Tesco Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Tesco Bundle
What is included in the product
Evaluates control held by suppliers and buyers, and their influence on pricing and profitability.
Instantly grasp Tesco's competitive landscape, visualizing threats and opportunities.
What You See Is What You Get
Tesco Porter's Five Forces Analysis
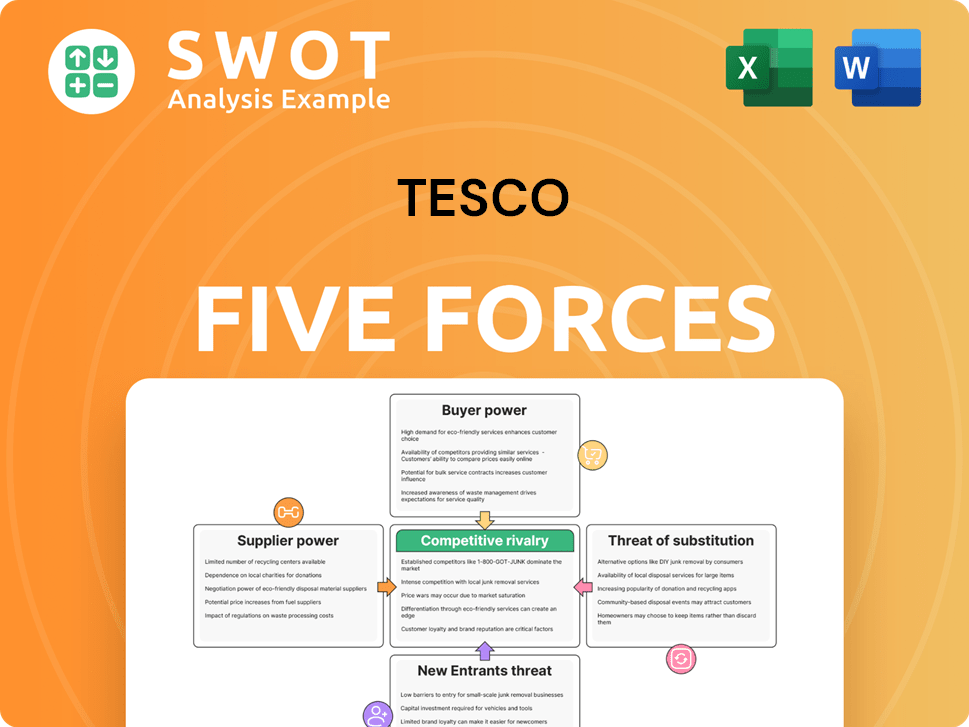
This preview details Tesco's Porter's Five Forces analysis; it's the document you'll receive. The analysis examines competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, threat of substitutes, and threat of new entrants. Each force's impact on Tesco is assessed, offering strategic insights. This document is complete and ready for immediate use after purchase.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
Tesco faces intense competition in the UK grocery market, battling powerful buyers (consumers) demanding low prices and high quality. Supplier power, particularly from large food producers, impacts margins. The threat of new entrants remains moderate, with high setup costs. Substitute products, like online delivery services and discounters, create pressure. Competitive rivalry, fueled by established players like Sainsbury's and Asda, is fierce.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Tesco’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Tesco's vast size gives it considerable bargaining power over suppliers. This allows Tesco to secure better pricing and terms, which can squeeze supplier profit margins. For instance, in 2024, Tesco's revenue was approximately £68 billion. However, suppliers of unique items may have increased power.
Switching suppliers presents challenges and expenses for Tesco, particularly for essential products. This complexity grants certain suppliers leverage, as Tesco is less inclined to switch often. For example, in 2024, Tesco's cost of goods sold was approximately £47 billion, highlighting the significant impact of supplier pricing. High switching costs can lead to supplier power.
