Zoom Video Communications Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Zoom Video Communications Bundle
What is included in the product
Detailed analysis of each competitive force, supported by industry data and strategic commentary.
Zoom's Five Forces Analysis provides instant insights through a visual spider/radar chart.
Full Version Awaits
Zoom Video Communications Porter's Five Forces Analysis
You’re previewing the final version—precisely the same Zoom Porter's Five Forces analysis document that will be available to you instantly after buying.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Template
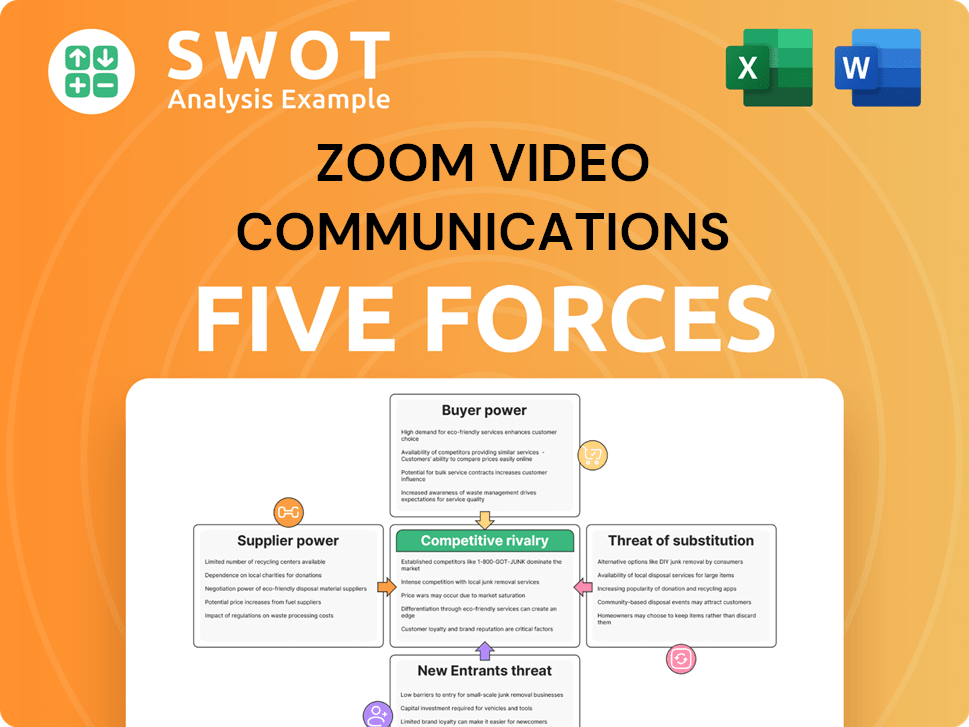
Zoom Video Communications operates in a competitive video conferencing market, facing pressures from both established players and agile startups.
Buyer power is moderate, as customers have multiple platform choices, but switching costs are a factor.
Threat of new entrants is high, given the low barriers to entry for cloud-based services.
Substitute products, like messaging apps, pose a constant threat.
Competitive rivalry is intense, with giants like Microsoft and Google vying for market share.
Supplier power is relatively low, with commoditized hardware and software components available.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Zoom Video Communications’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Zoom's reliance on multiple suppliers for hardware, software, and infrastructure limits supplier concentration. The availability of various suppliers reduces Zoom's dependency, diminishing their bargaining power. Diversification in the supply chain ensures Zoom can switch providers if necessary. In 2024, Zoom's supplier diversity helped maintain competitive costs amidst global supply chain challenges.
Zoom benefits from standardized components like servers and network equipment, easily sourced from multiple suppliers. This reduces supplier power. For example, in 2024, the cloud infrastructure market, where Zoom sources components, is highly competitive. The average server price decreased by approximately 8% in 2024 due to increased competition.
Zoom depends on cloud infrastructure, primarily AWS and Azure. These providers are massive, but competition keeps their power in check. In 2024, AWS held about 32% of the cloud market, and Azure about 25%. Zoom can negotiate and switch providers, reducing supplier influence.
