Caesars Entertainment Bundle
Who Really Owns Caesars Entertainment?
Understanding the ownership structure of Caesars Entertainment is crucial for anyone looking to invest, analyze, or simply understand this entertainment behemoth. From its humble beginnings in Reno, Nevada, to its current status as a global leader, Caesars' journey has been marked by significant shifts in ownership. The 2020 merger with Eldorado Resorts dramatically altered the landscape, making it the largest casino entertainment company in the U.S.

This exploration into Caesars Entertainment SWOT Analysis will uncover the key players who influence Caesars ownership and strategic decisions. We'll examine the evolution of Caesars Entertainment parent company, from its founders to today's institutional investors and public shareholders. Discover who the current owner of Caesars Entertainment is, and learn how the company's complex ownership structure impacts its financial performance and future prospects, including insights into the Caesars CEO and the company's leadership.
Who Founded Caesars Entertainment?
The genesis of the gaming giant, now known as Caesars Entertainment, can be traced back to Kirk Kerkorian. In 1937, Kerkorian began his journey by acquiring a small hotel in Reno, Nevada, which would eventually serve as the foundation for his gaming empire.
While precise details of the initial equity splits or shareholding percentages during Kerkorian's early ventures are not readily available in public records, his strategic investments in properties like the Flamingo Hotel in the 1960s and the original MGM Grand Hotel and Casino were instrumental in shaping the company. Early ownership was largely concentrated with Kerkorian and entities associated with him, reflecting a founder-driven model.
The early ownership structure of the company was primarily centered around Kerkorian and his associated entities. Public information detailing angel investors or specific stakes held by friends and family during this period is limited, suggesting a more concentrated initial ownership. Financial arrangements would have likely involved debt financing and private equity as the company expanded.
Early ownership was heavily influenced by Kirk Kerkorian, who laid the groundwork for the company's expansion. His strategic investments and acquisitions shaped the company's early growth. The initial ownership structure was largely concentrated, reflecting a founder-driven model.
Early agreements likely focused on financing large-scale resort developments. These agreements would have potentially involved debt financing and private equity arrangements as the company expanded. Any initial ownership disputes or buyouts were part of the private transactions that fueled Kerkorian's expansion.
The 'Caesars' brand itself was a later acquisition, integrating into a lineage of ownership changes. The acquisition of the 'Caesars' brand marked a significant milestone in the company's evolution. This integration reflected the company's strategic moves.
The early ownership of Caesars Entertainment was characterized by the influence of Kirk Kerkorian, whose strategic investments and acquisitions formed the bedrock of the company. The early agreements would have likely focused on financing large-scale resort developments. The 'Caesars' brand, a later addition, integrated into a lineage of ownership changes. The company's history reflects a series of ownership shifts and strategic decisions that have shaped its current structure. As of early 2024, the company continues to evolve, with its ownership structure reflecting a blend of institutional investors and public shareholders. The company's market capitalization fluctuates, but it remains a significant player in the global gaming industry. The merger with Eldorado Resorts in 2020 significantly altered the company's ownership landscape, consolidating its position in the market. The current Caesars CEO is Tom Reeg. The company's headquarters are located in Reno, Nevada. Investors can find Caesars Entertainment stock information through various financial platforms. The company's financial performance is regularly reported, with revenue and profitability metrics being key indicators of its success. The company has a diverse portfolio of Caesars Entertainment subsidiaries, contributing to its overall market presence. Understanding the Caesars Entertainment company ownership structure is essential for anyone looking to invest in the company. Key details about Caesars Entertainment major investors can be found in the company's filings. The Caesars Entertainment management team plays a crucial role in the company's strategic direction. The details of the Caesars Entertainment leadership are available in public records.
