CoreCivic Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
CoreCivic Bundle
What is included in the product
Analyzes the competitive forces shaping CoreCivic, including suppliers, buyers, and market entrants.
Customize pressure levels based on new data or evolving market trends.
What You See Is What You Get
CoreCivic Porter's Five Forces Analysis
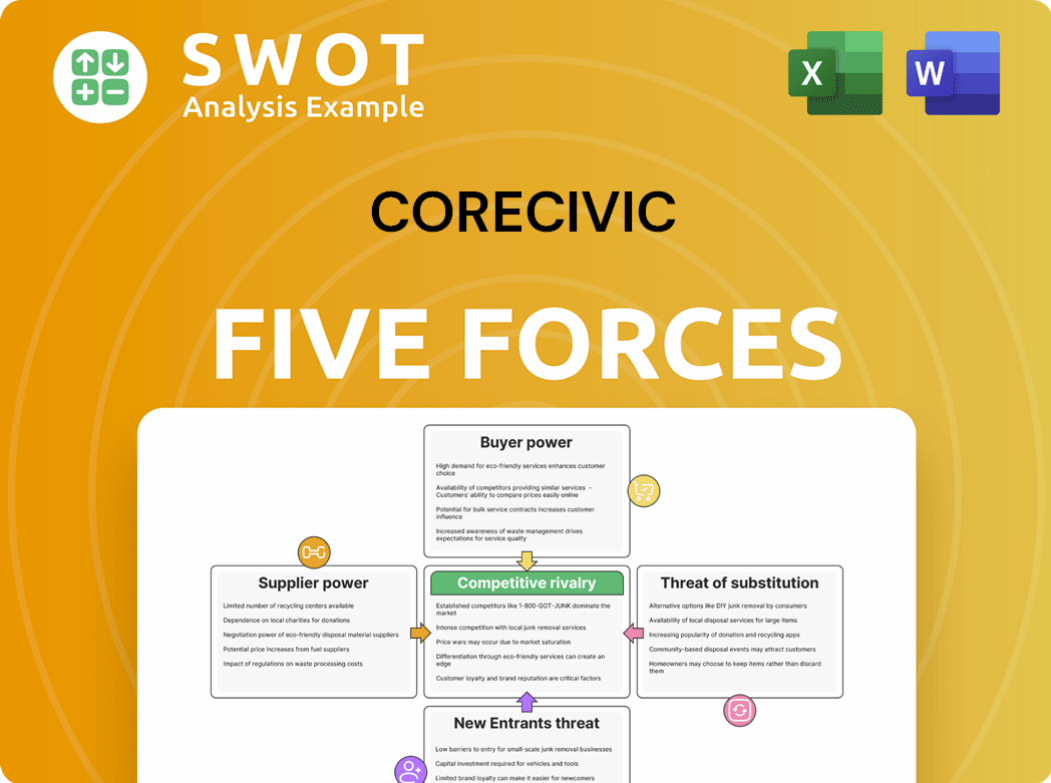
This preview showcases the complete CoreCivic Porter's Five Forces analysis you'll receive. It includes in-depth analysis of competitive rivalry, supplier power, and other forces.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
CoreCivic faces moderate rivalry, influenced by limited competitors in private prison services. Bargaining power of buyers (government entities) is substantial, impacting contract terms. Suppliers have some leverage due to specialized services. The threat of new entrants is low, due to high barriers. Substitute threats, mainly from criminal justice reform, pose a growing challenge.
This preview is just the starting point. Dive into a complete, consultant-grade breakdown of CoreCivic’s industry competitiveness—ready for immediate use.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
CoreCivic faces supplier power issues due to dependence on a few key providers for essential services. This concentration, including food, medical, and tech suppliers, empowers them to influence prices. CoreCivic's costs could increase if suppliers raise prices. In 2024, supplier costs were a significant factor in their financial performance.
CoreCivic faces strong supplier bargaining power due to the specialized needs of correctional facilities. Suppliers must meet unique demands, limiting the available options. For instance, in 2024, the company spent $600 million on goods and services, many requiring specific certifications. Switching suppliers is costly, as vetting and compliance checks can take months. This dependence gives suppliers leverage in pricing and contract terms.
Suppliers face strict regulatory compliance, reducing the supplier pool for CoreCivic. This concentration enhances supplier power. CoreCivic, managing over 70 facilities, must ensure supplier compliance to mitigate legal and operational risks. In 2024, the private prison industry's regulatory scrutiny intensified, increasing compliance costs for suppliers. This has further consolidated the supplier landscape.