Software development
Zoom's software development capabilities are a core strength. This internal focus reduces its dependence on external software suppliers. By developing its software, Zoom has more control over its product. This strategy minimizes supplier power.
- Zoom's R&D expenses in fiscal year 2024 were approximately $520 million.
- This investment in internal development strengthens its position.
- This internal control is key to their competitive advantage.
Telecommunication infrastructure
Zoom's services depend on telecommunication infrastructure, but the telecom industry is highly competitive. This competition among providers reduces the bargaining power of any single supplier over Zoom. The market is characterized by multiple providers offering similar services, limiting the ability of any one to dictate terms. For instance, in 2024, the global telecom market was valued at over $2 trillion, with numerous players vying for market share. This intense competition constrains suppliers' pricing power.
- Competitive Telecom Market: Many providers.
- Limited Supplier Power: Suppliers can't dictate terms.
- Market Value: Over $2 trillion in 2024.
- Zoom's Dependence: Relies on telecom infrastructure.
Zoom's diverse supplier base, including hardware, software, and infrastructure providers, diminishes supplier bargaining power. In 2024, competition in the cloud infrastructure market kept prices down. Internal software development and telecom market competition further limit suppliers' influence.
| Aspect | Details | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Market Share | AWS, Azure | AWS 32%, Azure 25% |
| Telecom Market Value | Global | Over $2 Trillion |
| R&D Expenses | Zoom's investment | Approximately $520 million |
Customers Bargaining Power
Zoom's extensive customer base, encompassing individuals and major corporations, dilutes the influence of any single entity. This broad reach protects Zoom from being overly reliant on any particular client. In 2024, Zoom reported over 200 million daily meeting participants, a testament to its diverse user base, which limits individual customer leverage.
Switching costs for Zoom's enterprise clients are moderate. Integrating a new platform, training staff, and migrating data present challenges. These factors create inertia, giving Zoom some leverage. In 2024, Zoom had a 32% market share in the video conferencing market.
Zoom's service differentiation, highlighted by its user-friendly interface and robust features, somewhat mitigates customer bargaining power. This differentiation allows Zoom to maintain pricing strategies. In 2024, Zoom's revenue reached approximately $4.5 billion, indicating its strong market position. The platform's reliability and specialized features enhance customer retention, reducing price sensitivity.
Subscription model
Zoom's subscription model is a cornerstone of its financial strategy, offering predictable revenue. This model reduces the impact of short-term customer demands, fostering long-term relationships. The recurring revenue stream bolsters financial stability, lessening customer bargaining power. Zoom's focus is on retaining subscribers, not just making individual sales.
- In Fiscal Year 2024, Zoom reported $4.5 billion in total revenue.
- Approximately 70% of Zoom's revenue comes from subscriptions.
- Zoom's net dollar expansion rate was above 100% in early 2024, reflecting strong customer retention.
Customer sensitivity to pricing
Zoom's customers, particularly small businesses and individual users, are price-sensitive. Competitive pricing is key to attracting and keeping customers in the video conferencing market. Zoom must carefully balance its pricing to stay competitive and profitable, recognizing its customers' price sensitivity.
- In 2024, Zoom's average revenue per user (ARPU) was around $140, reflecting pricing pressures.
- Competitors like Microsoft Teams and Google Meet offer aggressive pricing.
- Zoom's ability to grow depends on how well it navigates customer price sensitivity.
- Offering various subscription tiers helps address diverse customer budgets.
Customer bargaining power for Zoom is moderate, shaped by its large user base and subscription model. Switching costs create inertia, although customers are price-sensitive. Zoom's focus on user-friendly features and a diverse subscription model help manage this power. In 2024, 70% of Zoom’s revenue came from subscriptions, reducing the impact of short-term demands.
| Factor | Impact | Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| User Base | Dilutes customer influence | 200M+ daily meeting participants |
| Switching Costs | Creates inertia | Moderate |
| Subscription Model | Reduces bargaining power | 70% Revenue from subscriptions |
Rivalry Among Competitors
The video conferencing market is fiercely competitive, with Zoom facing giants like Microsoft Teams, Google Meet, and Cisco Webex. This competition drives price wars and constant innovation. For instance, in Q3 2024, Microsoft's Teams revenue grew by 20%, underscoring the pressure on Zoom. This intense rivalry demands aggressive marketing and strategic agility.
