Kia Motors Bundle
Who Really Controls Kia Motors?
Understanding the ownership of Kia Motors is key to grasping its global impact and future strategies. From its humble beginnings in South Korea to its current status as a global automotive powerhouse, Kia's journey is marked by significant ownership shifts. This article unravels the complex Kia Motors SWOT Analysis, exploring the key players and pivotal moments that have shaped the company.
The story of Kia's ownership, from its founders to the present, reveals a fascinating narrative of resilience and strategic adaptation. Examining the Kia parent company, its relationship with Hyundai Motor Group, and the influence of major stakeholders provides crucial insights. Delving into the Kia Motors ownership structure and the location of Kia headquarters will help you understand the company's direction and its place in the competitive automotive landscape.
Who Founded Kia Motors?
The story of Kia Corporation, initially known as Kyungsung Precision Industry, began in December 1944. Tracing the exact founding ownership structure with specific equity splits or shareholding percentages for individual founders is challenging due to limited public records.
The company's early days involved manufacturing steel tubing and bicycle parts, leading to the creation of Korea's first domestically produced bicycle, the Samchully, in 1951. This early focus on domestic manufacturing was closely tied to South Korea's post-war industrialization.
In 1952, Kyungsung Precision Industry changed its name to Kia Industries. Over the following decades, Kia expanded into motorcycles and, eventually, the automotive industry, producing its first truck in 1962 and its first passenger car in 1974. During these initial phases, ownership would have primarily been held by the original founders and perhaps a small group of early investors, likely individuals or private entities involved in South Korea's growing industrial sector. Details regarding early agreements such as vesting schedules, buy-sell clauses, or initial ownership disputes are not extensively documented in the public domain, indicating a more private and less complex ownership landscape during its formative years compared to modern corporate structures. The founding team's vision for a self-reliant Korean industry was evident in their continuous expansion into various manufacturing sectors, which laid the foundation for the future automotive giant.
The early ownership of Kia Motors, then known as Kyungsung Precision Industry and later Kia Industries, was primarily held by its founders and a small circle of initial investors. The company's evolution from manufacturing bicycle parts to producing vehicles showcases its growth. Kia's expansion into the automotive sector marked a significant shift, with the production of its first truck in 1962 and its first passenger car in 1974.
- The initial ownership structure is not widely detailed in public records.
- Kia's growth was linked to South Korea's post-war industrialization.
- The company expanded into motorcycles before entering the automotive industry.
- The early focus was on manufacturing for the domestic market.
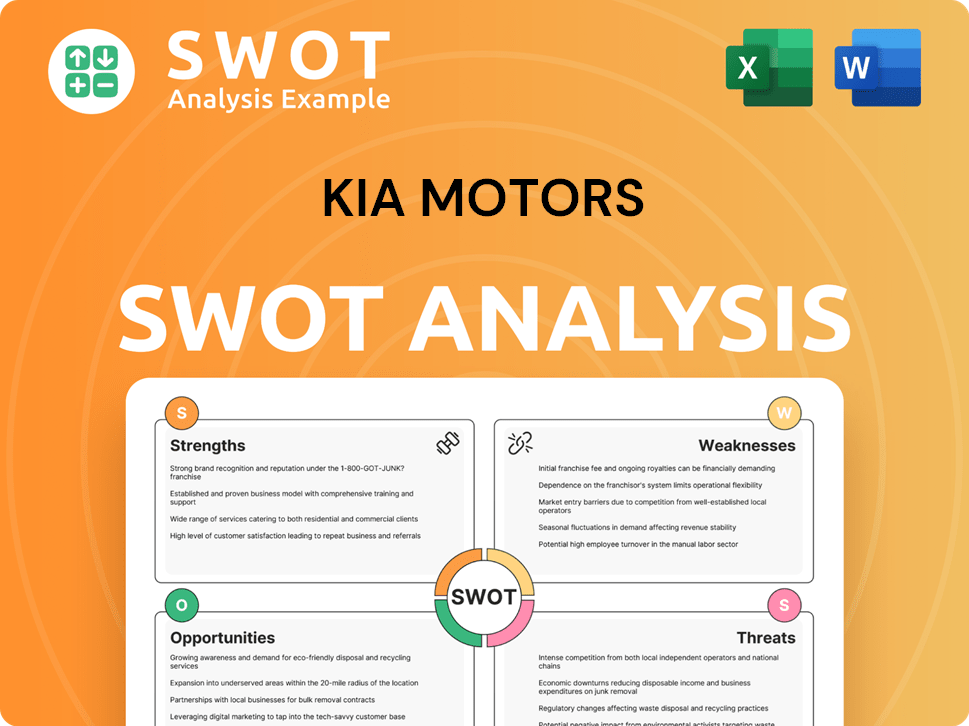
Kia Motors SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Kia Motors’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The ownership of Kia Corporation has been significantly shaped by key events, most notably the Asian financial crisis of the late 1990s. Facing financial difficulties, Kia was acquired by Hyundai Motor Company in 1998. This acquisition marked a pivotal moment, fundamentally altering Kia's ownership structure and setting the stage for its future within the Hyundai Motor Group. The acquisition allowed Kia to stabilize financially and leverage Hyundai's resources.
