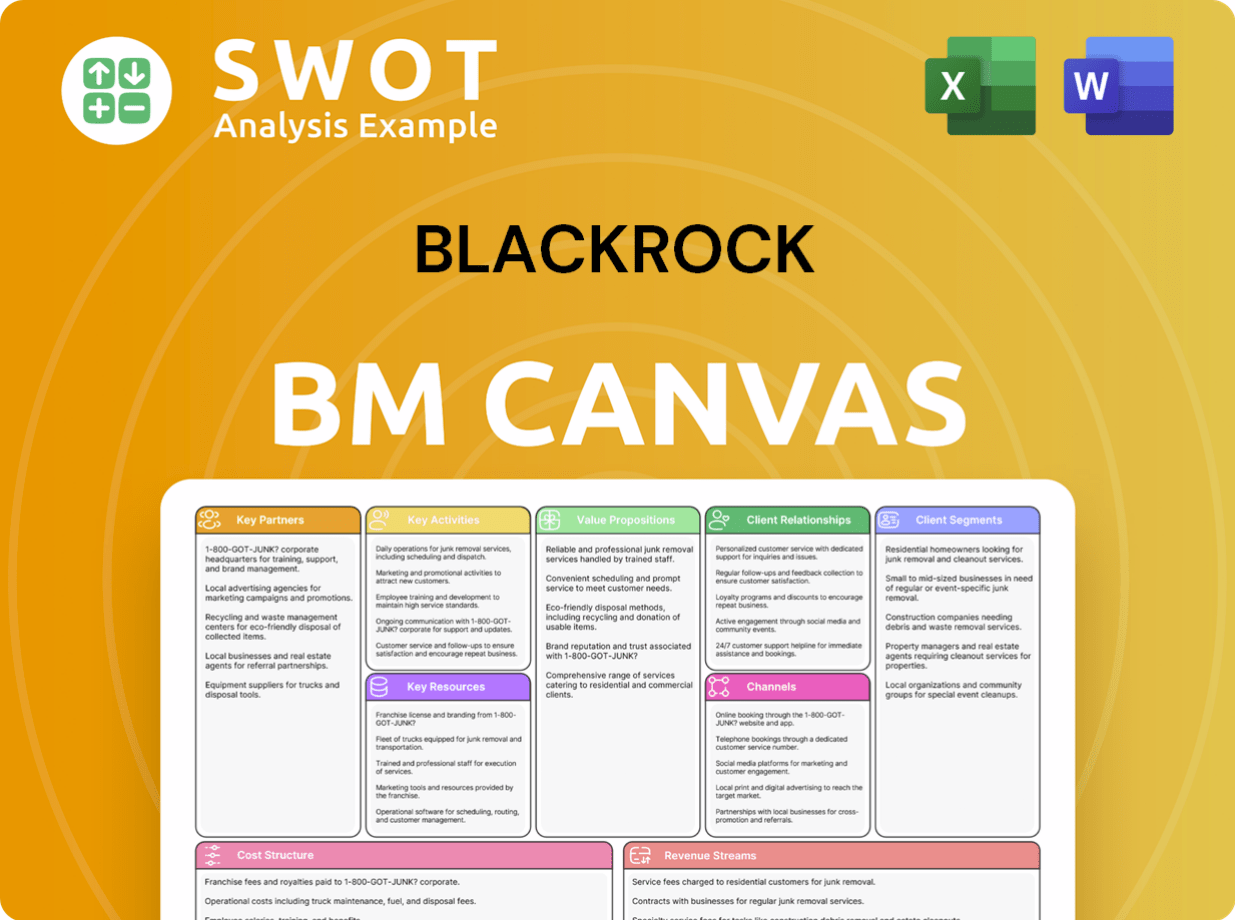
BlackRock Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for BlackRock?
