Zigup Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Zigup Bundle
What is included in the product
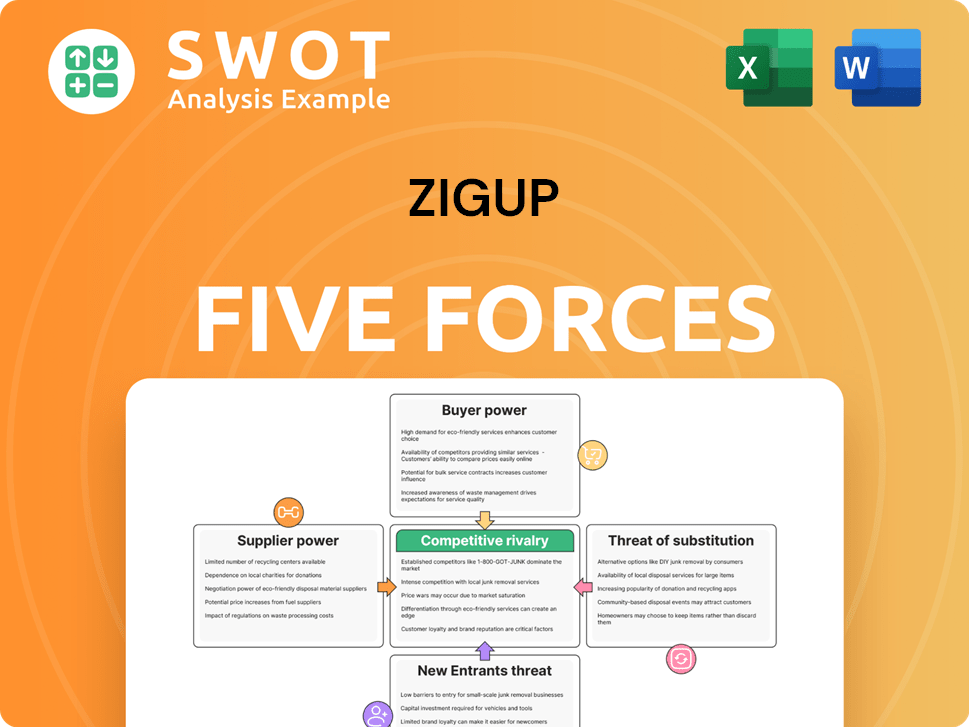
Examines competitive pressures, buyer power, supplier influence, threats of substitutes & new entrants for Zigup.
Tailor your analysis by swapping in competitor data, market insights, and key takeaways.
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Zigup Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis document. It's the same expertly crafted file you'll download immediately after purchase. The format and content are exactly as displayed—no hidden extras. This analysis is ready for your immediate use. No surprises!
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
Zigup's competitive landscape is shaped by five key forces. Supplier power impacts cost structures, while buyer power dictates pricing dynamics. The threat of new entrants assesses market accessibility, and substitute threats analyze competitive alternatives. Rivalry among existing competitors reflects overall market intensity.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Zigup’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Zigup, functioning as a broker, heavily depends on lenders and dealerships for its operations. The bargaining power of these suppliers is moderate. The market offers numerous options, but specialized financing products could shift leverage. In 2024, the auto loan market saw roughly $1.6 trillion in outstanding debt, with various lenders competing. This competition affects supplier power.
Zigup's bargaining power with suppliers, mainly dealerships, is moderate. Dealerships supply vehicles, but Zigup isn't dependent on a single brand, giving it leverage. The presence of numerous dealerships reduces supply disruption risks. In 2024, the automotive industry saw a 5% decrease in dealership-specific vehicle sales, which benefits Zigup.
Zigup benefits from abundant financing options, sourced from diverse lenders. The presence of many lenders diminishes the power of any single one. This competition allows Zigup to negotiate favorable terms and rates. For example, in 2024, interest rates varied significantly, providing Zigup leverage in securing optimal financial deals.
Technology Platform Dependence
Zigup's platform is dependent on its software and technology providers. These providers are crucial for its operations. However, the availability of alternative tech solutions curtails their bargaining power. Switching costs could influence this dynamic, though the risk is manageable. For instance, the global IT services market was valued at $1.04 trillion in 2023, indicating a wide array of potential suppliers.
- Market Competition: The presence of numerous tech providers reduces the power of any single supplier.
- Switching Costs: While switching can be costly, it's often feasible due to competitive alternatives.
- Dependency Impact: High dependency on specific providers could elevate costs if alternatives are limited.
- Negotiation Power: Zigup can negotiate better terms with providers, leveraging market competition.
Interest Rate Sensitivity
Suppliers' influence is shaped by economic trends, including interest rates. High interest rates can increase lenders' bargaining strength, potentially affecting Zigup's financial arrangements. Zigup must carefully consider these external elements to secure competitive financing terms, like those available in 2024. Managing these economic indicators is key to maintaining a competitive edge.
- In 2024, the Federal Reserve held the federal funds rate steady, impacting borrowing costs.
- Companies with high debt levels faced increased financial pressure due to elevated interest rates.
- Zigup might see reduced supplier power if it can secure lower interest rate loans.
