Coca-Cola Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Coca-Cola Bundle
What is included in the product
Analyzes Coca-Cola's position, exploring competitive forces like rivalry, substitutes, and buyer power.
Quickly identify competitive threats with a dynamic force-rating system.
Same Document Delivered
Coca-Cola Porter's Five Forces Analysis
You're previewing the complete Coca-Cola Porter's Five Forces analysis. This document examines industry rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitutes within Coca-Cola's market. The insights provided are comprehensive and thoroughly researched. This is the final deliverable: the same professionally crafted file you'll receive immediately after purchase.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
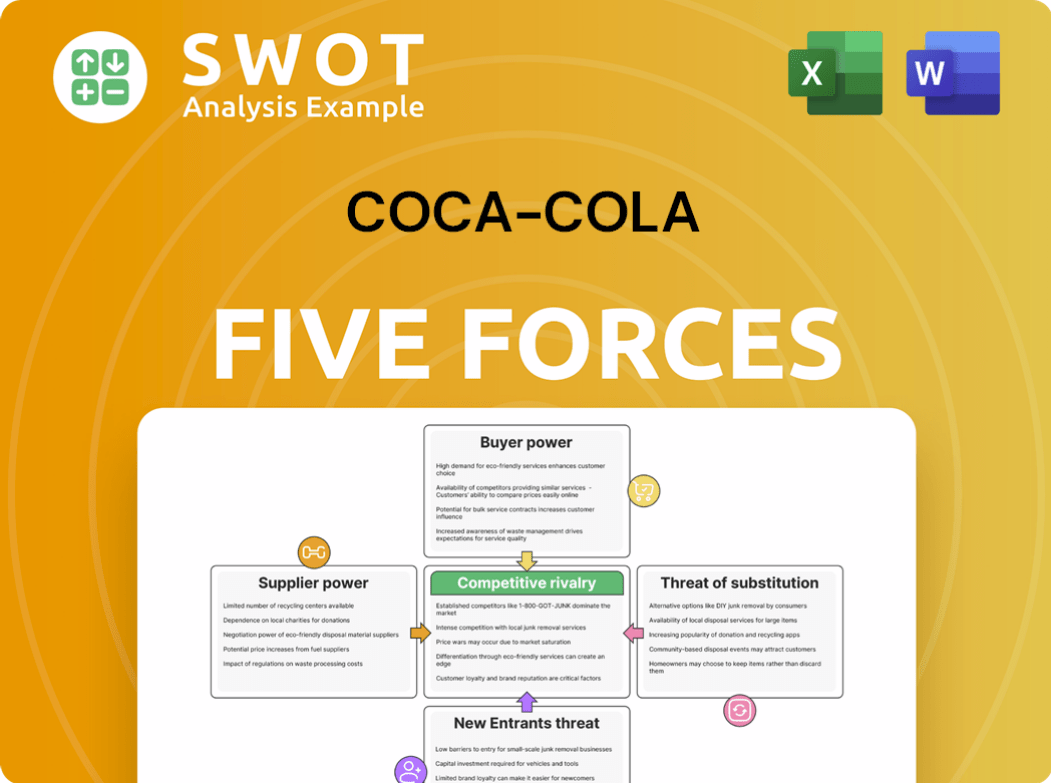
Coca-Cola faces intense competition due to the high rivalry within the beverage industry, particularly from PepsiCo. Buyer power is moderate, influenced by consumer choice and retailer influence. Suppliers have limited power given the availability of ingredients. The threat of new entrants is moderate due to brand strength and distribution networks. Substitute products, such as water and juices, pose a considerable threat.
Unlock key insights into Coca-Cola’s industry forces—from buyer power to substitute threats—and use this knowledge to inform strategy or investment decisions.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Coca-Cola relies on about 150 global suppliers, spending roughly $22.4 billion yearly. The market is concentrated for key inputs like corn syrup and packaging. This gives suppliers significant bargaining power. Concentrated supply can lead to higher costs for Coca-Cola.
Switching suppliers can be costly for Coca-Cola due to specific ingredient needs. Estimated switching costs average $3.5 million to $8.2 million per transition. These costs hinder Coca-Cola's ability to switch easily. This strengthens the suppliers' bargaining power, as per 2024 data.
