GE Aerospace Bundle
How did the merger of two electric companies shape the future of flight for GE Aerospace?
Imagine a company whose roots trace back to the dawn of electricity, eventually soaring to the forefront of the GE Aerospace SWOT Analysis. This is the story of GE Aerospace, a global titan in the aerospace industry, its narrative beginning in 1892 with the merger of Edison General Electric and Thomson-Houston Electric Company. From powering homes to propelling aircraft, the evolution of GE Aerospace is a testament to innovation and strategic foresight.

This brief history of GE Aerospace explores the early days of GE Aviation, tracing its transformation from an electrical pioneer to a leader in the Aerospace industry. The journey of the GE company is a compelling tale of adaptation and technological advancement, showcasing how a vision of harnessing electricity expanded to revolutionize aviation history. Delve into the key milestones and GE Aerospace acquisitions that shaped this aviation powerhouse, understanding its impact on the global market.
What is the GE Aerospace Founding Story?
The story of GE Aerospace begins with the formation of the General Electric Company (GE) on April 15, 1892. This pivotal moment came about through the merger of the Edison General Electric Company and Thomson-Houston Electric Company. While GE Aerospace as a distinct entity emerged much later, its roots are firmly planted in this foundational event.
Key figures like Thomas Edison, Charles A. Coffin, and Elihu Thomson were instrumental in shaping the parent company. Edison's inventive genius and Thomson's pioneering work in electrical engineering set the stage for GE's future innovations. The merger itself was a strategic move to consolidate competing electrical interests and establish a dominant player in the rapidly growing electrical industry.
The early business model of GE centered on a broad range of electrical products. These included everything from lighting and power generation equipment to transportation solutions. The initial funding for this venture came from the combined capital of the merged entities. This consolidation was driven by the economic climate of the late 19th century, characterized by rapid industrialization and increasing demand for electrical infrastructure. The intense competition in the electrical sector made this merger a strategic necessity.
GE's entry into the aerospace industry evolved over time, leveraging its expertise in electrical engineering and manufacturing. The company's involvement grew significantly throughout the 20th century, particularly during World War II, when it began producing aircraft engines.
- GE's initial focus was on electrical products, but it gradually expanded into aviation.
- World War II was a catalyst, driving GE's involvement in aircraft engine production.
- The company's growth in aerospace was fueled by technological advancements and strategic acquisitions.
- GE's early innovations laid the groundwork for its future in the aerospace sector.
GE's journey into the aerospace industry wasn't immediate. It was a gradual evolution, building on the company's core strengths in electrical engineering and manufacturing. The company's involvement in aviation gained significant momentum during World War II. This period saw GE begin producing aircraft engines, marking a crucial turning point in its history. This expansion was driven by technological advancements and strategic acquisitions.
The early innovations and the company's strategic vision laid the foundation for its future in the aerospace sector. GE's commitment to research and development has been a constant, leading to advancements in engine technology, materials science, and other critical areas. This commitment has enabled GE Aerospace to become a leading player in the global aerospace industry.
Over the years, GE Aerospace achieved several milestones, including significant advancements in engine technology and strategic acquisitions. These moves helped solidify its position in the market.
- Development of advanced engine technologies.
- Strategic acquisitions to expand capabilities.
- Strong growth in both commercial and military aviation sectors.
- Continuous investment in research and development.
Throughout its history, GE Aerospace has achieved several key milestones. These include significant advancements in engine technology and strategic acquisitions. These moves have helped solidify the company's position in the market. The company has consistently invested in research and development, leading to innovations that have driven its growth. This has resulted in strong growth in both commercial and military aviation sectors.
The company's focus on innovation and strategic expansion has been a constant theme. This has allowed GE Aerospace to adapt to changing market dynamics and maintain its leadership position. GE's commitment to innovation has enabled it to stay ahead of the competition. The company's ongoing investments in research and development have been critical to its success. The company's financial performance has been strong, reflecting its success in the aerospace industry.
In recent years, GE Aerospace has continued to innovate and adapt to the changing aerospace landscape. The company is focused on sustainable aviation and advanced technologies.
- Focus on sustainable aviation and reducing emissions.
- Development of advanced engine technologies.
- Strategic partnerships and collaborations.
- Continued investment in research and development.
In recent years, GE Aerospace has continued to innovate and adapt to the changing aerospace landscape. The company is focused on sustainable aviation and advanced technologies. GE Aerospace is actively working on reducing emissions and developing more fuel-efficient engines. The company is also investing in advanced materials and manufacturing processes.