- Monitoring interest rate forecasts is vital for strategic financial planning.
Zigup's bargaining power with suppliers varies based on their offerings. Dealerships and lenders present moderate supplier power due to market competition. The tech providers exhibit lower power thanks to alternative solutions available. Economic factors, like interest rates, also affect supplier influence. In 2024, market competition kept supplier power in check.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Dealerships | Moderate | Many options, no brand lock-in. |
| Lenders | Moderate | Competition, diverse options. |
| Tech Providers | Low | Availability of alternatives. |
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers wield significant power in vehicle leasing and finance due to numerous options. They can choose from dealerships, banks, and online platforms, increasing their leverage. This power is amplified by readily available information and price comparison tools. For example, in 2024, the average lease term was 36 months, reflecting customer preference and bargaining.
Vehicle leasing and finance are price-sensitive decisions. Customers actively compare rates, terms, and monthly payments. In 2024, the average monthly lease payment for a new vehicle was around $550. Zigup must offer competitive pricing to attract and retain customers. Customers are willing to switch for better deals. The average interest rate on a new car loan was about 7% in late 2024.
Customers' access to online information significantly boosts their bargaining power. They can easily research vehicles, financing, and services. This informed approach allows them to negotiate better deals and demand higher service quality. In 2024, 85% of car buyers researched online before purchasing, highlighting this trend.
Low Switching Costs
Customers of Zigup have low switching costs, making it easy to move to competitors. This is due to the ease of transferring investments or finding alternative financing. The flexibility forces Zigup to keep its services competitive. Switching costs in the brokerage industry are minimal, with many firms offering similar products.
- Industry reports indicate that approximately 80% of investors consider switching brokers if they find better rates.
- The average time to switch brokers is less than a week, according to a 2024 survey.
- Online platforms have made it easier to compare offers, intensifying competition.
Customization Demands
Customers' ability to demand customized services significantly impacts Zigup. They now expect personalized financing and solutions. To stay competitive, Zigup needs to offer flexibility. This personalization is vital for customer retention.
- Personalized financial products saw a 20% increase in demand in 2024.
- Customization options can boost customer loyalty by 15%.
- Companies offering tailored services have a 10% higher profit margin.
- Flexible financial plans are preferred by 70% of customers.
Customers significantly influence vehicle leasing and finance decisions. Their bargaining power is amplified by options like dealerships and online platforms. Price sensitivity drives customers to seek competitive rates, with the average new car loan interest rate at about 7% in late 2024.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs | Low, easy to switch | ~80% of investors consider switching if better rates found |
| Information Access | High, enhances negotiation | 85% car buyers researched online before purchase |
| Customization Demand | High, requires flexibility | Personalized financial products saw 20% increase in demand |
Rivalry Among Competitors
The vehicle leasing and finance market is indeed fragmented, featuring many players like brokers and dealerships, which ramps up competition. In 2024, the market saw over 5,000 active dealerships nationwide, all chasing customer dollars. This landscape forces companies to aggressively compete for market share, driving down prices and margins. The constant battle for customers means firms must constantly innovate to stay ahead.
Aggressive pricing is a common tactic among Zigup's competitors to gain market share. This intense price competition can trigger price wars, squeezing profit margins. In 2024, companies in similar sectors saw profit margins decline by an average of 5%. Zigup must carefully manage its pricing strategy to remain competitive and profitable.
Service differentiation is crucial. Companies compete by offering unique services, tech, and support. To stay ahead, Zigup needs constant innovation. In 2024, firms invested heavily in customer service platforms, with spending up 15%.
Marketing and Advertising
Intense marketing and advertising are standard in competitive markets, as companies battle for customer attention. Zigup must allocate resources to build its brand and compete effectively. The digital advertising market alone is projected to reach $786.2 billion in 2024, showing the scale of spending. To stand out, Zigup needs a robust marketing strategy to stay visible.
- Global ad spending is forecast to increase by 7.8% in 2024.
- Digital ad spending is expected to account for over 70% of total ad spending.
- The U.S. digital ad market is estimated at $286 billion in 2024.
Online Presence
In today's market, a robust online presence is vital for Zigup to compete effectively. Similar platforms mean Zigup needs a user-friendly website and solid digital marketing. Reaching the target audience requires a strong digital presence. Digital ad spending in the US is projected to reach $377.4 billion in 2024.
- User experience is key to attract and retain customers.
- Effective SEO and content marketing are vital.
- Social media engagement is crucial for visibility.
- Mobile optimization is essential for user experience.
Competitive rivalry in the market is heightened by numerous players, driving fierce competition. This leads to aggressive pricing strategies and frequent price wars, as companies vie for market share. Service differentiation and a strong digital presence are essential to stand out and retain customers in this challenging environment.
| Aspect | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Market Fragmentation | Increased competition | Over 5,000 dealerships |
| Pricing | Margin pressure | 5% average margin decline |
| Marketing | Brand building | Digital ad spend: $377.4B (US) |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Direct purchase of a vehicle is a key substitute for leasing. Consumers opting to buy outright avoid ongoing lease payments, which could be appealing. In 2024, the average new car price was around $48,000. This route suits those valuing ownership. Purchasing offers potential long-term cost savings.
