Enterprise Mobility Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Enterprise Mobility Bundle
What is included in the product
Identifies disruptive forces, emerging threats, and substitutes that challenge market share.
Customize pressure levels based on new data or evolving market trends.
Same Document Delivered
Enterprise Mobility Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This is the complete Enterprise Mobility Porter's Five Forces analysis. The preview provides the same in-depth, professionally written document you'll receive immediately after purchase.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
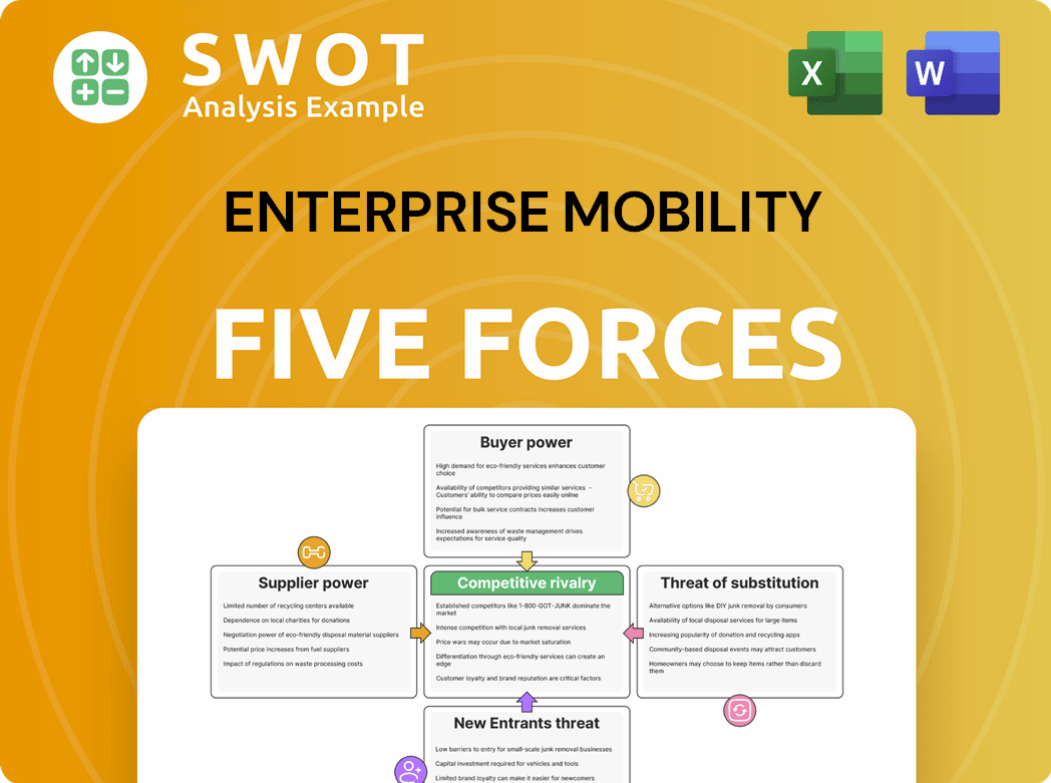
Enterprise mobility faces intense competition, particularly from established tech giants and nimble startups. Buyer power is substantial, as businesses can choose from various solutions. The threat of new entrants is moderate, with high initial investment costs but also significant market potential. Substitute products, like cloud-based solutions, pose a constant challenge. Finally, supplier bargaining power varies based on specific technology dependencies.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Enterprise Mobility’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers in the car rental industry, like Enterprise, is usually in the middle. Important suppliers are car makers, tech companies, and insurers. If only a few suppliers dominate, they can set prices and conditions, affecting Enterprise's profits. For instance, in 2024, the top 3 car manufacturers controlled about 60% of the global market. This concentration can pressure Enterprise.
Automobile manufacturers such as Ford, General Motors, and Toyota wield substantial power as suppliers. Their pricing and supply terms directly affect Enterprise's operational costs and fleet availability. For example, in 2024, Ford reported $176.2 billion in revenue. Supplier power strengthens if Enterprise depends on few manufacturers. Limited alternatives amplify this dynamic.
Enterprise's reliance on tech for operations gives suppliers leverage. Specialized tech, like fleet management software, boosts supplier power. In 2024, such tech costs rose, impacting Enterprise's margins. Proprietary systems further enhance supplier influence over pricing and service.