Coca-Cola's production is significantly dependent on raw materials like sugar, aluminum, and plastic, making it susceptible to supplier influence. Suppliers, therefore, have considerable power over pricing and supply conditions. In 2024, sugar prices saw fluctuations due to global supply issues. The company's reliance on these commodities exposes it to price swings and potential supply chain disruptions. For example, the cost of aluminum increased by 10% in the first half of 2024.
Contract Dynamics
Coca-Cola's supplier relationships are shaped by long-term contracts, typically spanning 5-7 years. These contracts often include price adjustment clauses, such as those linked to the Consumer Price Index (CPI), especially for key ingredients like sugar. While these agreements offer stability, they can also limit Coca-Cola's flexibility if market prices shift unfavorably, potentially increasing supplier power. For example, in 2024, sugar prices saw fluctuations, impacting contract terms.
- Long-term contracts stabilize supply chains.
- Price adjustments, like CPI, are common.
- Market changes can shift bargaining power.
- Sugar price fluctuations are a key factor.
Supplier Assessment Programs
Coca-Cola's supplier assessment programs are key in managing supplier power. These programs evaluate suppliers' alignment with sustainability objectives, impacting a large portion of its procurement budget. By fostering collaboration and transparency, Coca-Cola aims to reduce supplier influence. These programs promote shared accountability and strategic engagement with suppliers.
- Coca-Cola assessed 80% of its key suppliers in 2024 for sustainability.
- These assessments covered areas like water usage, waste management, and human rights.
- The company's goal is to have 100% of key suppliers assessed by 2026.
- In 2024, Coca-Cola spent approximately $55 billion on procurement.
Coca-Cola faces supplier power due to concentrated markets and switching costs. Significant raw material dependencies, like sugar and aluminum, amplify supplier influence on pricing. Long-term contracts with price adjustments try to balance stability and flexibility, but market shifts can alter the bargaining dynamic.
Coca-Cola actively manages supplier relationships through assessments, focusing on sustainability and collaboration. By 2024, 80% of key suppliers were assessed, aiming for 100% by 2026.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Supplier Base | Approx. 150 global suppliers; $22.4B spent annually (2024) |
| Switching Costs | $3.5M - $8.2M per supplier transition (average) |
| Raw Material Impact | Sugar price fluctuations, aluminum cost increased by 10% (H1 2024) |
| Contract Terms | 5-7 year contracts with CPI-linked price adjustments |
| Assessment Program | 80% key suppliers assessed in 2024 for sustainability, $55B procurement (2024) |
Customers Bargaining Power
Retail chains like Walmart wield substantial influence, exemplified by their $9.5 billion purchases from Coca-Cola in 2022. This significant buying power allows them to negotiate advantageous terms. These favorable deals directly affect Coca-Cola's profitability. The concentration of sales to large retailers amplifies their bargaining strength.
Consumers' price sensitivity significantly influences Coca-Cola. With many beverage options, customers can easily switch brands if prices rise. For instance, in 2024, Coca-Cola's average price per unit might be around $0.75, but a sudden increase could push consumers to cheaper alternatives. This sensitivity gives consumers considerable bargaining power, impacting pricing strategies.
Consumers' rising health consciousness significantly influences beverage choices, with a shift away from sugary drinks. This trend gives customers more power. For instance, in 2024, the demand for low-sugar alternatives grew by 15%. Coca-Cola must innovate to offer healthier options. This includes diversifying its product range, as seen with its investments in sparkling water brands.
Diverse Customer Base
Coca-Cola benefits from a broad customer base across 200 countries, including retailers, restaurants, and vending machines. This diversity helps to counter the bargaining power of any single customer. However, large retail chains still have significant influence. In 2024, Coca-Cola's revenue was approximately $46 billion, showcasing their extensive market reach.
- Global presence in over 200 countries.
- Revenue of about $46 billion in 2024.
- Customer base includes retail and food services.
- Retail chains have notable buyer power.
E-commerce Growth
The surge in e-commerce significantly boosts customer bargaining power. Consumers can effortlessly compare prices and switch between brands online. Coca-Cola faces increased pressure to offer competitive pricing and value. Brands must prioritize a strong online presence and excellent e-commerce experiences.
- E-commerce sales in the U.S. reached over $1.1 trillion in 2023, emphasizing online retail's dominance.
- Coca-Cola's online sales continue to grow, reflecting the need to adapt to digital consumer behavior.
- Customer reviews and social media influence impact brand perception and purchase decisions.
