Meyer Burger Bundle
How did Meyer Burger transform the solar industry?
Meyer Burger AG's story is a compelling narrative of innovation and adaptation within the dynamic solar industry. From its Swiss roots in 1953, this Meyer Burger SWOT Analysis reveals how the company evolved from a machinery supplier to a leading solar panel manufacturer. This transformation showcases the company's commitment to high-efficiency solar technology and its pivotal role in the energy transition.
The brief history of Meyer Burger solar highlights its strategic shift, marked by significant investments in European and U.S. production facilities. This Swiss company's journey reflects the evolution of the solar market, from its early stages to a globally critical industry. Understanding Meyer Burger's key milestones and its current market position provides valuable insights into its ambitions within the solar industry.
What is the Meyer Burger Founding Story?
The Meyer Burger history began in 1953 in Switzerland, a period marked by post-war industrial growth. The company's establishment reflects the Swiss dedication to precision engineering, initially focusing on machinery for processing hard and brittle materials. This focus would later prove crucial for the semiconductor and solar industries.
The early days of the Meyer Burger company saw it establish itself as a B2B provider of high-precision equipment. This business model allowed the company to cultivate a strong base in engineering expertise, capitalizing on the robust industrial environment of Switzerland. The company's formation was likely influenced by the culture of innovation and precision that is characteristic of Swiss business practices.
While specific details about the exact founding date within 1953 and the complete list of original founders are not widely publicized, the company's origins are firmly rooted in the post-war European industrial landscape. The initial focus on specialized machinery laid the groundwork for its future involvement in the solar industry. The company's early success was built on providing advanced manufacturing solutions to other businesses.
The Meyer Burger AG was founded in Switzerland in 1953, specializing in high-precision machinery. The initial focus was on machines for processing hard and brittle materials, later crucial for the solar industry.
- The company's early business model was B2B, supplying advanced manufacturing solutions.
- The Swiss industrial environment and culture of precision played a significant role in its establishment.
- The company's early focus on specialized machinery laid the groundwork for its future involvement in the solar industry.
- The company's early success was built on providing advanced manufacturing solutions to other businesses.
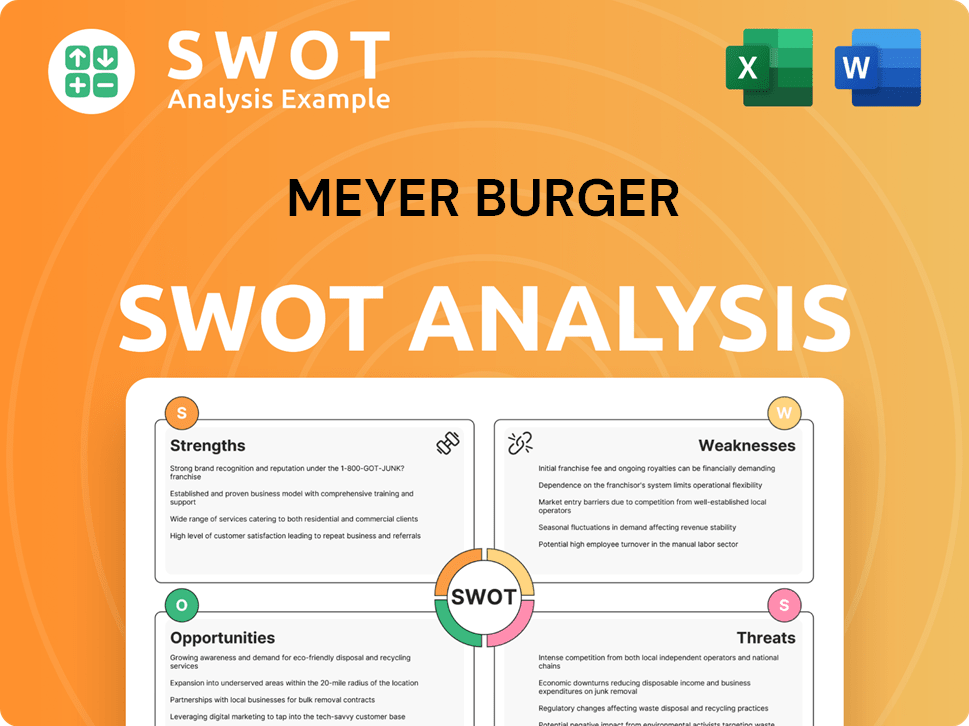
Meyer Burger SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Meyer Burger?
The early growth of the Meyer Burger company was defined by its emergence as a key supplier of production equipment for the solar and semiconductor industries. This Swiss company strategically pivoted towards the photovoltaic industry in the 1980s, aligning with the rising interest in renewable energy. Key developments included the introduction of advanced wafering technologies, crucial for efficient solar cell production.