Insurance Companies
Insurance companies hold a significant bargaining power over Enterprise Mobility, as insurance is essential for car rental services. Rising insurance costs directly impact Enterprise's operational expenses. These costs can squeeze profitability if they cannot be passed on to customers, affecting rental agreement margins.
- Insurance premiums are a substantial cost component for car rental companies, often representing a significant percentage of their operational expenses.
- In 2024, the average cost of car insurance increased by approximately 20% across the United States.
- Enterprise Mobility faces challenges in negotiating favorable insurance rates due to its large fleet size and associated risk profile.
- The ability to pass on increased insurance costs to customers is limited by market competition and pricing strategies.
Fuel Costs
Fuel costs represent a crucial factor influencing Enterprise Mobility's operational expenses. The volatility in fuel prices, driven by global oil and gas market trends, directly affects profitability. Enterprise, though not directly tied to a single fuel supplier, feels the impact of these market dynamics. Rising fuel expenses can pressure profit margins, necessitating adjustments in rental rates to maintain financial health.
- In 2024, the average gasoline price in the U.S. fluctuated, impacting rental car companies' operational costs.
- Enterprise adjusts rental rates to reflect fuel cost changes, a key strategy for managing supplier power.
- The company's financial performance is sensitive to fuel price fluctuations, making it a critical consideration.
Suppliers' power for Enterprise is moderate. Key suppliers include carmakers, tech firms, and insurers, impacting costs.
Carmakers' pricing affects costs; in 2024, Ford's revenue was $176.2B. Tech and insurance suppliers also influence margins significantly.
Fuel prices add another layer of supplier influence, with 2024's gas price fluctuations impacting operational costs, affecting Enterprise's profitability and requiring strategic rate adjustments.
| Supplier Type | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Carmakers | Pricing/Supply Terms | Ford's Revenue: $176.2B |
| Tech Firms | Specialized Tech Costs | Tech costs increased |
| Insurers | Insurance Costs | Car insurance up 20% (US) |
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers, particularly leisure travelers, are highly price-sensitive in the car rental market, boosting their bargaining power. This sensitivity allows them to easily switch to competitors offering lower rates, intensifying price competition. Enterprise, for instance, must strategically balance pricing to attract customers while ensuring profitability. In 2024, the average daily rental rate was about $60-$70, showcasing the importance of competitive pricing.
Customers have several alternatives to car rentals, boosting their bargaining power. Ride-sharing services like Uber and Lyft provide convenient options. Public transport and taxis also serve as alternatives. In 2024, the global ride-sharing market was valued at $100 billion, showing the strength of alternatives.
Enterprise Mobility benefits from brand recognition, yet customer loyalty faces challenges. Car rental services are often seen as commodities, making switching brands easy for customers. According to a 2024 study, price sensitivity significantly impacts customer choice, with 60% prioritizing cost. Building loyalty through programs and service is vital to retain customers.
Switching Costs
Switching costs in the car rental industry are generally low, allowing customers to readily compare prices and switch between providers like Enterprise with ease. This ease of switching significantly boosts customer bargaining power. In 2024, the average daily rental rate was around $60, encouraging consumers to seek the best deals. Consequently, Enterprise and its competitors must prioritize customer satisfaction and loyalty programs to retain customers.
- Average daily rental rate around $60 in 2024.
- Low switching costs empower customers.
- Focus on customer satisfaction is crucial.
- Loyalty programs are used for retention.
Information Availability
Customers wield significant power due to readily available information. Online comparison tools and review sites provide transparency, enabling informed decisions. This empowers customers to negotiate favorable deals, impacting enterprise mobility providers. Businesses must actively manage online reputations and pricing to stay competitive, especially in today's digital landscape. For example, in 2024, the use of online comparison tools increased by 15% among tech buyers.
- Increased price sensitivity due to easy price comparisons.
- Greater influence on product design and features through reviews.
- Higher expectations for customer service and support.
- Need for competitive pricing strategies and value propositions.
