easyJet Bundle
How Does easyJet Stay Airborne and Profitable?
easyJet, a titan of the skies, revolutionized European travel with its budget-friendly approach. Founded in 1995, this low-cost airline carved a niche by offering affordable, point-to-point flights. Today, it's a major player, carrying millions of passengers and generating billions in revenue.
This deep dive into easyJet SWOT Analysis will unpack the inner workings of easyJet operations, from its expansive route network map to its financial performance analysis. We'll explore how this budget airline leverages its business model to compete in the airline industry, examining everything from the easyJet flight booking process to its sustainability initiatives. Understanding easyJet's strategies is key for anyone interested in the airline's success, including how does easyJet make money and its competitive advantages.
What Are the Key Operations Driving easyJet’s Success?
The core operations of easyJet are designed around a low-cost, point-to-point model, primarily serving the European short-haul market. The airline focuses on both leisure and business travelers, offering affordable air travel options. Its primary product is the flight itself, complemented by a range of ancillary services.
easyJet's operational processes are centered on efficiency, high aircraft utilization, and direct sales channels. This approach enables the airline to offer competitive fares while maintaining profitability. The operational model emphasizes quick turnarounds at airports, maximizing the number of flights per aircraft per day. The airline operates a standardized fleet, predominantly Airbus A320 family aircraft, which contributes to cost efficiencies in maintenance, training, and spare parts.
The airline's business model is built on a foundation of cost control and a strong brand presence. The airline's robust digital platform facilitates seamless booking and ancillary service purchases, enhancing the customer experience while maintaining low operational costs. This operational efficiency and direct-to-consumer model differentiate easyJet from traditional full-service carriers and even some low-cost competitors, allowing it to consistently offer competitive pricing.
easyJet operates a fleet of over 300 aircraft, primarily Airbus A320 family aircraft. In 2024, the airline aimed to increase its fleet size to meet rising travel demands. The airline's focus on efficient operations includes quick turnaround times and high aircraft utilization rates to maximize flight frequency.
easyJet's route network covers a wide range of destinations across Europe, with a strong presence in key markets. The airline serves over 1,000 routes, connecting major European cities. easyJet focuses on point-to-point flights, avoiding hub-and-spoke models to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
The easyJet business model revolves around offering low fares and ancillary services. The value proposition includes affordable flights, frequent flight options, and a user-friendly booking process. The airline's focus on cost control and operational efficiency allows it to offer competitive pricing.
easyJet's financial performance is closely tied to its operational efficiency and market demand. In 2024, the airline aimed to improve its financial results by managing costs and increasing revenue. The airline's financial strategies include optimizing route networks and ancillary revenue generation. To learn more, read the Brief History of easyJet.
easyJet's operational strategies include a focus on cost control, high aircraft utilization, and direct sales. The airline aims to maximize efficiency and minimize expenses to offer competitive fares. These strategies are critical to the success of easyJet operations.
- Standardized Fleet: Utilizing a single aircraft type (Airbus A320 family) for easier maintenance and cost savings.
- Direct Sales: Primarily selling tickets through its website and mobile app to avoid third-party fees.
- Quick Turnarounds: Minimizing ground time at airports to increase flight frequency.
- Ancillary Revenue: Offering additional services like baggage allowance and seat selection to boost revenue.
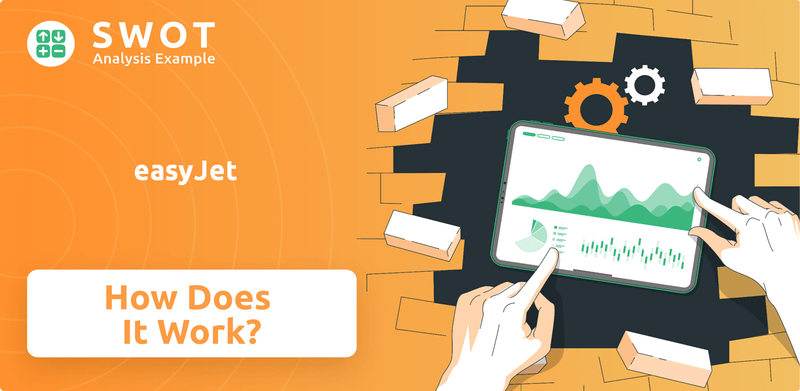
easyJet SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Does easyJet Make Money?
