Edison International Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Edison International Bundle
What is included in the product
Analyzes Edison International's position, assessing competition, supplier/buyer power, & entry barriers.
Instantly visualize Edison International's competitive landscape for strategic insights.
Same Document Delivered
Edison International Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview details Edison International's Porter's Five Forces analysis—exactly what you receive upon purchase.
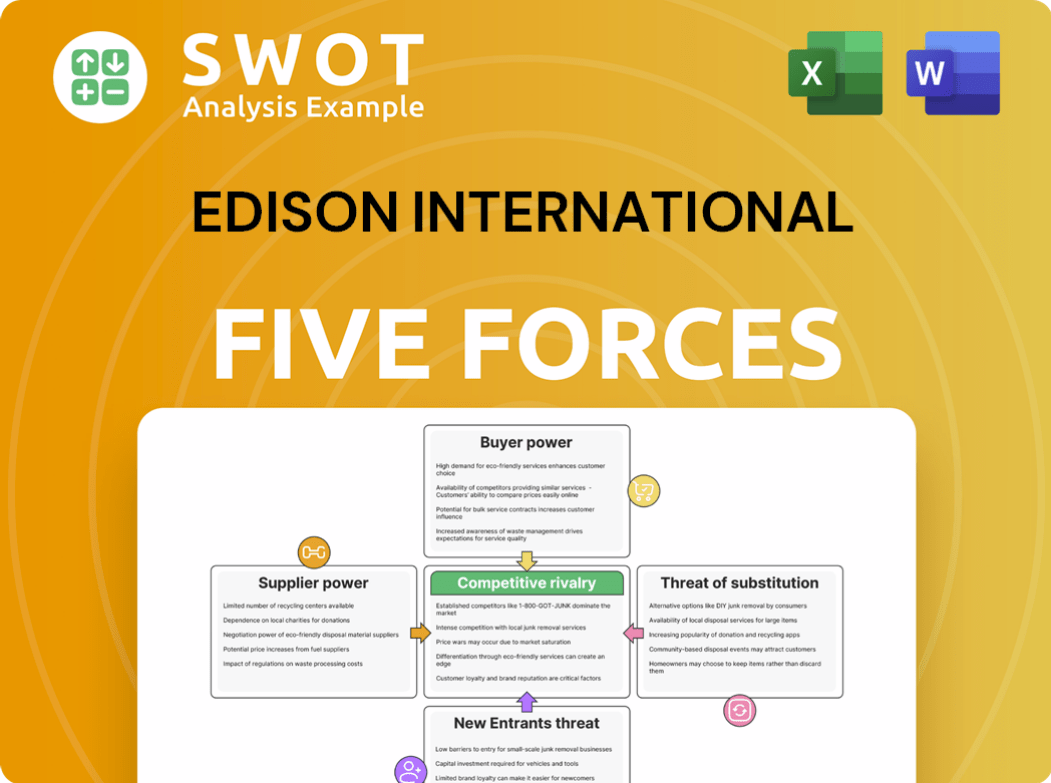
It breaks down industry rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, threat of substitutes, and new entrants.
The complete document is ready for download, offering a comprehensive understanding of Edison's competitive landscape.
This is the full, finalized report—fully formatted and ready for your immediate use.
No hidden extras; this is the deliverable you'll instantly access.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
Edison International operates within a dynamic utility sector, facing pressures from various forces. Examining supplier power reveals dependence on infrastructure providers and fuel sources. Buyer power is moderate due to regulated pricing and customer loyalty. The threat of new entrants is limited due to high capital costs and regulatory hurdles. Substitute products pose a growing challenge with renewable energy alternatives. Competitive rivalry is intense amongst existing utilities, and market consolidation.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Edison International’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Edison International, via SCE, faces supplier bargaining power. SCE depends on vendors for fuel and equipment. In 2024, SCE's reliance on specific fuel suppliers and vendors for grid upgrades impacts costs. High switching costs boost supplier leverage. The firm's 2024 capital expenditures were about $6.8 billion.
Fuel costs, especially for natural gas, are a major expense for Southern California Edison (SCE). Suppliers of natural gas, like those in the Permian Basin, hold power due to market prices and supply dynamics. In 2024, natural gas prices have fluctuated, directly impacting SCE's operational costs and, consequently, consumer electricity bills. While renewable energy is growing, its costs and intermittency still pose supplier-related challenges for SCE.
Equipment manufacturers, like those producing transformers and smart grid tech, wield bargaining power. Limited suppliers or essential tech, especially for grid upgrades, give them leverage. In 2024, the U.S. grid infrastructure spending reached $100 billion. Advanced tech for renewables integration is also crucial.
