Deutsche Bank Bundle
How Did Deutsche Bank Rise to Global Prominence?
Deutsche Bank's story is a compelling narrative of ambition, adaptation, and global impact. Founded in 1870, it emerged from a strategic vision to empower German international trade, challenging the established financial order. This journey, marked by significant milestones and strategic shifts, transformed a Berlin-based venture into a worldwide financial powerhouse.
From its early days facilitating German commerce to its current status as a global financial institution, understanding Deutsche Bank SWOT Analysis provides critical insights into its evolution. Exploring the DB history reveals a dynamic interplay of economic forces, strategic decisions, and global events. This exploration of Deutsche Bank history offers a deep dive into the German banking giant's past, present, and future, making it a fascinating study for anyone interested in the history of finance and the evolution of financial institutions.
What is the Deutsche Bank Founding Story?
The story of Deutsche Bank begins on March 10, 1870, in Berlin, Germany. This marked the formal inception of a financial institution that would become a significant player in global finance. The founders aimed to establish a bank that could support Germany's burgeoning international trade ambitions.
The founders of Deutsche Bank included Adelbert Delbrück, Ludwig Bamberger, and L.M. von der Heydt. Their collective vision was to create a financial institution independent of foreign banks, capable of fueling Germany's expanding commercial interests. This initiative was born out of the need for a strong, independent financial institution to support Germany's rapid economic expansion on the global stage.
Deutsche Bank's early business model centered on facilitating international trade, offering services like foreign exchange and issuing foreign loans. The bank's name itself, 'Deutsche Bank', was carefully chosen to reflect its commitment to German economic interests.
- The initial funding came from private investors and influential figures in German industry.
- The bank's creation was significantly influenced by Germany's unification and rapid industrialization.
- Deutsche Bank's early products and services were designed to provide credit and financial instruments for international transactions.
- The bank's early success was tied to its ability to support German companies in their global ventures, playing a crucial role in the nation's economic growth.
The bank's early years were shaped by the economic and cultural context of the time, including Germany's unification and rapid industrialization. The bank played a crucial role in supporting German companies in their global ventures, contributing significantly to the nation's economic growth. To understand more about the bank's core values and mission, you can read about the Mission, Vision & Core Values of Deutsche Bank.
Deutsche Bank SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Deutsche Bank?
The early growth of Deutsche Bank, a key player in Revenue Streams & Business Model of Deutsche Bank, was marked by rapid international expansion and diversification. Immediately after its founding, the bank established branches in London (1873) and Shanghai (1872), followed by Yokohama (1872), highlighting its early commitment to global trade finance. This early international focus was crucial in establishing its presence in major commercial hubs worldwide.
Deutsche Bank quickly expanded its operations internationally. The establishment of branches in London, Shanghai, and Yokohama within its first few years demonstrates its early commitment to international trade and finance. This strategic global expansion helped the bank establish its presence in key commercial centers.
The bank broadened its offerings beyond trade finance. It began underwriting industrial bonds, participating in railway financing, and engaging in stock exchange operations. This diversification reflected Germany's industrial boom and the evolving needs of its clients.
Key acquisitions and mergers played a significant role in its domestic expansion. The acquisition of Bergisch-Märkische Bank in 1914 and the merger with Disconto-Gesellschaft in 1929 were pivotal. These moves consolidated its position within Germany, expanding its branch network and client base.
Leadership transitions influenced the bank's direction. The role of Hermann Wallich in the late 19th and early 20th centuries guided the bank through significant economic changes and global conflicts. The bank's strategic shift from trade-focused operations to a comprehensive banking model was driven by the evolving needs of German industry.
Deutsche Bank PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Deutsche Bank history?