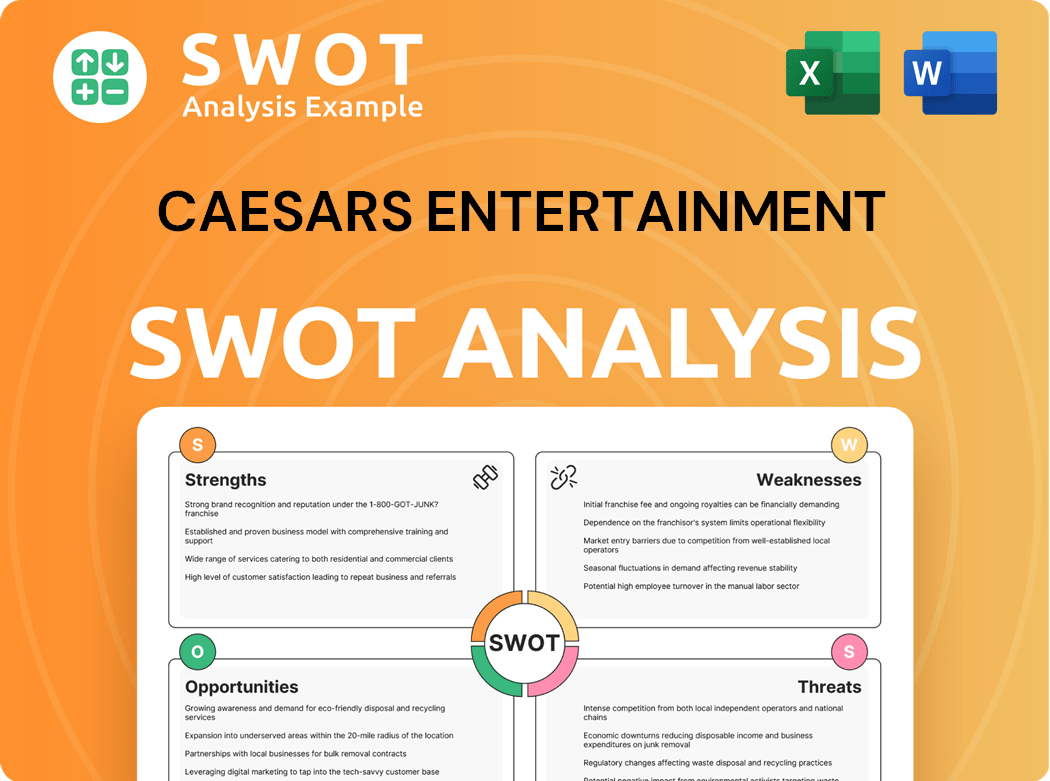
Caesars Entertainment SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Caesars Entertainment’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The ownership of Caesars Entertainment has seen significant shifts, largely driven by mergers and acquisitions. A key event was the 2005 acquisition by Harrah's Entertainment, which later adopted the Caesars Entertainment name. This merger combined two major players in the casino industry, reshaping the ownership structure. The most recent major change occurred in 2020, when Eldorado Resorts merged with Caesars Entertainment in a deal valued at $17.3 billion. This transaction resulted in Eldorado shareholders holding approximately 51% of the combined company, while former Caesars shareholders owned the remaining 49%.
The evolution of Caesars Entertainment's ownership reflects strategic moves to consolidate market share and adapt to the competitive landscape of the gaming industry. These changes have influenced the company's strategic direction and financial performance, impacting stakeholders and investors alike. Understanding these shifts is crucial for assessing the company's current position and future prospects.
| Shareholder | Percentage of Shares (as of early 2024) | Approximate Number of Shares |
|---|---|---|
| The Vanguard Group, Inc. | 11.23% | 24,008,667 |
| BlackRock Fund Advisors | 5.86% | 12,536,368 |
| Renaissance Technologies LLC | Data not available | Data not available |
As of early 2024, institutional investors hold a significant portion of Caesars Entertainment's shares. Major institutional shareholders include The Vanguard Group, Inc., and BlackRock Fund Advisors. Insiders, such as CEO Thomas Reeg, own a small percentage of the company's shares. This ownership structure, with a concentration among institutional investors, often influences the company's strategy, pushing for shareholder value creation through operational efficiency and capital allocation. The current ownership structure reflects a trend where large asset managers hold substantial stakes on behalf of their clients.
Caesars Entertainment's ownership is primarily held by institutional investors. Key shareholders include The Vanguard Group, Inc. and BlackRock Fund Advisors. The merger with Eldorado Resorts in 2020 significantly reshaped the ownership structure.
- Institutional investors hold a significant portion of shares.
- The 2020 merger with Eldorado Resorts was a major event.
- CEO Thomas Reeg holds a small percentage of shares.
- Ownership influences company strategy and financial performance.
