Ryanair Holdings Bundle
How Did Ryanair Holdings Revolutionize Air Travel?
Ever wondered how a small Irish airline became a European aviation giant? Ryanair Holdings, a name now synonymous with budget travel, has a fascinating history filled with bold moves and innovative strategies. From its humble beginnings in 1985 to its current status as a market leader, the Ryanair Holdings SWOT Analysis reveals the key factors behind its success. Prepare to uncover the story of Ryanair's remarkable journey and its profound impact on the industry.
This brief history of Ryanair Holdings plc explores the Ryanair company's evolution, from its early routes to its current extensive network. Discover how Michael O'Leary's leadership and Ryanair's low-cost model transformed air travel, facing controversies and challenges along the way. The Ryanair timeline reveals the key moments that shaped the airline's growth, including its aggressive expansion and acquisition of other airlines, solidifying its place in aviation history and changing how people fly across Europe.
What is the Ryanair Holdings Founding Story?
The story of Ryanair Holdings, a leading figure in the low-cost airline industry, began on July 15, 1985. Founded by Christy Ryan, Liam Lonergan, and Tony Ryan, an Irish businessman, the company emerged with a mission to challenge the high costs of air travel, a market then dominated by established airlines like Aer Lingus and British Airways. Their vision was to democratize air travel, making it accessible to a broader audience.
Ryanair's initial business model was straightforward: to offer low-cost, no-frills passenger services on short-haul routes. Their first flight took off between Waterford, Ireland, and London Gatwick. The company's name was a direct nod to its founder, Tony Ryan. The early days saw the company relying on Tony Ryan's personal wealth and business interests for funding, essentially bootstrapping the venture.
A key challenge for the fledgling airline was competing with established national carriers, which had significant market power. The founding team, especially Tony Ryan, brought extensive aviation experience from their previous venture, Guinness Peat Aviation (GPA), a major aircraft leasing company. This experience gave them valuable insights into aircraft acquisition and operational efficiency, crucial for launching a low-cost airline. The cultural context of the mid-1980s in Ireland, characterized by a desire for increased connectivity and economic growth, also played a role in the pursuit of this venture.
Ryanair's early strategy focused on providing affordable air travel by cutting costs and offering point-to-point routes.
- The company was founded in 1985.
- The first route was between Waterford, Ireland, and London Gatwick.
- Initial funding came from Tony Ryan's personal wealth.
- The airline aimed to challenge the high costs of air travel.
Ryanair Holdings SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Ryanair Holdings?
The early growth of the Ryanair company was marked by strategic expansion and a strong focus on reducing costs. After its initial route, the company quickly added more destinations in the UK and Europe. A key moment was the appointment of Michael O'Leary as CEO, who refined the low-cost model, drawing inspiration from Southwest Airlines. Early efforts focused on simplifying the passenger experience to keep fares low, making it a significant part of the Ryanair history.
Following its first route, the Ryanair company expanded rapidly. The company's early routes included key destinations across the UK and Europe. This expansion was crucial for establishing its presence in the market. The focus was on increasing the number of destinations served to attract more passengers and grow its market share. This rapid growth is a key aspect of the Ryanair timeline.
Michael O'Leary's role in Ryanair was pivotal, especially after his appointment as CEO. He refined the low-cost model, drawing inspiration from Southwest Airlines. This leadership helped to streamline operations and reduce costs. His strategies significantly influenced the company's trajectory, making him a central figure in the Ryanair history.
The company's initial public offering (IPO) in 1997 was a significant milestone. The IPO provided substantial capital, which fueled further expansion. This funding allowed the company to accelerate fleet acquisitions and open new bases across Europe. This financial move was crucial for the Ryanair timeline and its growth.
Early strategies focused on simplifying the passenger experience to keep fares low. This included removing unnecessary services. The company targeted underserved regional airports to lower landing fees and reduce congestion. Direct sales channels were used to bypass traditional distribution costs, a key part of what is Ryanair's business model.