The acquisition of Hennecke Systems in 1994, a German firm specializing in diamond wire saws, significantly boosted Meyer Burger's wafering technology capabilities. This expansion broadened its product portfolio, enhancing its position in the solar industry. These advancements were critical for improving the efficiency and reducing the cost of solar cell production.
The 2000s saw further expansion through acquisitions. The purchase of 3S Industries in 2010 added module lamination and solar module production equipment to its offerings. This period cemented Meyer Burger's role as a major player in the solar cell and module manufacturing supply chain. The company provided essential equipment to major solar producers globally.
A significant shift occurred with the move to manufacture its own high-performance solar cells and modules. This involved using heterojunction (HJT) and SmartWire Connection Technology (SWCT). This transition required substantial capital raises and investments in new production facilities, such as those in Germany and the USA.
This strategic shift, initiated in the early 2020s, aimed to capture more value within the solar value chain. The decision was influenced by the competitive landscape and the desire for greater energy independence in Europe and the US. The company's focus on high-efficiency, sustainably produced solar products, particularly in Western markets, has been a key driver.
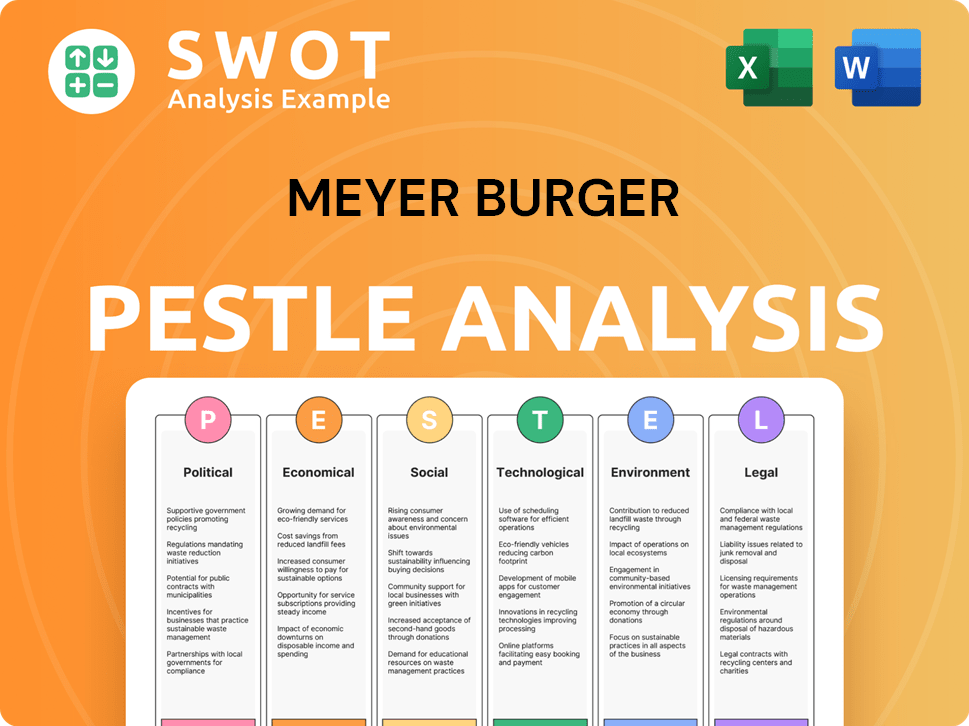
Meyer Burger PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Meyer Burger history?
The story of the Meyer Burger company is marked by significant shifts and advancements within the solar industry. The Swiss company has evolved, adapting to market changes and technological innovations to maintain a competitive edge. This journey reflects the dynamic nature of the solar panel manufacturer sector and the company's strategic responses to challenges and opportunities.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| Early 2000s | Established itself as a key player in the solar equipment market, providing advanced manufacturing solutions. |
| 2010s | Focused on technological advancements, including the development of heterojunction (HJT) technology and SmartWire Connection Technology (SWCT). |
| 2020 | Announced a strategic shift from equipment supplier to solar cell and module manufacturer. |
| 2021 | Opened its first solar module production facility in Freiberg, Germany. |
| 2022 | Started production at its first U.S. solar module factory in Goodyear, Arizona. |
| 2023 | Secured long-term supply agreements and expanded production capacity to meet growing demand. |
The company has pioneered several innovations, including its proprietary heterojunction (HJT) technology and SmartWire Connection Technology (SWCT). These technologies have enhanced the efficiency and durability of solar cells and modules, providing a competitive advantage in the solar industry. These advancements have also led to numerous patents, solidifying the company's intellectual property portfolio.