Tesco's wide range of own-brand products intensifies competition for suppliers. This strategy significantly diminishes supplier power, as Tesco can prioritize its own labels. In 2024, own-brand sales accounted for a substantial portion of Tesco's revenue, approximately 30%. This gives Tesco greater control, as it can easily substitute supplier products. This impacts supplier pricing and market share.
Global sourcing options
Tesco's global sourcing significantly boosts its bargaining power with suppliers. This means Tesco can find products worldwide, negotiating better prices and terms. This reduces dependence on any single supplier or region, enhancing its control. For instance, in 2024, Tesco sourced products from over 70 countries, diversifying its supply chain.
- Global presence allows Tesco to switch suppliers easily.
- Negotiating leverage is increased by having multiple sourcing options.
- Tesco can leverage volume purchasing to get favorable terms.
- Reduces the impact of any single supplier's price hikes.
Supplier dependence on Tesco
Some suppliers are very reliant on Tesco for a large chunk of their revenue. This reliance weakens their ability to negotiate, making them more likely to agree to Tesco's conditions to keep the business going. In 2024, Tesco's revenue was approximately £68 billion, showing its significant market presence. This size gives Tesco substantial leverage over suppliers.
- Tesco's vast scale allows it to dictate terms.
- Smaller suppliers are at a disadvantage.
- Dependence limits the ability to raise prices.
- Tesco can switch suppliers if needed.
Tesco's size gives it supplier bargaining power, securing better prices. Reliance on Tesco weakens supplier negotiation strength. Global sourcing and own brands further diminish supplier influence.
| Factor | Impact | Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Tesco's Size | Strong Bargaining Power | £68B Revenue |
| Supplier Reliance | Reduced Negotiation | Significant for many |
| Own Brands | Increased Control | ~30% of Sales |
Customers Bargaining Power
Tesco faces high customer bargaining power due to ample choices. Customers can easily swap to rivals like Sainsbury's or Aldi. In 2024, online grocery sales continue to grow, further boosting customer options. This intensifies price and service competition for Tesco.
Price sensitivity significantly impacts Tesco, particularly with economic pressures. The rising cost of living in the UK, with inflation rates fluctuating around 4% in early 2024, makes consumers highly price-conscious. To stay competitive, Tesco often runs promotions, like "Clubcard Prices," which in 2023, provided discounts to millions of members. This strategy increases customer bargaining power, as consumers can easily switch to cheaper alternatives, such as Aldi or Lidl, if Tesco's prices are not competitive.
Customers' ability to compare prices and product details online strengthens their bargaining power. This information access, through platforms like price comparison websites, allows them to seek better deals. For instance, in 2024, online grocery sales in the UK reached £18.6 billion, showing the impact of easy information access on consumer choices and Tesco's need to compete on value.
Loyalty programs
Tesco's Clubcard, while designed to boost customer retention, simultaneously strengthens customer power. Personalized offers and rewards allow customers to lower their spending, enhancing their bargaining position. This strategy gives customers the ability to choose where to shop based on the best deals. For instance, in 2024, Tesco reported that Clubcard holders represented a significant portion of sales, showing its impact on customer behavior.
- Loyalty programs provide personalized offers and rewards.
- Customers can reduce their overall spending.
- This increases customer's perceived bargaining power.
- Tesco Clubcard holders represented a significant portion of sales in 2024.
Switching costs are low
Customers of Tesco face low switching costs, making it easy to change supermarkets. This ease gives customers significant power, as they can quickly shift to competitors offering better prices or experiences. In 2024, the UK grocery market saw intense competition, with price wars impacting profit margins. This dynamic underscores how easily customers can move their business, influencing Tesco's strategies.
- Price sensitivity drives customer choices.
- Convenience and location play key roles.
- Loyalty programs offer some retention.
- Digital platforms enhance comparison shopping.