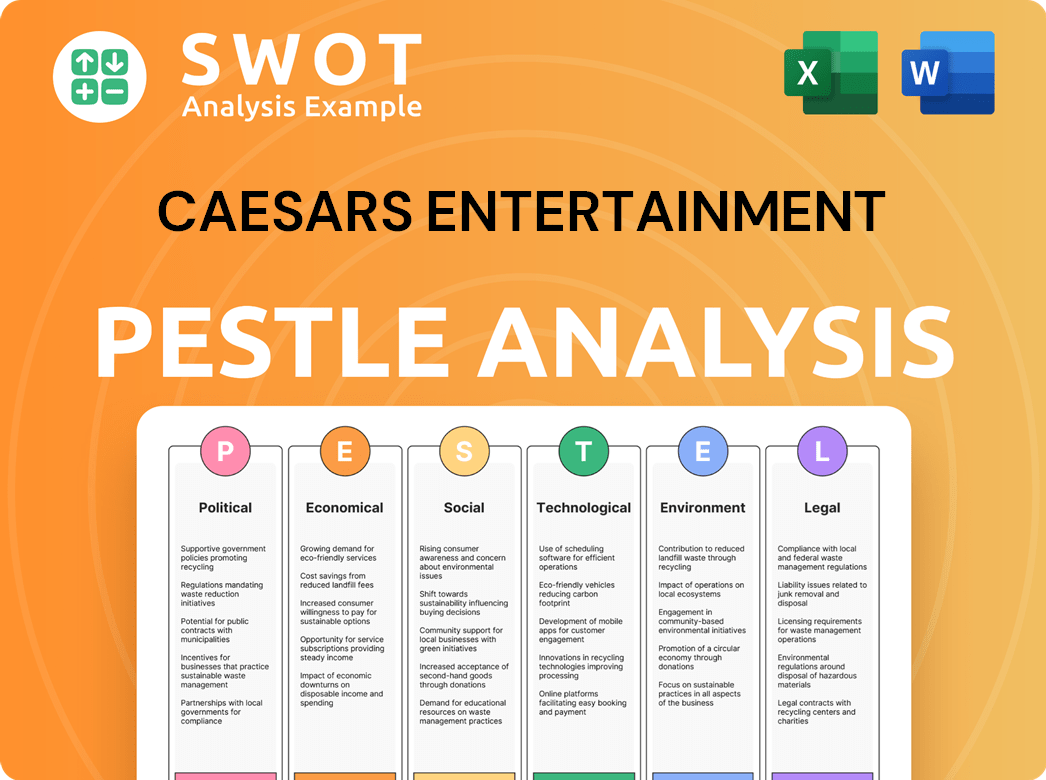
Caesars Entertainment PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Caesars Entertainment’s Board?
The current Board of Directors of Caesars Entertainment Inc. plays a crucial role in governance, balancing the interests of major shareholders with the strategic direction of the company. As of early 2024, the board includes a mix of individuals, including those representing significant shareholder interests and independent members. For instance, the CEO, Thomas Reeg, also serves on the board, representing executive leadership. The board's composition reflects the post-merger structure, with members often having backgrounds in finance, gaming, and hospitality, aligning with the company's core business. Understanding the Caesars Entertainment leadership is key to grasping its operational strategies.
The board's oversight of the company's financial performance, strategic acquisitions, and capital allocation directly impacts shareholder value. The structure ensures that the company is managed in a way that aligns with the objectives of its investors. The board's decisions are critical for the company's future, especially considering the dynamic nature of the gaming and hospitality industries. The composition of the board reflects the company's commitment to maintaining a strong and effective governance structure. If you're interested in understanding the company's customer base, you can learn more about it in this article: Caesars Entertainment's Target Market.
| Board Member | Title | Background |
|---|---|---|
| Thomas Reeg | CEO and Director | Finance, Gaming |
| David L. Bonderman | Director | Private Equity |
| Courtney Mather | Director | Finance |
The voting structure for Caesars Entertainment is generally based on a one-share, one-vote principle, common for publicly traded companies. This means that shareholders' voting power is directly proportional to the number of shares they own. There is no public indication of dual-class shares or special voting rights that would grant outsized control to specific individuals or entities beyond their equity stake. The influence of large institutional investors on governance is significant, as these major stakeholders can influence board elections and major corporate decisions.
The Board of Directors at Caesars Entertainment includes the CEO and independent members, ensuring a balance of interests.
- The voting structure follows a one-share, one-vote principle.
- Large institutional investors significantly influence corporate decisions.
- The board's oversight directly impacts shareholder value.
- The board's composition reflects the company's commitment to strong governance.
