Korean Air Bundle
Can Korean Air Conquer the Skies?
The aviation industry is a battlefield, constantly reshaped by global events and technological leaps. Korean Air, a titan in this arena, faces a dynamic Korean Air SWOT Analysis and a complex web of rivals. Understanding the Korean Air competitive landscape is crucial for investors, strategists, and anyone seeking to navigate the future of air travel.

This analysis delves into the Korean Air market analysis, examining its key Korean Air competitors and strategic positioning. We'll explore the Korean Air industry dynamics, evaluating its financial performance and competitive advantages to provide a comprehensive understanding of its current standing and future prospects within the global aviation market. The goal is to equip readers with the insights needed to make informed decisions in this ever-changing sector.
Where Does Korean Air’ Stand in the Current Market?
Korean Air maintains a significant market position within the global airline industry, particularly in the Asia-Pacific region. As South Korea's flag carrier, it holds a dominant share of the South Korean aviation market. The airline's primary operations include scheduled passenger flights, cargo transportation, and aircraft maintenance services. Its broad geographic presence covers major cities across Asia, Europe, North America, and Oceania, serving a diverse customer base.
The airline's value proposition centers on providing comprehensive air travel services, catering to both premium and budget markets. This is evident in its strategic moves, such as the acquisition of Asiana Airlines, aimed at creating a more extensive service offering. Korean Air has also invested in digital transformation, enhancing the passenger experience through online booking platforms and customer service technologies. The airline's financial health, as demonstrated by its 2023 operating profit, allows for continued investment in fleet modernization and network expansion.
In 2023, Korean Air reported an operating profit of approximately KRW 1.586 trillion (around USD 1.15 billion), showcasing its robust financial performance. This financial strength supports its competitive edge in the aviation industry. The airline's strategic location and efficient logistics operations give it a strong position in trans-Pacific and intra-Asia cargo routes. The planned acquisition of Asiana Airlines is expected to further solidify its market dominance in South Korea and boost its global competitiveness. For further insights into the company's strategies, consider the Marketing Strategy of Korean Air.
Korean Air holds a dominant position in the South Korean aviation market. It consistently ranks among the top airlines globally in terms of passenger and cargo traffic. The acquisition of Asiana Airlines is expected to increase this dominance.
The airline's financial health supports its competitive position. Operating profit in 2023 was approximately USD 1.15 billion. This financial stability allows for investment in fleet upgrades and expansion.
Korean Air provides a wide range of services, including passenger flights, cargo transport, and maintenance. It caters to both premium and budget travelers. Digital transformation efforts improve the passenger experience.
Its extensive network covers major cities across Asia, Europe, North America, and Oceania. This wide reach supports a diverse customer base. Strategic location aids in cargo route efficiency.
Korean Air's main competitive advantages include its strong brand reputation, extensive route network, and robust financial performance. It benefits from its strategic location in Asia, facilitating efficient cargo operations and passenger connections. The acquisition of Asiana Airlines is a strategic move to strengthen its market position.
- Dominant market share in South Korea.
- Strong presence in trans-Pacific and intra-Asia cargo routes.
- Investment in digital transformation for enhanced customer experience.
- Strategic acquisition to expand service offerings.
