Boeing Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Boeing Bundle
What is included in the product
Detailed analysis of each competitive force, supported by industry data and strategic commentary.
Customize pressure levels based on new data or evolving market trends.
Same Document Delivered
Boeing Porter's Five Forces Analysis
You're previewing the final version—precisely the same document that will be available to you instantly after buying. This Boeing Porter's Five Forces analysis examines industry rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, threat of substitutes, and threat of new entrants. The assessment provides a clear, concise evaluation of Boeing's competitive landscape. It includes detailed analysis and actionable insights. Upon purchase, you receive this comprehensive analysis ready for immediate use.
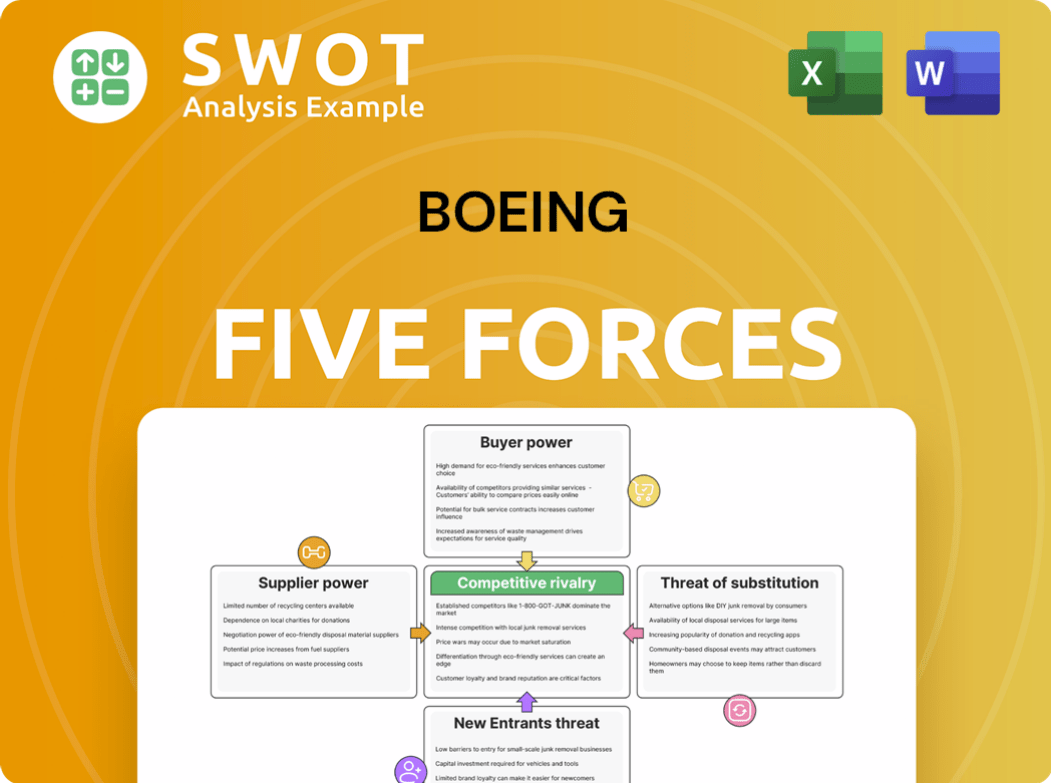
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
Boeing navigates a complex aviation market, facing powerful buyers like airlines and government entities. Supplier power, especially for raw materials and specialized components, poses challenges. The threat of new entrants is moderate, given high barriers to entry. Substitute products, such as alternative aircraft or travel methods, are a consideration. Competitive rivalry within the industry, particularly with Airbus, is intense.
Unlock key insights into Boeing’s industry forces—from buyer power to substitute threats—and use this knowledge to inform strategy or investment decisions.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Boeing depends on a global network of suppliers for aircraft parts. High concentration, especially for engines like CFM International and General Electric, boosts supplier power. These suppliers have unique tech and expertise, making quick switching difficult. For example, in 2024, engine costs represented a substantial portion of overall aircraft expenses, affecting Boeing's profitability.
Switching suppliers is difficult for Boeing, entailing re-certification, design shifts, and production delays. This dependency boosts suppliers' bargaining power. In 2024, Boeing's supply chain disruptions, particularly with Spirit AeroSystems, highlighted these vulnerabilities. The company has invested heavily in key supplier relationships, with over $20 billion in contracts in 2024, which, while stabilizing supply, further solidified supplier influence.
