MTU Aero Engines Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
MTU Aero Engines Bundle
What is included in the product
Evaluates control held by suppliers and buyers, and their influence on pricing and profitability.
Quickly assess competitive forces with color-coded charts and graphs.
Preview the Actual Deliverable
MTU Aero Engines Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases MTU Aero Engines Porter's Five Forces analysis, a complete and ready-to-use document.
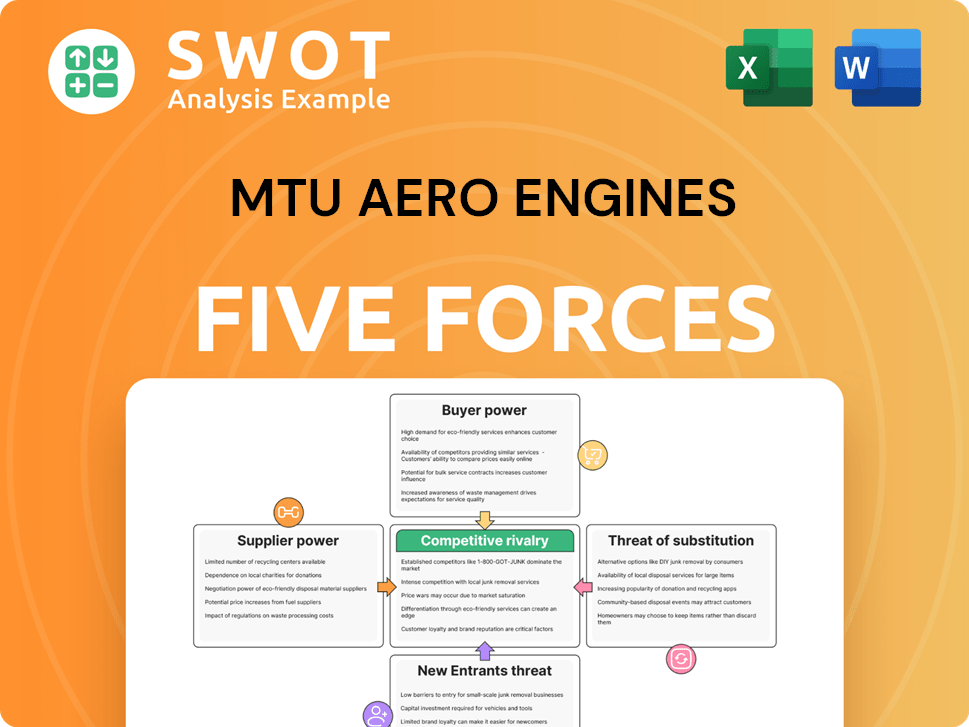
It examines competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, threat of substitutes, and threat of new entrants.
You're viewing the entire analysis, detailing each force's impact on MTU's industry position.
This in-depth document is fully formatted, ready for your review and strategic planning needs.
The analysis you see is exactly what you'll receive immediately after your purchase—no hidden content.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
MTU Aero Engines faces complex industry forces, with moderate supplier power due to specialized component needs.
Buyer power varies, influenced by airline consolidation and long-term service agreements.
The threat of new entrants is limited by high barriers to entry, including massive capital investments.
Substitute products, primarily other engine manufacturers, pose a moderate threat.
Intense rivalry among established players like Pratt & Whitney and Rolls-Royce defines the industry.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore MTU Aero Engines’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
MTU Aero Engines faces challenges because the aerospace engine industry depends on a few specialized suppliers. These suppliers, providing critical components like engines and avionics, hold considerable pricing power. For instance, in 2024, the global aerospace parts market was valued at approximately $200 billion, with a few key suppliers dominating. This concentration allows them to influence prices and terms, impacting MTU's costs. This dynamic can squeeze MTU's profit margins, especially during periods of high demand or supply chain disruptions.
High switching costs significantly bolster supplier power. MTU's specialized engine technologies and lengthy integration processes create substantial barriers for customers. Boeing's investment in supplier tech, as of 2024, averaged $500 million per aircraft model, making switching suppliers costly. This dynamic grants suppliers considerable leverage in negotiations.
