3D Systems Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
3D Systems Bundle
What is included in the product
Identifies disruptive forces, emerging threats, and substitutes that challenge market share.
Instantly understand strategic pressure with a powerful spider/radar chart.
Preview Before You Purchase
3D Systems Porter's Five Forces Analysis
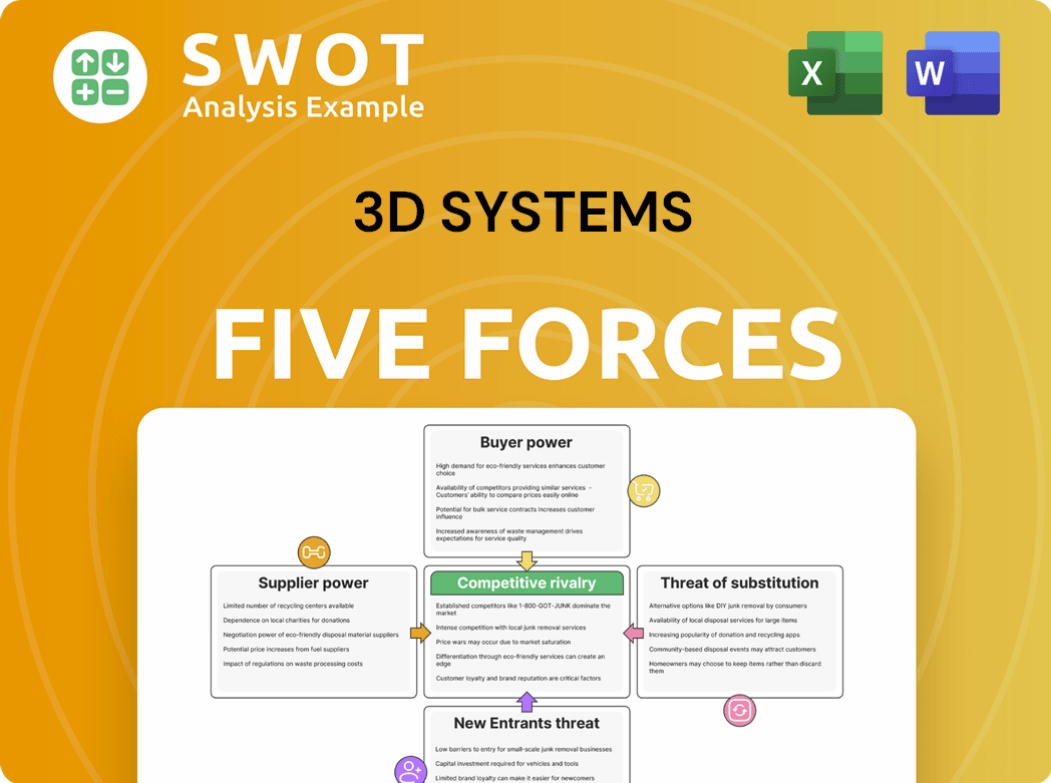
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces analysis of 3D Systems. It breaks down each force, including competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, threat of substitutes, and threat of new entrants, to give a full picture. The in-depth evaluation of each area will help you understand 3D Systems' market position. You're getting the actual analysis ready for your needs—fully formatted and ready to use.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
3D Systems faces a dynamic competitive landscape, heavily influenced by several key forces. The threat of new entrants remains moderate, given the industry's technological barriers and capital needs. Bargaining power of buyers is substantial, particularly from large industrial customers seeking cost-effective solutions. Suppliers possess moderate influence, with diverse material vendors. The risk of substitute products, like CNC machining, is present, yet not entirely dominant. Competitive rivalry is intense, featuring both established and emerging players.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore 3D Systems’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
3D Systems' profitability can be squeezed by suppliers of specialized 3D printing materials. Limited suppliers, especially for proprietary materials, increase supplier power. This can lead to higher input costs for 3D Systems. In 2024, the cost of materials accounted for a significant portion of the total manufacturing cost for 3D printing companies.
Switching material suppliers can be tough for 3D Systems, as it's costly and time-consuming. They'd have to re-calibrate printers and maybe change processes. This reliance on current suppliers boosts the suppliers' power. In 2024, 3D printing materials market was valued at $2.2 billion, showing the importance of these materials.