Suppliers with unique offerings, like advanced materials or software, hold significant bargaining power. These differentiated products are hard to replace, giving suppliers an advantage. Boeing depends on these specialized inputs, increasing the suppliers' ability to set prices. For example, Boeing's 2024 financial reports show significant costs related to specialized parts.
Threat of Forward Integration
The threat of forward integration by suppliers poses a challenge to Boeing, though it's less frequent due to the industry's complexity. Suppliers of crucial systems, like engine manufacturers, have the potential to become competitors. This potential forward integration allows suppliers to negotiate better terms with Boeing. For example, in 2024, engine suppliers like CFM International (a joint venture) and Pratt & Whitney held significant bargaining power.
- CFM International's LEAP engines powered a significant portion of Boeing's 737 MAX fleet in 2024.
- Pratt & Whitney's geared turbofan engines also competed for a share of the narrow-body market.
- The value of the global aircraft engine market was estimated to be over $60 billion in 2024.
Impact of Tariffs
Recent tariffs and trade disputes can significantly influence supplier power, particularly by increasing the cost of imported components and materials. Suppliers might transfer these added expenses to Boeing, potentially squeezing the company's profit margins. For instance, in 2024, tariffs on certain metals and electronics could have increased Boeing's production costs by up to 5%.
To counteract these effects, Boeing might need to diversify its supplier base, a strategy that can be both time-consuming and complicated. This diversification could involve establishing new partnerships or shifting production to regions with more favorable trade policies. Boeing's reliance on specific suppliers for critical parts makes them vulnerable to supply chain disruptions and cost increases.
- Impact of Tariffs: Increased costs for imported components.
- Supplier Behavior: Passing costs onto Boeing, reducing profitability.
- Mitigation Strategy: Diversifying supply chains to reduce tariff impact.
- Real-World Example: Potential 5% increase in production costs due to tariffs in 2024.
Boeing's suppliers, especially those with specialized tech or unique offerings, wield substantial bargaining power. High supplier concentration, such as with engine manufacturers, makes Boeing vulnerable to price increases and supply chain disruptions. In 2024, engine costs and specialized parts significantly affected Boeing’s profitability.
| Aspect | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Engine Costs | High impact on expenses | > $20B in contracts with key suppliers |
| Supply Chain | Disruptions & cost increases | 5% potential cost increase due to tariffs |
| Supplier Power | Influenced by tech & concentration | CFM & Pratt & Whitney had significant power |
Customers Bargaining Power
Boeing faces a concentrated customer base, mainly large airlines and governments. These customers buy aircraft in bulk, increasing their bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, Delta Air Lines ordered 200 Boeing 737 MAX aircraft. This allows them to negotiate prices and terms. Their large orders enable them to demand favorable deals and customized features.
Switching costs for airlines, though present, aren't overly restrictive. Training and maintenance adjustments are required, but airlines frequently swap between Boeing and Airbus. This flexibility allows airlines to negotiate favorable terms. In 2024, both Boeing and Airbus competed intensely for orders, highlighting customer leverage. For example, in Q3 2024, Airbus secured 1,060 gross orders, showcasing their competitive standing.
Customers, like airlines, have a strong alternative in Airbus. This competition gives them leverage. Airbus's presence enables customers to negotiate for better prices and terms. This choice significantly boosts customer bargaining power. In 2024, both Boeing and Airbus delivered hundreds of aircraft, showcasing the impact of their competition.
Price Sensitivity
Airlines, Boeing's primary customers, are notably price-sensitive due to aircraft's high cost. This sensitivity is heightened by the airline industry's volatile profitability. Customers meticulously assess total ownership costs, including fuel and maintenance, increasing their bargaining power. In 2024, global airline profits are projected to be $30.5 billion, underscoring the importance of cost control.
- Airlines focus on total cost of ownership.
- Profitability in the airline industry is highly variable.
- Fuel efficiency is a key factor in purchasing decisions.
- Maintenance costs significantly impact airline profitability.
Government Influence
Government customers, especially in defense, significantly influence Boeing. These customers, due to the scale and strategic importance of their contracts, can dictate design, technology, and pricing. Regulations and procurement processes strengthen their bargaining position. Boeing's dependence on these contracts means it must comply with government demands.
- In 2024, U.S. government contracts accounted for a significant portion of Boeing's revenue.