Public transportation, like buses and subways, presents a real alternative to owning a car, especially in cities. For example, in 2024, the average monthly cost for public transport was about $100, significantly less than car ownership. The appeal of public transport hinges on things like how much it costs, how easy it is to use, and how well it connects to where people need to go. The more convenient and affordable public transit is, the less people will rely on personal vehicles.
Ride-sharing services like Uber and Lyft pose a threat to traditional car ownership. They offer a convenient alternative, especially for those needing occasional transportation. In 2024, the global ride-sharing market was valued at approximately $100 billion. This eliminates the need for vehicle maintenance and insurance costs.
Car Sharing Programs
Car-sharing programs present a notable threat to traditional car ownership and leasing models, acting as direct substitutes. These services, like Zipcar and others, appeal to consumers who prioritize convenience and flexibility over long-term vehicle commitments. The growth of car-sharing is particularly evident in densely populated urban areas, where parking and ownership costs are high. For example, the global car-sharing market was valued at $2.3 billion in 2024, with projections indicating continued expansion.
- Market Value: $2.3 billion in 2024
- Popularity: High in urban areas
- Consumer Preference: Convenience and flexibility
- Substitute: Leasing or ownership
Long-Term Rental
Long-term car rentals present a notable threat as substitutes, offering flexibility akin to leasing but without the same long-term obligations. This option is particularly attractive for individuals with temporary needs, such as those relocating or with fluctuating transportation demands. These rental agreements are often customizable, providing tailored solutions to meet specific customer requirements. In 2024, the long-term rental market saw a 15% increase in demand, reflecting its growing appeal.
- Flexibility: Provides options without long-term commitments.
- Customization: Tailored agreements to meet specific needs.
- Market Growth: Increased demand in 2024, up by 15%.
The threat of substitutes includes direct vehicle purchases, appealing for ownership. Public transport and ride-sharing also serve as alternatives. In 2024, the ride-sharing market was worth $100 billion. Car-sharing and long-term rentals add to these options.
| Substitute | Market Value/Growth (2024) | Consumer Appeal |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Vehicle Purchase | Avg. Price ~$48,000 | Ownership, long-term savings |
| Public Transportation | Avg. Monthly Cost ~$100 | Affordability, convenience |
| Ride-sharing (Uber, Lyft) | $100 billion (Global) | Convenience, no maintenance |
| Car-sharing | $2.3 billion (Global) | Flexibility, urban focus |
| Long-term Rentals | 15% demand increase | Flexibility, temporary needs |
Entrants Threaten
Capital requirements pose a significant threat to new entrants in the electric vehicle (EV) market. Establishing partnerships with lenders and dealerships, developing a technology platform, and funding marketing campaigns demand substantial initial investments. For example, Rivian, a prominent EV startup, reported a net loss of $1.5 billion in Q3 2024, highlighting the financial strain. High initial investment acts as a barrier, deterring smaller companies.
Established companies often benefit from strong brand loyalty, making it difficult for new entrants to gain a foothold. Customers trust existing brands, which creates a barrier to entry. For example, in 2024, Apple's brand loyalty rate was around 90%, reflecting the challenge new competitors face. Building brand recognition and trust requires significant investment and time.
New vehicle finance entrants face strict regulatory hurdles. Compliance with consumer protection laws and lending regulations is crucial. This can involve significant upfront costs and ongoing expenses. For example, in 2024, the average cost of compliance for financial institutions rose by 7%. This increases the barriers to entry.
Technological Expertise
The threat from new entrants in the financial leasing sector is significantly influenced by technological expertise. A robust technology platform is crucial for efficiently connecting customers with financing choices and overseeing the leasing lifecycle. Building and sustaining such a platform demands considerable investment and specialized knowledge. This includes the need for secure data management, which can be costly. In 2024, tech spending in FinTech reached $177 billion globally, illustrating the high barrier to entry.
- High initial investment in technology infrastructure.
- Need for specialized technical skills.
- Ongoing costs for maintenance and updates.
- Cybersecurity and data privacy concerns.
Partnership Network
The threat of new entrants in the vehicle leasing industry hinges significantly on establishing robust partnership networks. Success in this sector requires building strong relationships with lenders and dealerships. New entrants face the challenge of cultivating these crucial connections, a process that demands considerable time and effort. This network is essential for competing effectively.
- Market entry can be slow due to the need for partnerships.
- Established players have existing networks.
- New entrants must offer competitive incentives.
- Building trust takes time.
High capital needs, like Rivian's $1.5B loss in Q3 2024, deter new EV entrants. Strong brand loyalty, such as Apple's 90% in 2024, also creates entry barriers. Strict regulations, increasing compliance costs by 7% in 2024, pose further challenges.
| Barrier | Impact | Example (2024 Data) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Needs | High initial investment | Rivian's $1.5B loss |
| Brand Loyalty | Difficult market entry | Apple's 90% loyalty |
| Regulations | Increased costs | Compliance cost +7% |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Zigup’s analysis leverages financial reports, market research, and competitive landscapes for accurate data.