Mary Kay Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Mary Kay Bundle
What is included in the product
Analyzes Mary Kay's competitive landscape, examining supplier/buyer power & threats of new entrants.
Quickly assess competitive forces and strategic positioning for data-driven decisions.
Full Version Awaits
Mary Kay Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the Mary Kay Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive. It's the complete document, fully analyzed and formatted. Expect instant access to this detailed, ready-to-use file after purchase. No hidden content or edits are needed, as this is the final product. Consider it a finished, professional analysis.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
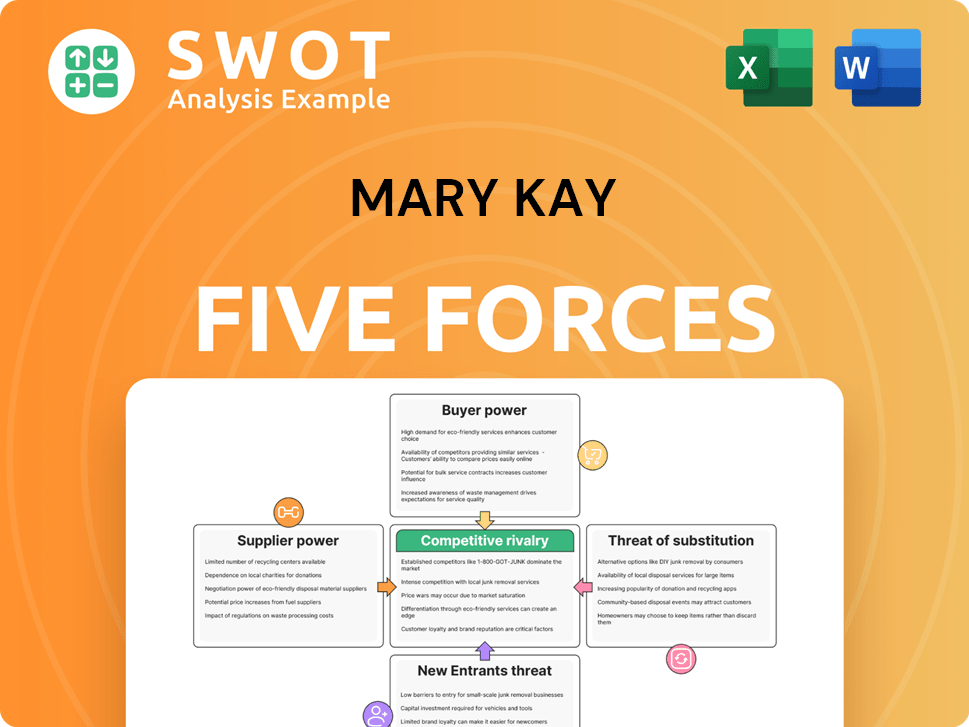
Mary Kay's competitive landscape is shaped by five key forces. Buyer power, influenced by direct selling models, impacts pricing. Supplier power, considering product sourcing, adds complexity. The threat of new entrants is moderated by brand recognition. Substitute products, like online retailers, pose a challenge. Finally, competitive rivalry with established beauty brands intensifies. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Mary Kay’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Mary Kay's suppliers offer standard cosmetic ingredients and packaging, lessening their power. This allows Mary Kay to change suppliers easily. For example, the global cosmetics market was valued at $279.4 billion in 2020, showing a wide range of suppliers. Commodity-like supplies prevent suppliers from setting strict terms.
The cosmetics industry enjoys a competitive supplier landscape, giving companies like Mary Kay multiple sourcing options. This dynamic limits the power any single supplier can exert. Mary Kay can weaken supplier influence by diversifying its sourcing base. For instance, a report in 2024 showed over 100 raw material suppliers.
Mary Kay benefits from low supplier switching costs, as cosmetic ingredients are often standardized. This ease of switching reduces suppliers' bargaining power. In 2024, the cosmetics industry saw over 2,000 ingredient suppliers, creating ample alternatives. This competitive landscape allows Mary Kay to negotiate favorable terms. The low switching cost enhances Mary Kay's profitability.