The DB history is marked by significant achievements, including its role in financing major industrial projects and its expansion into investment banking. The Deutsche Bank history showcases its evolution from a regional bank to a global financial powerhouse, with key milestones shaping its trajectory over the years.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1870 | Founded in Berlin to facilitate trade between Germany and other countries. |
| Early 20th Century | Instrumental in financing major industrial projects, including the Baghdad Railway. |
| 1957 | Merged with Norddeutsche Bank and Rheinisch-Westfälische Bank to form a significant financial institution. |
| 1989 | Acquired Morgan Grenfell, expanding its presence in investment banking. |
| 1999 | Acquired Bankers Trust, further strengthening its global reach. |
| 2019 | Announced a major restructuring plan, including job cuts and exiting equities sales and trading. |
Deutsche Bank pioneered early forms of syndicated lending, a crucial innovation for large-scale corporate financing. Its expansion into investment banking and asset management marked key innovations, allowing it to offer a more comprehensive suite of financial services.
Deutsche Bank was an early adopter of syndicated lending, which allowed it to finance large-scale projects by pooling resources from multiple lenders. This innovation was critical for supporting major industrial and infrastructure projects.
The bank's strategic expansion into investment banking provided a broader range of services, including underwriting, mergers and acquisitions advisory, and trading. This diversification helped to increase revenue streams and market presence.
Deutsche Bank's growth in asset management allowed it to manage investments for a diverse client base, including institutional and retail investors. This expansion was key to increasing its fee-based income.
The bank's strategic entry into global markets, particularly in the Americas and Asia-Pacific, expanded its reach and diversified its revenue streams. This global presence was crucial for its long-term growth.
Deutsche Bank has invested significantly in digital transformation, including online banking platforms, mobile apps, and data analytics. This has improved customer experience and operational efficiency.
The bank has launched several sustainable finance initiatives, including green bonds and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investments. This aligns with the growing demand for sustainable financial products.
Deutsche Bank has faced significant challenges, including legal battles and financial repercussions from the 2008 financial crisis. The bank has also undergone major restructuring efforts, including job cuts and divestments, to improve its financial standing.
The 2008 financial crisis led to significant fines and legal battles for Deutsche Bank, particularly related to mortgage-backed securities. These issues impacted its financial performance and reputation.
In 2019, the bank announced a major restructuring plan, including cutting approximately 18,000 jobs and exiting its equities sales and trading business. This was aimed at returning to profitability and improving its capital position.
Historical controversies, including its involvement during the Nazi era and issues with money laundering, have caused significant reputational damage. These issues have required extensive efforts at reconciliation and compliance improvements.
Deutsche Bank has faced increased regulatory scrutiny, leading to higher compliance costs and stricter oversight. This has impacted its operational efficiency and strategic flexibility.
The bank has struggled with profitability in recent years, facing challenges from low-interest rates, increased competition, and operational inefficiencies. This has prompted strategic shifts to improve financial performance.
Geopolitical risks, including economic instability and trade tensions, have created uncertainty for Deutsche Bank. These factors can impact its international operations and financial performance.
Deutsche Bank Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Deutsche Bank?
The story of Deutsche Bank history is one of significant growth and adaptation, reflecting its pivotal role in the evolution of German banking and global finance. Founded in Berlin in 1870, it initially focused on financing international trade. Over the years, it expanded its operations globally, navigated major economic and political events, and adapted to changing market dynamics. Key milestones include early international expansions, strategic mergers, and significant shifts in its business model. The bank has faced challenges, including the global financial crisis and the need for restructuring, but has consistently aimed to maintain its position as a key player in the financial industry.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1870 | Founded in Berlin, Germany, with a focus on financing international trade. |
| 1872 | Opens first international branches in Shanghai and Yokohama. |
| 1914 | Acquires Bergisch-Märkische Bank, expanding its domestic presence. |
| 1929 | Merges with Disconto-Gesellschaft, becoming the largest bank in Germany. |
| 1957 | Re-established as a unified bank after post-WWII decentralization. |
| 1989 | Acquires Morgan Grenfell, significantly expanding its investment banking capabilities. |
| 2001 | Lists shares on the New York Stock Exchange, increasing its global visibility. |
| 2008 | Faces significant challenges during the global financial crisis. |
| 2019 | Announces major restructuring plan, including job cuts and exit from equities sales and trading. |
| 2020 | Celebrates its 150th anniversary amidst ongoing transformation efforts. |
| 2023 | Reports strong financial results, indicating progress in its strategic transformation. |
| 2024-2025 | Continues to focus on digitalization, sustainability, and strengthening its core businesses. |
The bank is investing heavily in technology to improve customer experience and streamline operations. This includes enhancements to its digital platforms and the integration of advanced technologies like AI and machine learning. This focus on digital transformation aims to increase efficiency and offer more personalized services. In 2024, the bank is expected to increase its technology spending by around 5% to support these initiatives.