As of early 2024, the ownership structure of Kia Corporation is primarily defined by Hyundai Motor Company's substantial stake. Public filings and annual reports indicate that Hyundai Motor Company holds approximately 33.88% of Kia shares. This significant ownership stake gives Hyundai substantial control over Kia's strategic direction, product development, and global operations, solidifying the relationship between the two companies. Furthermore, Kia is a publicly traded company listed on the Korea Exchange (KRX), with a considerable portion of its shares held by institutional investors, mutual funds, index funds, and individual shareholders.
| Key Event | Date | Impact on Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| Asian Financial Crisis | Late 1990s | Led to Kia's financial instability and subsequent acquisition. |
| Hyundai's Acquisition of Kia | 1998 | Hyundai became the largest shareholder, reshaping Kia's ownership. |
| Public Listing on KRX | Ongoing | Introduced institutional and individual shareholders, diversifying ownership. |
The acquisition by Hyundai has allowed Kia to benefit from Hyundai's resources, particularly in research and development, global expansion, and economies of scale. This strategic alignment has significantly impacted Kia's strategy and governance, integrating it within the broader Hyundai Motor Group vision. For those interested in learning more about the company's origins, a Brief History of Kia Motors provides additional context.
Hyundai Motor Company is the primary owner of Kia, holding approximately 33.88% of the shares as of early 2024.
- Kia is a publicly traded company listed on the Korea Exchange (KRX).
- Institutional investors hold a significant portion of Kia's shares.
- The acquisition by Hyundai was a critical event in Kia's history.
- The relationship between Hyundai and Kia is a strategic partnership.
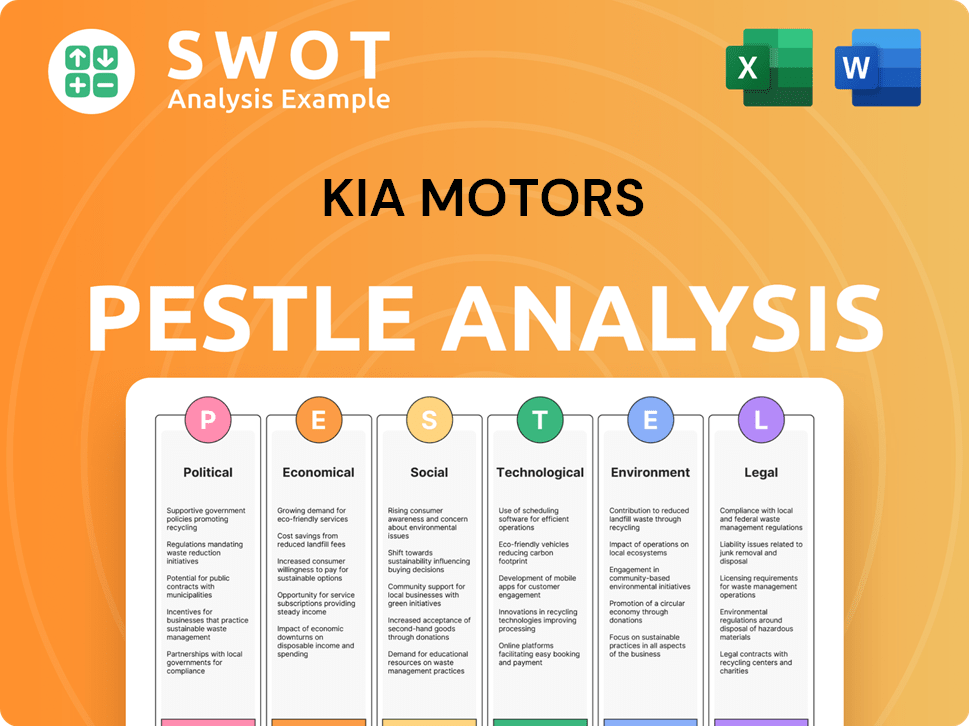
Kia Motors PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Kia Motors’s Board?