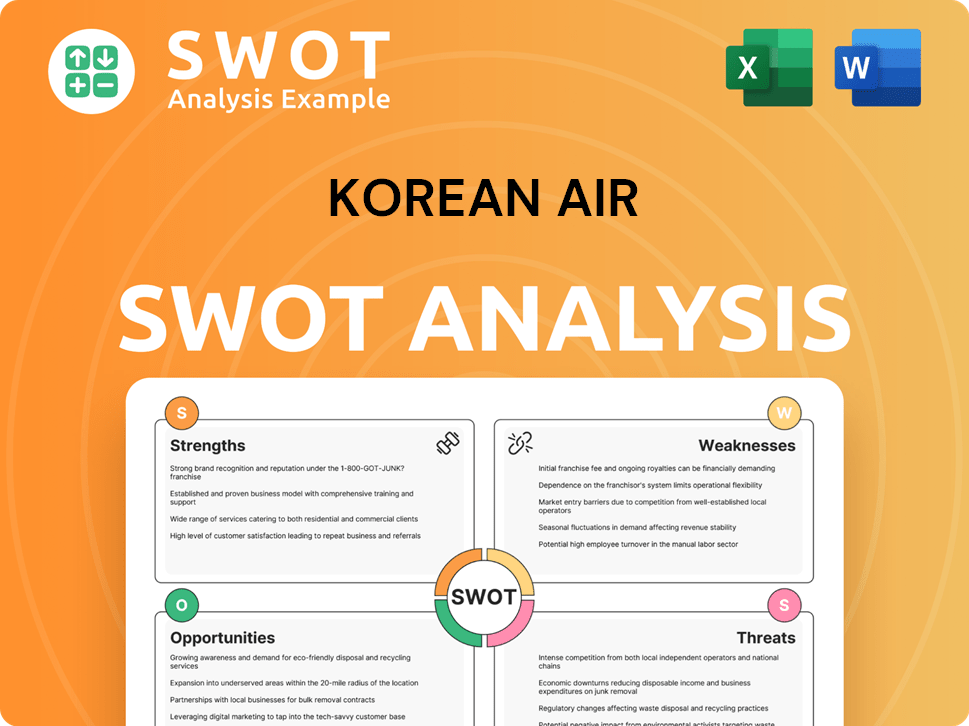
Korean Air SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
Who Are the Main Competitors Challenging Korean Air?
The Owners & Shareholders of Korean Air faces a complex and dynamic competitive landscape. This landscape is shaped by a variety of factors, including the ongoing merger with Asiana Airlines, the rise of low-cost carriers (LCCs), and intense competition from global airlines. Understanding these competitive dynamics is crucial for assessing the company's market position and future prospects.
In the domestic market, the merger with Asiana Airlines is poised to reshape the competitive environment significantly. However, Korean Air also contends with LCCs, which are gaining ground in short-haul routes. Globally, the company battles with major international airlines across various routes, and in the cargo sector, it faces competition from dedicated cargo carriers and the cargo divisions of other airlines.
The aviation industry in Korea and worldwide is constantly evolving, influenced by mergers, alliances, and changing market demands. This requires Korean Air to adapt its strategies to maintain its competitive edge. The company’s financial performance is closely tied to its ability to navigate this competitive landscape effectively.
The primary competitor in the domestic market has historically been Asiana Airlines. The merger will make Korean Air the dominant player. LCCs like Jeju Air, T'way Air, and Jin Air are significant competitors.
In the trans-Pacific market, competition comes from airlines such as Delta Air Lines, United Airlines, and American Airlines. European carriers like Lufthansa and British Airways are key rivals on routes to Europe. Asian carriers like ANA, Japan Airlines, and Cathay Pacific are also major competitors.
In the cargo sector, Korean Air competes with FedEx Express and UPS Airlines. The cargo divisions of other major passenger airlines also pose a challenge. Emerging players from Southeast Asia and the Middle East are expanding rapidly.
Alliances like SkyTeam, of which Korean Air is a member, impact competition. These alliances enable broader networks and seamless travel experiences. Mergers and partnerships intensify the battle for market share.
LCCs target budget-conscious travelers, increasing competition. They have steadily gained market share in recent years. Korean Air must respond strategically to maintain its position.
Korean Air must consider pricing strategies and network expansion. Customer satisfaction and strategic alliances are also key. The company's response to fuel prices also plays a crucial role.
Several factors influence the competitive landscape for Korean Air, including route network, pricing, and customer service. The company's ability to adapt to changing market conditions is crucial for sustained success.
- Route Network: Extensive route networks allow airlines to offer more travel options.
- Pricing Strategies: Competitive pricing is essential to attract price-sensitive customers.
- Customer Service: High-quality customer service builds brand loyalty.