- Government influence extends to stringent safety and performance standards.
- Boeing must navigate complex regulatory frameworks for compliance.
- Changes in government spending directly impact Boeing's financials.
Boeing's customers, including airlines and governments, wield significant bargaining power. Large orders allow customers to negotiate prices and terms effectively. The presence of Airbus provides a strong alternative, enhancing customer leverage.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High bargaining power | Delta ordered 200 737 MAX |
| Switching Costs | Moderate, allowing negotiation | Airbus secured 1,060 orders in Q3 |
| Alternatives | Strong, with Airbus competition | Projected airline profits: $30.5B |
Rivalry Among Competitors
Boeing and Airbus dominate the commercial aircraft market, forming a duopoly. This structure fuels intense competition in pricing and product development. In 2024, Boeing delivered ~330 aircraft, facing pressure from Airbus's ~735 deliveries. The rivalry drives innovation, with both firms investing heavily in new technologies.
Boeing and Airbus compete by differentiating their aircraft. They offer varied features, performance, and tech to attract different buyers. This differentiation fuels rivalry, with each aiming for specific customer segments. In 2024, Boeing's 737 MAX and Airbus' A320neo series are key examples. Continuous upgrades and new models, like Boeing's 777X, intensify competition. For example, in Q4 2024, Airbus delivered 277 aircraft, while Boeing delivered 104.
The aerospace industry's growth rate significantly impacts competitive rivalry. High growth periods, like the post-pandemic recovery in 2021-2023, saw increased demand, potentially easing rivalry between Boeing and Airbus. In 2023, global air traffic rose, but production challenges slightly slowed growth. During downturns or slow growth, such as the early 2020s, competition intensifies, with both companies vying for fewer orders. In 2024, the industry's growth is projected to be moderate, increasing rivalry.
High Exit Barriers
High exit barriers intensify competitive rivalry within the aerospace industry. Boeing and Airbus face significant hurdles, including specialized manufacturing facilities and stringent regulatory compliance, making it costly to leave the market. These factors ensure sustained competition, even during economic downturns or financial hardships. For instance, Boeing's debt increased to $52.3 billion by late 2023, yet it remains committed.
- Specialized Assets: Boeing's factories require huge investment.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments with airlines lock in.
- Regulatory Requirements: FAA compliance is costly and complex.
- High Fixed Costs: Significant investments in R&D and infrastructure.
Global Competition
Boeing faces intense competition, not just from Airbus but also from defense and space giants like Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman. These companies aggressively pursue government contracts and market share across various sectors. The industry's global reach amplifies rivalry, as firms chase international prospects. For instance, in 2024, Boeing's defense revenue was approximately $25 billion, competing directly with these rivals for lucrative contracts.
- Lockheed Martin's 2024 revenue exceeded $65 billion, highlighting the competitive pressure.
- Northrop Grumman's 2024 revenue also posed a significant challenge.
- Boeing's global presence necessitates navigating diverse regulatory landscapes.
- International collaborations and partnerships are critical for survival.
Competitive rivalry in Boeing's market is fierce. Boeing and Airbus dominate, leading to intense price and product battles. Key factors include differentiation, growth rates, and exit barriers. This rivalry extends to defense and space, like Lockheed Martin.
| Rivalry Factor | Impact | Example (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Market Duopoly | Intense competition | Boeing ~330, Airbus ~735 deliveries |
| Differentiation | Product feature wars | 737 MAX vs. A320neo series |
| Industry Growth | Influences competition intensity | Moderate growth increases rivalry |
| Exit Barriers | Sustained competition | Boeing's $52.3B debt |
| Defense & Space Rivals | Expanded competition | Lockheed Martin's $65B+ revenue |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Direct substitutes for commercial air travel are few, particularly for long-distance flights. High-speed rail and sea travel are options for shorter routes, yet they don't match air travel's speed and convenience. This constrains the threat of substitutes in the main commercial aircraft sector. In 2024, air travel remained dominant, with rail and sea accounting for a small share of passenger miles. For example, in 2023, air travel handled about 4.5 billion passengers worldwide.
Video conferencing acts as a substitute for business travel. This is more relevant for short-haul flights. For Boeing, this impact is limited. The global video conferencing market was valued at $14.6 billion in 2023. It is projected to reach $25.7 billion by 2028.
High-speed rail presents a substitute threat, especially in regions with developed networks. In 2024, the global high-speed rail market was valued at approximately $270 billion, showing growth. Infrastructure costs and limited reach curb its widespread impact on air travel.