If suppliers could produce 3D printers, they'd gain power. They could bypass 3D Systems, selling directly. This could hurt 3D Systems' profits. In 2024, 3D Systems faced challenges from material suppliers. This risk makes good supplier relations crucial.
Proprietary material formulations
Suppliers with proprietary material formulations hold significant power over 3D Systems. If these suppliers own patents or trade secrets for essential materials, 3D Systems' options are limited. This dependence can be crucial for specialized applications, increasing supplier influence. For instance, in 2024, materials represented a significant portion of 3D Systems' production costs.
- Proprietary materials limit 3D Systems' alternatives.
- Unique formulations drive up supplier bargaining power.
- Dependency affects 3D Systems' negotiation position.
- Material costs are a key factor in profitability.
Impact of material quality on final product
The quality of materials significantly impacts the final product's quality and reliability in 3D printing. Subpar materials can lead to product failures, potentially harming 3D Systems' reputation, making them vulnerable. This dependency increases 3D Systems' willingness to meet supplier demands to secure high-quality materials. Maintaining material quality is crucial for product integrity and market competitiveness.
- In 2024, the 3D printing materials market was valued at $2.4 billion.
- Material defects can cause up to 20% of product failures in 3D printing.
- High-performance materials can increase product lifespan by 30%.
- 3D Systems' material costs represent roughly 40% of their production expenses.
3D Systems faces strong supplier power, especially for unique 3D printing materials. Limited material options and proprietary formulations give suppliers leverage, impacting costs. In 2024, the 3D printing materials market reached $2.4 billion, highlighting their importance.
| Aspect | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Material Cost % of Production | Higher costs, lower margins | ~40% |
| Market Value of Materials | Supplier influence | $2.4 billion |
| Defect Rate from Materials | Product failure risks | Up to 20% |
Customers Bargaining Power
3D Systems faces substantial customer bargaining power, particularly if a few major clients drive a large part of its revenue. Key industries like aerospace and healthcare often wield considerable influence. For instance, in 2024, contracts with major healthcare providers could represent over 30% of 3D Systems’ revenue. Losing a significant client, such as a large medical device manufacturer, could severely impact earnings, as seen when a major aerospace client shifted contracts, affecting sales by about 15% in 2024.
Customers with significant needs might opt for in-house 3D printing, diminishing their dependence on 3D Systems. As technology advances, this shift becomes more feasible, potentially impacting 3D Systems' market share. This shift compels 3D Systems to offer competitive pricing and added services to retain clients. In 2024, the 3D printing market was valued at $30.8 billion, showing customer's growing interest.
The 3D printing services market is quite competitive, featuring numerous providers with similar offerings. Customers have the flexibility to choose from various options if 3D Systems doesn't meet their needs. This ease of switching significantly boosts customer bargaining power. In 2024, the market saw a 15% growth in the number of service providers.
Price sensitivity of customers
Price sensitivity significantly influences customer bargaining power for 3D Systems. In prototyping and less critical areas, clients often prioritize cost, potentially choosing lower-priced alternatives. This behavior intensifies price competition, compelling 3D Systems to adjust pricing strategies. For instance, in 2024, the average selling price for 3D printers in the entry-level segment decreased by approximately 7%. This trend highlights the customer's ability to influence pricing.
- Price sensitivity directly impacts purchasing decisions.
- Customers may switch to cheaper options.
- 3D Systems must manage pricing pressures.
- The entry-level printer segment saw a price drop.
Customers' knowledge and expertise in 3D printing
As customers gain expertise in 3D printing, their ability to negotiate with 3D Systems strengthens. They can now evaluate various offerings, understand value, and push for better deals. This shift in knowledge empowers customers, impacting 3D Systems' pricing and service strategies. This is especially true for larger clients in sectors like aerospace and healthcare, which represented a significant portion of 3D Systems' revenue in 2024.
- Advanced customer knowledge leads to tougher negotiations.
- Customers' ability to compare solutions increases.
- The balance of power shifts towards the customer.
- This impacts pricing and service terms.