- Strategic Alliances: Partnerships expand networks and enhance the customer experience.
- Fuel Prices: Fluctuating fuel costs impact profitability and pricing strategies.
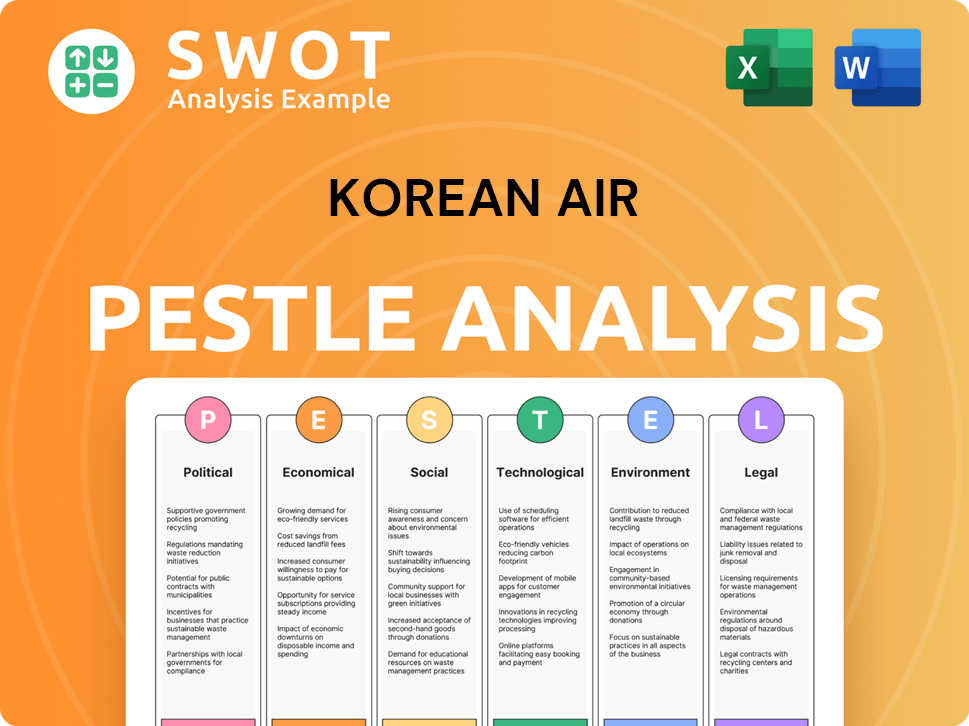
Korean Air PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What Gives Korean Air a Competitive Edge Over Its Rivals?
The competitive landscape of Korean Air is shaped by its strategic strengths and the dynamic nature of the aviation industry. The airline has cultivated a robust global presence and a strong brand reputation. Understanding its competitive advantages is crucial for analyzing its market position and future prospects. A detailed Brief History of Korean Air can provide further context to its evolution.
Korean Air faces competition from various airlines, including both full-service carriers and low-cost carriers. The airline's ability to maintain its competitive edge hinges on its operational efficiency, strategic partnerships, and adaptability to market changes. This analysis will delve into the key factors that define Korean Air's competitive advantages.
The airline's financial performance and market share are also critical indicators of its competitive standing. Recent data reveals the impact of fuel prices, economic conditions, and evolving consumer preferences on its operations. Analyzing these factors provides a comprehensive view of Korean Air's competitive landscape.
Korean Air boasts a vast international network, particularly strong in Asia, North America, and Europe. This expansive reach allows for a wide array of destinations and convenient connections. Membership in the SkyTeam alliance further enhances its network capabilities, attracting both passenger and cargo traffic.
Korean Air has historically been a leading global air cargo carrier, utilizing a dedicated freighter fleet. This capability proved crucial during the COVID-19 pandemic, boosting revenue. The airline's efficient logistics infrastructure supports its strong position in the cargo market.
Its strategic location in South Korea positions it as a key hub for connecting flights between Asia and the West. This geographical advantage facilitates efficient transit for passengers and cargo. This hub status is a significant competitive advantage.