Personal Vehicles
Personal vehicles present a minimal threat to Boeing. They lack the speed and reach necessary for long-distance travel, which is the core of Boeing's market. Air travel remains the dominant choice for covering significant distances efficiently. The cost and time associated with personal vehicle travel make it less appealing. Therefore, personal vehicles are not a significant substitute for Boeing's services.
- 2024: Air travel passenger numbers are projected to increase.
- Personal vehicle travel is less efficient for long distances.
- Boeing's market share in air travel remains substantial.
- The infrastructure for air travel supports its dominance.
Telepresence Technologies
Emerging telepresence technologies, like virtual and augmented reality, offer substitutes for physical travel, but their impact on Boeing is limited. These technologies are still developing, with adoption rates lagging; for example, the global VR market was valued at $28.1 billion in 2023, a fraction of the travel industry. Barriers include cost, technical issues, and user acceptance, so their threat is currently low. Boeing's strong position in air travel insulates it in the short term.
- Global VR market was valued at $28.1 billion in 2023.
- Adoption barriers include cost, technical issues, and user acceptance.
- Telepresence technologies pose a limited threat to air travel in the near term.
The threat of substitutes for Boeing is moderate. Video conferencing and high-speed rail offer alternatives, but their impact is limited compared to air travel's speed and reach. Boeing's strong market position and the continued dominance of air travel in 2024 further reduce the risk from substitutes.
| Substitute | Market Size (2023) | Impact on Boeing |
|---|---|---|
| Video Conferencing | $14.6B | Limited, mainly short-haul |
| High-Speed Rail | $270B | Regional impact |
| Air Travel | $887B (Global, 2024 est.) | Dominant |
Entrants Threaten
The aerospace sector demands substantial capital for R&D, factories, and supply chains. High capital needs form a major entry barrier. New entrants face securing significant funding to challenge Boeing. In 2024, Boeing's R&D spending was over $3 billion, showcasing the financial hurdle. Newcomers must match this investment to compete.
Stringent regulatory requirements pose a significant threat to new entrants in the aerospace industry. Agencies like the FAA and EASA enforce rigorous safety standards. Compliance necessitates navigating a complex regulatory landscape and extensive certification. These processes are time-consuming and costly, acting as barriers. In 2024, Boeing faced increased scrutiny and compliance costs from regulators.
Designing and manufacturing advanced aircraft demands significant technological expertise. Boeing, with its decades of experience, holds a substantial advantage. New entrants face the challenge of acquiring or developing this expertise. Consider that in 2024, Boeing invested billions in R&D to maintain its technological edge, a barrier for newcomers.
Established Brand Reputation
Boeing benefits from a strong brand reputation, a legacy of trust and reliability in the aviation industry. New competitors struggle to match this established credibility, which is crucial for securing orders. Building a comparable reputation demands substantial investments in marketing and customer support. This advantage significantly raises the bar for potential entrants.
- Boeing's brand value in 2024 is estimated at $20 billion.
- New entrants typically require over $5 billion in initial marketing and brand-building investments.
- Customer trust is a critical factor, with 85% of airlines prioritizing safety and reliability.
- Boeing's historical delivery rate of aircraft is 400-500 per year.
Economies of Scale
Boeing's established presence allows it to leverage substantial economies of scale, particularly in aircraft manufacturing. These advantages translate into lower per-unit production costs compared to what new competitors can achieve. New entrants face significant challenges in replicating Boeing's cost efficiencies early on, putting them at a disadvantage. This cost disparity acts as a barrier to entry, making it difficult for new companies to compete effectively.
- Boeing's manufacturing efficiency lowers production costs.
- New entrants struggle with initial cost disadvantages.
- Economies of scale create a significant barrier.
- Established supply chains and distribution networks give Boeing an edge.
Threat of new entrants is moderate for Boeing. High capital requirements, including over $3B in 2024 R&D, and stringent regulations pose hurdles. Boeing's brand, with a $20B valuation in 2024, further deters competition, alongside its economies of scale.
| Barrier | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Needs | High | R&D Spending: $3B+ |
| Regulations | Significant | FAA/EASA Compliance |
| Brand Value | Strong | Boeing's Brand: $20B |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
This analysis utilizes financial statements, industry reports, and market share data, combined with government and trade publications for Boeing's competitive assessment.