Understanding the revenue streams and monetization strategies of easyJet is key to grasping its easyJet business model. The airline's financial success is built on a combination of ticket sales and a variety of ancillary services. This approach allows easyJet operations to remain competitive in the airline industry.
easyJet generates revenue primarily through passenger ticket sales, which represent the base fare for flights. However, a significant portion of its revenue comes from ancillary services. These include fees for checked baggage, seat selection, speedy boarding, and onboard food and beverage sales, all of which contribute substantially to the airline's profitability.
For the fiscal year ending September 30, 2023, easyJet reported total revenue of £8,171 million. While specific breakdowns for 2024 are not yet fully available, historical trends indicate that a substantial portion of revenue comes from passenger ticket sales, representing the base fare for flights.
The core revenue stream for easyJet. This is the base fare passengers pay for their flights. The price varies based on demand, time of booking, and route.
Fees for services beyond the basic flight. Includes checked baggage, seat selection, and speedy boarding. Ancillary revenue per seat increased by 15% year-on-year in fiscal year 2023.
Package holiday business. Saw a 161% increase in customers in the first half of fiscal year 2024 compared to the previous year. Contributes significantly to revenue diversification.
Membership program offering benefits like free seat selection and dedicated bag drop. Creates a recurring revenue stream and fosters customer loyalty.
Cross-selling opportunities through partnerships, such as car rental and hotel bookings. Further expands the revenue base.
Offers different levels of flexibility and services. Allows passengers to choose options that suit their needs and budget.
easyJet has strategically expanded its ancillary offerings and developed its holiday business to diversify its revenue mix. This reduces reliance on ticket sales and enhances overall profitability. For a deeper dive into easyJet's strategic growth, consider reading about the Growth Strategy of easyJet.
easyJet PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Which Strategic Decisions Have Shaped easyJet’s Business Model?
The journey of easyJet, a prominent player in the airline industry, has been shaped by strategic decisions and key milestones. From its inception, the company has focused on providing low-cost flights, a strategy that has driven its growth and market share. Its evolution reflects a series of calculated moves designed to optimize operations and enhance its competitive edge within the budget airline sector.
A significant turning point for easyJet was its initial public offering in 2000, which provided capital for expansion. The acquisition of Go Fly in 2002 further solidified its position, increasing its fleet size and presence at key airports. More recently, easyJet has prioritized fleet modernization and sustainable growth, as demonstrated by its order for Airbus A320neo family aircraft.
The airline's business model is built on efficiency and cost control, enabling it to offer competitive fares. easyJet's direct sales model, primarily through its website and app, provides a cost advantage and direct customer relationship. Despite facing operational challenges, such as air traffic control strikes and airspace restrictions, easyJet has demonstrated resilience through agile capacity management and a focus on cost control.
easyJet's IPO in 2000 was a pivotal moment, providing capital for expansion. The acquisition of Go Fly in 2002 significantly boosted its market share. The airline has consistently focused on fleet optimization and sustainable growth.
The airline has strategically invested in new, fuel-efficient aircraft, such as the A320neo family, to reduce operational costs and address environmental concerns. Expansion into easyJet Holidays is a move to diversify revenue streams. The company focuses on operational resilience and digital innovation.
easyJet's strong brand, recognized for value and reliability, is a key advantage. Its well-established pan-European network and economies of scale from its large, standardized fleet contribute to its competitive position. The direct sales model provides a cost advantage.
In the first half of fiscal year 2024, easyJet noted a £41 million impact from the Israel-Hamas conflict. The airline's focus on cost control and efficient operations has been crucial for maintaining profitability. The company's financial strategies are designed to navigate industry challenges and maintain a competitive edge.
easyJet's competitive advantages include a strong brand, a well-established network, and economies of scale. The airline's direct sales model and focus on cost control further enhance its position. The company continuously adapts to market trends and competitive threats.
- Strong Brand Recognition: Known for value and reliability.
- Extensive Network: A well-established pan-European network.
- Cost Efficiency: Direct sales model and focus on cost control.
- Fleet Modernization: Investment in fuel-efficient aircraft.
easyJet's ongoing efforts to adapt to market dynamics and competitive pressures, including its investment in new aircraft and expansion of its holiday business, demonstrate its commitment to long-term sustainability. For more insights into the company's strategic direction, consider exploring the Growth Strategy of easyJet.
easyJet Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
How Is easyJet Positioning Itself for Continued Success?
In the competitive landscape of the European airline industry, easyJet firmly establishes itself as a major player. As a prominent low-cost airline, it competes with other budget carriers for a significant share of the market. With a well-recognized brand and a loyal customer base, it focuses on providing value and an extensive network of routes across Europe.