Korean Air benefits from strong brand equity and a reputation for high-quality service, which fosters customer loyalty. The airline's focus on customer experience and service excellence is a key differentiator. This reputation helps it maintain a competitive edge.
Korean Air's competitive advantages include its expansive global network, robust cargo operations, and strong brand reputation. The airline's strategic location in South Korea enhances its hub status, facilitating efficient transit for passengers and cargo. These advantages are crucial for maintaining its market leadership in the dynamic aviation industry.
- Extensive Global Network: Strong presence in Asia, North America, and Europe.
- Robust Cargo Operations: Dedicated freighter fleet and efficient logistics.
- Strategic Hub: Key hub for connecting flights between Asia and the West.
- Strong Brand Equity: Reputation for high-quality service and customer loyalty.
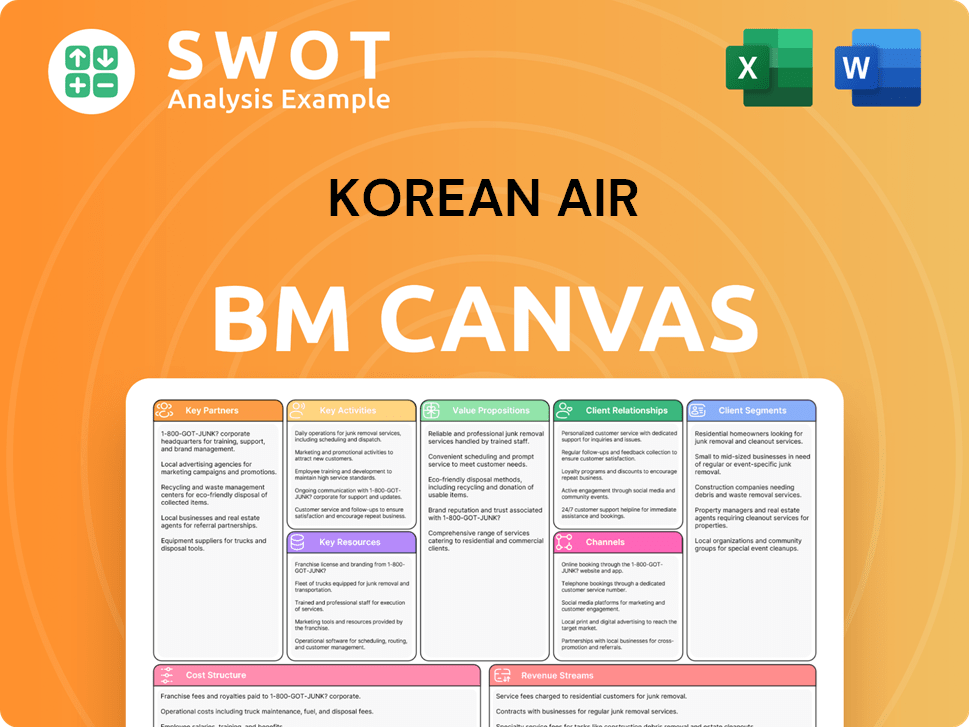
Korean Air Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Industry Trends Are Reshaping Korean Air’s Competitive Landscape?
The Korean Air competitive landscape is shaped by dynamic industry trends, presenting both challenges and opportunities. The airline faces evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, and stringent regulatory changes. Understanding these factors is crucial for assessing its future prospects and strategic positioning within the aviation industry.
Risks include fluctuating fuel prices, geopolitical instability, and intense competition. Opportunities stem from expanding in emerging markets, investing in sustainable technologies, and operational efficiencies. Korean Air's ability to navigate these complexities will determine its success in the coming years.
The aviation industry is experiencing rapid technological advancements, particularly in sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) development and digitalization of customer services. Regulatory changes, especially those concerning environmental sustainability and carbon emissions, are also reshaping operations. Furthermore, consumer preferences are shifting towards personalized experiences and sustainable practices.