Customers' bargaining power in car rentals is substantial due to price sensitivity and easy switching. Competitors like Uber and Lyft offer viable alternatives, intensifying competition. In 2024, the industry saw an average daily rental rate hovering around $60, making price comparisons crucial.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | High | 60% of customers prioritize cost |
| Switching Costs | Low | Avg. daily rental rate ~$60 |
| Alternatives | Significant | Ride-sharing market ~$100B |
Rivalry Among Competitors
The car rental market is saturated with major players vying for customers. This intense competition among companies such as Enterprise, Hertz, and Avis fuels rivalry. For example, in 2024, the U.S. car rental market was valued at approximately $30 billion. This saturation leads to price wars and aggressive marketing.
The car rental industry's consolidation, driven by mergers and acquisitions, intensifies rivalry. Companies like Enterprise face greater competition from larger entities. Enterprise's strategic adaptation is crucial, especially as the industry's top players account for significant market share. In 2024, the top three rental companies controlled over 70% of the U.S. market.
Differentiation in enterprise mobility, like fleet variety and customer service, lessens rivalry. Enterprise excels with diverse vehicles and services for varied clients. In 2024, companies offering unique services saw higher customer retention rates. Effective differentiation is crucial for market success.
Pricing Strategies
Aggressive pricing strategies are prevalent in the car rental sector, like Enterprise. Promotional pricing and discounts are frequently used to attract customers. These strategies can boost short-term revenue, but erode profit margins. Enterprise must balance pricing with profitability.
- 2024 data shows that car rental prices have fluctuated significantly due to supply chain issues and demand.
- Companies like Hertz and Avis also employ various pricing tactics, creating intense price competition.
- Enterprise's ability to offer competitive prices while maintaining profitability is crucial.
- A recent report indicated that price wars in the industry have led to margin pressures.
Geographic Reach
The geographic scope of car rental firms significantly shapes their competitive landscape. Enterprise Rent-A-Car, with its expansive global presence, holds a notable advantage, yet confronts competition from regional and local entities. Maintaining and broadening geographic reach is critical for staying competitive in this sector. In 2024, Enterprise operates in over 90 countries. This global footprint allows for greater market penetration.
- Enterprise operates in over 90 countries.
- Global presence supports market penetration.
- Regional players offer competition.
- Geographic reach is a key differentiator.
Competitive rivalry in enterprise mobility is intense, marked by price wars and consolidation. In 2024, the top three car rental firms controlled over 70% of the U.S. market, intensifying competition. Differentiation and geographic reach are key strategies for success, especially for players like Enterprise.
| Aspect | Details | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Market Saturation | U.S. car rental market valued at $30B in 2024 | Intense competition |
| Consolidation | Mergers and acquisitions among companies | Greater competition |
| Differentiation | Fleet variety, customer service | Reduced rivalry |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Ride-sharing services, such as Uber and Lyft, are a substantial threat to traditional car rental businesses. They provide convenient and, in many cases, more affordable options, especially for shorter trips. For instance, in 2024, ride-sharing revenue reached approximately $80 billion globally. Enterprise must evolve its strategies to remain competitive against these popular alternatives.
Public transportation, including buses, trains, and subways, acts as a substitute for Enterprise's car rentals, especially in cities. Efficient public transit can decrease car rental demand for local trips. In 2024, urban public transit ridership saw increases, potentially impacting Enterprise's market share. Enterprise must monitor public transit's growth to adapt its strategies.
Car-sharing programs like Zipcar are a direct substitute, providing short-term rentals. These services appeal to customers needing cars for brief periods, thus threatening traditional rental companies. In 2024, the car-sharing market was valued at approximately $2.6 billion globally, highlighting its growing impact. Enterprise must differentiate through longer-term options and customer service.
Personal Vehicle Ownership
For many, owning a personal vehicle serves as a direct substitute for Enterprise's car rentals. This substitution hinges on factors such as how often a customer needs a car, the total cost of owning a vehicle, and the ease of access. Enterprise must attract customers who value the flexibility and ease of renting over the long-term commitment and costs of ownership. In 2024, the average annual cost to own a car in the U.S. was around $12,182, according to AAA, which includes depreciation, fuel, insurance, and maintenance.
- Owning a car offers the convenience of immediate availability, eliminating the need to book or travel to a rental location.
- The total cost of ownership, including depreciation, fuel, insurance, and maintenance, can be a barrier for some, making rentals an attractive alternative.
