McCormick Bundle
Who Really Owns McCormick & Company?
Ever wondered who steers the ship at this global spice giant? Understanding McCormick SWOT Analysis is crucial to making informed investment decisions. McCormick & Company, a name synonymous with flavor, has a fascinating ownership story that shapes its strategic direction. From its humble beginnings in 1889 to its current status as a market leader, the evolution of its ownership reveals key insights.

This exploration of McCormick ownership delves into the company's history, key stakeholders, and the impact of its ownership structure on its operations. Discover the evolution of this spice company and its journey from a small Baltimore-based business to a global powerhouse. Learn about the major shareholders and how their influence shapes the future of this iconic brand, including its market share and long-term vision. This deep dive into who owns McCormick is essential for anyone interested in the company's stock price, its brands, and its place in the global market.
Who Founded McCormick?
The story of the McCormick Company began in 1889. Willoughby M. McCormick launched the business in Baltimore, Maryland. He started with just three employees in a single room. Initially, the company focused on flavoring extracts and fruit syrups.
Willoughby M. McCormick was the founder and the primary owner. The early ownership structure was straightforward, reflecting the founder's direct control. His vision centered on quality and flavor, which guided the company's early development.
Over time, the company expanded its product line. Spices, food colors, and other household products were added. Information about angel investors or early significant shareholders is not widely available. Ownership likely remained within the McCormick family or closely associated individuals during the initial decades.
Early ownership of the McCormick Company was primarily held by Willoughby M. McCormick. The company's initial ownership reflected a closely held private entity under the founder's control.
- The company's early growth was organic, with expansion into spices and other products.
- There is no widely published information detailing angel investors or significant early shareholders.
- Ownership likely remained within the McCormick family or closely associated individuals.
- Early ownership disputes or buyouts are not prominently documented in public records.
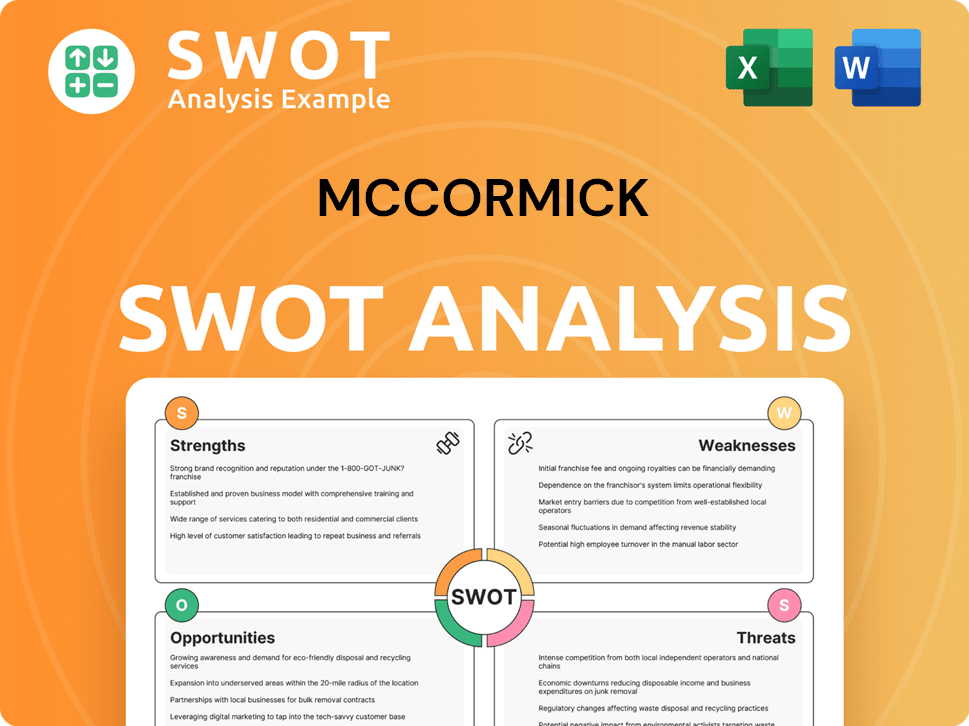
McCormick SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has McCormick’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The Brief History of McCormick reveals that the company's ownership structure has evolved significantly over time. Initially a privately held entity, McCormick & Company transitioned to a publicly traded company in 1947, listing on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE). This initial public offering (IPO) marked a pivotal shift, broadening the ownership base beyond the founding family and allowing for investment from institutional and individual investors.