The standardization of the Ryanair fleet to Boeing 737s was a pivotal decision, reducing maintenance costs. By the early 2000s, Ryanair had become a major player in the European aviation market. The company's success is a testament to its effective strategies. For more details on the financial aspects, you might find insights in Owners & Shareholders of Ryanair Holdings.
Ryanair Holdings PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Ryanair Holdings history?
The story of Ryanair Holdings is marked by significant milestones that have shaped its journey from a small regional airline to one of Europe's largest. The Ryanair company has consistently evolved, adapting to market dynamics and technological advancements. The Ryanair history showcases a relentless pursuit of efficiency and cost reduction, transforming the air travel landscape.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1985 | Founded as a regional airline, operating between Waterford and London Gatwick. |
| 1991 | Michael O'Leary joins as CEO, initiating the low-cost model transformation. |
| 1990s | Expanded rapidly across Europe, challenging established airlines with lower fares. |
| 1997 | Launched its website, pioneering online booking and reducing distribution costs. |
| 2000s | Continued expansion and route network growth, becoming a major player in European aviation. |
| 2014 | Launched "Always Getting Better" program to improve customer service and experience. |
| 2017 | Pilot rostering issues led to flight cancellations, prompting operational changes. |
| 2024 | Reported a record after-tax profit of €1.92 billion for the fiscal year ending March 31, 2024. |
Ryanair Holdings has been at the forefront of several innovations that have reshaped the airline industry. The early adoption of online ticketing revolutionized booking processes, significantly cutting operational expenses. Furthermore, its focus on rapid aircraft turnarounds and optimized route planning has enhanced efficiency.
Pioneered online booking in the late 1990s, reducing distribution costs and improving accessibility for customers.
Implemented rapid turnaround times, ensuring high aircraft utilization rates and maximizing revenue potential.
Developed highly optimized route planning strategies to maximize profitability and minimize operational costs.
Focused relentlessly on cost control across all aspects of the business, from fuel to staffing.
Strategically implemented ancillary fees for services such as baggage and seat selection to boost revenue.
Operated a standardized fleet of Boeing 737 aircraft to reduce maintenance and training costs.
Despite its successes, Ryanair's journey has faced several challenges, including economic downturns and competitive pressures. The airline has also dealt with public relations issues and internal operational crises. For a deeper understanding, explore the Marketing Strategy of Ryanair Holdings.
Market downturns, such as the 2008 financial crisis, impacted passenger demand and profitability, requiring strategic adjustments.
Faced competition from other low-cost carriers and the strategic responses of traditional airlines, necessitating continuous innovation and cost-efficiency.
Dealt with public relations challenges stemming from strict ancillary fee policies and a no-frills approach, requiring efforts to improve customer service.
Internal crises, such as pilot rostering issues in 2017, led to significant flight cancellations and reputational damage, necessitating operational improvements.
Navigated various regulatory hurdles and environmental pressures, requiring adaptability and strategic compliance.
The airline's performance is subject to market volatility, including fluctuations in fuel prices and currency exchange rates, which can impact profitability.
Ryanair Holdings Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Ryanair Holdings?
The Ryanair history is marked by significant milestones, from its inception to its current status as a major player in the aviation industry. Founded in 1985, the company initially operated with a single route before adopting a low-cost model under the leadership of Michael O'Leary, which fueled its rapid expansion across Europe. The company went public in 1997, and has since navigated various challenges, including the COVID-19 pandemic. Today, Ryanair Holdings plc encompasses several airlines, and has demonstrated a strong recovery in passenger numbers and profitability.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1985 | Ryanair was founded by Tony Ryan, Christy Ryan, and Liam Lonergan. |
| 1986 | The first route was launched between Waterford and London Gatwick. |
| 1991 | Michael O'Leary was appointed CEO, implementing the low-cost model. |
| 1997 | An Initial Public Offering (IPO) was held, raising capital for expansion. |
| 2000s | Aggressive expansion took place across Europe, establishing dominance. |
| 2013 | Acquisition of Laudamotion (later Lauda Europe) occurred. |
| 2017 | A pilot rostering crisis led to significant flight cancellations. |
| 2019 | Ryanair Holdings plc was established as the parent company. |
| 2020-2021 | The COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted operations. |
| 2023-2024 | Strong recovery in passenger numbers and profitability, with a record after-tax profit of €1.92 billion for fiscal year ending March 31, 2024. |
| 2025 | Continued focus on fleet expansion and sustainability initiatives. |
The future for Ryanair Holdings involves substantial fleet expansion. The company has ordered 300 Boeing 737 MAX 10 aircraft. This is expected to increase passenger traffic to 300 million annually by March 2034. This expansion will allow Ryanair to enter new markets and increase frequency on existing routes.
