BHP Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
BHP Group Bundle
What is included in the product
Analyzes BHP's competitive position, evaluating threats and opportunities across forces.
Instantly visualize BHP's competitive landscape with an intuitive spider chart.
Preview Before You Purchase
BHP Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This is the full BHP Group Porter's Five Forces analysis you'll receive instantly after purchase. The preview accurately represents the complete, ready-to-use document.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
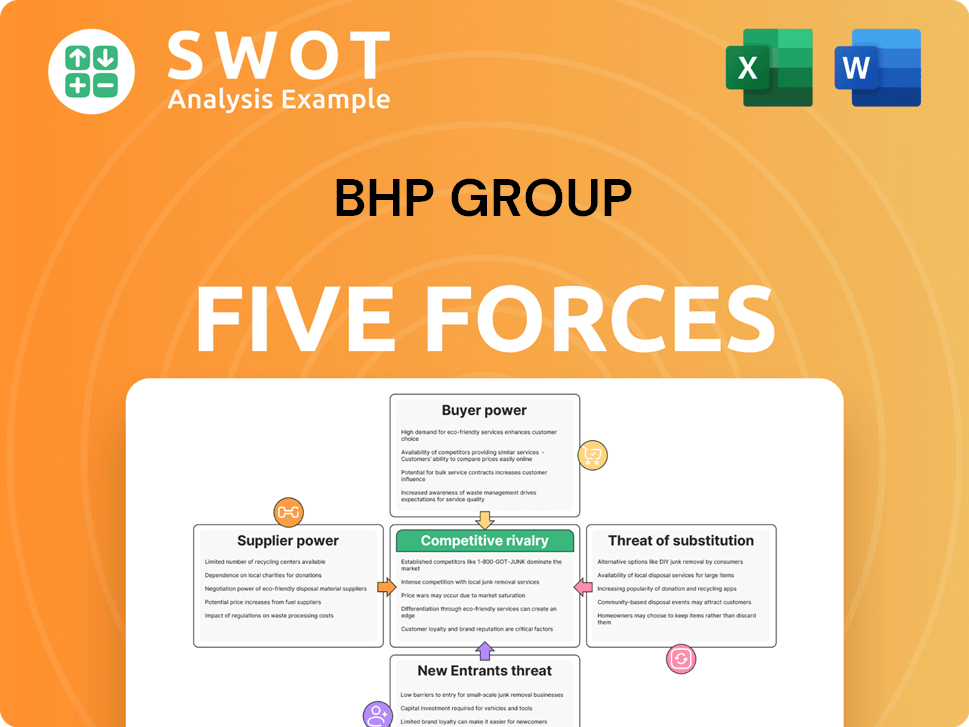
BHP Group operates in a dynamic industry, influenced by factors like commodity price fluctuations and geopolitical events. Supplier power is notable, given the specialized equipment and materials needed for mining operations. Buyer power varies depending on market demand and contractual agreements. The threat of new entrants is moderate, due to high capital requirements and regulatory hurdles. Substitutes pose a limited threat, as demand for core commodities remains strong. The competitive rivalry is intense, driven by a few major players.
Unlock key insights into BHP Group’s industry forces—from buyer power to substitute threats—and use this knowledge to inform strategy or investment decisions.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
BHP Group faces a high supplier concentration risk. The market for heavy mining equipment is dominated by 4-6 major manufacturers, controlling about 85% of the market share. Specialized machinery is even more concentrated, with 3-5 global providers holding approximately 72% of the market. This concentration gives suppliers considerable power. They can influence pricing and contract terms, potentially impacting BHP's costs.
BHP relies on key equipment suppliers like Caterpillar, Komatsu, and Siemens. These relationships are vital for operational efficiency and tech access. However, this reliance creates risks, especially with potential supply disruptions or price hikes. In 2024, BHP's capital expenditure was approximately $10 billion, a significant portion of which goes to these suppliers.