GE Aerospace is also pursuing strategic partnerships and collaborations to enhance its capabilities and expand its market reach. The company's commitment to research and development remains strong. This is essential for maintaining its competitive edge. The company's future outlook is positive, with continued growth expected in both commercial and military aviation sectors. To understand the company's target market in more detail, you can read this article: Target Market of GE Aerospace.
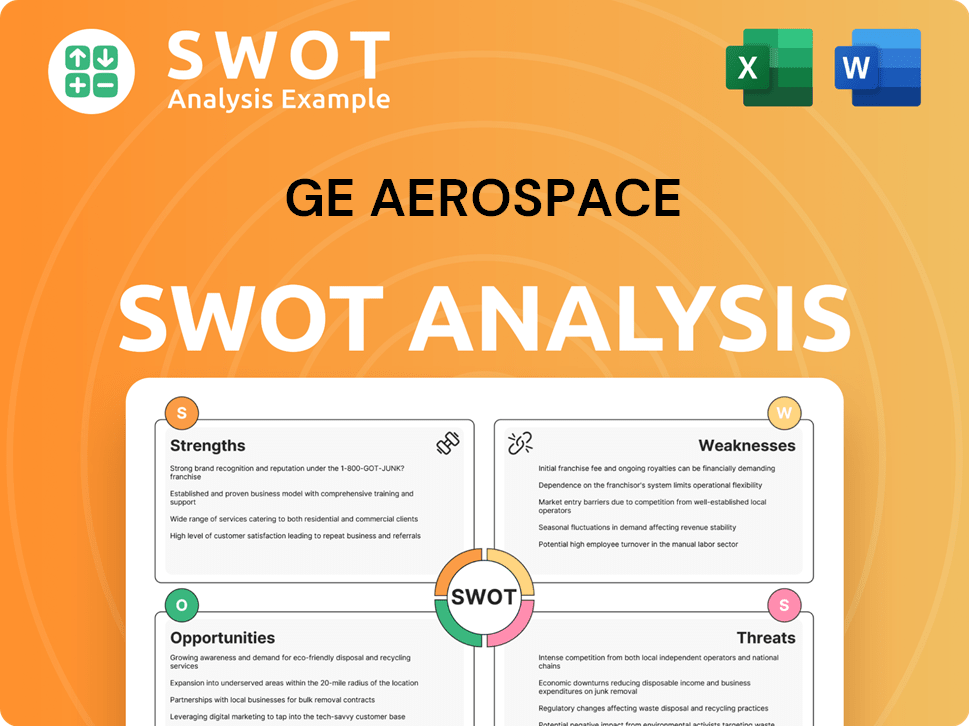
GE Aerospace SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of GE Aerospace?
The early growth of what is now known as GE Aerospace, stemmed from its parent company, General Electric's, early diversification. GE's foray into the aerospace industry was gradual, building upon its electrical expertise. The company's initial steps in aviation were marked by advancements in turbosuperchargers and the development of America's first jet engine. This early period laid the foundation for GE's future in the aerospace sector.
Early expansion involved recruiting engineers and scientists specializing in propulsion and power systems. Initially, facilities were integrated within existing GE manufacturing plants. This approach allowed for leveraging existing infrastructure and resources. The focus was on building a dedicated team to drive innovation and development in the emerging aerospace field.
The aerospace market entry was fueled by the growing demand for both military and commercial aircraft, especially after World War II. This demand spurred significant growth and investment in the aerospace industry. The strategic focus was on capitalizing on the opportunities presented by the expansion of air travel and military needs.
Key leadership transitions within GE's various divisions played a crucial role in fostering the growth of its aviation-related ventures. Strategic shifts involved a growing focus on gas turbine technology, recognizing its potential for aircraft propulsion. This forward-thinking approach helped GE establish a strong foothold in the evolving aerospace industry. Read about the Mission, Vision & Core Values of GE Aerospace.
This early growth phase was characterized by significant investment in research and development, driven by both wartime necessity and the long-term vision for air travel. The competitive landscape was initially shaped by other emerging aviation pioneers and established engine manufacturers. GE's commitment to innovation and technological advancement helped it stand out in the competitive aerospace industry.