The BlackRock history reflects a remarkable journey in the investment management industry. Founded in 1988, the company quickly ascended to become a global leader. Key milestones include going public in 1999, strategic acquisitions like Barclays Global Investors (BGI) in 2009, and a strong focus on sustainable investing, particularly highlighted in Larry Fink's annual letters. BlackRock's growth trajectory has been fueled by both organic expansion and strategic acquisitions, solidifying its position as a dominant force in financial services.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1988 | BlackRock Financial Management was founded, marking the beginning of its journey in investment management. |
| 1992 | Assets under management (AUM) reached $10 billion, a significant milestone in its early growth. |
| 1995 | BlackRock became an independent company, setting the stage for its future expansion. |
| 1999 | BlackRock went public on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), opening a new chapter for the company. |
| 2005 | Acquired State Street Research & Management, expanding its asset base. |
| 2006 | Merged with Merrill Lynch Investment Managers, further increasing its market share. |
| 2009 | Acquired Barclays Global Investors (BGI), including iShares, significantly boosting its ETF offerings. |
| 2017 | Launched BlackRock's 'Future of Finance' initiative, focusing on technological innovation. |
| 2020 | Larry Fink's annual letter emphasized sustainability as a core investment theme, influencing the firm's strategy. |
| 2024 | Continues to expand its Aladdin platform and sustainable investing offerings. |
BlackRock is investing heavily in its Aladdin platform, aiming to enhance its capabilities for risk management, portfolio construction, and sustainable investing. This technological focus is crucial for maintaining its competitive edge. The company plans to integrate advanced analytics and AI to improve investment outcomes. BlackRock's commitment to technology is a key part of its strategy.
BlackRock sees significant growth opportunities in private markets, including private equity, private debt, and infrastructure. These assets offer diversification and potentially higher returns for institutional investors. Expanding its private market offerings is a strategic priority. This expansion aims to attract new clients and increase AUM.
Sustainable investing remains a core strategic initiative for BlackRock. The firm continues to integrate ESG considerations across its investment spectrum. They develop new sustainable products to meet growing client demand. BlackRock is committed to long-term value creation through responsible investing, and this focus aligns with evolving investor preferences.
BlackRock is strategically positioned to capitalize on key trends. The company leverages its scale, technological prowess, and diversified product offerings. Leadership statements from Larry Fink consistently underscore the importance of long-term value creation. Analyst predictions suggest BlackRock will maintain its dominant position in the investment management industry.
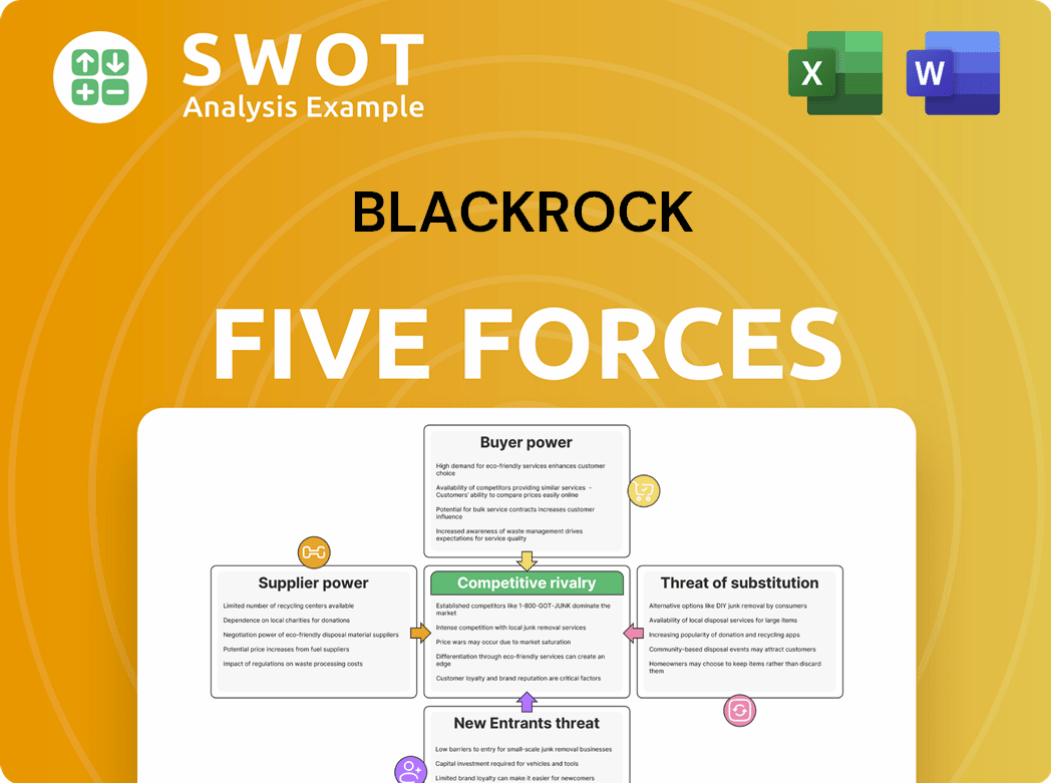
BlackRock Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of BlackRock Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of BlackRock Company?
- How Does BlackRock Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of BlackRock Company?
- What is Brief History of BlackRock Company?
- Who Owns BlackRock Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of BlackRock Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.