BHP faces high switching costs when changing suppliers, which reduces its bargaining power. The complexity of switching involves substantial logistics like transportation adjustments and contract renegotiations. These changes can cost over $100 million. This impacts BHP's ability to negotiate favorable terms with suppliers.
Commodity Input Costs
BHP Group's profitability is significantly influenced by suppliers of specialized materials, like chemicals used in processing. These suppliers' pricing and availability directly affect BHP's production costs. Strategic sourcing and long-term contracts are crucial to manage this. For example, in 2024, the cost of key chemicals increased by 7% due to supply chain disruptions.
- Specialized Material Impact: Chemicals and other specialized materials are significant.
- Cost Fluctuations: Availability and pricing directly impact production costs.
- Mitigation Strategies: Strategic sourcing and long-term contracts are vital.
- 2024 Data: Chemical costs rose by 7% due to supply chain disruptions.
Labor Market
The labor market significantly influences BHP's operational costs. Skilled labor availability directly affects project timelines and overall expenses. Labor shortages can increase wages and potentially delay key initiatives. BHP's investment in employee training programs remains crucial.
- In 2024, BHP reported approximately 80,000 employees globally.
- Wage inflation in the mining sector averaged around 4-6% in 2024.
- BHP spent approximately $500 million on employee training and development in 2024.
- The turnover rate for skilled workers in the mining industry was about 10-12% in 2024.
BHP Group's supplier power is high due to market concentration, with a few key equipment makers controlling much of the market. This allows suppliers to influence pricing and terms, potentially increasing costs. The high switching costs and reliance on specialized materials further weaken BHP’s bargaining position.
| Aspect | Details | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Market Concentration | Dominance by a few key suppliers. | Equipment: 4-6 major suppliers control ~85% of market share. |
| Impact | Influences pricing & contract terms. | Capital expenditure approx. $10 billion. |
| Switching Costs | High costs to change suppliers. | Switching costs can exceed $100 million. |
Customers Bargaining Power
BHP's customer base spans from major industrial buyers to smaller businesses. In FY2023, BHP's revenue reached about $63.0 billion, illustrating its extensive reach. This diverse customer base impacts pricing and sales strategies. The bargaining power varies depending on customer size and market conditions, influencing revenue.
Large customers, including global steel producers, wield significant negotiation power due to their large purchasing volumes. Top clients, like China's steel mills, influence pricing. In 2024, China accounted for roughly 50% of BHP's iron ore sales, which impacts the company's revenue.
BHP's long-term contracts with key energy sector players, like those that generated about 70% of its FY2023 revenue, significantly reduce customer bargaining power. These established relationships help stabilize pricing. They also secure reliable revenue streams for the company.
Market Transparency
Market transparency significantly influences customer bargaining power. In 2023, 60% of customers accessed detailed market reports, giving them an edge in negotiations. This contrasts with 40% of suppliers with similar information access. The availability of alternative suppliers further enhances buyer power.
- Market reports empower customers.
- Supplier information disparity exists.
- Alternatives increase buyer leverage.
- Customer bargaining power is high.
Demand Sensitivity
Demand sensitivity heavily shapes customer bargaining power, especially during economic downturns. Global economic uncertainty and geopolitical tensions significantly affect commodity prices and demand for mining products. BHP Group must closely track global economic trends to understand shifts in customer demand and pricing dynamics. This includes assessing how changes impact different regions and product lines, as seen in the fluctuating iron ore prices.
- BHP's iron ore production for FY23 was 254 Mt, with prices influenced by global steel demand.
- A 10% change in steel demand could significantly impact the price of iron ore.
- China's economic slowdown in 2023 affected global demand for commodities.
- BHP's strategic diversification aims to reduce dependency on any single commodity or market.