MTU Aero Engines faces supplier pricing control, especially for specialized components. Limited sources and raw material price hikes, like the 2024 surge in titanium costs, boost supplier leverage. This can directly impact MTU's production expenses. In 2024, raw material costs increased by 10-15% due to supply chain issues. This increased operational costs.
Long-term contracts
Long-term contracts with suppliers can help MTU Aero Engines manage costs and ensure a steady supply of necessary components. Such contracts often include agreed-upon pricing, which offers some protection against short-term price volatility. Still, these agreements might not fully offset the impact of significant raw material price hikes or unforeseen cost increases, as seen in 2023 when many aerospace suppliers faced rising expenses. For example, in 2024, Boeing experienced supply chain issues that caused production delays and cost overruns.
- Secures pricing and supply over extended periods.
- May not fully protect against raw material price fluctuations.
- Can mitigate supplier power to some extent.
- Offers some protection against short-term price volatility.
Global supply chain risks
MTU Aero Engines faces global supply chain risks. These risks stem from dependencies that can affect component availability and pricing. Managing and diversifying supply chains is crucial for companies like MTU. The COVID-19 pandemic revealed vulnerabilities in supply chains, impacting various industries.
- In 2023, supply chain disruptions cost businesses an estimated $2.4 trillion globally.
- MTU's reliance on specific suppliers for critical engine components increases its vulnerability.
- Diversification of suppliers can mitigate risks associated with geopolitical tensions or economic downturns.
MTU Aero Engines contends with supplier power due to concentrated markets and high switching costs. Specialized suppliers, controlling essential components, exert significant pricing power, impacting MTU's profit margins. Raw material price hikes, like a 10-15% increase in 2024, further enhance supplier leverage.
| Aspect | Impact | Data (2024) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Market Concentration | Supplier Pricing Power | Aerospace parts market: $200B | |
| Switching Costs | Supplier Negotiation Power | Boeing's tech investment: $500M/model | |
| Raw Material Prices | Increased Operational Costs | Titanium cost surge in 2024 |
Customers Bargaining Power
Major airlines, MTU Aero Engines' key customers, wield substantial bargaining power. They place massive orders, allowing them to negotiate advantageous pricing and terms. For instance, in 2024, discounts on engine maintenance contracts could significantly impact MTU's revenue. This negotiation strength stems from the airlines' ability to switch engine suppliers.
High competition in the aircraft engine market, including players like Rolls-Royce and General Electric, boosts customer influence. This rivalry gives airlines, the primary customers, significant leverage. For instance, in 2024, Airbus and Boeing's duopoly intensifies this dynamic, increasing customer bargaining power.
MTU Aero Engines faces customer bargaining power due to customization demands. Customers' need for tailored engine solutions boosts their negotiating strength. This requires MTU to be adaptable, impacting pricing and profitability. In 2024, customization accounted for 20% of MTU's engine orders.
Purchase volume impact
Purchase volume greatly influences customer bargaining power, meaning bigger orders often get better deals. This is especially true in commercial aviation, where airlines frequently place substantial fleet orders. For instance, in 2024, major airlines like United and Delta placed large orders, affecting pricing negotiations. These bulk purchases give customers leverage.
- Large fleet orders boost customer bargaining strength.
- Airlines' bulk purchases influence pricing.
- 2024 saw significant orders impacting negotiations.
Financing options
Customer bargaining power in the context of financing significantly affects MTU Aero Engines. The availability and terms of financing options influence customer decisions, impacting their choices. Attractive financing, either offered directly or facilitated by MTU, can strengthen its competitive edge in the market. This is particularly relevant in the aerospace industry, where large-scale purchases are common.
- Financing Options Impact: Favorable financing terms boost purchasing decisions.
- Competitive Advantage: Offering attractive financing enhances MTU's market position.
- Industry Relevance: High-value purchases in aerospace rely on financing.