Potential for supplier consolidation
The correctional services market may experience supplier consolidation, boosting their bargaining power. Mergers and acquisitions could diminish competition, giving remaining suppliers more pricing control. This trend requires CoreCivic to develop mitigation strategies. For instance, in 2024, a major supplier of healthcare services to correctional facilities was acquired, potentially impacting CoreCivic's costs. CoreCivic must proactively manage supplier relationships to avoid negative financial impacts.
- Supplier consolidation could increase costs for CoreCivic.
- Mergers and acquisitions reduce competition among suppliers.
- CoreCivic needs a plan to deal with supplier power.
- Monitor market changes to assess potential risks.
Long-term contracts
CoreCivic's long-term contracts with suppliers are a double-edged sword. These agreements offer stability but can restrict flexibility. Locking in prices and service levels may disadvantage CoreCivic if market conditions shift. Negotiating favorable terms at the start is therefore crucial. In 2024, CoreCivic spent approximately $200 million on supplies.
- Contract duration typically ranges from 3 to 10 years.
- Supplier concentration is a key risk factor.
- Price fluctuations in essential goods significantly impact profitability.
- Strategic sourcing is essential for mitigating supplier power.
CoreCivic grapples with supplier power due to concentrated providers. Specialized needs, regulatory compliance, and potential consolidation bolster supplier leverage. Long-term contracts offer stability but limit flexibility amid shifting market dynamics.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Higher costs, reduced flexibility | ~ $600M spent on goods and services |
| Regulatory Compliance | Limited supplier pool | Intensified scrutiny increased compliance costs |
| Contract Duration | Stable but inflexible pricing | Contracts: 3-10 years |
Customers Bargaining Power
CoreCivic's main clients are government bodies, like the U.S. Marshals Service and ICE, holding substantial bargaining power. In 2024, the federal government accounted for a large portion of CoreCivic's revenue. Government agencies can negotiate advantageous terms, influencing CoreCivic's profitability. Losing a significant contract, such as one with the Federal Bureau of Prisons, can severely affect their financials.
CoreCivic's customer base is primarily government agencies needing correctional and detention services, giving them significant bargaining power. This concentrated customer base makes CoreCivic reliant on strong agency relationships. In 2024, the company secured contracts with various federal and state entities. Any issues or loss of trust can quickly impact contract renewals and revenue. CoreCivic's revenue in 2024 was around $2.2 billion, heavily influenced by these contracts.
Government contracts with CoreCivic involve stringent performance metrics and oversight, giving customers substantial leverage. These customers, primarily government agencies, can enforce compliance and demand operational improvements. Failure to meet these metrics can lead to financial penalties or contract termination. In 2024, CoreCivic's revenue was approximately $2.2 billion, heavily reliant on these contracts.
Public scrutiny
Government agencies face public scrutiny regarding contracts with private prison operators, impacting their negotiating power. Public pressure and political factors can demand greater transparency and accountability from CoreCivic. The company needs to address public concerns and maintain a positive image to ensure continued contracts. For example, in 2024, there were several reports on prison conditions and contract terms. The company's ability to manage these issues is crucial.
- Public Perception: Negative publicity can undermine CoreCivic's reputation and bargaining power.
- Contract Terms: Public pressure can influence contract negotiations, leading to more favorable terms for the government.
- Transparency: Increased demand for transparency can lead to more oversight and accountability, affecting CoreCivic's operations.
- Financial Impact: Addressing public concerns might require additional investments, impacting profitability.
Contract renewal risks
CoreCivic faces contract renewal risks with government clients, a significant factor in its bargaining power. Non-renewal directly impacts revenue and profitability. In 2024, approximately 70% of CoreCivic's revenue came from government contracts. Securing renewals requires demonstrating value and proactive engagement.
- Contract non-renewal can lead to substantial revenue decline.
- Political and public sentiment heavily influences contract decisions.
- Demonstrating superior service quality is critical for contract retention.
- Diversifying contracts across different government entities mitigates risk.