Customer bargaining power significantly affects 3D Systems. Key clients can influence revenues, and losing them hurts earnings. Competition and price sensitivity empower customers to seek better deals. As expertise grows, negotiations become tougher.
| Aspect | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Client Concentration | High risk | Top clients >30% revenue |
| Market Competition | Increased pressure | Service provider growth: 15% |
| Price Sensitivity | Pricing impact | Entry-level printer price drop: 7% |
Rivalry Among Competitors
The 3D printing market is fiercely competitive, with major players like Stratasys and HP constantly battling for dominance. Companies compete on multiple fronts, including price, technological advancements, and customer service to secure market share. This intense rivalry forces 3D Systems to continually innovate. In 2024, the global 3D printing market was valued at over $30 billion.
The 3D printing market's competitive nature can spark price wars, particularly in commodity services. This can squeeze 3D Systems' profit margins. For instance, in 2024, average selling prices (ASPs) for certain 3D printing materials decreased by up to 5%. To stay ahead, 3D Systems must cut costs and boost service value.
Competitive rivalry in 3D printing is fierce, with companies constantly pushing technological boundaries. 3D Systems must aggressively invest in R&D for new tech and materials. Failure to innovate means losing ground; in 2024, R&D spending was about 10% of revenue. Staying competitive requires constant innovation.
Importance of application-specific expertise
Competitive rivalry in 3D printing hinges on application-specific expertise. Success demands deep industry understanding, like healthcare or automotive. Companies with specialized knowledge gain an edge. 3D Systems must highlight and market its application-specific proficiency. This differentiation strategy is vital for market competitiveness.
- 3D Systems reported $133.6 million in revenue for Q1 2024, showing the importance of focusing on specialized applications.
- The medical and dental sectors are key growth areas, representing significant application-specific opportunities.
- Partnerships with industry leaders can boost application-specific expertise and market reach.
- Investing in R&D for application-specific solutions is critical.
Consolidation in the 3D printing industry
The 3D printing industry is seeing consolidation, with bigger firms buying smaller ones. This could heighten competition and concentrate the market. 3D Systems must monitor these changes closely and adjust its approach. For instance, Stratasys acquired MakerBot in 2013. In 2024, the 3D printing market was valued at $30.8 billion.
- Increased market concentration can reduce the number of competitors.
- Acquisitions can lead to access to new technologies and markets.
- Competition may intensify as companies fight for market share.
- Strategic adaptation is critical for survival and growth.
Competitive rivalry in 3D printing is very intense, with constant battles for market share. Firms compete on price, tech, and service, requiring continuous innovation. In Q1 2024, 3D Systems had $133.6M in revenue, showing focus on specific applications is key. Consolidation and acquisitions further shape the competitive landscape.
| Aspect | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Price Wars | Margin pressure | ASP of materials down 5% |
| Tech Race | R&D investment | R&D = 10% of revenue |
| Consolidation | Market change | Market value $30.8B |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Traditional manufacturing, including machining and injection molding, poses a significant threat as a substitute for 3D printing. These methods can be more cost-effective for large-scale production runs. 3D Systems must highlight 3D printing's advantages in customization and speed. In 2024, traditional manufacturing still holds a substantial market share, with injection molding alone generating billions in revenue annually.
Alternative additive manufacturing technologies, like Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), offer customers choices beyond 3D Systems. These alternatives can serve as substitutes. In 2024, the global 3D printing market was valued at $30.8 billion, showing the broad range of options.
Advanced simulation and prototyping software presents a threat to 3D Systems. These tools allow for virtual testing, reducing the need for physical prototypes. This shift can lower demand for 3D printing services, particularly in early design phases. To stay competitive, 3D Systems must integrate its offerings with these software solutions. In 2024, the simulation software market was valued at $5.5 billion, highlighting the scale of this potential substitute.
Outsourcing to low-cost manufacturing countries
Outsourcing manufacturing to low-cost countries presents a threat to 3D Systems. This is especially true for high-volume production runs. Companies might find traditional manufacturing more cost-effective. 3D Systems must emphasize 3D printing's unique advantages.
- Labor costs in China and India are significantly lower, offering cheaper alternatives.
- In 2024, the global outsourcing market was valued at over $92.5 billion.
- 3D Systems needs to focus on specialized, complex parts where 3D printing excels.
