CHS Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
CHS Bundle
What is included in the product
Analyzes CHS's competitive position, evaluating forces like suppliers, buyers, and new entrants.
Visualize competitive forces and find vulnerabilities within the CHS market—quickly assess risks.
Preview the Actual Deliverable
CHS Porter's Five Forces Analysis
You're previewing the final version—the exact same document that analyzes CHS using Porter's Five Forces.
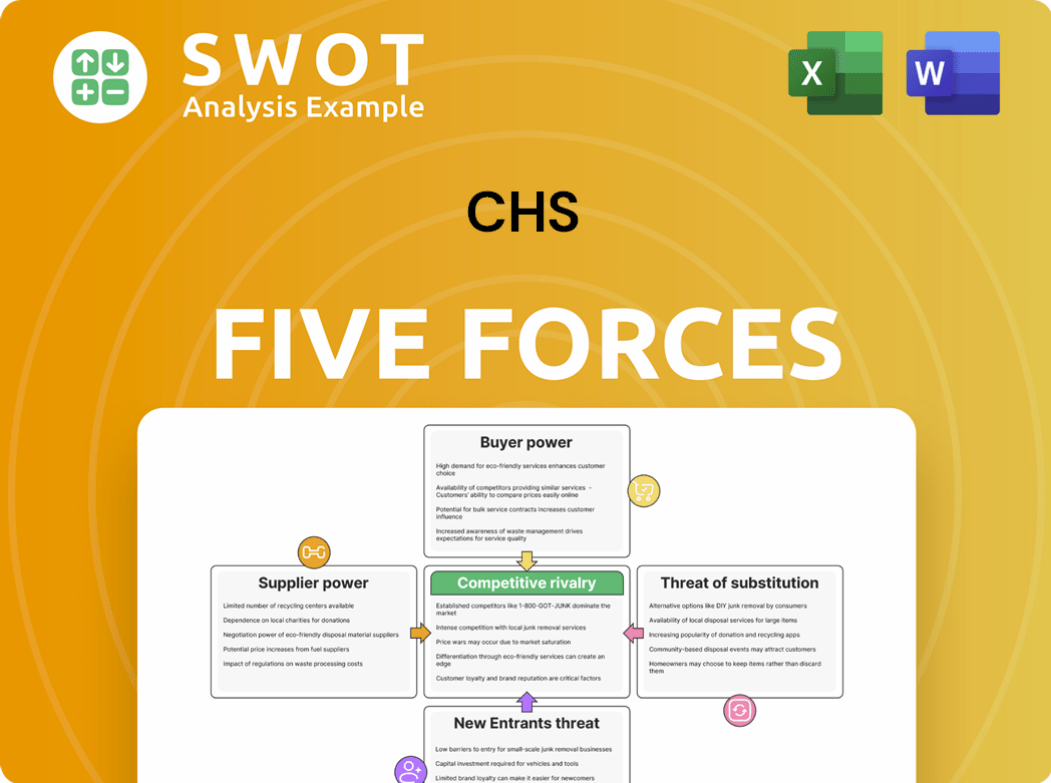
This analysis covers competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, threat of substitutes, and threat of new entrants.
The format is professional, offering a complete assessment ready for your immediate use.
Upon purchase, you will receive this same, fully realized, ready-to-use analysis.
No adjustments or extra steps are needed; it's ready to download and implement.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
Analyzing CHS through Porter's Five Forces reveals intense competition in the agricultural sector. Bargaining power of suppliers and buyers significantly impacts profitability. The threat of new entrants, while moderate, still poses a challenge. Substitute products offer some pressure, requiring CHS to innovate. Competitive rivalry within the industry remains a key driver.
Our full Porter's Five Forces report goes deeper—offering a data-driven framework to understand CHS's real business risks and market opportunities.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Healthcare providers, such as Community Health Systems (CHS), are significantly affected by specialized equipment suppliers. These suppliers, often holding patents or unique technology, wield considerable power. CHS's dependence on specific, high-tech medical equipment boosts supplier bargaining power. For example, the global medical equipment market was valued at $499.8 billion in 2023.
Pharmaceutical companies, particularly those with patented drugs, wield considerable bargaining power. Hospitals like CHS rely heavily on these medications, creating a dependency that favors drug companies in negotiations. In 2024, the pharmaceutical industry's net profit margin was approximately 15%, showcasing their financial strength. CHS's profitability is directly influenced by the pricing strategies of these suppliers, impacting its bottom line. For instance, a 10% increase in drug costs can significantly reduce CHS's profit margins.