The Board of Directors of Kia Corporation is pivotal in guiding the company, shaped significantly by its ownership structure. As of early 2024, the board typically includes representatives from Hyundai Motor Company, the primary shareholder, alongside independent directors. This composition aims to balance internal executives, major shareholder representatives, and independent experts to ensure robust corporate governance. Individuals associated with Hyundai Motor Group often hold key positions, including executive roles and board seats, reflecting Hyundai's substantial ownership stake. This structure underscores the influence of the Kia parent company in strategic decision-making.
The board's structure and decision-making processes are heavily influenced by the strategic alignment within the broader Hyundai Motor Group. The board's role includes overseeing the company's strategic direction, financial performance, and risk management, ensuring that Kia remains competitive in the global automotive market. The board's oversight is crucial for maintaining stakeholder confidence and driving sustainable growth. For detailed insights, you can explore the Revenue Streams & Business Model of Kia Motors.
| Board Member | Role | Affiliation |
|---|---|---|
| Ho Sung Song | President and CEO | Kia Corporation |
| Chang Kyu Choi | Director | Hyundai Motor Company |
| Seong Moon Kim | Independent Director | Various |
Kia operates with a one-share-one-vote structure, meaning voting power is directly proportional to share ownership. Hyundai Motor Company's 33.88% stake is highly influential in major decisions, such as director elections and significant corporate actions. This ownership structure gives Hyundai substantial control, although there are no widely reported dual-class shares or special voting rights outside of direct shareholding. There have been no recent significant proxy battles or activist investor campaigns challenging Hyundai's control, indicating a stable governance environment.
Hyundai Motor Group's significant ownership directly influences Kia's governance and strategic decisions. Kia's board includes Hyundai representatives and independent directors to ensure balanced oversight.
- Hyundai Motor Company holds a substantial stake.
- One-share-one-vote system.
- Stable governance environment.
- Board influenced by strategic alignment within Hyundai Motor Group.
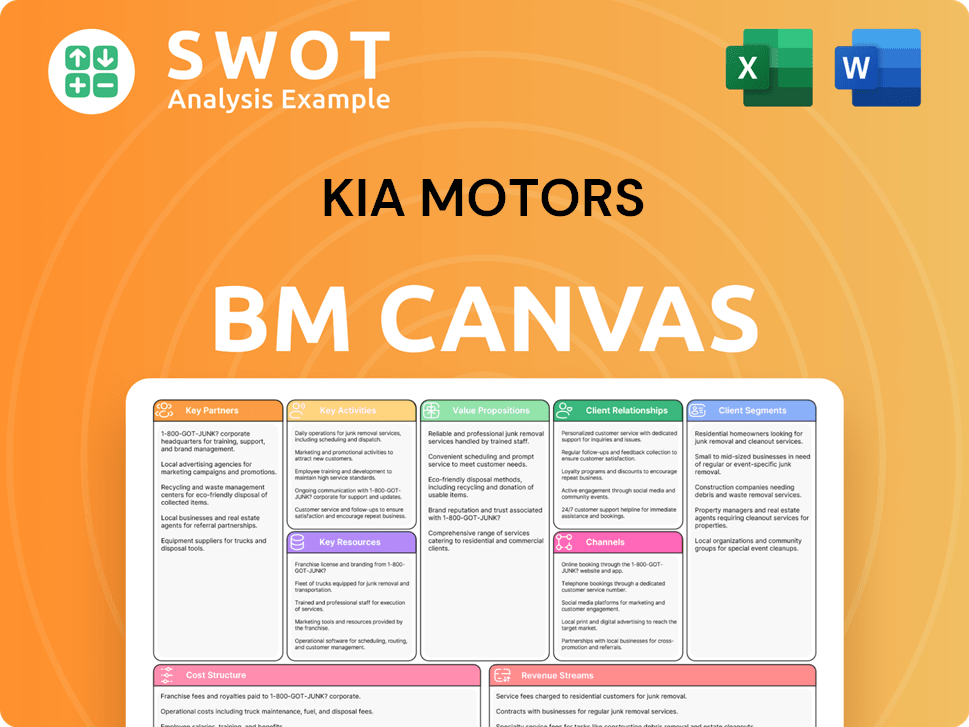
Kia Motors Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Kia Motors’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the ownership structure of Kia has seen continued dominance by Hyundai Motor Company. Hyundai's stake has remained relatively stable, hovering around 33.88%, which highlights the enduring strategic alliance between the two entities. Kia has been actively pursuing strategies to enhance shareholder value. These include considering share buybacks or dividend policies, although no significant large-scale share buybacks have been reported that would substantially alter the ownership percentages.