Service Providers
Edison International's (SCE) reliance on outsourced services, like maintenance and IT, affects its supplier power. The bargaining power of these service providers hinges on their specialization and the number of competitors. Companies with unique expertise or few rivals can negotiate better terms. SCE must manage contracts and develop alternative service options. In 2024, SCE spent a significant portion of its operational budget on external services.
- Outsourcing costs are a significant factor in Edison International's operational expenses.
- Specialized service providers may have increased bargaining power due to their unique offerings.
- Contract management and the availability of alternative providers are key for SCE.
- SCE's ability to control service costs directly impacts its profitability.
Regulatory Constraints
Regulatory policies and environmental standards indirectly shape supplier power for Edison International. Stricter rules on emissions might force SCE to depend more on specific suppliers compliant with these standards. Compliance expenses and mandated renewable energy investments can boost certain suppliers' influence. These factors can affect Edison International's cost structure and operational flexibility. In 2024, Edison International invested billions in grid modernization and renewable energy, highlighting regulatory impacts.
- Environmental regulations increase the cost of compliance.
- Renewable energy mandates can increase reliance on specific suppliers.
- Compliance costs and investments affect the balance of power.
- Edison International invested billions in grid modernization.
Edison International's supplier power is shaped by fuel, equipment, and service providers, significantly affecting its costs and operations. In 2024, natural gas prices fluctuated, impacting operational costs. Equipment manufacturers, particularly for grid upgrades, hold leverage. Outsourcing costs and regulatory impacts further influence supplier dynamics.
| Supplier Type | Impact on SCE | 2024 Data Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel (Natural Gas) | Cost Volatility | Price Fluctuations: ~$3-$5/MMBtu |
| Equipment | Supply Chain & Cost | Grid Spending: ~$100B (U.S.) |
| Outsourced Services | Operational Costs | Significant portion of budget |
Customers Bargaining Power
Southern California Edison (SCE) serves around 15 million people. While residential customers are numerous, large industrial and commercial clients wield more power. These customers can negotiate rates, driving down potential revenue by up to 5% in 2024, or invest in self-generation.
Switching costs for Edison International's residential customers are generally low; they can switch providers. In 2024, the residential sector accounted for approximately 36% of Edison's total revenue. Commercial and industrial clients may face higher costs, but they have options. For instance, in 2024, about 12% of U.S. electricity came from renewable sources like solar, offering alternatives.
Electricity, a necessity, makes customers price-sensitive, notably impacting low-income households. High prices invite political pressure and regulatory scrutiny, potentially restricting SCE's rate adjustments. In 2024, California's average residential electricity rate was about 25 cents/kWh. Demand response and efficiency programs help manage consumption and counter price sensitivity.
Alternative Energy Options
Customers now have more power due to alternative energy. Options like solar panels and battery storage are readily available. This allows them to generate their own power, reducing reliance on Southern California Edison (SCE).
This trend is changing the energy landscape. Community Choice Aggregators (CCAs) offer different energy choices. In 2023, CCAs in California served over 11 million customers, indicating significant market influence.
SCE must adapt to stay competitive. They are innovating with new services and pricing. The California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) is also influencing the changes.
This shift affects SCE's business model. The increased customer choice challenges its traditional approach. It forces SCE to focus on customer needs and offer better value.
- Rooftop solar adoption has grown significantly.
- Battery storage is becoming more affordable.
- CCAs are expanding their service areas.
- SCE is investing in grid modernization.
Regulatory Oversight
Regulatory oversight significantly shapes customer power over Edison International. Agencies like the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) protect customer interests. The CPUC controls rates and service quality, curbing SCE’s customer influence. Regulatory decisions directly affect SCE's finances and customer contentment. In 2024, CPUC approved a $6.2 billion rate increase for SCE.
- CPUC approval of rate increases directly impacts customer costs and satisfaction.
- Regulatory scrutiny ensures service standards and prevents excessive pricing.
- The CPUC's role is vital, as seen with the 2024 rate increase.
- Edison International must adhere to these regulations.
Edison International's customers, from residential to large industrial clients, possess considerable bargaining power. Large commercial clients can negotiate rates, potentially reducing revenue. Residential customers can switch providers, impacting around 36% of revenue in 2024.
Alternative energy sources such as solar and battery storage increase customer options. Community Choice Aggregators (CCAs) also offer alternatives, serving over 11 million customers in California by 2023.
