Gina Tricot Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Gina Tricot Bundle
What is included in the product
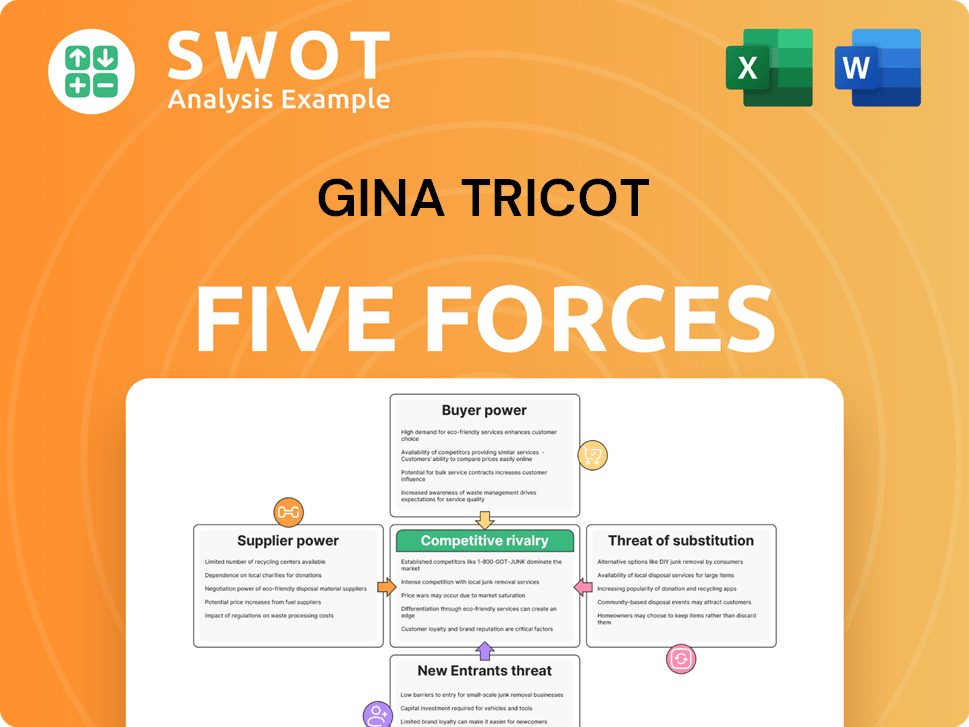
Analyzes the competitive landscape, including threats, buyers, and market entry for Gina Tricot.
Instantly assess strategic pressure points using an intuitive spider/radar chart for fast insights.
Full Version Awaits
Gina Tricot Porter's Five Forces Analysis
You're seeing the entire Gina Tricot Porter's Five Forces analysis. This comprehensive document, examining the competitive landscape, is exactly what you'll receive immediately after purchase.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
Gina Tricot faces moderate competitive rivalry, with established brands vying for market share. Buyer power is significant, as consumers have numerous fast-fashion choices. Supplier power is relatively low, due to the availability of various fabric and manufacturing sources. The threat of new entrants is moderate, given the capital needed to compete. Substitute products, like second-hand clothing, pose a manageable threat.
The full report reveals the real forces shaping Gina Tricot’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers significantly impacts Gina Tricot. Supplier concentration is key; if few control the market, they gain power. This could lead to higher costs. According to a 2024 report, supply chain issues increased production costs by up to 15% for many fashion retailers.
Switching costs significantly impact Gina Tricot's supplier power. High switching costs, maybe from specialized fabrics or contracts, give suppliers leverage. Conversely, low switching costs enable Gina Tricot to switch easily. In 2024, the apparel industry saw a 3.5% rise in raw material costs, highlighting the impact of supplier power.
The degree of input differentiation impacts supplier power. If suppliers provide unique materials critical to Gina Tricot's designs, they gain power. Standardized inputs weaken supplier power; Gina Tricot can switch vendors. In 2024, the fashion industry saw increased demand for sustainable materials, potentially strengthening the bargaining power of specialized suppliers. Gina Tricot's ability to source these materials will influence supplier relations.