HJT technology combines crystalline silicon with thin-film layers, boosting solar cell efficiency. This innovation allows for higher energy conversion rates, leading to more powerful solar modules.
SWCT uses a network of thin wires to connect solar cells, improving module performance. It reduces shading and enhances the module's ability to capture sunlight, increasing overall energy yield.
The company produces high-efficiency solar modules that can convert a higher percentage of sunlight into electricity. These modules are designed for residential, commercial, and utility-scale applications, maximizing energy production.
The company employs advanced manufacturing processes to ensure quality and performance. These processes include precise cell sorting, optimized module assembly, and rigorous testing procedures to meet industry standards.
The company has formed strategic partnerships to expand its market reach and enhance its technological capabilities. These collaborations involve supply chain optimization, technology sharing, and joint development efforts.
The company is expanding its manufacturing footprint globally to meet the growing demand for solar modules. This expansion includes establishing new production facilities and distribution networks in key markets.
The Swiss company has faced several challenges, including intense competition and market fluctuations. The transition from an equipment supplier to a solar panel manufacturer required significant investment and navigating a competitive landscape. Geopolitical factors, such as the impact of the US Inflation Reduction Act, have also presented uncertainties.
The solar industry is subject to market fluctuations, including changes in demand and pricing. These fluctuations can impact the profitability of solar panel manufacturers, requiring strategic adjustments to maintain competitiveness.
Competition from Asian manufacturers, which often benefit from lower production costs, poses a significant challenge. The company must continuously innovate and improve efficiency to compete effectively in the global market.
Disruptions in the global supply chain can affect the availability of raw materials and components. The company has to manage these risks through diversified sourcing and strategic partnerships to ensure smooth operations.
Securing sufficient funding for expansion and technological advancements is crucial. The company must attract investment and manage its financial resources effectively to support its growth plans and maintain its competitive position.
Geopolitical factors, such as trade policies and regulatory changes, can impact the solar industry. The company must navigate these risks by adapting its strategies and operations to comply with international regulations and market conditions.
The rapid pace of technological advancements requires continuous innovation and investment. The company must stay at the forefront of solar technology to maintain its competitive edge and meet evolving market demands.
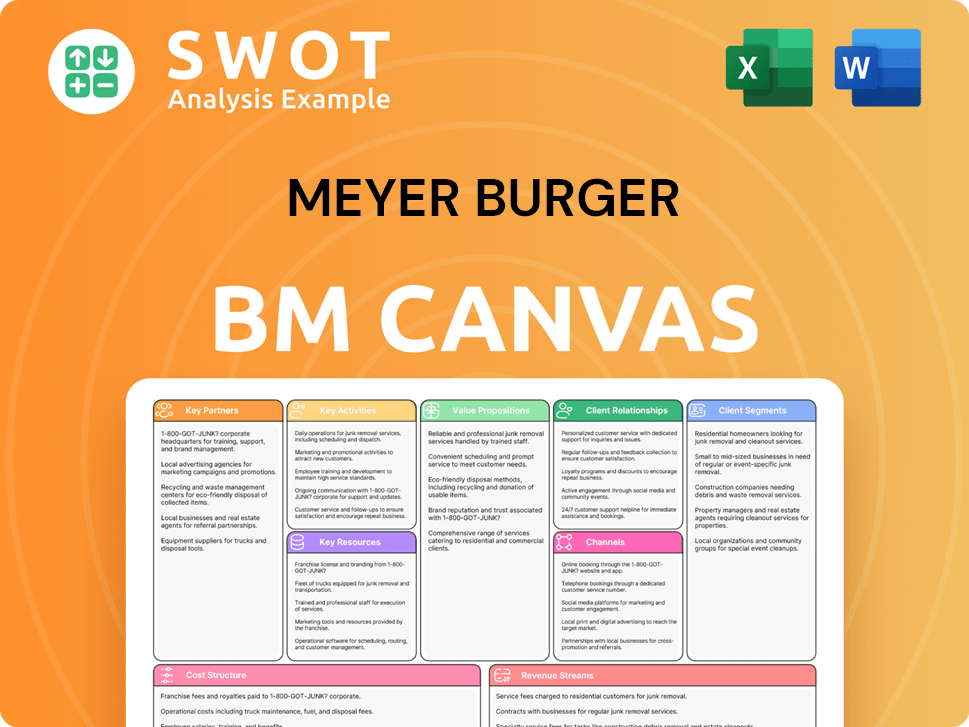
Meyer Burger Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Meyer Burger?