The automotive industry's shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) and future mobility solutions has attracted considerable interest from institutional investors. These investors are increasingly focused on ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria. This has led to a growing emphasis on institutional ownership, particularly from funds specializing in sustainable investments. Kia's strong performance in 2023 and early 2024, with popular EV models like the EV6 and EV9, has boosted investor confidence. This could potentially lead to shifts in institutional holdings as funds rebalance their portfolios. The relationship between Kia's target market and its ownership structure is crucial for understanding the company's strategic direction.
There have been no public announcements regarding a potential privatization or major changes in Hyundai's controlling stake. This suggests a continued strategic partnership and shared vision within the Hyundai Motor Group for the foreseeable future. The focus remains on collaborative development and market leadership in the changing automotive sector. The company's commitment to innovation and its performance in the EV market continue to be key factors influencing investor sentiment and ownership dynamics.
| Metric | Value | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Hyundai's Stake | ~33.88% | 2024 |
| Kia's Global Sales (2023) | Around 3.08 million units | 2023 |
| Market Capitalization | Varies, but in the billions of USD | 2024 |
Hyundai Motor Company's consistent ownership stake in Kia provides stability. This ongoing relationship is a key factor in the company's strategic planning. The structure also influences investment decisions and market perception.
Kia's success in the electric vehicle market has influenced ownership trends. Increased investor interest in EVs could lead to shifts in institutional holdings. The focus on ESG criteria is also a significant factor.
The strong relationship between Hyundai and Kia is crucial for future growth. This collaboration is key for product development and market expansion. Both companies benefit from shared resources and expertise.
Institutional investors are playing a larger role in Kia's ownership. Funds focusing on sustainable investments are increasing their holdings. This shift is influencing corporate strategy and decision-making.
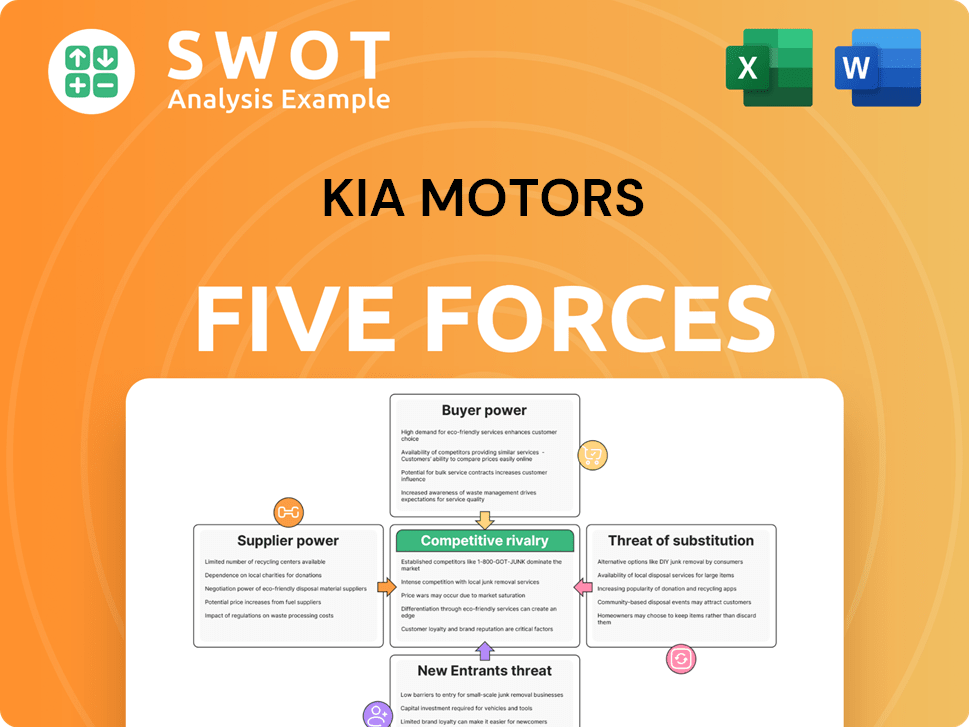
Kia Motors Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Kia Motors Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Kia Motors Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Kia Motors Company?
- How Does Kia Motors Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Kia Motors Company?
- What is Brief History of Kia Motors Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Kia Motors Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.