Customer bargaining power at Tesco is high due to easy switching. Price sensitivity is key, amplified by inflation, around 4% in early 2024. Online comparison shopping and loyalty programs, like Clubcard, also boost customer power.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | High | UK inflation ~4% |
| Switching Costs | Low | Easy supermarket swaps |
| Online Sales | Growing | £18.6B in UK |
Rivalry Among Competitors
The UK grocery market is fiercely competitive. Tesco faces strong rivals, including Sainsbury's, Asda, and Morrisons. This competition demands Tesco's constant innovation. In 2024, Tesco's market share was around 27%, closely contested by its rivals.
Price wars significantly affect supermarkets, decreasing profit margins. Tesco faces continuous pressure to monitor and respond to competitor pricing. In 2024, Tesco's operating profit margin was around 4.5%, reflecting these competitive pressures. Constant adjustments to pricing strategies impact Tesco's profitability.
Competitors are increasingly differentiating themselves. For example, Aldi and Lidl focus on low prices. Waitrose emphasizes premium products and customer service. In 2024, Tesco's revenue reached approximately £68 billion. To compete, Tesco must innovate its offerings, such as its Clubcard loyalty program, to maintain market share.
Market consolidation
Market consolidation significantly impacts competitive rivalry. Mergers and acquisitions within the supermarket sector can heighten competition substantially. This consolidation could provide competitors with better economies of scale and increased bargaining power, which presents challenges for Tesco. For example, in 2024, Sainsbury's and Asda's combined market share was around 30%, intensifying the competitive landscape.
- Mergers and acquisitions change the competitive balance.
- Consolidation leads to economies of scale.
- Increased bargaining power challenges Tesco.
- Market share shifts indicate rivalry intensity.
Online competition
The online grocery market intensifies competitive rivalry for Tesco. The rise of online retailers like Ocado and Amazon Fresh presents a direct challenge. Tesco needs to strengthen its online presence. This requires investment in its digital platform and delivery infrastructure.
- In 2024, online grocery sales accounted for approximately 12% of the total UK grocery market.
- Ocado's revenue for 2023 was £2.7 billion, reflecting strong online demand.
- Amazon Fresh continues to expand its delivery services, increasing competition.
- Tesco's online sales grew by 8.6% in the first half of 2024, indicating ongoing efforts.
The UK grocery market is highly competitive, with Tesco facing strong rivals. Price wars and margin pressures are constant challenges. Competitors differentiate through pricing and product focus, requiring Tesco to innovate. Online grocery services intensify rivalry, demanding digital investments.
| Metric | 2023 Data | 2024 (Projected/Partial) |
|---|---|---|
| Tesco Market Share | 27% | ~27% |
| Tesco Operating Margin | 4.2% | ~4.5% |
| Online Grocery Market Share | 11% | ~12% |
| Ocado Revenue | £2.7B | Not Available Yet |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Discount retailers such as Aldi and Lidl present a considerable threat by offering lower prices. In 2024, Aldi and Lidl's combined UK market share reached approximately 18%, drawing price-conscious consumers. This directly impacts Tesco's sales, as customers may opt for cheaper alternatives. Tesco's efforts to compete include price matching and expanding its value ranges.
Convenience stores pose a threat to Tesco, offering quick shopping experiences. They appeal to customers valuing speed, even if prices are higher. In 2024, the UK convenience store market was estimated at £46.3 billion. This sector's growth rate was around 2.5% in the same year.
Ready-meal services and meal-kit delivery companies are growing substitutes for grocery shopping. These services offer convenience and save time for busy consumers. The global meal kit market was valued at $13.7 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach $23.2 billion by 2028, reflecting this shift.
Restaurants and takeaways
Restaurants and takeaway services pose a threat to Tesco as substitutes for home cooking. The convenience and variety offered by these options can draw consumers away from grocery shopping. The UK's food service market, including restaurants and takeaways, generated approximately £94.6 billion in 2023. This competition impacts Tesco's sales by offering ready-made meal alternatives.
- UK food service market generated £94.6 billion in 2023.
- Takeaway and restaurant options compete directly with Tesco's grocery sales.
- Consumer preference for convenience influences demand for substitutes.