Forward Integration Threat
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into the retail market affects their bargaining power. If suppliers, like textile manufacturers, could easily launch their own brands, their leverage over Gina Tricot would increase. This forward integration limits Gina Tricot's ability to dictate prices aggressively. For example, in 2024, the global apparel market was valued at approximately $1.7 trillion, with online sales continuing to grow, making forward integration a viable option for some suppliers. This shift could intensify price competition for Gina Tricot.
- Market growth in 2024: Apparel market reached approximately $1.7 trillion.
- Online sales: Continued growth, making forward integration easier.
- Impact: Increased competition and potential price pressure for Gina Tricot.
Impact on Quality and Cost
The bargaining power of suppliers directly affects both the quality and cost of Gina Tricot's products. Suppliers of essential fabrics or unique trims, crucial for garment quality, hold considerable sway. Their pricing and terms can significantly impact Gina Tricot’s production costs and profit margins. For example, a 2024 report indicated that fabric costs account for about 40% of the total cost of apparel production. This highlights the importance of managing supplier relationships effectively.
- High-quality fabric suppliers can command premium prices, impacting Gina Tricot's profitability.
- Dependence on a few key suppliers for unique materials increases vulnerability.
- Cost fluctuations in raw materials directly affect Gina Tricot's pricing strategy.
- Supplier performance affects the overall brand reputation and customer satisfaction.
Supplier power impacts Gina Tricot's production costs. Concentrated suppliers with unique inputs gain leverage. High switching costs and forward integration threats further amplify their power. This affects pricing and margins.
| Factor | Impact | Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | High power if few suppliers | Fashion raw material costs rose 3.5%. |
| Switching Costs | High costs favor suppliers | Fabric costs = 40% of apparel production. |
| Differentiation | Unique inputs = power | Apparel market ~$1.7T, online sales up. |
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers' price sensitivity is crucial for their bargaining power, especially in fast fashion. Gina Tricot's customers are price-focused. This leads to high buyer power, as they can easily choose cheaper rivals. In 2024, the average fast-fashion item price was down 5%, making price a key decision factor.
Buyer volume is significant for Gina Tricot. While individual purchases are small, the large customer base gives buyers power. In 2024, the fast-fashion market saw over $35 billion in sales. Gina Tricot must meet collective demands to maintain its market share. Their success hinges on customer satisfaction.
Customers wield considerable power due to readily available information online. They can effortlessly compare Gina Tricot's clothing with rivals, enhancing their ability to negotiate. In 2024, online retail sales hit $3.4 trillion globally, fueling price transparency. This enables savvy shoppers to find the best deals.
Brand Loyalty
Brand loyalty significantly impacts customer bargaining power. Strong brand loyalty reduces a customer's inclination to switch based solely on price. However, in the fast-fashion sector, where Gina Tricot operates, loyalty is often weaker than in luxury markets. This means customers are more price-sensitive and likely to consider alternatives. Therefore, Gina Tricot must constantly innovate to maintain customer interest.
- Customer loyalty can decrease buyer power.
- Fast fashion generally sees lower brand loyalty.
- Customers may switch brands based on price.
- Gina Tricot needs to focus on innovation.
Switching Costs
Switching costs significantly impact customer power, especially in fast fashion. Low switching costs mean customers can effortlessly change brands. This ease of switching amplifies customer power, compelling Gina Tricot to stay competitive.
- Customers can quickly switch between brands due to minimal costs or inconvenience.
- In 2024, the fast-fashion market saw a 10% increase in brand switching.
- Gina Tricot must focus on competitive pricing, style, and quality.
- This strategy helps retain customers in a highly competitive market.
