Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering Bundle
What is included in the product
This analysis examines external factors influencing Korea Shipbuilding across Political, Economic, Social, etc. dimensions.
Provides a concise version that can be dropped into PowerPoints or used in group planning sessions.
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering PESTLE Analysis
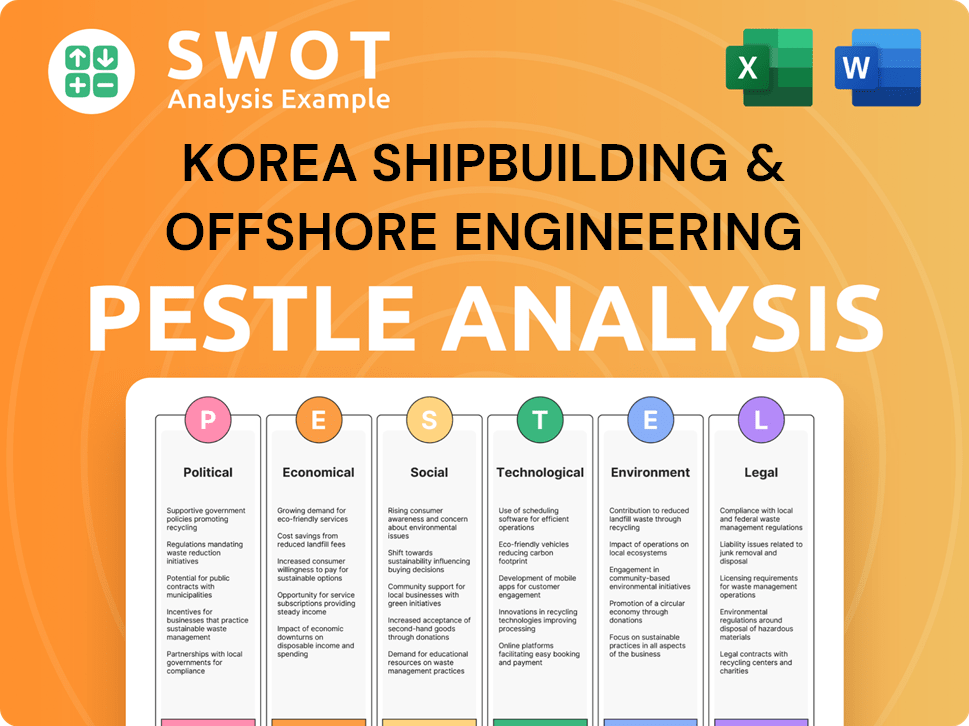
The preview shows a PESTLE analysis of Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering.
This analysis considers Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors.
Each section offers key insights affecting the company's future.
What you're previewing is the actual file—ready to download after purchase.
Enjoy comprehensive market analysis at your fingertips.
PESTLE Analysis Template
Navigating the complex world of shipbuilding requires sharp insights, and our PESTLE analysis provides precisely that for Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering. We delve into the political landscape, analyzing regulations impacting the industry and global trade dynamics. Our analysis explores economic factors, examining market trends, raw material costs, and currency fluctuations, crucial for strategic planning. Discover the social influences affecting demand and the environmental pressures shaping sustainability efforts. Stay ahead of the curve and be well-prepared with your business plan. Download the complete PESTLE analysis today!
Political factors
The South Korean government has a history of backing the shipbuilding industry. This includes financial aid, friendly policies, and promoting partnerships. The K-Shipbuilding Super Gap Vision 2040 is a key initiative, focusing on green tech. The government has set aside substantial funds to bolster the industry's advancement. In 2024, the government's support is projected to reach $2 billion.
Geopolitical instability, including events like the Red Sea crisis, disrupts shipping, potentially increasing shipbuilding demand due to route adjustments. Trade disputes, notably U.S.-China tensions, reshape global trade patterns. In 2024, the shipbuilding industry saw fluctuations linked to these factors. The Baltic Dry Index reflects shipping cost volatility influenced by these tensions.