Specialty food stores
Specialty food stores pose a threat to Tesco by offering differentiated products and shopping experiences. These stores, including butchers and farmers' markets, appeal to customers seeking unique or high-quality items. They can draw customers away from Tesco, particularly those willing to pay a premium for specialized goods. In 2024, the UK's specialty food market saw steady growth, with an estimated value of £10 billion. This competition necessitates Tesco to innovate and enhance its offerings to retain its customer base.
- Specialty stores offer unique, high-quality products.
- They attract customers seeking specific items or experiences.
- This can divert sales from Tesco's offerings.
- The UK specialty food market was worth £10 billion in 2024.
Tesco faces substitution threats from various retail formats. Discount retailers like Aldi and Lidl, with an 18% UK market share in 2024, offer lower prices. Convenience stores, valued at £46.3 billion in 2024, also compete.
| Substitute | Market Value (2024) | Impact on Tesco |
|---|---|---|
| Discount Retailers | Significant, ~18% UK market share | Price competition, loss of customers |
| Convenience Stores | £46.3 billion | Offers quick shopping, higher prices |
| Meal Kits | $13.7 billion (2023, global) | Convenience, saves time |
Entrants Threaten
The supermarket industry demands substantial capital, including real estate, distribution networks, and initial inventory. This high initial investment discourages new competitors. For example, in 2024, setting up a major supermarket chain could require an initial investment of hundreds of millions of dollars.
Tesco benefits from established brand loyalty, making it tough for new supermarkets to gain customers. The cost of building a brand and attracting customers is significant. In 2024, Tesco's market share in the UK grocery market was approximately 27%, highlighting its strong customer base. New entrants face the hurdle of overcoming this established customer preference.
Established supermarkets like Tesco leverage economies of scale, offering lower prices. In 2024, Tesco's operating margin was around 4.1%, reflecting cost efficiencies. New entrants, facing higher initial costs, find it hard to compete on price. This advantage, seen in Tesco's 2024 revenue of £61.5 billion, creates a significant barrier.
Regulatory hurdles
Regulatory hurdles pose a significant threat to new entrants in the supermarket industry. Compliance with food safety standards and obtaining planning permissions are complex and time-consuming processes. These requirements can delay market entry and increase initial costs, deterring potential competitors. For instance, in 2024, the average time to secure necessary permits in the UK was approximately 6-12 months. This regulatory burden favors established players like Tesco, who have the resources to navigate these challenges.
- Compliance costs: 2024 data shows that new entrants face significant upfront costs for meeting food safety standards, which can be up to £500,000.
- Permitting delays: The average time to secure necessary permits and planning permissions in the UK in 2024 was between 6-12 months.
- Legal complexities: Navigating the legal landscape often requires specialized legal teams, adding to the overall expenses.
- Market impact: These hurdles make it difficult for smaller or new businesses to compete effectively.
Intense competition deters entry
The UK grocery market is fiercely competitive, presenting a significant barrier to new entrants. Established players like Tesco, with a market share around 27% as of early 2024, fiercely protect their positions. This aggressive defense often involves price wars and promotional activities, making it difficult for newcomers to compete. Potential entrants also face high capital costs for establishing stores and supply chains.
- Tesco's UK market share was approximately 27% in early 2024.
- The UK grocery market is dominated by a few major players.
- Price wars and promotions are common strategies to defend market share.
- High capital investment is required for new entrants.
The supermarket sector's high entry barriers, like substantial capital needs and brand loyalty, deter new entrants. Tesco's strong market position, with a 27% UK share in early 2024, also hinders newcomers. Regulatory hurdles, such as compliance costs up to £500,000, further limit competition.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | High initial costs | Hundreds of millions of dollars to start |
| Brand Loyalty | Established customer base | Tesco's 27% UK market share |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Delays and expenses | Compliance costs up to £500,000 |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
This Porter's Five Forces analysis is built using Tesco's annual reports, market research, and competitor analysis.