China Mobile Bundle
How Did China Mobile Become a Global Telecom Powerhouse?
Witness the extraordinary transformation of China Mobile, a company that mirrors China's own ascent on the world stage. From its inception in 1997 as China Telecom (Hong Kong) Limited, this China Mobile SWOT Analysis reveals a journey of strategic decisions and technological leaps. Explore how China Mobile, initially focused on providing accessible mobile services, revolutionized communication across China.
The brief history of China Mobile showcases its evolution from a state-owned enterprise to the world's largest mobile network operator, a testament to its remarkable growth and development. Understanding China Mobile's early years and its strategic moves, including its 5G rollout and international expansion, is crucial for grasping its current status and future plans. This deep dive into China Mobile's history provides essential insights into the Chinese telecommunications landscape and its impact on China's economy.
What is the China Mobile Founding Story?
The story of China Mobile begins on September 3, 1997. This marked the official incorporation of China Mobile Communications Corporation in Hong Kong. The establishment of this company was a strategic move by the Chinese government.
The goal was to separate mobile services from China Telecom. This separation allowed for focused development and market-driven growth. The burgeoning demand for mobile communication in China was the main problem at the time. The existing structure struggled to meet this demand efficiently.
The opportunity was to create a dedicated entity. This entity could rapidly expand mobile network infrastructure and services across China. The company's initial focus was on providing mobile voice and basic data services. This was aimed at a rapidly growing subscriber base.
China Mobile was created to meet the rising demand for mobile services in China. The company's initial business model centered on mobile voice and basic data services. The company's name, China Mobile, clearly indicated its business and national reach.
- The company's initial offerings included GSM mobile services.
- Funding came from state investment and public listings.
- China Mobile (Hong Kong) Limited was listed on the New York Stock Exchange and the Hong Kong Stock Exchange in October 1997.
- This dual listing was important for raising capital for network expansion.
The late 1990s in China were characterized by increasing urbanization. There was also a growing middle class. This provided a good environment for mobile services to grow quickly. The company's early years were marked by rapid expansion. This was driven by the increasing demand for mobile phones.
In 2024, China Mobile's market capitalization was approximately $160 billion USD. The company has consistently been a leader in the Chinese telecommunications market. It has also been a major player globally. The company's growth and development have been impressive. It has played a key role in China's economic and technological advancement. For more details on its financial performance, consider reading Revenue Streams & Business Model of China Mobile.
China Mobile's impact on China has been significant. It has connected millions of people. It has also contributed to economic growth. The company continues to invest in technological advancements. It is also focused on expanding its services. This includes its 5G rollout and other initiatives.
China Mobile SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of China Mobile?
The early growth and expansion of China Mobile were marked by rapid development and extensive network infrastructure build-out across China. Following its 1997 listing, the company focused on expanding its GSM network. Early product launches, such as prepaid mobile services and SMS, gained significant traction, fueling unprecedented customer acquisition. These initial years laid the groundwork for its future dominance in the Chinese telecommunications market.
China Mobile's early years involved a monumental effort to build out its GSM network across China's vast geography. This included strategic investments in base stations and infrastructure, enabling broader coverage. The company strategically established offices in major provincial capitals, creating regional operational hubs to support its expansion.
The introduction of prepaid mobile services and SMS was pivotal in attracting a large customer base. These services were accessible and affordable, contributing to the company's rapid growth. By 2002, China Mobile had reached a milestone of 100 million subscribers, showcasing its early success in the market.
Expansion involved extending network coverage to more remote areas and diversifying service offerings. Acquisitions primarily involved absorbing provincial telecommunication assets from China Telecom, consolidating its national footprint. This strategic move helped China Mobile strengthen its position as a leading mobile network operator.
Initially, China Unicom was a major competitor, but China Mobile quickly established a commanding lead. Key decisions during this period included significant investments in network capacity and the early adoption of new mobile technologies. By 2006, China Mobile had surpassed 300 million subscribers, demonstrating its exponential growth and market dominance.
China Mobile PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in China Mobile history?
The China Mobile history is marked by significant achievements and expansions, establishing it as a leading Chinese telecommunications provider. From its inception, the company has consistently pushed boundaries, contributing significantly to the evolution of the mobile communications landscape.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2000 | China Mobile was listed on the New York Stock Exchange and the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. |
| 2008 | China Mobile launched its 3G network based on the TD-SCDMA standard, a significant move in China mobile services. |
| 2013 | The company began the rollout of its 4G network, greatly enhancing mobile broadband capabilities. |
| 2019 | China Mobile officially launched its 5G services, becoming a leader in 5G technology. |
| 2023 | China Mobile had over 1.94 million 5G base stations, solidifying its position as the world's largest 5G network. |
China Mobile has consistently embraced technological advancements, leading to numerous innovations. Its early adoption and expansion of 3G and 4G networks significantly improved mobile services across China.
China Mobile pioneered the deployment of 3G using the TD-SCDMA standard, a significant step in the China Mobile history. This initiative helped to increase mobile internet access across the country.
The rapid rollout of 4G (TD-LTE) networks dramatically improved mobile broadband services. This expansion supported the growing demand for data-intensive applications and services.
China Mobile has built the world's largest 5G network, demonstrating its commitment to cutting-edge technology. This has positioned the company at the forefront of the 5G revolution.
Collaborations with equipment vendors such as Huawei and ZTE have been crucial. These partnerships have helped China Mobile to advance its network infrastructure and service offerings.