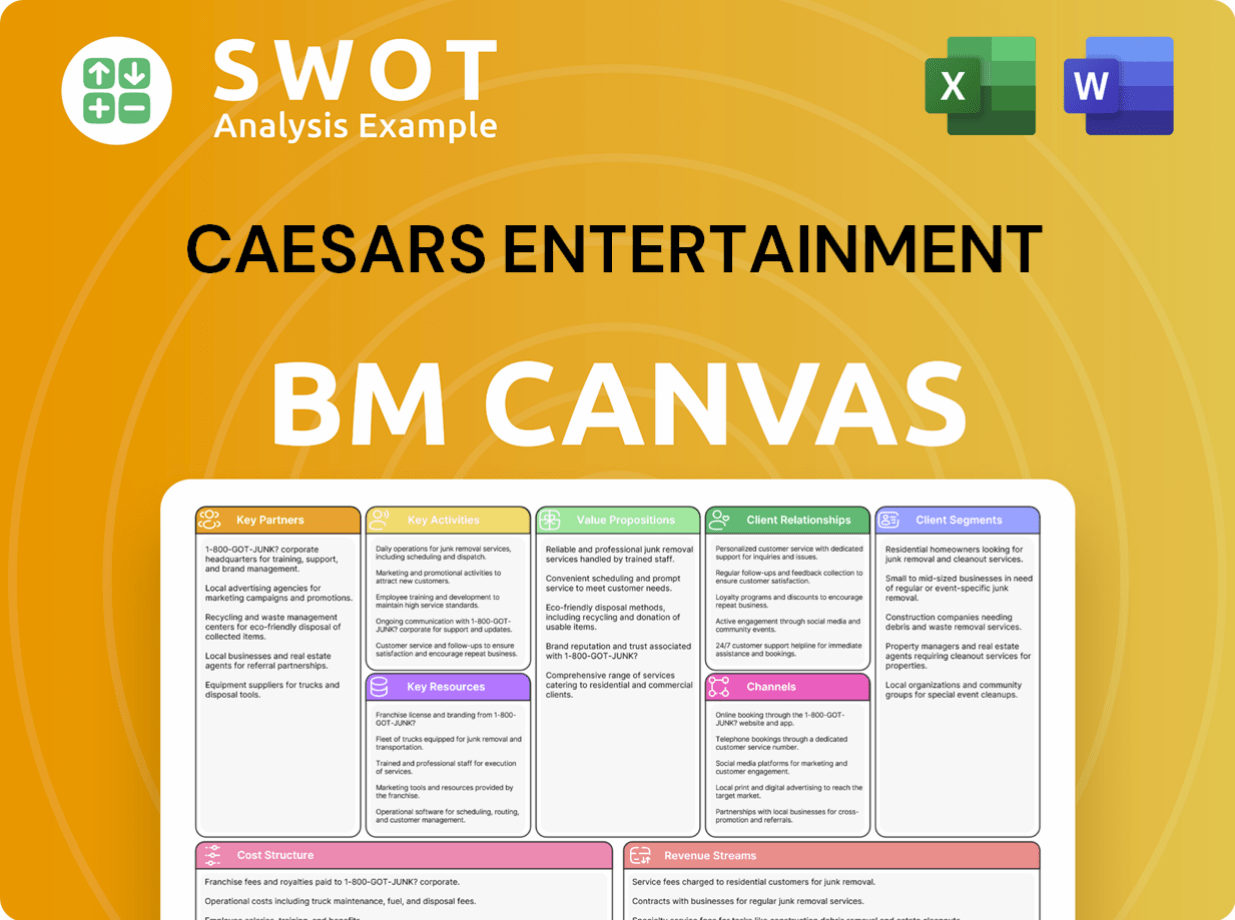
Caesars Entertainment Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Caesars Entertainment’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the ownership of Caesars Entertainment has seen significant shifts, primarily due to the merger with Eldorado Resorts. This union, finalized in 2020, reshaped the company's structure and influenced its shareholder base. Post-merger, Caesars Entertainment has focused on integrating its expanded portfolio, which includes numerous properties across the United States. The company has also engaged in strategic asset sales, such as the sale of the Rio All-Suite Hotel & Casino, to streamline its operations and financial position.