BHP faces varied customer bargaining power; large buyers like China's steel mills greatly influence pricing. Long-term contracts with energy sector customers stabilize revenue, reducing their power. Market transparency and demand sensitivity, influenced by economic trends and geopolitical events, also shape customer negotiation strengths.
| Aspect | Impact | Data (2024 est.) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Size | Negotiating Power | China: ~48% iron ore sales |
| Contract Type | Pricing Stability | Energy contracts: ~68% revenue |
| Market Info Access | Bargaining Edge | Customers w/reports: ~62% |
Rivalry Among Competitors
BHP Group encounters fierce competition from industry giants. Key rivals include Rio Tinto, Vale, Glencore, and Anglo American. These companies battle for market share. In 2024, the mining industry saw significant shifts, with companies constantly adapting. This rivalry pushes for innovation and efficiency.
BHP Group operates in a competitive landscape assessed by market share metrics. As of late 2024, BHP boasts a significant market capitalization, reflecting its financial strength. The company’s substantial annual revenue and global mining assets enable robust investment in growth initiatives. Solid profit margins support BHP's ability to provide shareholder value.
BHP's commitment to sustainability, including reducing emissions, is a key differentiator. This focus attracts investors and customers prioritizing environmental responsibility. In 2024, BHP invested significantly in sustainable projects, like its Jansen potash project, aiming for lower emissions. This approach helps BHP stand out amidst rivals. For example, BHP's 2023 Sustainability Report highlights these efforts.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements significantly shape competitive rivalry in mining. BHP Group faces pressure to adopt technologies like automation and AI to boost efficiency. This need stems from the industry's shift towards smarter operations. Staying ahead requires substantial investment in innovation.
- BHP's tech spending rose, with $1.5 billion allocated to digital transformation by 2024.
- Automation in mining can boost output by 15-20%, as seen in pilot projects.
- AI-driven predictive maintenance cuts downtime by up to 30%.
- Data analytics improve resource allocation, increasing productivity by 10%.
Global Presence
BHP's vast global footprint and robust supply chain are key competitive strengths. This allows BHP to tap into diverse markets and resources efficiently. Operating worldwide helps BHP spread its revenue sources and reduces risks tied to any single market. In 2023, BHP's revenue was $53.8 billion, demonstrating its global reach.
- Operations across continents.
- Diversified revenue streams.
- Access to resources.
- 2023 revenue: $53.8B.
Competitive rivalry in BHP Group is intense, involving key players like Rio Tinto and Vale. These firms compete on market share, requiring innovation and efficiency. BHP Group leverages its global presence and supply chain for competitive advantages. For example, its 2023 revenue was $53.8 billion.
| Metric | BHP Group | Industry Average |
|---|---|---|
| Market Share (2024) | Significant | Variable |
| Revenue (2023) | $53.8B | Dependent on company |
| Digital Transformation Spend (2024) | $1.5B | Dependent on company |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for BHP Group is limited, particularly for its core mineral commodities. Globally, the iron ore substitution rate is low, around 0.2%. In 2023, BHP produced 249 million tonnes of iron ore, highlighting its significant market position. Copper faces slightly more substitution potential, with alternatives representing roughly 3-5%.
The threat of substitutes for BHP Group's iron ore is currently low. The global substitution rate for iron ore is only about 0.2%, indicating minimal risk. Steel scrap is a growing substitute, with additions expected to reach about half of total demand by 2050. This is up from around one-third today.
Copper faces moderate substitution risks. Alternatives could claim 3-5% of the market share. Despite this, copper is vital for decarbonization, boosting demand. In 2024, copper prices fluctuated, reflecting supply and demand dynamics. Demand growth outstrips supply, signaling copper's enduring importance.
Technological Innovation
Technological innovation presents a significant threat to BHP Group through the emergence of substitutes. Advancements, like hydrogen-based steel production, challenge traditional metallurgical coal. This shift could reduce demand for BHP's products. The company must adapt to these changes.
- Hydrogen steel production is projected to grow, potentially impacting coal demand.
- BHP's 2024 financial reports will show how they are responding to these technological shifts.
- The adoption rate of new technologies will directly influence BHP's revenue streams.
- Investment in innovative solutions becomes crucial for long-term competitiveness.