China Mobile has secured numerous patents in mobile communication technologies. This intellectual property supports its competitive advantage in the market.
China Mobile has expanded its services beyond basic mobile connectivity. The company now offers a wide range of digital services to meet evolving consumer needs.
Despite its successes, China Mobile has faced several challenges. Market competition and the need for large capital investments have been constant hurdles.
Intense competition from China Unicom and China Telecom has led to pricing pressures and service innovation challenges. Maintaining market share requires constant strategic adjustments.
The transitions from 3G to 4G and then to 5G required significant capital expenditure and technological upgrades. Managing these transitions efficiently is crucial for maintaining competitiveness.
Economic downturns and changes in consumer spending have impacted the telecommunications sector. Adapting to these fluctuations requires careful financial planning.
Managing a vast subscriber base while ensuring high service quality is a constant challenge. China Mobile continually invests in its infrastructure to meet these demands.
The telecommunications industry is subject to strict regulatory oversight, which can impact operations and strategic decisions. Navigating this environment is essential for compliance and growth.
The high capital expenditure required for network upgrades and expansion is a significant financial challenge. Strategic investment decisions are critical for long-term success.
China Mobile Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for China Mobile?
Here's a look at the key milestones in the history of China Mobile, a leading player in Chinese telecommunications. The company's journey from its inception to its current status as a global mobile network operator reflects significant technological advancements and market dominance. The company has consistently adapted to the evolving demands of the mobile services sector.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1997 | China Telecom (Hong Kong) Limited, later known as China Mobile, was incorporated and listed on the NYSE and HKEX. |
| 2000 | The company rebranded as China Mobile and separated from China Telecom. |
| 2002 | China Mobile surpassed 100 million mobile subscribers. |
| 2008 | The company launched its 3G (TD-SCDMA) network. |
| 2013 | Commercial 4G (TD-LTE) services were commenced. |
| 2014 | China Mobile became the world's largest mobile operator by subscriber count. |
| 2019 | Commercial 5G services were launched. |
| 2021 | The company reached 1 billion mobile subscribers. |
| 2023 | China Mobile built over 1.94 million 5G base stations, solidifying its 5G leadership. |
| 2024 | The company continues to expand its 5G network and explores 5G-Advanced and 6G technologies. |
China Mobile is focused on deepening its 5G penetration across China. It's also exploring 5G-Advanced and 6G technologies to stay at the forefront of mobile communication. Investments in research and development are crucial for future mobile communication standards.
The company plans to expand into new digital services, integrating 5G with AI, cloud computing, and big data. Market expansion includes further penetration into the enterprise market with customized solutions. China Mobile is also exploring international opportunities.
Analyst predictions suggest continued strong performance due to China Mobile's dominant market position. The ongoing demand for mobile and digital services in China supports this outlook. The company benefits from its vast subscriber base and extensive network infrastructure.
China Mobile's strategic initiatives include '5G+' development to create new industry solutions. The company's long-term vision is to connect people and businesses, providing ubiquitous and intelligent information services. Leadership is committed to high-quality network infrastructure and innovative service offerings.
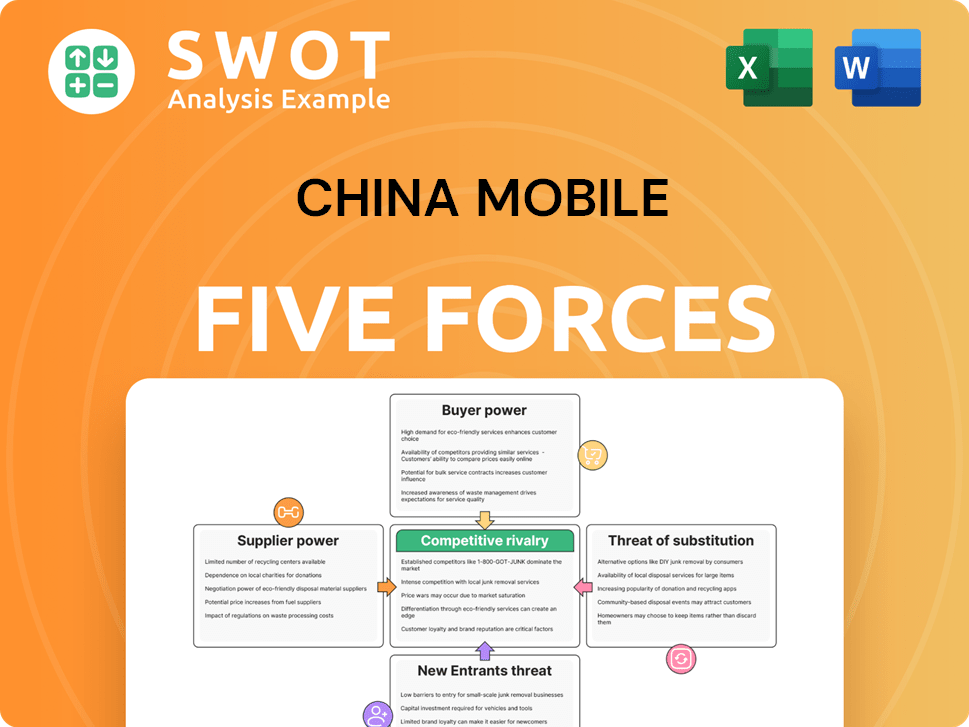
China Mobile Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of China Mobile Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of China Mobile Company?
- How Does China Mobile Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of China Mobile Company?
- What is Brief History of China Mobile Company?
- Who Owns China Mobile Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of China Mobile Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.