This transition to public ownership has shaped McCormick's trajectory, influencing its strategic decisions and financial performance. The move provided access to capital markets, enabling the company to pursue growth opportunities through acquisitions and expansions. The shift also introduced greater scrutiny and accountability, as the company became answerable to a wider array of shareholders.
| Ownership Milestone | Details | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Private to Public | IPO on NYSE in 1947 | Expanded investor base, increased capital access. |
| Institutional Dominance | Growing holdings by institutional investors | Increased focus on financial performance and shareholder value. |
| Strategic Acquisitions | Acquisitions of brands like Frank's RedHot and French's Mustard | Market expansion and growth driven by shareholder expectations. |
Currently, McCormick's ownership is largely dominated by institutional investors. As of the first quarter of 2025, prominent shareholders include Vanguard Group Inc., holding a substantial stake, often exceeding 10% of outstanding shares. Other significant institutional investors include BlackRock Inc. and State Street Corp. These institutional investors manage assets on behalf of their clients through various funds and portfolios. The shift towards institutional ownership has increased pressure for consistent financial performance and adherence to ESG principles. For example, McCormick's acquisition of FONA International in 2021 for $710 million, reflects strategic moves supported by its institutional investor base seeking growth and market expansion.
McCormick's ownership structure has evolved from private to public, with institutional investors now holding a significant portion of the shares.
- The shift to public ownership in 1947 broadened the investor base.
- Institutional investors, such as Vanguard and BlackRock, play a major role.
- Ownership structure influences strategic decisions and financial performance.
- The company's acquisitions are often driven by shareholder expectations for growth.
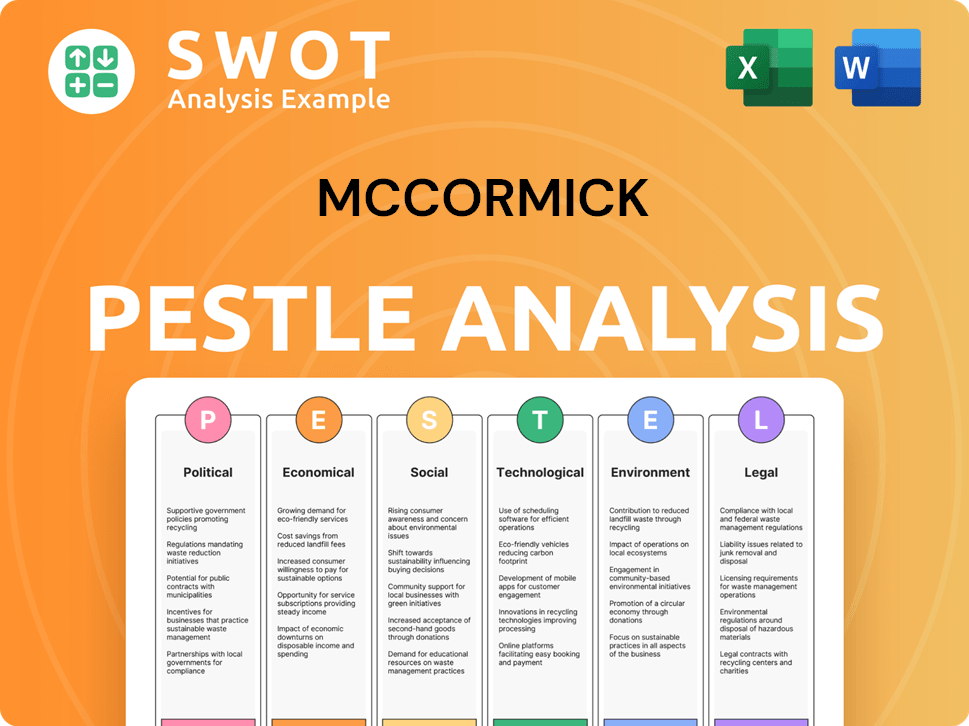
McCormick PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on McCormick’s Board?
The Board of Directors at McCormick & Company, as of early 2025, includes a mix of independent directors and executives. This structure is designed to balance oversight with strategic leadership. The board typically includes the Chairman and CEO, along with several independent directors. These independent directors bring a variety of expertise from different industries. While specific board members representing major shareholders aren't explicitly identified, institutional investors like Vanguard and BlackRock influence decisions through their significant voting power.