South Korea's alliances, especially with the U.S., significantly affect shipbuilding. The U.S. Navy's procurement plans may boost orders for Korean shipyards. Increased defense spending by allies often translates to more business for KSOE. In 2024, the U.S. defense budget was approximately $886 billion, potentially benefiting KSOE through collaborative projects.
National Security Implications
The shipbuilding industry's national security implications are significant, tying into maritime defense and economic stability. Governments often prioritize a robust domestic shipbuilding capability, leading to strategic investments. For example, in 2024, South Korea allocated $1.5 billion to naval vessel construction, directly benefiting companies like Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering (KSOE). This support can manifest as preferential orders and funding for advanced technologies.
- Government contracts can provide a stable revenue stream.
- Investments can drive innovation and competitiveness.
- National security concerns can shield the industry from international pressures.
- Geopolitical tensions can increase demand for naval vessels.
Regulatory Environment and Compliance
Political factors significantly shape the regulatory landscape for Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering (KSOE). Changes in international maritime regulations, driven by political agreements such as those within the International Maritime Organization (IMO), directly affect shipbuilding practices. For example, the IMO's 2020 mandate on sulfur emissions significantly altered vessel designs. Compliance with these regulations is essential for market access and operational viability.
- IMO 2020 sulfur cap compliance led to increased demand for scrubbers or LNG-powered vessels, impacting KSOE's design and production choices.
- The enforcement of ballast water management regulations has driven the need for advanced treatment systems in new vessels.
- Political stability in key shipbuilding markets (e.g., EU, US, China) affects regulatory enforcement and demand patterns.
South Korean government backing, projected at $2 billion in 2024, supports shipbuilding via financial aid and policy. Geopolitical shifts and trade disputes influence demand and shipping costs, affecting KSOE. U.S. alliances and defense spending, around $886 billion in 2024, can boost KSOE's business, including naval vessel contracts.
| Factor | Impact | Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Govt. Support | Financial aid and policy backing | Projected $2B |
| Geopolitics | Shipping demand & costs | Baltic Dry Index fluctuations |
| U.S. Alliances | Increased orders | $886B defense budget |
Economic factors
The shipbuilding industry thrives on global economic health and trade. Strong economic growth boosts trade volume, necessitating more ships. In 2024, global trade is projected to grow, potentially increasing shipbuilding orders. Conversely, economic downturns can significantly reduce demand, impacting companies like Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering.
Ocean freight rates' volatility impacts shipbuilding. In 2024, rates saw fluctuations due to geopolitical events and supply chain shifts. High rates encourage new orders, boosting the shipbuilding industry. Conversely, low rates can decrease demand, affecting profitability. The Baltic Dry Index (BDI) is crucial, reflecting shipping costs.
South Korean shipbuilders, including Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering, encounter fierce competition. China dominates in specific vessel types, impacting pricing and market share. In 2024, China's shipbuilding output was approximately 48% of the global total, while South Korea's was around 24%. This environment demands constant innovation for a competitive advantage.
Currency Exchange Rates
Currency exchange rates are crucial for Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering (KSOE). Fluctuations directly affect material and labor costs, impacting export price competitiveness. Favorable exchange rates can significantly boost profitability. The Korean won's value against the US dollar is a key factor. In 2024, the won-dollar rate averaged around 1,300 KRW/USD, influencing KSOE's financial performance.
- Won's fluctuation affects profitability.
- Exchange rates impact material costs.
- Export prices are influenced by rates.
- 2024 rate: ~1,300 KRW/USD.
Access to Capital and Financing
The shipbuilding industry, including Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering (KSOE), heavily relies on capital. Securing favorable financing is vital for winning major contracts and upgrading technology. Government support significantly impacts KSOE's financial health and competitiveness. Access to capital affects its ability to innovate and expand.
- KSOE's debt-to-equity ratio was approximately 1.08 as of Q1 2024, highlighting its reliance on financing.
- South Korean government provides substantial export credit guarantees for shipbuilding, supporting KSOE's access to capital.
- Interest rate fluctuations in 2024/2025 directly influence KSOE's borrowing costs and profitability.
Economic conditions globally affect shipbuilding, with growth boosting demand. Ocean freight rate volatility impacts orders and profitability; the Baltic Dry Index is key. Intense competition from China, which produced roughly 48% of global output in 2024, challenges KSOE.