Many video conferencing platforms have similar features, resulting in feature parity. This makes it difficult for Zoom to differentiate itself solely on functionality. In 2024, Zoom's revenue was $4.5 billion, showing the need for strong differentiation. Competition drives Zoom to innovate and offer unique value to stand out.
The competitive landscape, including Microsoft Teams and Google Meet, significantly pressures Zoom's pricing strategies. Competitors frequently offer aggressive pricing models or bundle video conferencing with other services, impacting Zoom's revenue. For instance, in 2024, Microsoft Teams' aggressive pricing strategy has directly challenged Zoom's market share, especially in the enterprise sector. Zoom must carefully balance competitive pricing with the need to maintain profitability, demonstrated by their Q3 2024 results, where a slight dip in average revenue per user was observed due to pricing adjustments.
Innovation imperative
Innovation is crucial for Zoom to stay competitive. They must constantly update their platform with new features and enhancements. This helps them remain ahead of rivals in the market. Failure to do so could mean losing customers. In 2024, Zoom's R&D spending was approximately $500 million.
- Zoom's R&D spending in 2024 was around $500 million.
- Regular updates and new features are essential.
- The market share could decrease without innovation.
- Competition demands continuous improvement.
Marketing and brand
Effective marketing and strong brand recognition are crucial for attracting and retaining customers in the video conferencing market. Zoom faces competition from established brands with substantial marketing budgets. Maintaining brand loyalty needs continuous investment in marketing and customer experience. Zoom's marketing spend was $190.5 million in Q3 2024, up from $167.1 million the prior year. This is essential to compete with rivals like Microsoft Teams and Google Meet.
- Zoom's marketing spend increased in 2024.
- Brand recognition is key for customer retention.
- Competition includes firms with large marketing resources.
- Customer experience impacts brand loyalty.
Zoom faces fierce competition from Microsoft, Google, and Cisco. This rivalry fuels innovation and price wars. In Q3 2024, Microsoft Teams' revenue grew 20% highlighting market pressure. Strong marketing and differentiation are vital.
| Metric | Zoom | Competitors |
|---|---|---|
| R&D Spending (2024) | $500M | Significant, undisclosed |
| Marketing Spend (Q3 2024) | $190.5M | Larger, varied |
| Market Share | Competitive | Variable |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Free video conferencing platforms like Google Meet provide essential features without charging. This attracts budget-conscious customers who may opt for free services. The availability of these substitutes consistently threatens Zoom's market share, especially impacting individual users and small businesses. In 2024, Google Meet held a significant portion of the market share, posing a direct challenge to Zoom's user base. Zoom's revenue in Q3 2024 was $1.13 billion, and it needs to keep attracting users.
Traditional audio conferencing, like phone calls, serves as a substitute for Zoom, particularly when visuals aren't crucial. Its simplicity and lower cost, with services like FreeConferenceCall offering basic features, make it a persistent alternative. While Zoom's revenue in 2024 was approximately $4.5 billion, audio conferencing maintains its niche. This makes it a cost-effective option for some communications needs.
Collaboration tools, such as Slack and Microsoft Teams, pose a threat to Zoom. These platforms bundle communication features, including video conferencing, potentially reducing reliance on separate video conferencing apps. This integrated approach presents a substitute for Zoom's standalone services. For instance, Microsoft Teams had approximately 320 million monthly active users in 2024, demonstrating the scale of this competitive threat. The rise in bundled solutions directly impacts Zoom's market share and revenue streams.
In-person meetings
In-person meetings represent a significant substitute for Zoom's video conferencing services, especially as travel becomes more accessible. These meetings allow for deeper personal connections, which video calls often lack. The comeback of in-person interactions directly challenges the demand for video conferencing solutions like Zoom. This shift is crucial for Zoom's market position.
- Travel spending in the US is projected to reach $1.2 trillion in 2024, showing a strong rebound in face-to-face interactions.
- Zoom's revenue growth slowed to 3.2% in Q4 2023, highlighting the impact of returning in-person activities.