The board's responsibilities include overseeing corporate strategy, risk management, and executive compensation. They also ensure the company's long-term success while upholding shareholder value. The composition of the board, with a majority of independent directors, aims to ensure objective decision-making and strong corporate governance. This structure supports the company's commitment to maintaining a strong market position in the spice industry and related food products.
| Board Member | Title | Affiliation |
|---|---|---|
| Lawrence E. Kurzius | Chairman of the Board, President and Chief Executive Officer | McCormick & Company |
| Michael B. Polk | Lead Independent Director | Former CEO of Newell Brands |
| W. Geoffrey Carpenter | Independent Director | Former CFO of Campbell Soup Company |
McCormick operates under a one-share-one-vote structure for its common stock. This means each share of common stock generally entitles its holder to one vote on matters brought before shareholders, including the election of directors. The company does not have publicly disclosed dual-class shares or other arrangements that grant outsized control to specific individuals or entities through special voting rights. This structure promotes a democratic shareholder voting process, where larger institutional holders naturally have more influence due to the volume of shares they own. The company's commitment to this structure reflects its dedication to fair governance and shareholder value. For more insights into the company's market approach, consider reading about the Marketing Strategy of McCormick.
The Board of Directors at McCormick & Company includes a mix of independent directors and executives, ensuring a balance of oversight and strategic leadership.
- McCormick operates under a one-share-one-vote structure, promoting a democratic shareholder voting process.
- Major institutional investors like Vanguard and BlackRock influence decisions through their significant voting power.
- The board oversees corporate strategy, risk management, and executive compensation.
- The company's governance structure supports its long-term success and shareholder value.
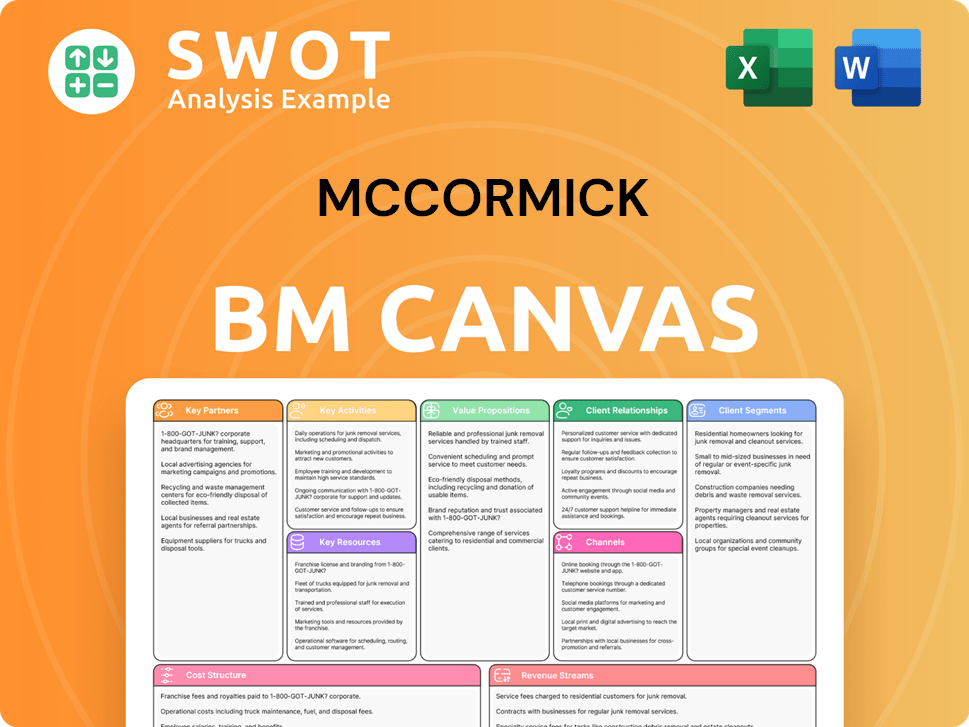
McCormick Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped McCormick’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years (2022-2025), the ownership structure of McCormick & Company has remained relatively stable, with a continued focus on strategic growth and market expansion. The company has prioritized acquisitions and organic growth initiatives over significant share buybacks. The acquisition of FONA International in 2021 for $710 million, which closed in the first quarter of 2021, is a prime example of its strategic moves to strengthen its position in the flavor solutions market. This acquisition, financed through a combination of cash and debt, did not fundamentally alter the public ownership model.