Medical supply distributors hold considerable bargaining power over CHS. Their efficiency and reliability are critical for CHS's operations. Supply chain disruptions or price hikes from distributors directly affect CHS's care delivery and cost management. In 2024, the medical supplies market was valued at approximately $160 billion, highlighting the distributors' significant influence.
Healthcare IT Vendors
Healthcare IT vendors wield considerable power because their systems are vital for patient data management, billing, and compliance. The market is concentrated, with a few major vendors controlling a significant share. This concentration allows these vendors to influence pricing and dictate terms, impacting CHS's administrative efficiency. In 2024, the healthcare IT market was valued at over $100 billion, with top vendors like Epic and Cerner holding a large market share.
- Market dominance by a few key players.
- Critical role in data management and compliance.
- Impact on administrative costs and efficiency.
- High switching costs for healthcare providers.
Contract Labor and Staffing Agencies
Contract labor and staffing agencies wield significant bargaining power due to the persistent shortages of nurses and healthcare professionals. These agencies, capitalizing on high demand, can command elevated rates, directly affecting CHS's labor expenses. Managing these costs is critical for CHS's profitability, especially in areas with substantial healthcare staffing needs. This dynamic necessitates careful cost management strategies.
- In 2024, the healthcare staffing market is projected to reach $40.6 billion.
- Travel nurse rates have increased by approximately 15% in the past year.
- CHS's labor costs account for about 55% of its total operating expenses.
- Regions with high demand, such as California and Texas, see the most significant rate hikes.
Suppliers hold considerable sway over Community Health Systems (CHS). Specialized equipment makers, pharmaceutical companies, and medical supply distributors impact CHS's costs and operations. Strong bargaining power stems from market concentration and essential product offerings. This influences CHS's profitability and efficiency.
| Supplier Type | Impact on CHS | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Medical Equipment | High dependency; Cost increases | Global market: $525B |
| Pharmaceuticals | Pricing dictates profitability | Net profit margin: ~15% |
| Medical Supplies | Supply chain; Cost management | Market size: ~$170B |
Customers Bargaining Power
Patients, particularly those with high-deductible plans or without insurance, are becoming more price-conscious. This can lead them to seek cheaper healthcare alternatives, influencing CHS's patient numbers. For instance, in 2024, the average healthcare deductible hit $1,669. Addressing patient price concerns is therefore vital for CHS to retain its market share.
Large employers, wielding considerable purchasing power, regularly negotiate favorable healthcare rates. This directly impacts CHS's revenue, potentially lowering prices. For example, in 2024, major insurance companies and large corporations drove significant price reductions. CHS must cultivate strong employer relationships and offer competitive pricing to mitigate this.
Government payers, like Medicare and Medicaid, hold significant bargaining power over CHS. In 2024, these programs accounted for a substantial portion of CHS's patient volume. Medicare and Medicaid reimbursement rates, often below private insurance rates, directly impact CHS's revenue and profitability. CHS needs to manage costs effectively to maintain financial health under these government payment structures.
Influence of Insurance Companies
Insurance companies wield substantial bargaining power, steering patients toward specific healthcare providers via their network designs. This influence directly impacts Community Health Systems (CHS). Maintaining positive relationships with major insurers is crucial for CHS to secure a consistent patient flow. These relationships influence the rates CHS can negotiate and the patient volume it receives.
- In 2024, UnitedHealth Group, a major insurer, reported revenues of over $370 billion.
- CHS relies heavily on these contracts, with a significant portion of its revenue tied to reimbursements from insurance providers.
- Negotiated rates with insurers directly affect CHS's profitability and financial performance.
Patient Choice and Preferences
Patients today have more control over their healthcare decisions, choosing providers based on factors like convenience, reputation, and service quality. This shift demands that CHS prioritizes high-quality care and a positive patient experience to stay competitive. Patient satisfaction and positive outcomes are crucial in attracting and keeping patients in this environment. In 2024, patient satisfaction scores directly impacted hospital reimbursement rates, highlighting the importance of patient-centric care.
- Increased competition from outpatient facilities and specialized clinics.
- Emphasis on patient reviews and online reputation.
- Impact of value-based care models on patient choices.