- Loyalty programs and personalized offers are crucial for retaining customers in the digital age.
Customer bargaining power significantly shapes Coca-Cola's strategies. Large retailers, like Walmart, leverage their buying volume for favorable terms. Consumers' price sensitivity, fueled by diverse beverage options, enhances their influence. Digital platforms amplify this power, impacting pricing and brand loyalty.
| Factor | Impact | Example (2024 Data) |
|---|---|---|
| Retailer Power | High | Walmart's $9.5B purchases |
| Price Sensitivity | High | Price point: $0.75/unit |
| E-commerce | Increased | U.S. e-commerce: $1.1T+ |
Rivalry Among Competitors
Coca-Cola faces fierce competition in the global beverage market. PepsiCo and Nestlé are key rivals, impacting market share. In 2024, Coca-Cola's revenue was approximately $46 billion, highlighting the competitive landscape. This intense rivalry pressures pricing and innovation.
Coca-Cola faces intense rivalry, particularly in marketing and innovation. Competitors launch aggressive campaigns and new products to attract consumers. Coca-Cola's response includes significant investments; in 2023, it allocated $4.1 billion, or 9.5% of revenue, to marketing and innovation to stay competitive.
Coca-Cola benefits from strong brand loyalty, which helps secure its market share. Loyal customers are less inclined to switch to rival brands. Competitors like Pepsi also invest heavily in brand loyalty. In 2024, Coca-Cola's brand value reached approximately $106 billion, demonstrating its powerful market position. This ongoing battle for consumer preference fuels constant competitive pressure.
Regional Competitors
Regional competitors, such as Refresco and National Beverage Corp., significantly impact local markets, posing a challenge to Coca-Cola's widespread dominance. Craft beverage brands are also intensifying the competitive landscape, with smaller players gaining traction. To maintain its position, Coca-Cola must tailor its strategies to meet local tastes and adapt to varying market dynamics. This includes offering diverse product lines and focusing on regional marketing efforts to stay competitive.
- Refresco's revenue in 2024 was approximately $12 billion.
- National Beverage Corp. reported net sales of $1.3 billion in fiscal year 2024.
- Coca-Cola's global volume grew by 2% in 2024.
Price and Volume Balance
Coca-Cola's competitive landscape involves a delicate balance of price and volume. The company's pricing power is evident, but sustainable growth demands more than just price hikes. Coca-Cola must prioritize volume growth through innovation, and effective marketing strategies. This dual approach ensures long-term market share and profitability.
- Coca-Cola's organic revenue growth in 2023 was 12%, driven by pricing and volume.
- In Q4 2023, concentrate sales volume grew 2%, with price/mix contributing 9%.
- The company's focus includes expanding its product portfolio and enhancing marketing efforts.
- Coca-Cola's strategy aims for a balance of price increases and volume gains.
Coca-Cola's competitive rivalry is marked by intense battles for market share, with competitors like PepsiCo and Nestlé investing heavily. The company's brand value, reaching approximately $106 billion in 2024, is a key advantage. Regional and craft beverage brands also add to the pressure, requiring Coca-Cola to adapt.
| Metric | Value (2024) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Coca-Cola Revenue | $46 Billion | Reflects competitive pressure. |
| Coca-Cola Brand Value | $106 Billion | Indicates strong market position. |
| Marketing & Innovation Spend (2023) | $4.1 Billion | Represents 9.5% of revenue. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Coca-Cola faces substantial competition from various substitutes. Consumers can readily opt for water, tea, coffee, juices, or energy drinks. This poses a considerable threat, as preferences and health trends shift. In 2024, the global non-alcoholic beverage market was valued at approximately $1.2 trillion. Switching costs are low, intensifying the threat.
The rising focus on health and wellness significantly boosts the appeal of healthier drinks. Bottled water, unsweetened teas, and natural juices are becoming more popular. This shift impacts Coca-Cola's market share. In 2024, the global bottled water market reached $300 billion. Coca-Cola responds with low-sugar and sugar-free options.
The plant-based beverage market, a key substitute, is forecasted to hit $123.5 billion by 2027, posing a significant threat to Coca-Cola. Functional beverages and prebiotic sodas also offer alternatives. These options draw in health-focused consumers, impacting traditional soda sales. Coca-Cola must innovate to stay competitive in this evolving landscape.