Regulatory bodies, like the CPUC, further influence customer power, protecting interests and controlling rates. The CPUC approved a $6.2 billion rate increase for SCE in 2024, directly affecting customer costs.
| Factor | Impact | Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Rate Negotiation | Reduced Revenue | Up to 5% for large clients |
| Residential Revenue | Customer Influence | 36% of total revenue |
| Average Electricity Rate | Price Sensitivity | 25 cents/kWh in California |
Rivalry Among Competitors
SCE, a major player, has a strong market share in Southern California's electric utility sector. This dominance faces challenges from other utilities and energy providers. Competition necessitates ongoing investments in infrastructure and customer service. In 2024, SCE's operational revenue reached approximately $20 billion.
Edison International faces intense competition due to California's strict regulatory environment. Policies favor renewable energy and grid upgrades, impacting Southern California Edison (SCE). Compliance mandates create challenges for SCE. The regulatory environment fosters sector competition and innovation. In 2024, California's energy market saw significant shifts due to these regulations.
Technological advancements, including smart grids and energy storage, are reshaping the utility sector. SCE faces increased competition from firms offering these innovative solutions, demanding adaptation. The integration of new technologies is crucial for SCE to remain competitive. The rapid pace of technological change intensifies competitive rivalry, as seen in the 2024 surge in renewable energy projects. For example, the solar power capacity has increased by 15% in the last year.
Service Differentiation
Service differentiation is vital for Edison International (EIX) as utilities offer a standard product: electricity. Southern California Edison (SCE), a subsidiary, competes by enhancing reliability and customer service. They also provide value-added services like energy audits and demand response programs, which are increasingly important. Customer engagement and satisfaction are key for maintaining a competitive advantage in the evolving energy landscape.
- In 2024, SCE invested heavily in grid modernization to improve reliability.
- Customer satisfaction scores (measured by J.D. Power) are closely watched.
- Demand response programs saw increased participation, reducing peak load.
- Investments in smart grid technologies enhanced service offerings.
Wildfire Mitigation Costs
Wildfire mitigation expenses are a major competitive factor for Edison International (SCE). These costs are substantial and directly impact profitability, necessitating a delicate balance between safety investments and customer rates. SCE's ability to handle and recoup these expenses influences its competitiveness within the utility sector. The escalating wildfire risk in California demands proactive strategies to manage these financial burdens effectively.
- In 2023, SCE allocated approximately $1.5 billion to wildfire mitigation efforts.
- These costs have led to rate increases, potentially affecting customer satisfaction and market share.
- Effective cost recovery strategies are crucial for maintaining financial health and competitive positioning.
- The company faces pressure to implement advanced technologies and strategies to mitigate risks and manage costs.
Competitive rivalry in Edison International's sector is fierce, driven by market share battles among utilities. Strict regulations and technological shifts intensify competition, demanding adaptation. Service differentiation and wildfire mitigation costs significantly affect competitiveness. In 2024, SCE's operational revenue was around $20 billion.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Market Share | Highly competitive | SCE maintained a strong market share in Southern California. |
| Regulations | Influence costs | California's energy policies favored renewable energy projects. |
| Technology | Drives innovation | Solar power capacity increased by 15%. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Energy efficiency measures, including better insulation and smart appliances, act as substitutes, reducing electricity demand. Government incentives and public awareness also boost energy efficiency, lowering the need for SCE's services. In 2024, residential energy efficiency programs saved an estimated 2,500 GWh of electricity. Investing in efficiency programs helps lessen this threat. In California, the Residential Energy Efficiency Rebate Program offered up to $2,000 for home upgrades in 2024.
Rooftop solar poses a significant threat as it allows customers to generate their own electricity, reducing dependence on Southern California Edison (SCE). The falling costs of solar panels and government incentives make it a compelling alternative. In 2024, residential solar capacity in California increased, indicating growing adoption. SCE must adapt by providing grid services and integrating distributed generation.
Battery storage poses a threat to Edison International (EIX) by offering alternatives to traditional electricity. These systems, at grid level and behind-the-meter, compete directly. The ability of battery storage to integrate renewable energy and reduce peak demand lessens the reliance on SCE's services. The U.S. installed battery storage capacity grew to 10.9 GW in 2023. This promotes energy independence and resilience, impacting EIX.
Community Choice Aggregators (CCAs)
Community Choice Aggregators (CCAs) are a significant threat to Southern California Edison (SCE). CCAs enable local communities to procure electricity from diverse sources, including renewables. This gives customers more control over their energy options and pricing, directly impacting SCE's market share. To counter this, SCE must compete aggressively on both rates and service quality.
- As of 2024, CCAs serve a substantial portion of California's electricity customers.