Ryanair is committed to sustainability, planning to use sustainable aviation fuels (SAFs). The goal is to power 12.5% of flights with SAFs by 2030. Furthermore, the company aims to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050. These initiatives reflect a broader industry trend towards sustainable travel.
Enhancing digital platforms and improving customer experience are key strategic initiatives. These improvements are designed to streamline operations and increase customer satisfaction. Ryanair's focus on digital enhancements reflects the evolving demands of the modern traveler.
Analyst predictions point to continued strong financial performance for Ryanair, driven by its efficient operations. The company's market leadership is expected to be a key factor in its ongoing success. Ryanair's history of low fares and disciplined growth is expected to continue.
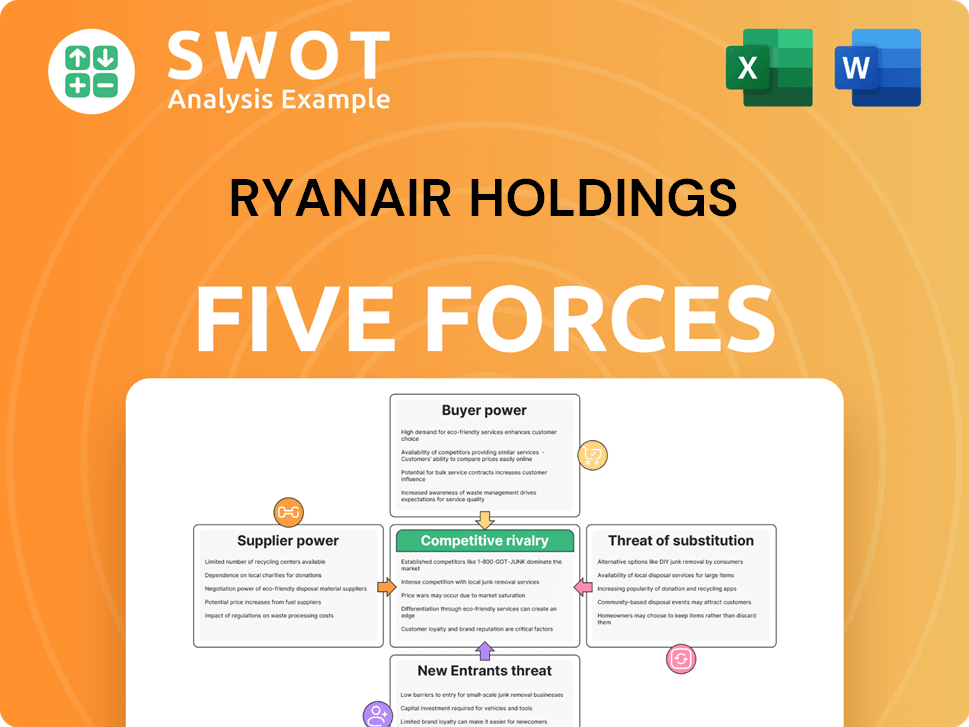
Ryanair Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Ryanair Holdings Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Ryanair Holdings Company?
- How Does Ryanair Holdings Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Ryanair Holdings Company?
- What is Brief History of Ryanair Holdings Company?
- Who Owns Ryanair Holdings Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Ryanair Holdings Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.