Substitution Risks
The threat of substitutes significantly impacts Coca-Cola's market position. Consumers can easily switch to alternatives like water, energy drinks, and tea. These beverages compete directly with soft drinks for consumer dollars. In 2023, the water market alone was valued at $218.3 billion.
- Water market: $218.3 billion in 2023.
- Energy drinks market: $86.5 billion in 2023.
- Tea market: $55.3 billion in 2023.
- These markets offer alternative choices.
Product Diversification
Coca-Cola actively addresses the threat of substitutes through product diversification. This strategy involves offering a broad spectrum of beverages beyond its core sodas. By including options like water, teas, and low-sugar alternatives, Coca-Cola aims to satisfy varied consumer demands. This approach is crucial for maintaining its market position in a competitive landscape.
- Coca-Cola's product portfolio includes over 500 brands globally.
- In 2024, the company's water, sports drinks, and tea categories saw growth.
- Low/no-sugar beverages account for a significant portion of its sales.
- Coca-Cola invests heavily in innovation to create new products.
Coca-Cola faces strong competition from substitute drinks. Consumers can easily switch to water, tea, or energy drinks. This variety limits Coca-Cola's pricing power. The global energy drinks market was $86.5B in 2023.
| Market | 2023 Value |
|---|---|
| Bottled Water | $218.3B |
| Energy Drinks | $86.5B |
| Tea | $55.3B |
Entrants Threaten
The beverage industry faces low entry barriers, making it easy for new brands to emerge. Consumer switching costs are minimal, and capital needs are relatively low. This ease of entry intensifies competition, posing a threat to Coca-Cola. In 2024, the market saw numerous new brands, some priced similarly to Coke, increasing the pressure.
Coca-Cola's brand recognition is a major hurdle for new beverage companies. The company's strong brand and customer loyalty create a significant barrier. Coca-Cola's brand value was estimated at $106 billion in 2024. This gives it a competitive edge, making it hard for new brands to attract customers. Maintaining this requires consistent marketing.
Coca-Cola's vast distribution network poses a significant barrier to new entrants. The company’s global presence and well-established relationships with bottlers and distributors ensure products reach consumers worldwide. Coca-Cola spends billions annually on its distribution infrastructure. New beverage companies struggle to match this scale and efficiency.
Economies of Scale
Coca-Cola's extensive economies of scale present a significant barrier to new entrants. The company's massive production volumes and established distribution networks drive down per-unit costs, making it difficult for smaller competitors to match pricing. New beverage companies face challenges in achieving similar cost efficiencies, hindering their ability to compete effectively. Coca-Cola's global presence and efficient supply chain provide a substantial advantage.
- Coca-Cola's operating margin was approximately 29.8% in 2024, reflecting its cost efficiency.
- New entrants typically struggle with higher production and distribution costs.
- Established brands often have stronger negotiating power with suppliers.
Emerging Market Opportunities
Emerging markets offer growth opportunities for Coca-Cola, but they also attract new competitors. The high Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) for carbonated soft drinks in Africa makes it a particularly attractive market. New entrants can capitalize on changing consumer preferences and less established brand loyalties. Coca-Cola's existing presence and ability to adapt to local tastes are crucial for maintaining its competitive advantage.
- Africa's carbonated soft drink market is projected to grow significantly, attracting new entrants.
- Coca-Cola must leverage its established presence and adapt to local preferences to stay competitive.
- New competitors can exploit shifts in consumer tastes in emerging markets.
- Adapting to local tastes is a key strategy for Coca-Cola.
The beverage industry’s low entry barriers make it easy for new competitors to emerge, increasing competition for Coca-Cola. Strong brand recognition and vast distribution networks offer Coca-Cola a significant advantage. Coca-Cola's brand value in 2024 was approximately $106 billion, posing a hurdle for new brands. Emerging markets attract new entrants; for instance, Africa's carbonated soft drink market is projected to grow significantly, attracting new competitors.
| Barrier | Impact on Coca-Cola | 2024 Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Low Entry Barriers | Increased competition | Numerous new brands in the market |
| Brand Recognition | Competitive Advantage | Brand value ~$106B |
| Distribution Network | Competitive Advantage | Global presence |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
We gather insights from Coca-Cola's annual reports, market research, and industry publications for supplier power and competitive intensity. Competitive forces are examined using data from financial statements and competitor analyses.