Currency exchange rates and capital availability critically influence Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering. The Korean won's fluctuations affect material costs and export prices, with rates around 1,300 KRW/USD in 2024. Access to capital and government support also determine KSOE’s financial health, including an approximate debt-to-equity ratio of 1.08.
| Factor | Impact on KSOE | 2024 Data/Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Global Economic Growth | Higher Demand for Ships | Projected Trade Growth in 2024 |
| Ocean Freight Rates | Impacts Orders/Profit | BDI Fluctuations |
| Currency Exchange (Won/USD) | Affects Costs, Prices | ~1,300 KRW/USD (2024) |
| Capital Access/Govt. Support | Financial Health, Innovation | Debt-to-equity ratio 1.08 (Q1 2024) |
Sociological factors
South Korea's shipbuilding industry struggles with labor shortages, particularly skilled workers. The sector must address its aging workforce and attract younger talent. Data from 2024 indicates a decline in shipbuilding employment. Integrating foreign labor becomes crucial to meet production demands. This impacts KSOE's operational efficiency and cost management.
Labor disputes and strikes pose significant risks to shipbuilding, potentially halting production and delaying deliveries. In 2024, South Korea saw several labor disputes, with implications for various industries. Stable labor relations are vital for operational efficiency and maintaining project timelines. The shipbuilding industry's reliance on skilled labor makes harmonious relations crucial for financial stability. Addressing worker concerns proactively can mitigate disruptions and safeguard the company's reputation.
Workplace safety is a major concern in South Korean shipyards. Recent data shows a slight decrease in workplace accidents in the shipbuilding industry, with 2.5 accidents per 100 workers in 2024. KSOE has invested heavily in safety training, aiming for a further reduction in 2025. Improved conditions boost morale and efficiency.
Public Perception and Social Responsibility
Public perception significantly shapes the shipbuilding industry's operations, particularly concerning environmental impact and labor standards. Stakeholders increasingly demand corporate social responsibility and sustainable practices. KSOE's reputation hinges on addressing these societal expectations to maintain its "social license." The industry faces scrutiny, requiring transparent and ethical conduct.
- South Korea's shipbuilding industry aims for eco-friendly ships to meet environmental standards by 2030.
- In 2024, ESG-related investments in South Korea surged, reflecting societal demand for responsible business.
- KSOE's focus on green technologies and labor welfare directly addresses these public concerns.
Education and Training Systems
South Korea's education and training systems significantly influence the shipbuilding sector's workforce quality. These systems must evolve to meet the industry's needs for skilled labor. Partnerships between shipbuilders and educational bodies are crucial for providing specialized training. According to the Korea Research Institute for Vocational Education and Training, initiatives to enhance vocational training are ongoing.
- Government spending on education in South Korea was approximately ₩78.8 trillion in 2023.
- The shipbuilding industry faces a shortage of skilled workers, with an estimated 10,000 vacancies in 2024.
- Collaboration between universities and KSOE increased by 15% in 2024 to address skills gaps.
Labor shortages, including aging and declining workforce, strain shipbuilding operations. Labor disputes present production and delivery risks, demanding harmonious worker relations. Addressing workplace safety is paramount to maintain morale, improve efficiency and, enhance brand reputation. Public perception, with focus on environmental impact, labor standards and CSR drive sustainable practices.
| Factor | Impact | Data (2024-2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Labor Shortage | Operational Inefficiency | ~10,000 vacancies. Collaboration with educational entities increased by 15%. |
| Labor Disputes | Production Delays, Increased Costs | Various industrial implications; shipbuilding industry relies on skilled labor. |
| Workplace Safety | Morale & Efficiency Issues | 2.5 accidents/100 workers in 2024, Reduction focus in 2025. |
Technological factors
The push for greener shipping is huge. This means tech like LNG, methanol, ammonia, and hydrogen-powered ships are gaining traction. KSOE is responding by investing heavily in these eco-friendly solutions to meet new regulations. In 2024, the global market for green shipping technologies was estimated at $200 billion, expected to reach $350 billion by 2025.