Airlines' substantial orders enable strong pricing negotiations with MTU Aero Engines. Competition among engine manufacturers and the Airbus/Boeing duopoly amplify customer influence. Customization demands also boost airline bargaining power, affecting MTU's profitability.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Order Volume | Influences Pricing | United, Delta placed large orders, affecting pricing. |
| Customization | Boosts Bargaining | Customization accounted for 20% of engine orders. |
| Financing Terms | Affects Choices | Attractive financing strengthens market position. |
Rivalry Among Competitors
The aerospace industry faces fierce rivalry, especially among Boeing, Airbus, and engine makers. MTU competes with GE Aviation and Rolls-Royce, driving innovation. In 2024, the global aerospace market was valued at $838 billion. This competition impacts pricing and market share dynamics.
Price competition significantly affects MTU Aero Engines, especially in large projects and defense contracts. Intense pricing strategies can pressure profit margins, impacting profitability. For instance, in 2024, defense contracts accounted for a notable portion of MTU's revenue. This highlights the impact of price wars. The company's operating profit margin was 13.6% in 2023.
Continuous innovation and technological advancements fuel intense rivalry among engine manufacturers. Companies like MTU Aero Engines invest significantly in R&D. For example, in 2023, MTU's R&D expenses reached €759 million, underscoring the commitment to developing advanced engine technologies. This focus on innovation drives competition.
Aftermarket services competition
The aftermarket services sector, encompassing maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO), presents significant competitive rivalry. MTU competes against both original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and independent MRO providers, fighting for market share. Differentiation hinges on service quality, turnaround time, and cost-effectiveness. The global MRO market was valued at approximately $85.8 billion in 2023, demonstrating substantial competition.
- MTU's aftermarket revenue was a significant portion of its total revenue in 2024.
- Independent MRO providers often offer competitive pricing.
- OEMs leverage their original design expertise in MRO.
- Turnaround time is critical for airline operational efficiency.
Market share concentration
The turbofan engine market exhibits significant concentration, with a few dominant companies controlling a substantial market share. This concentration fuels fierce competition among the key players, such as MTU Aero Engines, which directly impacts pricing and innovation strategies. In 2024, the top three engine manufacturers held over 80% of the market share. This dynamic environment necessitates continuous adaptation and strategic positioning for MTU.
- High concentration intensifies competition.
- Top 3 manufacturers control over 80% market share in 2024.
- MTU must strategically adapt.
Competitive rivalry in the aerospace industry is fierce. MTU Aero Engines faces strong competition, especially in pricing and innovation. The concentration of the turbofan engine market intensifies the competition. In 2024, the global aerospace market was valued at $838 billion, showcasing the scale of competition.
| Aspect | Details | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Market Value | Global Aerospace Market | $838 billion |
| R&D Spend | MTU R&D Expenses (2023) | €759 million |
| MRO Market | Global MRO Market (2023) | $85.8 billion |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Electric and hybrid aircraft present a growing threat as the aviation industry focuses on emissions reduction. Airbus is investing in electric models, aiming for a substantial market share by 2040. Research indicates the electric aircraft market could reach $48.7 billion by 2032. This shift could impact MTU's core engine business over time.
The rise of sustainable technologies poses a threat. Environmental regulations and industry goals drive the adoption of alternative propulsion systems. The aviation sector targets a substantial reduction in carbon emissions by 2050. The market for sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) is projected to reach $15.8 billion by 2028. This shift could impact demand for traditional engines.
Alternative transportation, like high-speed rail, poses a threat to MTU Aero Engines. Efficient rail networks can diminish demand for shorter flights. For example, in 2024, high-speed rail saw increased ridership, especially in Europe. This shift impacts engine demand for regional jets. MTU must monitor rail developments to adapt its strategy.
Advanced materials
Advanced materials, such as composites, pose a threat as they enhance aircraft efficiency, potentially reducing the demand for new engines. These materials contribute to lighter and more fuel-efficient aircraft designs. The adoption of advanced materials can extend the lifespan of existing engines. This can reduce the need for engine replacements or upgrades.
- In 2024, the global composite materials market was valued at approximately $97 billion.
- The use of composites can reduce aircraft weight by up to 30%, improving fuel efficiency.