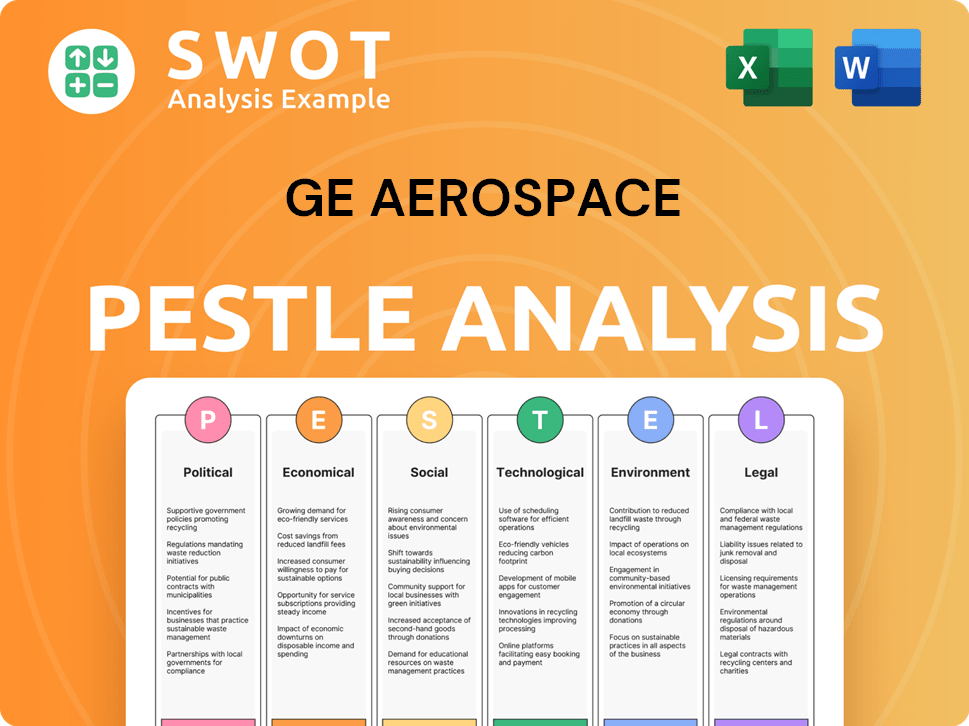
GE Aerospace PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in GE Aerospace history?
The Owners & Shareholders of GE Aerospace history is marked by significant achievements in the aviation sector. The company, formerly part of the larger GE company, has consistently pushed the boundaries of aerospace technology. Its journey is a testament to innovation and resilience within the dynamic aerospace industry.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1942 | Development of the I-A, America's first jet engine, a pivotal moment in GE Aviation history. |
| 1950s | The J79 engine entered service, powering numerous military aircraft and becoming a cornerstone of military aviation. |
| 1970s | The CFM56 engine, a joint venture with Safran Aircraft Engines, was launched, eventually becoming the best-selling commercial aircraft engine. |
| Ongoing | Continuous advancements in engine efficiency, materials science, and propulsion systems, securing numerous patents. |
| 2024 | Continued focus on sustainable aviation technologies and expansion of services and aftermarket support. |
GE Aerospace has consistently introduced groundbreaking innovations in the aerospace industry. These innovations have significantly improved engine performance and efficiency, contributing to advancements in aviation history.
GE Aerospace pioneered jet engine technology, developing the I-A in 1942, marking a crucial early step in GE Aviation history. This innovation set the stage for future advancements in propulsion systems.
The CFM56 engine, a joint venture with Safran, revolutionized commercial aviation. It became the best-selling commercial aircraft engine, showcasing GE's collaborative innovation.
GE Aerospace has made significant strides in materials science, leading to lighter, more durable, and more efficient engines. These advancements have improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
The company has integrated digital technologies for engine monitoring and predictive maintenance. This has enhanced operational efficiency and reduced downtime for aircraft.
GE Aerospace is investing in sustainable aviation technologies, including advanced engine designs and alternative fuels. This is a response to growing environmental concerns and regulations.
GE Aerospace utilizes additive manufacturing (3D printing) to create complex engine components. This allows for innovative designs and reduces manufacturing lead times.
Despite its successes, GE Aerospace has faced various challenges throughout its history. Market fluctuations and competitive pressures have required continuous adaptation and strategic adjustments.
Economic downturns, such as the global financial crisis, impacted demand for new aircraft and engine orders. This necessitated cost management and strategic adjustments to maintain profitability.
Competition from other major engine manufacturers has driven the need for continuous innovation and efficiency improvements. This has led to increased investment in research and development.
Product failures, though rare, have led to rigorous investigations and design improvements. These incidents have underscored the importance of stringent quality control and testing.
The broader GE conglomerate faced periods of restructuring and financial challenges, which indirectly impacted the aerospace division. This led to strategic pivots and efficiency measures.
The aerospace industry, including GE Aerospace, has faced supply chain disruptions in recent years. These disruptions have impacted production schedules and increased costs.
Evolving environmental regulations and safety standards pose ongoing challenges. GE Aerospace must continually adapt its products and services to meet these requirements.