Technological advancements in automation, digitalization, and AI are key. They're driving smart, potentially autonomous vessels and shipbuilding. This boosts efficiency, productivity, and safety. The smart shipping market is projected to reach $158.8 billion by 2030. Digitalization reduces operational costs by up to 20%.
Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering (KSOE) benefits from innovation in manufacturing. For example, advanced welding and modular construction reduce build times. Digital production management boosts efficiency. In 2024, KSOE invested $150 million in these technologies. This led to a 10% reduction in production time.
Materials Science and Engineering
Materials science advancements drive shipbuilding efficiency. South Korea's shipbuilding sector, including KSOE, benefits from lighter, stronger materials. This enhances fuel economy and vessel durability. In 2024, the global demand for eco-friendly ships increased.
- KSOE aims to increase its order backlog to 25% with green ships by 2025.
- New materials could reduce ship weight by up to 15%, improving fuel efficiency.
- Advanced composites and alloys extend vessel lifespans by 20%.
Cybersecurity in Maritime Operations
Cybersecurity is a key technological factor for Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering. The increasing digitalization of ships and shipbuilding processes means protecting against cyber threats is essential for safe and reliable operations. The maritime industry faces rising cyber attacks; in 2023, there was a 40% increase in cyber incidents compared to the previous year.
- The global maritime cybersecurity market is projected to reach $3.6 billion by 2025.
- In 2024, the average cost of a maritime cyber breach is estimated at $350,000.
- KSOE is investing heavily in cybersecurity measures to protect its operations.
Green shipping fuels tech investments. KSOE focuses on eco-friendly solutions with the market hitting $350B by 2025. Automation, AI, and digitalization boost efficiency, with the smart shipping market reaching $158.8B by 2030. Cybersecurity is critical; maritime cybersecurity market expected to reach $3.6B by 2025.
| Technology | Impact | 2025 Forecast |
|---|---|---|
| Green Shipping | Reduced emissions, regulatory compliance | Market: $350B |
| Smart Shipping | Increased efficiency, automation | Market: $158.8B by 2030 |
| Cybersecurity | Protection against cyber threats | Market: $3.6B |
Legal factors
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) sets global standards for maritime safety, security, and environmental protection. These regulations, crucial for shipbuilding, directly influence design and operational requirements. Compliance with IMO standards is mandatory for international shipping, impacting Korean shipbuilding. Notably, the IMO's 2020 regulations on sulfur emissions significantly affected shipbuilding, increasing costs by 5-10% for new vessels.
South Korea's shipbuilding industry, including Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering, operates under strict domestic laws. These laws cover labor, safety, and technical standards, ensuring compliance. In 2024, South Korea's shipbuilding orders increased by 20% compared to the previous year, highlighting the importance of adherence. National laws align with international maritime conventions, influencing operational practices.
Trade regulations significantly impact Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering. South Korea's shipbuilding industry is heavily reliant on international trade. In 2024, the shipbuilding sector's exports reached $40 billion. Tariffs and trade agreements with countries like China and the EU influence material costs and market access. Geopolitical tensions can alter these legal frameworks, affecting supply chains and profitability.
Contract Law and Лиability
Shipbuilding contracts at Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering (KSOE) are intricate, detailing specifications, delivery schedules, and liability clauses. These contracts must comply with South Korean and international maritime laws. In 2024, KSOE faced legal challenges over contract disputes, impacting project timelines.
Understanding contract law and product liability is vital for KSOE to mitigate risks in its shipbuilding projects. Legal frameworks influence cost management and dispute resolution processes. Recent data shows that legal costs in the shipbuilding industry have increased by 15% due to complex litigation.
KSOE's adherence to these legal factors directly influences its financial performance and reputation. Product liability cases can lead to significant financial penalties and reputational damage. Effective legal risk management is essential for sustainable growth.
- Contract disputes can delay project completion, impacting revenue.
- Product liability claims can result in substantial financial penalties.
- Compliance with legal frameworks ensures operational stability.
- Legal risk management is critical for long-term profitability.