Industry trends suggest an increasing concentration of ownership among institutional investors. Firms like Vanguard and BlackRock have increased their stakes, leading to a greater focus on long-term value creation and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. As a publicly traded company, McCormick & Company has seen a natural dilution of the founding family's ownership over time. The company's public listing allows access to capital markets, which supports future growth and acquisitions. Leadership changes, such as the transition of Lawrence E. Kurzius to Executive Chairman and Brendan B. McCrann becoming CEO in 2023, reflect internal succession planning rather than shifts in ownership.
| Metric | Details | Data |
|---|---|---|
| Market Capitalization (Approximate) | Reflects the total value of the company's outstanding shares. | Around $20 billion as of late 2024 |
| Institutional Ownership | Percentage of shares held by institutional investors. | Typically over 70% |
| Major Shareholders | Key institutional investors. | Vanguard, BlackRock, State Street |
McCormick & Company's commitment to its public listing indicates a strategy focused on continued growth and market leadership. The company's focus remains on expanding its market share and product offerings through strategic investments. For more insights into the company's financial strategies, consider exploring the Revenue Streams & Business Model of McCormick.
The acquisition of FONA International in 2021 expanded McCormick's presence in the flavor solutions market. The acquisition cost $710 million and was financed through a combination of cash and debt.
Institutional ownership continues to rise, with firms like Vanguard and BlackRock holding significant stakes. Founder dilution has occurred as the company has grown.
The company emphasizes organic growth and strategic acquisitions over share buybacks. Leadership transitions reflect internal succession planning.
McCormick & Company maintains a strong position in the spice and flavor market. The company is committed to its publicly traded structure.
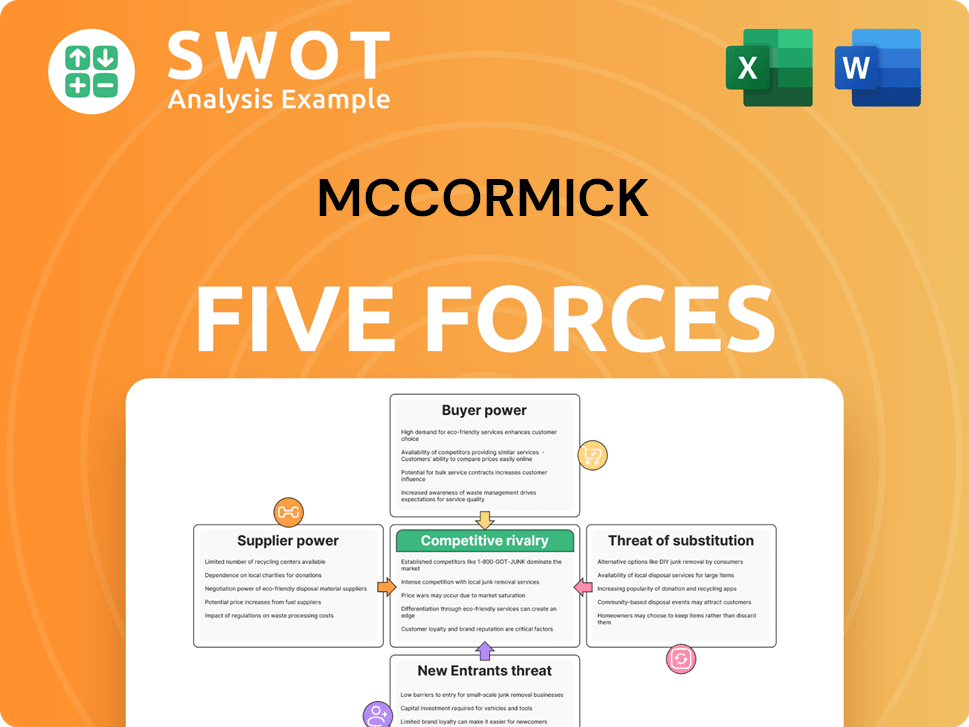
McCormick Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of McCormick Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of McCormick Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of McCormick Company?
- How Does McCormick Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of McCormick Company?
- What is Brief History of McCormick Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of McCormick Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.