Impact on Product Differentiation is Low
Mary Kay's products don't heavily rely on unique ingredients, so supplier power is low. Branding and sales are key differentiators. This means suppliers of base materials have limited influence on Mary Kay's success. The focus is on the brand and sales, not the raw materials.
- Base ingredients are commodities.
- Marketing and branding are more crucial.
- Direct sales model reduces supplier impact.
- Suppliers lack leverage.
Mary Kay's Negotiating Power
Mary Kay, being a large cosmetics company, wields considerable power over its suppliers due to its substantial purchasing volume. This allows Mary Kay to negotiate favorable prices and terms. Suppliers are keen to keep Mary Kay as a client, ensuring a steady stream of revenue. This dynamic typically results in Mary Kay having a strong bargaining position. In 2024, the global cosmetics market was valued at approximately $500 billion, with Mary Kay holding a significant share, further amplifying its supplier leverage.
- High purchasing volume gives Mary Kay leverage.
- Suppliers are motivated to retain Mary Kay's business.
- Mary Kay can negotiate favorable terms.
- Market size supports Mary Kay's power.
Mary Kay's supplier power is low because of standard ingredients and many suppliers. They can easily switch suppliers due to the competitive landscape. Mary Kay's large purchasing volume gives it leverage, allowing it to negotiate favorable terms.
| Aspect | Details | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Options | Over 2,000 ingredient suppliers in 2024 | Lowers supplier bargaining power |
| Switching Costs | Low for standard cosmetic ingredients | Enhances Mary Kay's negotiation |
| Mary Kay's Size | Global cosmetics market ~$500B in 2024 | Increases leverage over suppliers |
Customers Bargaining Power
Individual customer spending on Mary Kay products is generally low, lessening the financial impact if a single customer stops buying. The customer base is broad and fragmented, which further dilutes the influence of any one customer. In 2024, Mary Kay's revenue was approximately $2.6 billion, indicating a diverse customer base. This wide distribution of sales diminishes the bargaining power of individual customers.
Customers in the cosmetics and skincare market wield significant power due to the vast array of choices available. Consumers can purchase products from department stores, drugstores, and direct sales companies, among others. The high availability of substitutes strengthens customer bargaining power. In 2024, the global beauty industry generated over $580 billion in revenue, highlighting the competitive landscape. This competition gives customers leverage to seek better deals and alternatives.
Customers of Mary Kay face low switching costs, making it easy to switch to competitors. This is because there are no significant costs or inconveniences associated with switching brands. This ease of switching gives customers considerable bargaining power. In 2024, the direct selling industry, which includes Mary Kay, saw over $35 billion in retail sales in the U.S., showcasing readily available alternatives.
Price Sensitivity
Cosmetics customers, armed with numerous choices, often exhibit price sensitivity. This reality pressures Mary Kay to offer competitive pricing to attract and retain customers. The emphasis on value—balancing cost with perceived quality—is crucial for customer loyalty within the cosmetics industry. In 2024, the global beauty market was valued at approximately $580 billion, highlighting the intense competition.
- Price comparisons are easy due to online shopping.
- Discount retailers offer alternative products.
- Customer loyalty is influenced by perceived value.
- Market competition is high.
Information Availability
Customers' bargaining power increases with readily available information. Online access to product reviews, tutorials, and price comparisons enables informed decisions. For example, in 2024, the global beauty and personal care market was valued at approximately $570 billion. This accessibility intensifies competition among cosmetic brands. This shift influences pricing and product strategies.
- Online reviews and comparisons are easily accessible.
- Customers can make informed choices.
- The beauty market was worth $570 billion in 2024.
- This intensifies competition.
Mary Kay's customer base is broad, with individual spending being low, reducing single-customer impact. The cosmetics market's vast options empower customers to seek better deals and alternatives. Switching costs are low, increasing customer bargaining power. In 2024, the global beauty market was valued at approximately $580 billion, intensifying competition.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Power | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Base | Fragmented, low individual spend | Mary Kay Revenue: ~$2.6B |
| Market Competition | High, many alternatives | Global Beauty Market: ~$580B |
| Switching Costs | Low, easy to switch brands | Direct Selling Sales (US): ~$35B |
Rivalry Among Competitors
The cosmetics industry, where Mary Kay operates, is fiercely competitive. Many companies fight for market share, including giants like L'Oréal and Estée Lauder. In 2024, the global beauty market was worth over $580 billion. Companies battle for shelf space, customer loyalty, and consultant recruitment.