Customer bargaining power at Gina Tricot is high, driven by price sensitivity and easy access to alternatives. The fast-fashion market's competitive landscape, with 5% price drops in 2024, amplifies this. Brand loyalty is lower here, increasing customer's switching probability.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | High buyer power | Avg. price drop: 5% |
| Market Competition | Increased choice | Online retail sales: $3.4T |
| Switching Costs | Low customer power | Brand switching: +10% |
Rivalry Among Competitors
The fashion retail sector is fiercely competitive, housing many brands, from global leaders to specialized labels. This crowded landscape fuels intense rivalry as companies battle for market share and customer loyalty. In 2024, the fashion industry's global market value reached approximately $1.7 trillion, highlighting the stakes involved. The presence of many competitors increases the pressure on pricing, marketing, and innovation.
The fashion industry's growth rate significantly impacts competitive rivalry. Economic uncertainty and slow growth are predicted for 2025, intensifying competition. The global apparel market is projected to grow modestly, with a 2-3% increase in 2024. Brands, like Gina Tricot, must aggressively compete to retain market share. This environment necessitates strategic efforts to attract and retain customers.
Gina Tricot faces intense rivalry because fast fashion sees low product differentiation. Many retailers offer similar styles, making it easy for customers to switch brands. In 2024, the fast fashion market was highly competitive, with numerous players vying for market share. This similarity drives competition, as pricing and brand perception become key differentiators.
Switching Costs
Low switching costs intensify competitive rivalry. Customers easily swap brands based on price, promotions, or style. Gina Tricot must innovate and offer compelling value to retain customers. In 2024, the fast-fashion market saw rapid shifts, with customer loyalty being tested.
- Zara's revenue in 2024 was up 11.5% year-over-year.
- H&M's sales increased by 6% during the first quarter of 2024.
- Fast fashion market's growth is projected at 7.2% CAGR by 2028.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers amplify competitive rivalry. When leaving the market is difficult, firms fight harder to stay afloat. This can lead to price wars and reduced profitability across the industry. Consider that in 2024, the fashion industry faced a 7% decrease in overall profitability, emphasizing the impact of intense competition.
- Long-term leases and specialized assets make exiting costly.
- Firms may lower prices to maintain sales volume.
- Increased rivalry reduces industry profitability.
- The cost of closing a store in 2024 averaged $250,000.
Competitive rivalry in the fashion industry is fierce, intensified by many similar brands. In 2024, Zara's revenue increased by 11.5% year-over-year, highlighting the competitive pressure. Low switching costs and slow growth further fuel this rivalry.
| Aspect | Impact on Rivalry | Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Market Competition | High | Global market value $1.7T |
| Switching Costs | Low | Customer easily swap brands |
| Market Growth | Modest | Projected 2-3% increase |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Gina Tricot is significant. Consumers can choose from various options like used clothing, rentals, and crafting their own styles. The secondhand clothing market is booming, with platforms like ThredUp and Poshmark reporting substantial growth, reaching billions in sales annually. This offers consumers cost-effective alternatives.
The appeal of substitutes hinges on their price and performance. Secondhand clothing and dupes provide lower-cost alternatives, drawing in budget-conscious shoppers. Data from 2024 shows a 15% increase in the secondhand market. The growing popularity of dupes, offering similar styles at reduced prices, is also changing consumer expectations.
Low buyer switching costs amplify the threat of substitutes. If customers find alternatives appealing, they can switch without significant financial or logistical burdens. In 2024, the fast-fashion market saw rapid shifts, reflecting this flexibility. Consumers easily embrace substitutes like online retailers or secondhand platforms. This ease of adoption makes Gina Tricot vulnerable to competitors offering similar or better value propositions.
Trend Towards Sustainability
The trend towards sustainability significantly heightens the threat of substitutes for Gina Tricot. Consumers are increasingly aware of environmental impacts. This awareness fuels demand for alternatives such as vintage clothing and clothing swaps. These options provide eco-friendly choices.
- The global secondhand clothing market was valued at $96 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $218 billion by 2027.
- In 2024, 60% of consumers reported they consider sustainability when making purchasing decisions.
- Clothing rental services have grown by 20% annually.