- CCAs often provide electricity at competitive or lower rates compared to investor-owned utilities like SCE.
- The rise of CCAs reflects a shift towards decentralized energy markets and customer choice.
Microgrids
Microgrids pose a threat to Edison International (EIX) as they offer an alternative to the traditional grid. These localized energy grids enhance reliability, particularly in areas susceptible to outages. The increasing development of microgrids diminishes customer reliance on EIX's central grid. This shift provides customers with greater energy independence, potentially impacting EIX's revenue streams.
- Microgrid market size in North America was valued at USD 50.4 billion in 2023.
- It is projected to reach USD 109.3 billion by 2028.
- The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is expected to be 16.7% from 2023 to 2028.
- EIX's 2023 revenue was $15.3 billion.
Substitutes like energy efficiency and solar significantly threaten Edison International's (EIX) market share. In 2024, California saw increased residential solar adoption, directly competing with EIX's electricity supply. Battery storage and microgrids further offer alternatives, impacting EIX's revenue. Community Choice Aggregators (CCAs) add to this pressure.
| Substitute | Impact on EIX | 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces demand | Residential programs saved 2,500 GWh |
| Rooftop Solar | Reduces reliance | Residential solar capacity increased |
| Battery Storage | Offers alternatives | U.S. installed 10.9 GW by 2023 |
| CCAs | Competes on price | Substantial CA customer share |
Entrants Threaten
The electric utility sector demands immense initial capital, essential for constructing power plants, transmission lines, and distribution networks. These substantial capital needs significantly deter new competitors from entering the market. In 2024, the average cost to build a new nuclear power plant can range from $9 to $12 billion. Obtaining funding and regulatory clearances pose major obstacles for prospective entrants.
The electric utility sector faces significant regulatory hurdles, including stringent licensing and environmental compliance. New entrants must navigate complex approval processes, which can be time-consuming and costly. This regulatory burden creates a barrier, especially when considering that in 2024, the average time to get regulatory approval for major infrastructure projects can exceed 5 years. Incumbent utilities, like Edison International's Southern California Edison (SCE), benefit from established relationships and deep expertise in these regulatory environments.
Established utilities like Edison International possess significant economies of scale, reducing their per-unit costs due to their extensive customer base. New entrants face a disadvantage, as their smaller scale results in higher per-unit costs, making it challenging to compete on price. For instance, Edison International reported approximately $15.3 billion in operating revenues in 2023, showcasing the scale benefits. Building a substantial customer base and achieving comparable economies of scale demands considerable time, substantial marketing efforts, and operational proficiency.
Access to Technology
Advanced technologies are vital for modern utility operations, creating a barrier for new entrants due to the need for specialized knowledge. Incumbent utilities, like Edison International, possess a technological advantage through established infrastructure. Implementing smart grids and cybersecurity systems demands significant investment and expertise, which are difficult for newcomers to acquire quickly. The cost of entry is substantial, hindering potential competitors.
- Edison International invested $6.5 billion in grid modernization from 2020-2023.
- Cybersecurity spending for utilities increased by 15% in 2024.
- Smart grid deployments are projected to reach $20 billion by 2026.
- New entrants face average initial technology costs of $500 million.
Brand Recognition and Customer Loyalty
Edison International (EIX), through its subsidiary Southern California Edison (SCE), benefits from strong brand recognition and customer loyalty, acting as a significant barrier to new entrants. Building trust and a reputation for reliable service is a lengthy process, requiring substantial investment in customer service and operational excellence. Incumbent utilities like SCE have long-standing relationships with customers, which are hard for new competitors to replicate. This established position gives SCE a competitive advantage, making it challenging for new companies to gain market share.
- SCE serves approximately 15 million people across a 50,000-square-mile service area.
- In 2023, SCE's customer satisfaction scores were high, reflecting strong brand loyalty.
- New entrants face high customer acquisition costs due to SCE's established market presence.
The electric utility sector presents considerable obstacles to new entrants due to high capital requirements, which can reach billions for infrastructure. Regulatory hurdles, including long approval processes and stringent compliance, pose major challenges. Established firms, such as Edison International, benefit from economies of scale and brand recognition, creating significant barriers.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Needs | High initial investment | Nuclear plant cost: $9-$12B |
| Regulatory Burden | Complex, time-consuming approvals | Approval time: 5+ years |
| Economies of Scale/Brand | Disadvantage vs. incumbents | Edison revenue (2023): $15.3B |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
The Edison International analysis utilizes SEC filings, annual reports, and industry publications for financial and operational data. We also consider competitor analyses and market research reports.