- The rise of telehealth options and their influence.
The bargaining power of customers significantly affects Community Health Systems (CHS). Patients, especially with high deductibles, seek affordable options. Large employers and insurance companies negotiate favorable rates, impacting CHS's revenue. Government payers also influence pricing and profitability.
| Customer Type | Bargaining Power Level | Impact on CHS |
|---|---|---|
| Patients | Medium to High | Price sensitivity, choice of alternatives |
| Employers | High | Negotiated rates, price reductions |
| Government Payers (Medicare/Medicaid) | High | Reimbursement rates, financial health |
Rivalry Among Competitors
The concentration of competitors significantly impacts competitive intensity in the hospital market. CHS faces higher rivalry in markets with numerous hospitals. For example, in 2024, markets with low hospital concentration saw less price competition compared to highly concentrated ones. This increased competition can lead to price wars. Increased marketing expenses and margin pressures are inevitable.
Service differentiation significantly shapes CHS's competitive stance. Providing specialized services or exceptional patient experiences allows CHS to attract and retain patients effectively. Investments in advanced technology and skilled personnel can establish a notable competitive advantage. In 2024, CHS's focus on specialized care, like its heart and vascular programs, shows this strategy in action. This approach helps CHS stand out in a crowded market.
The healthcare market's growth rate in CHS's areas influences competition. If growth slows, hospitals fight harder for patients. CHS needs to innovate to stay competitive. In 2024, the U.S. healthcare spending is projected to reach $4.8 trillion, growing slower than in previous years, intensifying rivalry.
Strategic Consolidation
Strategic consolidation is significantly changing healthcare competition. Bigger health systems gain economies of scale, improving their negotiating power with insurers. CHS must adapt, possibly through acquisitions or partnerships to remain competitive. The healthcare M&A market saw over 1,300 deals in 2023. This trend indicates a need for strategic adjustments.
- Healthcare M&A activity remains high, with over 1,300 deals in 2023.
- Larger systems often secure better payment rates.
- CHS may pursue acquisitions or partnerships.
- Consolidation impacts market share and pricing.
Impact of For-Profit vs. Non-Profit
The healthcare market features a mix of for-profit and non-profit hospitals, creating a complex competitive landscape. Non-profit hospitals, driven by community benefit rather than pure profit, may offer services or pricing structures that differ from Community Health Systems (CHS). CHS must analyze these distinctions to effectively compete, understanding the motivations and strategies of both types of organizations. The competition in the hospital market is very high, as shown by the fact that the number of U.S. hospitals decreased from 6,090 in 2010 to 6,093 in 2022.
- U.S. hospital revenue in 2023 was about $1.6 trillion.
- Non-profit hospitals often reinvest profits in community services.
- For-profit hospitals focus on shareholder value and profitability.
- CHS needs to assess how non-profits impact market share.
Competition among hospitals, like CHS, is fierce, significantly influenced by market concentration and service differentiation. The healthcare market's growth rate and strategic consolidation also shape rivalry. CHS competes with both for-profit and non-profit hospitals.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Market Concentration | High rivalry | Markets with few hospitals see less price wars |
| Service Differentiation | Competitive advantage | CHS's heart programs are key. |
| Market Growth | Intensifies competition | U.S. healthcare spending: $4.8T |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Urgent care centers pose a significant threat as substitutes, providing an accessible and affordable option for non-critical medical needs. These centers can divert patients from hospital emergency departments, potentially impacting CHS's revenue streams. In 2024, the urgent care market is projected to reach $41.9 billion, indicating its growing influence. CHS could integrate urgent care services to compete effectively and retain market share.
Telehealth services pose a threat by offering virtual consultations and monitoring, reducing the need for in-person hospital visits. This shift can impact traditional hospital service demand. In 2024, telehealth utilization increased, with approximately 30% of all medical consultations occurring virtually. CHS can counter this by investing in telehealth. This strategy allows for more convenient and accessible care options for patients.
Retail clinics, situated in pharmacies and stores, provide convenient basic healthcare. They focus on routine needs, potentially drawing patients away from hospitals and physician offices. In 2024, the retail clinic market saw significant growth, with CVS Health and Walgreens expanding their clinic footprints, capturing more market share. CHS might explore partnerships or integrated models to compete effectively. This strategic move could help retain patients and enhance service delivery.