Environmental Laws and Standards
Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering (KSOE) must adhere to strict environmental laws. These laws cover emissions, waste management, and ballast water treatment. Non-compliance can lead to significant penalties and operational restrictions. KSOE's compliance costs could rise, impacting profitability.
- IMO 2020 regulations reduced sulfur emissions, increasing compliance costs.
- The EU's Emissions Trading System (ETS) may impose carbon costs on shipping.
- Ballast Water Management Convention implementation has been delayed until 2025, but is still required.
Legal factors significantly affect Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering (KSOE). Strict compliance with domestic and international maritime laws is essential for operations and international trade. In 2024, KSOE faced contract disputes, increasing legal costs by 15%. Effective legal risk management ensures financial stability and reputational integrity.
| Legal Factor | Impact | Data |
|---|---|---|
| IMO Regulations | Increased Compliance Costs | 5-10% cost increase on new vessels (2020 sulfur rules) |
| Trade Agreements | Affects Material Costs & Market Access | South Korea's shipbuilding exports reached $40B in 2024 |
| Contract Law | Influences Project Timelines & Revenue | KSOE's project delays impacted project timeline in 2024 |
Environmental factors
Regulations on greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions are becoming stricter for ships. The International Maritime Organization (IMO) and national governments are pushing for lower emissions. This forces shipbuilders to innovate with cleaner fuels. For example, the IMO aims to reduce GHG emissions from international shipping by at least 40% by 2030.
The transition to alternative fuels is driven by global decarbonization efforts, pushing the shipping industry to adopt LNG, methanol, ammonia, and hydrogen. This shift requires considerable R&D and investment in new ship designs. For example, in 2024, orders for LNG-powered ships increased by 20% globally. KSOE must strategically adapt to these changes.
Ballast Water Management (BWM) regulations, aimed at preventing the spread of invasive species, necessitate the installation of approved ballast water treatment systems (BWTS) on ships. These regulations, driven by international bodies like the IMO, affect shipbuilding, requiring modifications to ship designs and outfitting processes. The global BWTS market is expected to reach $3.9 billion by 2028, reflecting the significant investment needed to comply with these environmental standards. As of early 2024, over 40,000 ships have already installed BWTS.
Waste Management and Recycling
Waste management and recycling are increasingly critical for Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering. The shipbuilding process generates significant waste, necessitating compliance with environmental regulations. This includes managing hazardous materials and promoting sustainable practices. The company must also address the recycling of end-of-life vessels, which is heavily regulated to prevent environmental damage.
- In 2024, South Korea's waste recycling rate was approximately 80%.
- The global ship recycling market was valued at $2.5 billion in 2024.
- The International Maritime Organization (IMO) regulates ship recycling to ensure environmental safety.
Impact of Climate Change on Sea Levels and Routes
Long-term environmental shifts, like rising sea levels and Arctic ice changes, pose risks. These changes could disrupt shipping routes, impacting shipbuilding demand. For example, the global average sea level has risen about 0.21 feet since 1900. This affects vessel designs and operational strategies. The Arctic's ice extent in 2024 was significantly below average, altering navigation possibilities.
- Sea levels rose by about 3.6 mm per year between 2013 and 2022.
- Arctic sea ice minimum extent in September 2024 was the 10th lowest on record.
- Shipping routes through the Arctic could increase in use.
- Increased demand for ice-class vessels and alternative propulsion systems may occur.
Environmental factors greatly impact KSOE. Regulations like the IMO’s push for lower emissions. Shifting to alternative fuels is vital. Waste management and recycling are also critical.
| Environmental Issue | Impact on KSOE | Data/Fact (2024/2025) |
|---|---|---|
| GHG Emissions | Requires innovation in ship design. | IMO aims for at least 40% GHG reduction by 2030. LNG-powered ship orders up 20% globally in 2024. |
| Alternative Fuels | Drives R&D, investment in new tech. | Orders for LNG ships saw a 20% increase. |
| Ballast Water | Needs BWTS installation. | Global BWTS market forecast $3.9B by 2028. Over 40,000 ships have BWTS installed. |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
This PESTLE analysis relies on industry reports, government publications, and financial databases to assess relevant factors.