Key challenges include the rising costs and limited availability of SAF, which hinder decarbonization efforts. Intense competition from budget carriers and other full-service airlines continues to pressure yields. Geopolitical instability and economic downturns can significantly impact international travel demand. Successfully integrating Asiana Airlines also poses operational and cultural complexities.
Growing demand for air travel in emerging markets, particularly in Asia, offers expansion prospects. Investing in sustainable aviation technologies can enhance brand image and attract environmentally conscious travelers. Digitalization can improve operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. Strategic partnerships and joint ventures can boost network reach and market share.
Fleet modernization, network optimization, and continued investment in cargo operations are crucial. The consolidation with Asiana Airlines is expected to create a more resilient entity, increasing market control and operational synergies. Korean Air aims to focus on sustainable growth, technological adoption, and enhanced customer experience to maintain a competitive edge.
Korean Air's success will depend on its ability to adapt to the evolving aviation industry. The company must strategically navigate challenges while capitalizing on emerging opportunities. Key factors include managing fuel costs, enhancing customer experience, and expanding its global presence.
- Sustainability: Investing in SAF and reducing carbon emissions to meet regulatory requirements.
- Competition: Differentiating services and managing costs to compete with budget airlines and other full-service carriers.
- Market Expansion: Capitalizing on growth opportunities in Asia and other emerging markets.
- Operational Efficiency: Leveraging digitalization and strategic partnerships to improve efficiency and customer satisfaction.
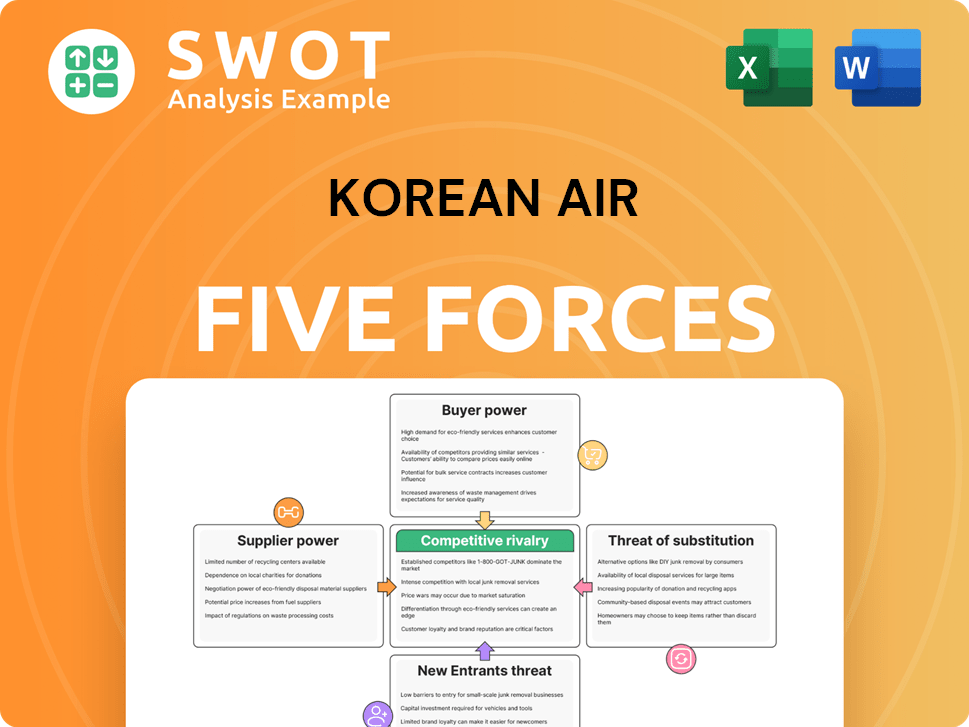
Korean Air Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Korean Air Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Korean Air Company?
- How Does Korean Air Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Korean Air Company?
- What is Brief History of Korean Air Company?
- Who Owns Korean Air Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Korean Air Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.