However, easyJet faces several risks that could impact its business. These include fluctuating fuel prices, geopolitical events, and evolving regulations. The airline also confronts the intense competition within the low-cost market and the potential for technological disruptions. Understanding these factors is crucial for assessing easyJet's overall performance and future prospects.
easyJet is a leading low-cost airline in Europe, consistently ranking among the top carriers in terms of passenger volume. It operates on numerous routes, focusing on both leisure and business travelers. The airline's strong brand recognition and customer loyalty support its position in the airline industry.
easyJet faces risks such as fluctuating fuel prices, geopolitical events, and regulatory changes. Competition in the budget airline market is intense, with new entrants and aggressive expansions. Technological advancements also pose risks if the company fails to adapt to the digital environment.
easyJet is focusing on sustainable growth and operational efficiency, including fleet modernization with new Airbus A320neo aircraft. Expansion of easyJet Holidays is a key strategic initiative, aiming to diversify revenue streams. The airline's strategy involves disciplined capacity growth, maintaining a strong balance sheet, and leveraging technology.
The airline's strategic plan includes enhancing the customer experience and improving operational performance. easyJet plans to sustain profitability by providing affordable air travel, optimizing ancillary revenue, and growing its holiday package business. Cost control and operational excellence remain central to its strategy.
easyJet's strategy focuses on sustainable growth and operational efficiency, including a fleet modernization program with Airbus A320neo aircraft. The expansion of easyJet Holidays is a key initiative for revenue diversification. The airline is also committed to disciplined capacity growth and leveraging technology.
- Fleet modernization with Airbus A320neo aircraft enhances fuel efficiency and reduces emissions.
- Expansion of easyJet Holidays aims to increase revenue diversification and customer lifetime value.
- Commitment to disciplined capacity growth and maintaining a strong balance sheet.
- Leveraging technology to improve the customer journey and enhance operational performance.
For more detailed information about the ownership structure, you can refer to Owners & Shareholders of easyJet.
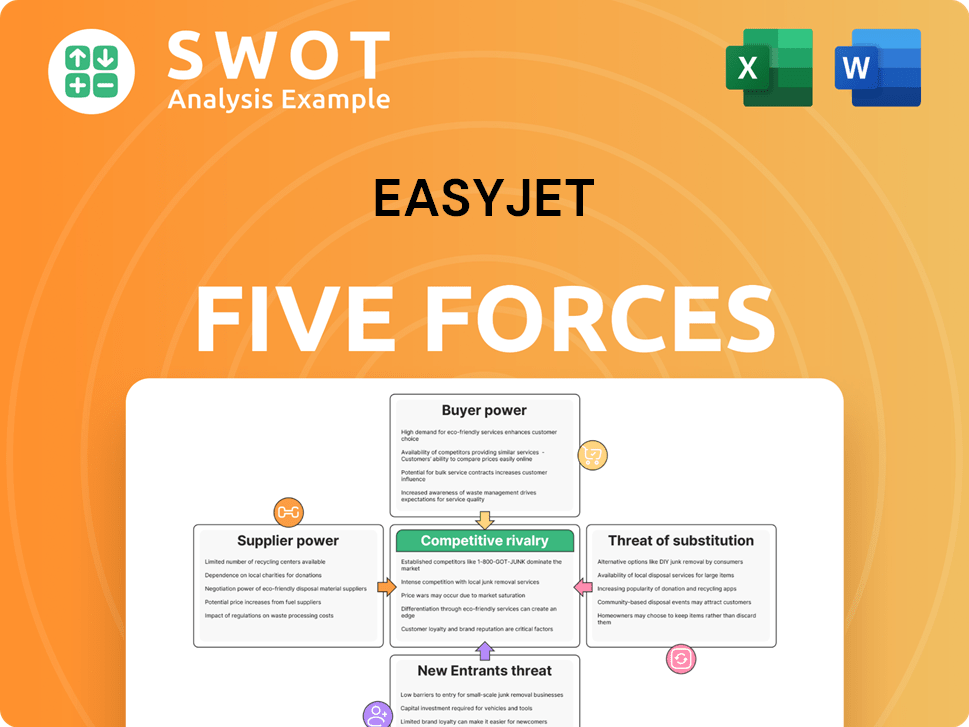
easyJet Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of easyJet Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of easyJet Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of easyJet Company?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of easyJet Company?
- What is Brief History of easyJet Company?
- Who Owns easyJet Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of easyJet Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.