Mary Kay's competitive landscape includes giants like L'Oréal, which reported over $40 billion in revenue in 2023, and Estée Lauder, with around $17 billion. This presence from both large and smaller brands fuels strong rivalry. The beauty industry's diverse segments each experience unique competitive pressures, impacting Mary Kay's strategic choices. The competition demands continuous innovation and effective market strategies.
Many cosmetic products, like those from L'Oréal and Estée Lauder, offer similar benefits and use comparable ingredients, intensifying competition. This similarity reduces product differentiation, pushing companies toward price competition to attract customers. For instance, in 2024, the global beauty market saw aggressive pricing strategies. Innovation in product formulas and marketing campaigns becomes vital for Mary Kay to distinguish itself. In 2024, the beauty industry's marketing spend was over $18 billion.
Aggressive Marketing and Promotions
Cosmetics companies aggressively use marketing and promotions to gain customers. Advertising, celebrity endorsements, and promotional pricing are common strategies. These tactics intensify competition in the cosmetics industry. For example, in 2024, L'Oréal spent over $10 billion on advertising and promotions globally. This level of spending reflects the high stakes in the market. These activities significantly increase competitive pressures.
- High marketing investments drive competition.
- Celebrity endorsements boost brand visibility.
- Promotional pricing attracts price-sensitive consumers.
- Competition is intensified by these efforts.
Consultant Recruitment
Multi-level marketing (MLM) firms like Mary Kay intensely compete to attract and keep independent beauty consultants. A robust and driven sales team is crucial for the sales model's success. The contest for consultants intensifies the competitive rivalry. According to recent data, the beauty and personal care market in the U.S. generated approximately $100 billion in 2024. This creates a high-stakes environment for consultant recruitment.
- MLM companies compete to recruit and retain consultants.
- Sales model success depends on a strong sales force.
- Competition for consultants adds to rivalry.
- The U.S. beauty market generated $100 billion in 2024.
Competition is high in the cosmetics industry, with many players vying for market share. L'Oréal and Estée Lauder are major competitors, impacting Mary Kay's strategic choices. The industry's diverse segments see unique pressures. Continuous innovation and effective marketing are crucial for success.
| Aspect | Details | Impact on Mary Kay |
|---|---|---|
| Market Size (2024) | Global beauty market value: Over $580 billion | High competition for customer spending. |
| Key Competitors (2023 Revenue) | L'Oréal: Over $40B, Estée Lauder: ~$17B | Direct competition for market share and consultant recruitment. |
| Marketing Spending (2024) | Industry marketing spend: Over $18B | Increased pressure for effective advertising and promotions. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Customers can easily switch to various beauty products, increasing the threat. These alternatives include established brands and emerging competitors, intensifying the pressure. The wide availability of substitutes, from drugstore finds to high-end options, limits Mary Kay's pricing power. In 2024, the global cosmetics market was valued at over $500 billion, showcasing the extensive range of alternatives available to consumers. This competition necessitates Mary Kay to constantly innovate and offer competitive value.
Switching from Mary Kay to a substitute is easy and cheap. Customers can easily try new brands. Low switching costs raise substitution risks. In 2024, the beauty industry's growth was 5%, with many alternatives. This makes it easier to switch.
Customers constantly assess the price-performance ratio of Mary Kay's offerings versus alternatives. Competitors like Avon and direct-to-consumer brands provide options. In 2024, the beauty industry saw a rise in affordable skincare, impacting premium brands. Value perception is critical; a lower-priced substitute with similar results can sway buyers. Mary Kay's need to justify its price point is crucial.
Changing Beauty Trends
Changing beauty trends pose a threat to Mary Kay. Shifting consumer preferences, such as the rise of natural skincare, can lead to substitution. Consumers might favor new products or approaches over traditional cosmetics. Mary Kay must adapt to remain relevant in the market. The global cosmetics market was valued at $280.7 billion in 2023, with projected growth to $346.8 billion by 2027.
- Natural and organic beauty product sales are increasing.
- Demand for personalized cosmetics is growing.