The bank is committed to becoming a leader in sustainable finance. It's offering more green financing and investment solutions, aiming to support environmentally friendly projects. This includes a focus on ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) factors in its investment decisions. By 2025, the bank plans to increase its sustainable finance assets by 15%, reflecting its commitment to this area.
Recent financial results show progress in its strategic transformation, with improved profitability and a strengthened balance sheet. The bank’s leadership is focusing on disciplined capital allocation and maintaining a strong control environment. Analysts project a further increase in revenue of around 7% in 2024, driven by these strategic initiatives and improved market conditions.
The bank is navigating increasing regulatory scrutiny, the rise of fintech, and the growing demand for sustainable finance. These trends are expected to significantly shape its future. The bank is actively adapting to these changes, investing in compliance and risk management. The evolving regulatory landscape is expected to influence the bank's operational costs, with an estimated increase of 3% in compliance expenses by 2025.
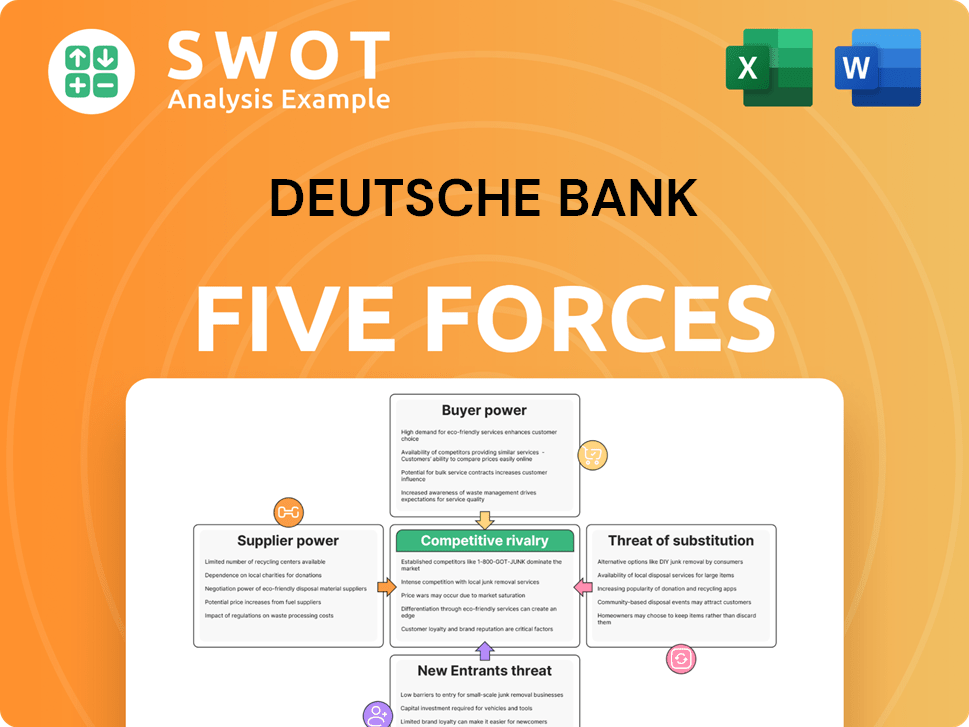
Deutsche Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Deutsche Bank Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Deutsche Bank Company?
- How Does Deutsche Bank Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Deutsche Bank Company?
- What is Brief History of Deutsche Bank Company?
- Who Owns Deutsche Bank Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Deutsche Bank Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.