- Companies are increasingly encouraging in-person work, with 60% of US companies planning to have employees in the office at least three days a week by the end of 2024.
Decreasing dependency on video
The threat of substitutes for Zoom arises from shifting work dynamics and alternative communication methods. With hybrid work models, some organizations might reduce their reliance on continuous video calls. This change could lessen the need for dedicated video conferencing tools like Zoom. Asynchronous communication tools, such as project management software, also offer partial substitutes.
- Remote work decreased from 12.7% in 2023 to 10.8% in January 2024, according to WFH Research.
- Slack reported a 22% revenue growth in 2023, indicating strong adoption of asynchronous communication.
- Microsoft Teams' user base increased, with 320 million monthly active users by the end of 2023.
Zoom faces strong competition from substitutes, including free platforms like Google Meet, which directly challenge its market share by offering similar services at no cost. Audio conferencing remains a cost-effective alternative. Collaboration tools like Microsoft Teams bundle video conferencing, impacting Zoom's market position. In-person meetings and asynchronous communication methods offer further substitutes. The US travel spending is projected to reach $1.2 trillion in 2024.
| Substitute | Description | Impact on Zoom |
|---|---|---|
| Free Video Conferencing | Google Meet, etc. | Direct competition for users |
| Audio Conferencing | Phone calls, etc. | Cost-effective alternative |
| Collaboration Tools | Microsoft Teams, Slack | Bundled video conferencing |
| In-Person Meetings | Face-to-face interactions | Challenges demand for Zoom |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the video conferencing market demands substantial investment in technology infrastructure and software development. The necessity for a dependable infrastructure forms a significant barrier. High upfront costs, potentially millions, can deter new entrants. For example, Zoom's R&D expenses in 2024 were around $400 million. This financial commitment presents a considerable hurdle.
The video conferencing market features well-established firms with strong brands and large customer bases. Newcomers face tough competition from these incumbents. Established firms possess market presence and customer loyalty advantages. Zoom competes with Cisco, Microsoft, and Google. Microsoft Teams had 320 million monthly active users in 2024.
Video conferencing platforms like Zoom thrive on network effects, where more users enhance the platform's value. This creates a significant barrier for new entrants, as attracting users is tough. To compete, new platforms need strong marketing and a unique offering. Zoom's Q3 2024 revenue was $1.1 billion, demonstrating the strength of its network.
Technological expertise
Developing a competitive video conferencing platform demands significant technological expertise. This includes proficiency in video encoding, real-time communication protocols, and network optimization. Without this specialized knowledge, new companies struggle to enter the market. The high barrier to entry, due to this need, protects existing players like Zoom. The costs associated with acquiring and maintaining this technology can be substantial.
- Zoom's R&D expenses in 2024 were approximately $450 million, reflecting the investment needed to maintain technological leadership.
- The video conferencing market is projected to reach $50 billion by 2026, highlighting the value of technological prowess.
- Companies that lack this expertise often struggle to compete, as seen with several smaller startups in 2024.
Regulatory hurdles
Regulatory hurdles pose a significant threat to new entrants in the video conferencing market, especially concerning data privacy and security. Compliance with regulations like GDPR [8] and CCPA [9] demands considerable financial investment and specialized expertise. These requirements can be a substantial barrier, deterring smaller companies from entering the market. For instance, ensuring data protection and secure infrastructure necessitates ongoing costs and technical capabilities.
- GDPR and CCPA compliance require significant investment.
- Data protection and secure infrastructure require ongoing costs.
- Smaller companies may be deterred from entering the market.
- Regulatory requirements can be a substantial barrier.
New entrants face high financial barriers due to technology and infrastructure needs. Incumbents like Microsoft and Cisco have strong brands, increasing the competitive hurdle. Network effects, where platform value grows with users, also create an entry barrier.
| Factor | Impact | Data |
|---|---|---|
| High Costs | Significant barrier | Zoom R&D: $450M (2024) |
| Strong Brands | Competitive advantage | Microsoft Teams: 320M users |
| Network Effects | Entry difficult | Video conferencing market projected at $50B by 2026 |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our analysis utilizes financial reports, market research, competitor analysis, and industry publications to assess each force. This is coupled with regulatory filings and expert opinions.