- Enterprise can target customers who may not use a car frequently enough to justify ownership or who prefer not to deal with the responsibilities of car ownership.
- In 2024, the average new car price in the U.S. was about $48,756, according to Kelley Blue Book, further increasing the financial commitment of ownership.
Remote Work and Virtual Meetings
The surge in remote work and virtual meetings poses a significant threat to Enterprise Mobility. This shift has decreased the necessity for business travel, directly affecting car rental demand. Enterprise needs to innovate to retain customers and explore diverse revenue sources. Adapting to evolving work dynamics is essential for Enterprise's longevity. The global business travel market was valued at $698.4 billion in 2023, a figure Enterprise must navigate.
- Decline in Business Travel: Corporate travel spending decreased significantly.
- Virtual Meeting Adoption: Increased use of platforms like Zoom and Microsoft Teams.
- Revenue Diversification: Enterprise exploring alternatives like subscription services.
- Market Adaptation: Enterprise adjusting strategies to cater to local and leisure travel.
Enterprise Mobility faces substitute threats from various sources, influencing its market position.
Ride-sharing, car-sharing, and public transit offer alternatives to traditional car rentals, with ride-sharing generating roughly $80B in revenue in 2024.
Personal vehicle ownership and the rise of remote work also challenge Enterprise, requiring strategic adaptations.
| Substitute | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Ride-sharing | Direct alternative, convenience, cost | $80B global revenue |
| Public Transit | Reduces demand in cities | Increased ridership in urban areas |
| Car Ownership | Frequent use; cost-sensitive | $12,182 annual ownership cost (U.S.) |
Entrants Threaten
The car rental industry demands substantial capital for fleet purchases, maintenance facilities, and tech. This high cost of entry, a major barrier, protects existing firms. For instance, in 2024, Enterprise's fleet value exceeded $30 billion, showcasing the capital needed. New entrants struggle to match this, limiting competition.
Enterprise's strong brand recognition gives it an advantage. New mobility services struggle to build awareness and trust. Without brand recognition, attracting customers is tough. In 2024, Enterprise's revenue was $30.9 billion. This highlights its brand strength.
The car rental industry faces stringent regulations like licensing and insurance, increasing the difficulty for new entrants. Compliance can be expensive, creating a barrier to entry. These regulatory demands limit the number of potential competitors. In 2024, the costs associated with regulatory compliance increased by approximately 8%, particularly affecting smaller businesses.
Economies of Scale
Established enterprise mobility companies, like Enterprise, possess significant economies of scale, enabling them to provide competitive pricing and services. New entrants face challenges in matching this efficiency and cost-effectiveness, struggling to compete on price. This advantage allows established firms to lower operational costs per unit. The disparity in scale places new companies at a disadvantage when entering the market.
- Enterprise Mobility market size was valued at USD 77.60 billion in 2023.
- The market is projected to reach USD 247.70 billion by 2032.
- The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is 13.8% from 2024 to 2032.
- Large companies can negotiate better deals with vendors.
Access to Distribution Channels
Enterprise has a strong advantage in accessing customers through its extensive distribution network. They utilize airport locations, partnerships, and online platforms to reach a broad customer base. New car rental businesses face the challenge of building their own distribution systems to compete effectively. Securing prime locations and forming partnerships, like those Enterprise has, present significant barriers to entry.
- Enterprise's market share in the U.S. car rental market was approximately 30% in 2023.
- The U.S. car rental market is projected to reach $40.94 billion by 2028.
- New entrants need substantial capital to establish distribution channels.
- Partnerships with airports and other entities require significant negotiation and resources.
New entrants in enterprise mobility face high capital costs and brand recognition challenges. Stiff regulations, compliance expenses, and the need to build distribution networks also create hurdles. Despite the market's projected growth to $247.70 billion by 2032, these barriers limit new competition.
| Barrier | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Costs | High investment in fleets and infrastructure | Enterprise fleet value exceeded $30 billion |
| Brand Recognition | Difficult to build customer trust | Enterprise's revenue was $30.9 billion |
| Regulations | Expensive compliance | Compliance costs increased by 8% |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
We analyzed Enterprise Mobility data from market reports, financial statements, and competitor analyses for a robust industry view. These sources allowed assessment of competition & strategic forces.