- Lighter aircraft can lead to operational cost savings of up to 20% in fuel expenses.
- MTU's competitors, like GE, are actively investing in composite technologies.
Improved engine efficiency
Improved engine efficiency presents a key factor in mitigating the threat of substitutes for MTU Aero Engines. Continued advancements in traditional engine technology, such as those seen in the latest engine designs, enhance competitiveness. These improvements, focused on fuel consumption and overall performance, reduce the immediate need for airlines to adopt entirely new propulsion systems. This strategy helps MTU maintain its market position by optimizing current engine capabilities.
- MTU's focus on sustainable aviation fuels (SAF) and efficiency gains.
- Investment in advanced engine technologies like the GTF (Geared Turbofan) engine.
- Reduction in fuel consumption by up to 16% with GTF engines.
- Partnerships with airlines to test and implement fuel-saving measures.
The threat of substitutes for MTU Aero Engines is multifaceted, ranging from electric aircraft to high-speed rail. Alternative propulsion systems and advanced materials also present challenges to traditional engine demand. These factors drive the need for MTU to innovate.
| Substitute | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Aircraft Market | Potential decline in demand for traditional engines. | Market expected to reach $48.7B by 2032. |
| Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) | Shifts demand and impacts engine technology. | SAF market projected to hit $15.8B by 2028. |
| High-Speed Rail | Reduces demand for shorter flights. | Increased ridership in Europe. |
Entrants Threaten
The aerospace engine sector demands considerable upfront capital, acting as a major hurdle for new companies. Significant investments are crucial for specialized equipment, research and development, and meeting rigorous industry standards. For example, in 2024, MTU Aero Engines allocated a substantial portion of its budget to R&D, highlighting the financial commitment needed. This financial burden limits new entrants, as evidenced by the dominance of established players.
Deep technological expertise in core engine components is crucial, posing a significant barrier for newcomers. MTU's intellectual property and long-standing experience offer a strong advantage. New entrants face challenges due to the complexity and high costs of replicating this expertise.
Stringent regulations and certification processes represent a substantial barrier to entry for new competitors in the aerospace industry. Meeting aviation safety standards and environmental requirements demands considerable time and financial investment. For example, obtaining FAA certification for a new aircraft engine can take several years and cost hundreds of millions of dollars. These high compliance costs and lengthy processes significantly deter new entrants, protecting established players like MTU Aero Engines.
Established relationships
Established relationships are a significant hurdle for new entrants in the aero engine market. MTU Aero Engines, for example, benefits from long-standing partnerships with major airlines and aircraft manufacturers. These existing alliances often involve risk-sharing agreements, which solidify the bonds. Newcomers find it challenging to compete with these established collaborations, as these relationships are built on trust and proven performance. This makes it tough to break into the market.
- MTU's partnerships with Airbus and Pratt & Whitney are examples of established relationships.
- Risk-sharing agreements provide financial stability and shared commitment.
- New entrants face high switching costs for customers.
- These relationships often span decades, creating a barrier.
Supply chain complexity
The aerospace supply chain is incredibly complex, posing a significant barrier to new entrants. Established companies, like MTU Aero Engines, have decades of experience navigating this intricate network, giving them a considerable advantage. New entrants struggle to replicate these established networks, which impacts reliability and cost-effectiveness. Building these supplier relationships takes time and significant investment, creating a substantial hurdle.
- MTU Aero Engines benefits from its long-standing supplier relationships.
- New entrants face challenges in building efficient supply chains.
- Supply chain complexity increases entry barriers.
High capital requirements deter new entrants; MTU's R&D spending in 2024 reflects this. Complex tech and IP create barriers; MTU's expertise is a strong defense. Strict regulations and certifications also increase the costs. All of these are the main problems for the new entrants.
| Barrier | Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Needs | High upfront costs | R&D spending by MTU. |
| Technical Expertise | Difficult to replicate | MTU's IP advantage. |
| Regulations | Long, costly processes | FAA certification costs. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
We gather data from MTU's annual reports, industry news, competitive analyses, and market share databases for a detailed view.