Market Impact
The threat of substitutes significantly influences BHP's market position across different commodities. Iron ore, a core product, currently faces a low threat due to limited viable alternatives. Copper, however, encounters a moderate threat from substitutes like aluminum and plastics, which can replace copper in various applications. In 2024, the price of copper fluctuated significantly, reflecting market concerns about demand and substitution. Continuous monitoring of these trends is crucial.
- Iron ore's substitution risk is low due to its unique properties and cost-effectiveness.
- Copper faces moderate substitution risk from materials like aluminum in electrical wiring.
- Technological advancements can lead to the development of new substitute materials.
- Market analysis is vital to understand consumer preference shifts and potential substitutes.
BHP faces limited substitution threats, especially for iron ore. The iron ore substitution rate remains low, around 0.2%, due to a lack of readily available alternatives. However, copper sees moderate risks with substitutes claiming 3-5% of the market.
| Commodity | Substitution Rate | Substitute Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Iron Ore | 0.2% | Steel scrap |
| Copper | 3-5% | Aluminum, Plastics |
| Metallurgical Coal | Growing | Hydrogen steel |
Entrants Threaten
BHP Group faces a significant threat from new entrants due to the extremely high initial capital investment needed. For instance, BHP's mining operations require massive upfront investments. Greenfield projects alone can cost around $3.8 billion.
Furthermore, the average exploration and development expenses for a mining project vary from $500 million to $2.5 billion. These substantial financial barriers make it challenging for new companies to enter the market. As of 2024, this remains a considerable deterrent.
New entrants face regulatory hurdles, like complex frameworks and permits. Environmental compliance adds time and cost. For example, BHP Group's 2023 annual report highlights significant costs related to environmental compliance. These can be substantial, potentially delaying or deterring new market players.
The threat of new entrants to BHP is moderate, primarily due to significant barriers. Securing access to high-quality mineral deposits is difficult because existing players control many prime locations. BHP's 'Tier 1' asset strategy, which focuses on top-quartile deposits, provides a competitive edge. In 2024, BHP invested heavily in existing assets to maintain this advantage.
Economies of Scale
BHP benefits from substantial economies of scale, presenting a significant barrier to new entrants. This operational scale allows BHP to achieve lower per-unit costs compared to smaller mining operations. For example, in 2024, BHP's iron ore division reported a unit cost of $18.40 per wet metric tonne, underscoring its cost advantage. New companies struggle to match these figures due to their limited production volumes. This cost efficiency gives BHP a competitive edge in pricing and profitability.
- Lower production costs due to large-scale operations.
- Ability to negotiate better deals with suppliers.
- Efficient use of infrastructure and resources.
- Established brand recognition and market presence.
Market Knowledge
BHP Group faces a moderate threat from new entrants due to established market knowledge. Existing players like BHP have built strong relationships and possess extensive industry expertise, creating significant barriers.
BHP’s global presence and established supply chains give it a competitive edge in accessing essential resources and markets. New entrants would struggle to replicate this scale and reach.
The mining industry demands substantial capital investments and regulatory compliance, further hindering new competitors. These factors protect BHP's market position.
In 2024, BHP's market capitalization was around $150 billion, reflecting its strong position. New entrants would need considerable financial backing.
- Established market knowledge and relationships create barriers.
- BHP's global reach and supply chain are competitive advantages.
- High capital requirements and regulations limit entry.
- BHP's large market capitalization underscores its strength.
BHP faces moderate threats from new entrants. High capital costs, such as up to $3.8 billion for greenfield projects, and regulatory hurdles deter new players. Established scale, with iron ore unit costs at $18.40/wet metric tonne in 2024, provides a significant advantage. Market knowledge and global supply chains further protect BHP's position.
| Barrier | Impact | Example (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| High Capital Costs | Significant | Greenfield Project: ~$3.8B |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Moderate | Environmental Compliance Costs |
| Economies of Scale | Substantial | Iron Ore Unit Cost: $18.40/t |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our analysis uses BHP Group's annual reports, industry surveys, and market share data from research firms for a complete view.