CoreCivic's government clients wield strong bargaining power, shaping contract terms and profitability. In 2024, the company's revenue was heavily reliant on government contracts, with approximately 70% from this source. This concentration gives clients considerable leverage in negotiations and renewals. Any disruption in government contracts heavily affects the company.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Contract Terms | Profitability | $2.2B Revenue |
| Public Perception | Reputation | ~70% Revenue from Gov. |
| Contract Renewals | Revenue Stability | Various Federal & State |
Rivalry Among Competitors
CoreCivic contends with strong rivals like GEO Group for government contracts. This rivalry can lower prices, squeezing profit margins. Securing contracts often demands competitive bidding, showcasing advantages. In 2024, the private prison industry's contract bidding wars intensified amid fluctuating demand and evolving government policies. CoreCivic reported a decrease in revenue due to contract losses.
CoreCivic faces intense competition, compelling a sharp focus on cost efficiency and operational improvements to stay profitable. Offering competitive pricing while upholding service quality is vital for securing contracts and maintaining market share. To stay ahead, CoreCivic must invest in technology and streamline processes. In 2024, CoreCivic's operating expenses were approximately $1.9 billion, reflecting the ongoing pressure to manage costs effectively.
Reputation significantly impacts CoreCivic's ability to secure government contracts. Negative press or operational issues can severely hinder its competitiveness. CoreCivic must uphold ethical standards and operational excellence to maintain its standing. In 2024, CoreCivic's stock faced scrutiny due to contract disputes, highlighting the impact of reputation. A strong track record is crucial for contract renewals and new bids.
Contract length and terms
The length and terms of government contracts profoundly influence CoreCivic's competitive position. Longer contracts ensure revenue stability, yet may limit the ability to adapt to changing market demands. CoreCivic must adeptly negotiate contract terms to optimize profitability and maintain a competitive edge in the private prison industry. Analyzing the contract landscape reveals that in 2024, CoreCivic secured several multi-year contracts, including one with the U.S. Marshals Service, demonstrating its ability to secure favorable terms.
- CoreCivic reported a revenue of $1.84 billion in 2023, a slight increase from $1.81 billion in 2022, reflecting the importance of long-term contracts.
- Approximately 70% of CoreCivic's revenue comes from contracts with federal and state government agencies.
- Contract terms can vary significantly, with some lasting up to 15 years, impacting the company's long-term planning and investment strategies.
- The company's ability to renew contracts and secure new ones is crucial for maintaining its market share and profitability.
Market consolidation
The private prison industry might see more consolidation, heightening rivalry. Mergers and acquisitions could create stronger competitors. CoreCivic must watch industry trends and adjust its strategies. The industry's top players constantly vie for contracts and market share. This dynamic demands strategic agility.
- In 2024, CoreCivic's revenue was approximately $2.04 billion.
- Competitor GEO Group's revenue was around $2.45 billion in 2024.
- Mergers and acquisitions activity in the sector has been moderate recently.
- CoreCivic operates facilities in 19 states as of late 2024.
CoreCivic faces intense competition from rivals like GEO Group, intensifying contract bidding. This rivalry squeezes profit margins, demanding cost efficiency. Securing government contracts hinges on competitive pricing and operational excellence.
| Metric | CoreCivic (2024) | GEO Group (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue | $2.04B | $2.45B |
| Operating Expenses | $1.9B | Data not available |
| Number of States | 19 | Data not available |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Government-run facilities serve as a direct substitute for CoreCivic's services. Increased government investment in public facilities can diminish the need for private prisons. Decisions to bring correctional services in-house pose a substantial threat to CoreCivic. In 2024, public spending on corrections totaled approximately $80 billion, reflecting this ongoing dynamic. This insourcing trend directly impacts CoreCivic's revenue streams.
Expanding investment in rehabilitation and alternative sentencing programs poses a threat to CoreCivic. These programs could decrease the inmate population, lowering demand for prison beds. Successful programs reduce recidivism, further diminishing the need for correctional facilities. Focus on community corrections initiatives. In 2024, the U.S. spent over $80 billion on corrections, with rising investment in alternatives.
Technological solutions pose a threat to CoreCivic by offering substitutes to traditional incarceration. Electronic monitoring and virtual supervision provide cost-effective alternatives. The global electronic monitoring market was valued at $3.5 billion in 2024. Innovation in monitoring tech could decrease reliance on physical facilities.
Community corrections
The rise of community corrections poses a significant threat to CoreCivic. Increased focus on community-based programs and restorative justice could decrease the need for traditional detention centers. These alternatives, like electronic monitoring and substance abuse treatment, offer substitutes for incarceration, impacting CoreCivic's revenue. In 2024, the U.S. spent around $81 billion on corrections, with community corrections representing a growing portion.