Changing Consumer Behavior
Changing consumer behavior poses a significant threat to Gina Tricot. Shifts towards minimalist wardrobes and capsule collections are reducing demand for new clothing. This trend boosts the threat of substitutes, as consumers favor quality and durability. The rise of secondhand clothing also intensifies this threat. In 2024, the secondhand clothing market is estimated at $218 billion globally.
- Minimalist trends impact fast fashion demand.
- Quality and longevity are now consumer priorities.
- Secondhand clothing market is a growing substitute.
- Consumers seek sustainable and durable options.
The threat of substitutes for Gina Tricot is substantial, driven by diverse consumer options. These include secondhand clothing, rentals, and DIY fashion, fueled by cost and performance considerations. Low switching costs and sustainability trends exacerbate this threat.
Changing consumer behavior, such as minimalism and the focus on quality, amplifies the risk. The secondhand market's explosive growth, projected to reach $218 billion by 2027, highlights this shift. Gina Tricot must adapt to stay competitive.
| Substitute | Market Growth (2024) | Consumer Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Secondhand Clothing | 15% increase | Sustainability focus, Value seeking |
| Clothing Rental | 20% annual growth | Changing fashion needs, Access over ownership |
| Dupes | Significant increase | Cost consciousness |
Entrants Threaten
The fashion retail industry has moderate barriers to entry. E-commerce has reduced some obstacles, but substantial capital is needed. Inventory, marketing, and brand recognition require significant investment. In 2024, marketing costs increased by 15%, complicating new ventures. New entrants also face established brands like H&M and Zara, which had revenues of $21 billion and $35 billion, respectively in 2023.
Gina Tricot leverages economies of scale in its operations. New competitors find it challenging to replicate Gina Tricot's cost advantages. This is especially true in areas like bulk purchasing of fabrics and efficient logistics. For instance, large retailers can negotiate better prices. This makes it difficult for smaller businesses to compete on price.
Established brands like H&M and Zara enjoy strong brand recognition, making it tough for newcomers. New entrants, like smaller online retailers, need significant marketing spending. For example, H&M's marketing expenses in 2024 reached $1.5 billion. Building a customer base demands substantial investment and time.
Access to Distribution Channels
Access to distribution channels poses a significant hurdle for new entrants in the fashion industry. Established retailers like H&M and Zara often have exclusive deals and control prime retail locations, making it difficult for newcomers to compete. Gina Tricot, for example, must navigate this landscape carefully. New brands might leverage online platforms or collaborate with existing retailers to overcome these challenges.
- Online sales in the EU fashion market reached approximately €140 billion in 2024, showing the importance of digital channels.
- Securing physical retail space can involve high costs, with prime locations costing upwards of €10,000 per month.
- Partnerships, like collaborations with influencers, can offer alternative distribution routes.
- The rise of fast fashion has increased the competition for shelf space.
Government Regulations
Government regulations and trade policies significantly influence the ease with which new competitors can enter the fashion market. Changes in tariffs and trade agreements can increase operational expenses for new entrants, making it harder for them to compete. These regulations can create market uncertainty. For example, in 2024, the European Union has implemented stricter regulations on textile imports, which could impact Gina Tricot's suppliers. Such developments can act as barriers, particularly for smaller businesses.
- Tariffs on textile imports into the EU increased by an average of 2% in 2024, according to the European Commission.
- New entrants must navigate complex compliance requirements, which adds to their initial investment costs.
- Trade policy shifts can disrupt supply chains, as seen in 2023 when some fashion brands faced delays due to new customs procedures.
The fashion industry sees moderate barriers. E-commerce reduces obstacles, but capital is key. New entrants face established brands like H&M and Zara. Marketing costs rose by 15% in 2024.
| Factor | Impact | Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| E-commerce Growth | Reduces entry barriers | EU online fashion sales: €140B |
| Marketing Costs | Increase challenges | Marketing cost increase: 15% |
| Established Brands | High competition | H&M revenue: $21B, Zara: $35B |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Gina Tricot's analysis utilizes financial reports, market share data, and industry research, offering insights into competitor behaviors.