- Companies can save up to 40% by outsourcing manufacturing.
Hybrid manufacturing approaches
Hybrid manufacturing poses a threat as it combines 3D printing with traditional methods. This allows companies to create molds via 3D printing and then use them for injection molding. Such strategies offer a flexible and potentially cost-effective alternative to 3D Systems' offerings. To stay competitive, 3D Systems must integrate its solutions with these hybrid approaches.
- 2024: Hybrid manufacturing market is growing, with a projected value of $1.2 billion.
- Companies are increasingly adopting hybrid methods to reduce production costs by 15-20%.
- 3D Systems' revenue in 2024 reached $573.4 million, which can be affected by the trend.
The threat of substitutes for 3D Systems is significant, coming from various sources. Traditional manufacturing methods, like injection molding, can offer cheaper alternatives, particularly for large-scale production. Alternative 3D printing technologies and hybrid manufacturing approaches further increase the substitution possibilities. To compete, 3D Systems must highlight its unique advantages and adapt to these evolving market dynamics.
| Substitute | Description | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Manufacturing | Machining, injection molding. | Injection molding market share: billions in revenue. |
| Alternative 3D Printing | FDM, other additive methods. | Global 3D printing market: $30.8B. |
| Hybrid Manufacturing | Combines 3D printing with traditional. | Hybrid market value: $1.2B, cost reduction: 15-20%. |
Entrants Threaten
High capital investment is a significant threat for new entrants to the 3D printing market. Entering requires substantial investments in machinery, R&D, and marketing. The need for specialized facilities and advanced tech further increases costs. These factors create a high barrier, making it tough for new firms to rival 3D Systems. In 2024, the 3D printing market was valued at approximately $30.8 billion.
3D Systems and established firms possess many patents on 3D printing tech, materials, and software. These patents pose a significant barrier, making it tough for newcomers to compete without IP infringement. Developing unique, non-infringing tech is costly. In 2024, patent litigation costs can be substantial, potentially reaching millions.
3D Systems benefits from a well-established brand reputation and long-standing customer relationships. New competitors face significant hurdles in building brand awareness and trust, requiring substantial marketing and sales investments. This advantage is reflected in their 2024 revenue, with a reported $569.5 million, showcasing customer loyalty. The difficulty in replicating these relationships acts as a barrier, reducing the threat of new entrants.
Economies of scale in manufacturing and distribution
3D Systems leverages economies of scale in manufacturing and distribution, enhancing its pricing power. This advantage allows it to offer competitive prices, a significant barrier for new firms. New entrants often struggle to match these cost efficiencies, impacting their ability to compete. Building a large-scale network demands substantial investment, increasing entry barriers.
- 3D Systems' revenue in 2023 was approximately $556 million, reflecting its established market presence.
- The cost of setting up a comparable manufacturing facility can range from tens to hundreds of millions of dollars.
- Established distribution networks can handle thousands of orders daily, a feat that requires years to replicate.
- The company's gross profit margin was 35.7% in 2023, reflecting its operational efficiency.
Access to specialized materials and expertise
The 3D printing industry presents a challenge for new entrants due to the necessity of specialized materials and expertise. These newcomers often face difficulties in securing and keeping skilled professionals in fields like materials science and software development. Building a team with the required skills and knowledge significantly raises the barrier to entry, impacting the competitive landscape. This demand for specialized talent complicates market entry.
- The global 3D printing market was valued at USD 30.87 billion in 2023.
- It is projected to reach USD 88.23 billion by 2030.
- The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 16.24% from 2023 to 2030.
New entrants face substantial barriers in the 3D printing market. High capital needs and patent protections by 3D Systems create obstacles. Established brand recognition and economies of scale further limit new competition. The industry's rapid growth, with a projected value of $88.23 billion by 2030, attracts entrants despite the challenges.
| Barrier | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | High costs for machinery, R&D, and marketing. | Raises the stakes, deterring smaller players. |
| Patents | 3D Systems' strong IP portfolio. | Limits opportunities for innovation, legal challenges. |
| Brand & Scale | Established reputation and efficient operations. | Competitive advantage, harder to win market share. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's analysis uses SEC filings, industry reports, and market share data, along with financial statements, to examine 3D Systems' competitive landscape.