The Meyer Burger history showcases a journey from its Swiss origins to becoming a key player in the solar industry. The
Meyer Burger company
has evolved significantly, adapting to market trends and technological advancements. It has strategically shifted its focus and manufacturing locations, solidifying its role as a solar panel manufacturer.| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1953 | Founding of Meyer Burger in Switzerland. |
| 1980s | The company begins its focus on the photovoltaic industry. |
| 1994 | Acquisition of Hennecke Systems, strengthening wafering technology. |
| 2010 | Acquisition of 3S Industries, expanding into module lamination and solar module production equipment. |
| 2020 | Strategic pivot announced, shifting from equipment supplier to manufacturer of high-performance solar cells and modules, focusing on HJT and SWCT. |
| 2021 | Commissioning of the first solar cell and module production facilities in Bitterfeld-Wolfen and Freiberg, Germany. |
| 2023 | Announcement of plans for a significant solar module manufacturing facility in Goodyear, Arizona, USA. |
| 2024 | Continued ramp-up of European production and focus on establishing U.S. manufacturing capabilities, facing challenges related to market conditions and policy uncertainty. |
| 2025 | Expected operationalization of the Goodyear, Arizona plant, contributing to Meyer Burger's presence in the North American market. |
The company is actively expanding its manufacturing presence in the United States, with a focus on the Goodyear, Arizona facility. This expansion is designed to capitalize on incentives provided by the Inflation Reduction Act. This strategic move aims to increase its market share in the North American solar market, which is experiencing significant growth.
Meyer Burger is investing in enhancing its high-efficiency solar cell technologies, including HJT and SWCT. These advancements are expected to improve the performance and efficiency of their solar modules. The company's focus on innovation is critical for maintaining a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving solar industry, with a goal to reach higher conversion efficiencies.
The company is working on optimizing production processes and strengthening its global sales and distribution networks. These initiatives are crucial for efficiently scaling production and managing geopolitical risks. The financial strategy involves navigating the complexities of the solar market and securing long-term sustainability.
The demand for sustainably produced, high-performance solar modules is expected to continue growing, driven by climate goals and energy security concerns. Analyst predictions suggest that the company’s success will depend on efficient production scaling and effective competition. The
Meyer Burger AG
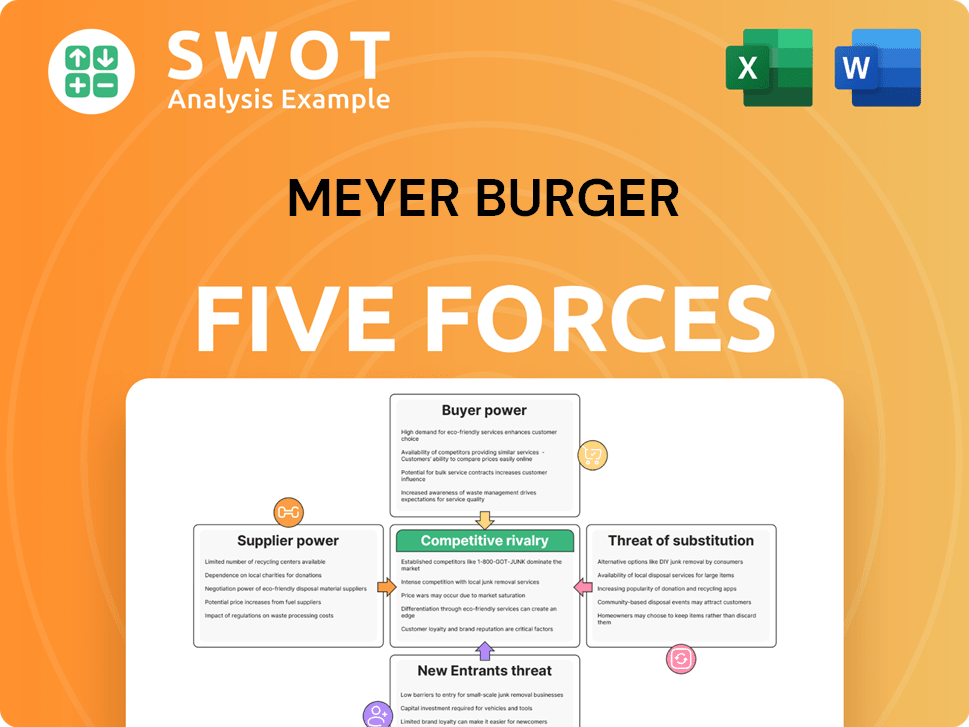
aims to drive the energy transition with premium solar products.Meyer Burger Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Meyer Burger Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Meyer Burger Company?
- How Does Meyer Burger Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Meyer Burger Company?
- What is Brief History of Meyer Burger Company?
- Who Owns Meyer Burger Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Meyer Burger Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.