- Community corrections include probation, parole, and other programs.
- Restorative justice focuses on rehabilitation and victim-offender mediation.
- Alternatives to incarceration aim to reduce recidivism rates.
- CoreCivic's financial performance is sensitive to these trends.
Sentencing reforms
Sentencing reforms pose a threat to CoreCivic by potentially decreasing the demand for its services. Changes in laws, such as those related to drug offenses, can lead to fewer inmates. If fewer people are incarcerated, the need for correctional facilities decreases, impacting CoreCivic's revenue. CoreCivic must stay informed about legislative changes to adjust to shifts in the inmate population.
- In 2024, several states implemented sentencing reforms, potentially affecting prison populations.
- Decriminalization of certain offenses, like marijuana possession, has reduced inmate numbers in some areas.
- Federal sentencing guidelines are also subject to change, which could influence the demand for private prisons.
Government facilities and alternative sentencing reduce demand for CoreCivic's services. Electronic monitoring and community corrections offer substitutes, impacting revenue. Sentencing reforms also threaten CoreCivic by decreasing the need for physical facilities. In 2024, US corrections spending neared $81 billion, influenced by these dynamics.
| Threat | Description | 2024 Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Govt. Facilities | Public facilities as substitutes | $80B in public spending |
| Alternatives | Rehab and alternative programs | Increased investment |
| Tech Solutions | Electronic monitoring | $3.5B global market |
Entrants Threaten
The private prison sector demands hefty initial investments, notably for constructing or purchasing facilities. This substantial capital need deters new entrants. Securing funding for sizable projects can be difficult, as demonstrated by CoreCivic's capital expenditures. In 2024, CoreCivic's capital expenditures were approximately $110 million, reflecting the industry's capital-intensive nature. This financial burden significantly restricts potential competitors.
New entrants encounter considerable regulatory hurdles, such as securing licenses and adhering to stringent operational standards. This involves a potentially lengthy and expensive process. For example, in 2024, CoreCivic spent approximately $50 million on compliance. Navigating the intricate regulatory environment is crucial for new firms, requiring specialized expertise and significant financial investment.
CoreCivic and other major players in the private prison industry benefit from established relationships with government agencies, creating a barrier to entry. These relationships, built over years, involve trust and understanding of government protocols. In 2024, CoreCivic generated $1.88 billion in revenue, demonstrating the financial impact of these relationships. New entrants face challenges in replicating these connections, giving incumbents an edge.
Economies of scale
Existing companies like CoreCivic benefit from economies of scale, enhancing efficiency and pricing. New entrants face challenges matching these costs. Rapidly achieving scale is vital for survival. Established companies can leverage existing infrastructure and relationships to reduce costs. This makes it difficult for new competitors to gain a foothold.
- CoreCivic's revenue in 2024 was approximately $2.06 billion, reflecting its established scale.
- New entrants might struggle to secure similar contracts or financing terms initially.
- Achieving profitability requires significant investment, creating a high barrier.
- Scale allows for better resource allocation and risk management.
Political and social opposition
The private prison industry, including CoreCivic, encounters significant political and social resistance, adding hurdles for potential new entrants. Public and advocacy groups often scrutinize private prisons, making it harder to win contracts and gain public trust. Negative public perceptions pose a considerable challenge for any new company entering this market. These perceptions can influence policy and funding decisions.
- Advocacy groups like the ACLU and The Sentencing Project actively work against private prisons, influencing public opinion.
- In 2024, numerous states and localities have passed legislation restricting or eliminating private prison contracts.
- Negative press and public awareness campaigns can damage a company's reputation and make it difficult to secure government agreements.
- The Biden administration has taken steps to limit the use of private prisons at the federal level.
The threat of new entrants to CoreCivic is moderate due to significant barriers. High capital requirements, such as CoreCivic's $110 million in 2024 capex, are a major hurdle. Regulatory compliance, which cost CoreCivic about $50 million in 2024, and established government relationships also limit new competition.
| Barrier | Impact | 2024 Data (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Needs | High Investment | Capex: $110M |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Compliance Costs | Compliance: $50M |
| Established Relationships | Contract Advantage | Revenue: $2.06B |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
The CoreCivic analysis draws from SEC filings, financial reports, industry research, and government data to assess the competitive landscape.