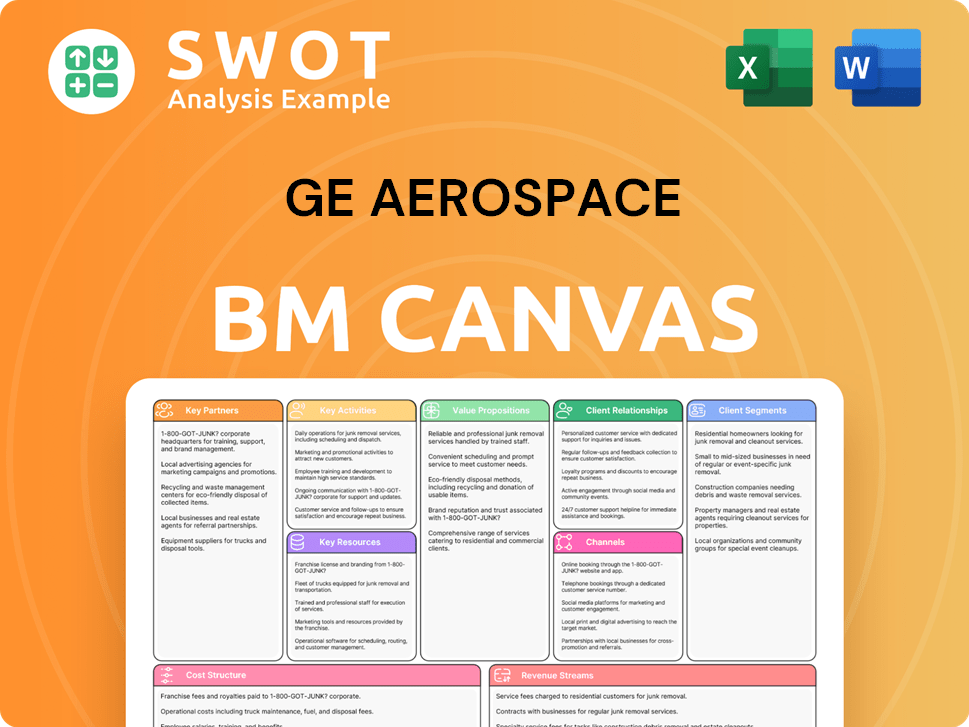
GE Aerospace Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for GE Aerospace?
The Growth Strategy of GE Aerospace has a rich history, evolving from its parent company, General Electric. The journey of GE Aerospace, formerly GE Aviation, is marked by significant technological advancements and strategic shifts. From pioneering jet engine development to its recent emergence as an independent entity, the company's evolution reflects the dynamic nature of the aerospace industry.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1892 | Formation of General Electric Company, the parent company of what would become GE Aerospace. |
| 1917 | GE began developing turbosuperchargers for aircraft engines, marking its early entry into the aviation sector. |
| 1942 | GE developed the I-A, America's first jet engine, a pivotal moment in aviation history. |
| 1950s-1960s | Development of iconic military engines like the J79, solidifying GE's position in the aerospace industry. |
| 1974 | Formation of CFM International, a joint venture with Safran Aircraft Engines, which would become highly successful. |
| 1980s-1990s | The CFM56 engine, developed through CFM International, became the best-selling commercial aircraft engine. |
| 2000s | Continued development of advanced commercial engines like the GE90 and GEnx, showcasing technological innovation. |
| 2010s | Focus on additive manufacturing and advanced materials for engine components, enhancing efficiency and performance. |
| 2021 | GE Aviation rebrands to GE Aerospace, signaling a broader focus. |
| 2023 | GE completed the spin-off of GE HealthCare, streamlining its focus on aerospace. |
| 2024 | GE Aerospace officially becomes an independent public company, marking its complete separation from GE Vernova. |
GE Aerospace is investing heavily in sustainable aviation technologies. This includes exploring open fan architectures and hybrid-electric propulsion systems. The goal is to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2050, aligning with global environmental targets.
GE Aerospace plans to expand its global service network and leverage data analytics for predictive maintenance. The company is targeting emerging markets for commercial aviation and aiming to secure new military contracts. These strategies are aimed at broadening its market presence and revenue streams.
The aerospace industry is witnessing increased demand for fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and digital integration. GE Aerospace is well-positioned to capitalize on these trends. The company's technological leadership and extensive installed base provide a strong foundation for future growth.
Analyst predictions suggest continued growth in the aerospace sector. GE Aerospace's commitment to innovation and sustainable flight positions it favorably. Recent financial reports indicate a positive trajectory, with a focus on long-term value creation and strategic investments in key areas.
GE Aerospace Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked

Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of GE Aerospace Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of GE Aerospace Company?
- How Does GE Aerospace Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of GE Aerospace Company?
- What is Brief History of GE Aerospace Company?
- Who Owns GE Aerospace Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of GE Aerospace Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.