The ownership landscape of Caesars Entertainment continues to be shaped by industry trends. Institutional investors hold a substantial portion of the company's stock, reflecting a broader pattern of increased institutional involvement in the gaming sector. This trend often leads to greater emphasis on corporate governance and long-term value creation. The merger with Eldorado Resorts significantly altered the ownership structure, diluting the holdings of pre-merger Caesars shareholders. This change underscores the dynamic nature of ownership in the context of large-scale corporate transactions. For a deeper understanding, consider exploring the Brief History of Caesars Entertainment.
| Key Development | Impact on Ownership | Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Eldorado Resorts Merger | Dilution of pre-merger Caesars shareholders; increased institutional ownership. | Completed in 2020 |
| Strategic Asset Sales | Streamlining of assets, potential impact on investor sentiment and stock performance. | Ongoing |
| Growth in Sports Betting and Online Gaming | Potential to attract new investors and influence ownership trends. | Ongoing |
As of early 2024, Caesars Entertainment continues to navigate the evolving market landscape. The company's focus on debt reduction, market expansion, and growth in areas like sports betting and online gaming directly impacts investor sentiment and, by extension, ownership trends. The performance of Caesars Entertainment's stock and the strategic decisions made by its leadership, including the Caesars CEO, are key factors that influence the company's ownership structure.
A significant portion of Caesars Entertainment stock is held by institutional investors. This trend reflects a broader industry pattern.
The merger with Eldorado Resorts significantly altered the ownership structure of Caesars, diluting some shareholders.
Caesars Entertainment is focused on debt reduction and expansion into new markets like sports betting.
The company's performance and strategic decisions greatly influence investor sentiment and ownership trends.
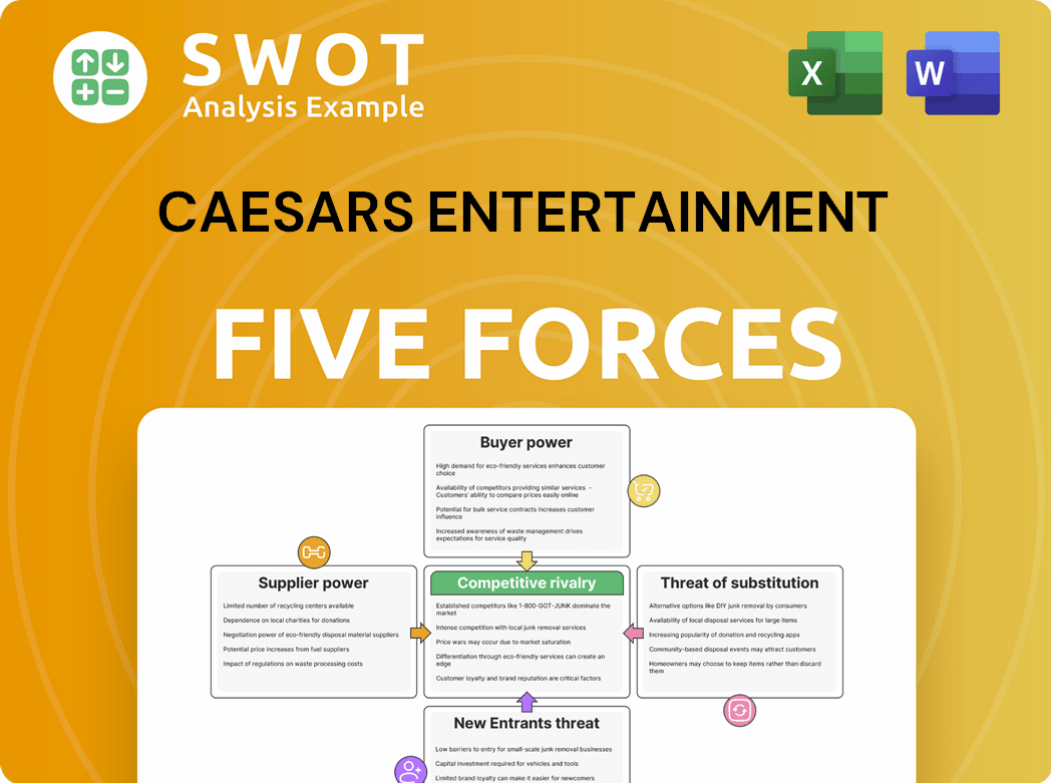
Caesars Entertainment Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Caesars Entertainment Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Caesars Entertainment Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Caesars Entertainment Company?
- How Does Caesars Entertainment Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Caesars Entertainment Company?
- What is Brief History of Caesars Entertainment Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Caesars Entertainment Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.