- Consumers are influenced by social media trends.
- The rise of direct-to-consumer brands.
Natural and Organic Alternatives
The rising popularity of natural and organic cosmetics poses a significant threat to Mary Kay. Consumers increasingly prefer these alternatives, potentially shifting away from traditional brands. To counter this trend, Mary Kay must adapt its product offerings and marketing strategies. Ignoring this could lead to market share loss and decreased profitability. In 2024, the global organic cosmetics market was valued at approximately $17.8 billion.
- Market shift towards natural and organic products.
- Risk of customers switching to alternatives.
- Need for Mary Kay to innovate its product line.
- Impact on market share and profitability.
The threat of substitutes in Mary Kay's market is high because of various beauty product options. Switching costs are low, making it easy for customers to try alternatives. The rise of natural cosmetics and changing trends increases the pressure on Mary Kay to adapt.
| Factor | Impact on Mary Kay | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Alternatives | Limits pricing power | Global cosmetics market: $500B+ |
| Switching Costs | Easy for customers | Beauty industry growth: 5% |
| Changing Trends | Requires adaptation | Organic cosmetics market: $17.8B |
Entrants Threaten
High capital requirements pose a significant barrier to entry in the cosmetics industry. New companies need substantial funds for R&D, manufacturing, and marketing. Achieving economies of scale quickly is challenging for new entrants. For example, L'Oréal's 2024 marketing expenses were over $10 billion, showcasing the financial hurdle. This financial commitment makes it difficult for new firms to compete.
Established cosmetics brands like L'Oréal and Estée Lauder boast considerable brand loyalty, making it tough for newcomers. In 2024, L'Oréal reported a global market share of around 14%, reflecting strong consumer preference. New entrants face significant hurdles in building brand recognition and trust. Overcoming this established loyalty requires substantial investment in marketing and product differentiation to attract consumers.
Accessing distribution channels presents a significant hurdle for new beauty product entrants. Mary Kay, with its direct sales force, has a well-established network. New brands often struggle to secure shelf space in retail, as seen with Ulta's 2024 focus on established brands. Innovative strategies like e-commerce and influencer marketing, which saw a 30% growth in 2024, are key for new players.
Regulations and Compliance
The cosmetics industry faces strict regulations on product safety and labeling, creating a barrier for new entrants. Compliance with these rules can be expensive and time-intensive, potentially deterring smaller companies. Navigating these regulatory hurdles adds complexity and cost, affecting the ease with which new firms can enter the market. In 2024, the FDA issued over 1,000 warning letters related to cosmetic products, highlighting the strict oversight.
- Compliance costs can range from $100,000 to over $1 million for new cosmetic brands.
- The average time to get a new cosmetic product approved is 6-12 months.
- Failure to comply with regulations can lead to fines and product recalls, which can cost the company millions of dollars.
- The FDA inspected over 4,000 cosmetic facilities in 2024, enforcing product safety standards.
Mary Kay's Strong Direct Sales Network
Mary Kay's extensive network of independent beauty consultants presents a formidable barrier to new competitors. This established direct sales model, crucial to Mary Kay's success, is difficult to replicate quickly. New entrants face significant challenges in building a comparable network and brand recognition. The need to invest heavily in recruitment, training, and support further deters potential rivals.
- The global cosmetics market was valued at USD 309.07 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 482.87 billion by 2032.
- Mary Kay operates in the direct sales channel, which often involves a more personalized customer experience.
- Building a direct sales force requires significant time, resources, and effective management to match Mary Kay's existing structure.
- The cosmetics market is highly competitive, with many established brands and evolving consumer preferences.
New entrants face considerable hurdles in the cosmetics market. High capital needs, like L'Oréal's $10B+ marketing spend in 2024, create financial barriers. Established brand loyalty, with L'Oréal holding ~14% global market share in 2024, poses a significant challenge.
| Barrier | Details | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Needs | R&D, marketing, manufacturing | High investment, slow ROI |
| Brand Loyalty | L'Oréal's 14% market share | Difficult to gain market share |
| Distribution | Retail shelf space access | Challenges in reaching customers |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
The Mary Kay analysis is built with financial statements, market research, and industry reports to understand the competitive landscape. Company websites and press releases add additional insights.