Home Healthcare
Home healthcare services are a significant substitute for hospital stays, offering care in patients' homes. This option is attractive, especially for the elderly and those with chronic conditions. CHS could expand home healthcare to compete effectively. The home healthcare market was valued at $349.8 billion in 2023.
- Market growth is projected to reach $667.6 billion by 2030.
- The aging population is a primary driver of this expansion.
- Home healthcare reduces costs and improves patient satisfaction.
- CHS can leverage this trend to diversify its services.
Alternative Medicine
The rise of alternative medicine, including acupuncture and chiropractic care, poses a threat to traditional healthcare providers like CHS. Patients might opt for these alternatives for certain treatments, impacting CHS's market share. In 2024, the global alternative medicine market was valued at approximately $100 billion, showing its growing influence. CHS could mitigate this threat by incorporating complementary medicine options.
- Market size: The global alternative medicine market reached $100 billion in 2024.
- Patient choice: Alternative medicine influences healthcare decisions.
- Strategic response: CHS can offer complementary medicine services.
- Impact: Reduced demand for traditional treatments.
Substitute threats, like urgent care and telehealth, challenge CHS by offering accessible and cost-effective healthcare alternatives. These options can divert patients, potentially impacting CHS's revenue and market share. The home healthcare market, valued at $349.8 billion in 2023, also poses a significant alternative. By 2030, this market is projected to hit $667.6 billion.
| Substitute | Description | 2024 Market Size |
|---|---|---|
| Urgent Care | Walk-in clinics for immediate needs | $41.9 billion |
| Telehealth | Virtual consultations and monitoring | 30% of consultations |
| Home Healthcare | In-home medical services | $349.8 billion (2023) |
Entrants Threaten
The hospital industry, including CHS, faces a threat from new entrants, but high capital requirements act as a significant barrier. Building hospitals demands substantial investments in facilities, advanced medical equipment, and cutting-edge technology. These considerable upfront costs make it challenging for new players to enter the market. For instance, in 2024, constructing a new hospital wing can cost upwards of $100 million. CHS leverages its existing infrastructure and scale to maintain a competitive edge.
The healthcare sector faces stringent regulatory oversight, including licensing and accreditation. New entrants must navigate complex and costly regulations, creating a barrier. CHS benefits from its established compliance infrastructure, giving it an edge. In 2024, healthcare regulatory compliance costs increased by an average of 7% for new facilities. This advantage helps protect CHS from potential competitors.
Established hospitals like CHS benefit from strong brand recognition, fostering patient trust. New entrants face the challenge of building brand awareness. CHS uses its reputation to attract and keep patients. Gaining patient trust demands time and resources; a 2024 survey shows patient loyalty is key. CHS's market cap in 2024 was about $1.8 billion.
Economies of Scale
Large hospital systems such as CHS leverage economies of scale, especially in purchasing, administration, and daily operations. New entrants often find it challenging to match these cost efficiencies. CHS can utilize its scale to provide competitive pricing and a wide array of services. In 2024, CHS reported revenues of approximately $19.6 billion, highlighting its significant operational scale.
- CHS has a large geographic presence, which supports economies of scale.
- New entrants face high capital costs to match CHS's infrastructure.
- CHS can negotiate better prices with suppliers due to its size.
Access to Physician Networks
Access to established physician networks is a significant barrier for new entrants in the hospital industry. New hospitals face the time-consuming task of building relationships with physicians to attract patients. CHS benefits from its existing, well-established connections with physicians, giving it a competitive edge. This advantage is critical in a market where physician referrals are key to patient volume and revenue.
- Physician referrals significantly influence patient choice.
- Building relationships with physicians takes time and resources.
- CHS's network provides a strong competitive advantage.
- Recruitment efforts are crucial for maintaining these relationships.
New entrants face challenges in the hospital industry, including high capital costs and regulatory hurdles. CHS benefits from its existing infrastructure, brand recognition, and economies of scale. Established physician networks give CHS a competitive edge.
| Barrier | Impact on CHS | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| High Capital Costs | Competitive Advantage | New hospital wing costs $100M+ |
| Regulatory Compliance | Established Infrastructure | Compliance costs up 7% for new facilities |
| Brand Recognition | Patient Trust | CHS market cap ~$1.8B |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
This Porter's Five Forces analysis utilizes SEC filings, financial news, industry reports, and market analysis for comprehensive insights.