Alstom Bundle
How did Alstom evolve into a global mobility leader?
Journey back in time to uncover the fascinating Alstom SWOT Analysis and the remarkable story of Alstom, a company that began over a century ago with ambitious goals. From its roots in electrical engineering and mechanical construction, Alstom has become a major player in sustainable mobility. Discover how this company has shaped the future of transportation.
The Alstom company story is one of continuous adaptation and innovation, marked by strategic acquisitions and a relentless pursuit of technological advancements. From its Alstom's founding in 1928 to its current global presence in over 60 countries, the company has consistently redefined the landscape of rail transport and energy solutions. This exploration will examine the Alstom history, key milestones, and the pivotal moments that have shaped Alstom's trajectory, highlighting its impact on the Alstom transportation sector and beyond.
What is the Alstom Founding Story?
The Alstom company has a rich history, originating from a strategic merger of two significant French industrial entities. This union was driven by the vision to capitalize on the electrification of railway systems and the broader industrial landscape. The official establishment of Alsthom, later known as Alstom, occurred on January 1, 1928.
The merger was a direct response to the opportunities presented by post-World War I industrial expansion and increasing infrastructure electrification across Europe. The founders, representing the leadership of Société Alsacienne de Constructions Mécaniques (SACM) and Thomson-Houston, recognized the synergy between their mechanical and electrical engineering strengths. Their initial business model focused on providing comprehensive solutions for railway electrification, including locomotives and power generation.
The company's name, a portmanteau of Alsace and Thomson, reflected its geographical roots and the key contributing entity, Thomson-Houston. This foundational period emphasized integrating the diverse expertise of the merging companies to meet the evolving needs of the transportation and energy sectors. Learn more about the Marketing Strategy of Alstom.
Alstom's history begins with the merger of SACM and Thomson-Houston in 1928, a strategic move to capitalize on electrification trends.
- SACM, founded in 1872, manufactured locomotives and mechanical equipment.
- Thomson-Houston, a subsidiary of the American company, specialized in electrical equipment.
- The merger aimed to provide comprehensive solutions for railway electrification.
- The first products included electric locomotives and electrical equipment.
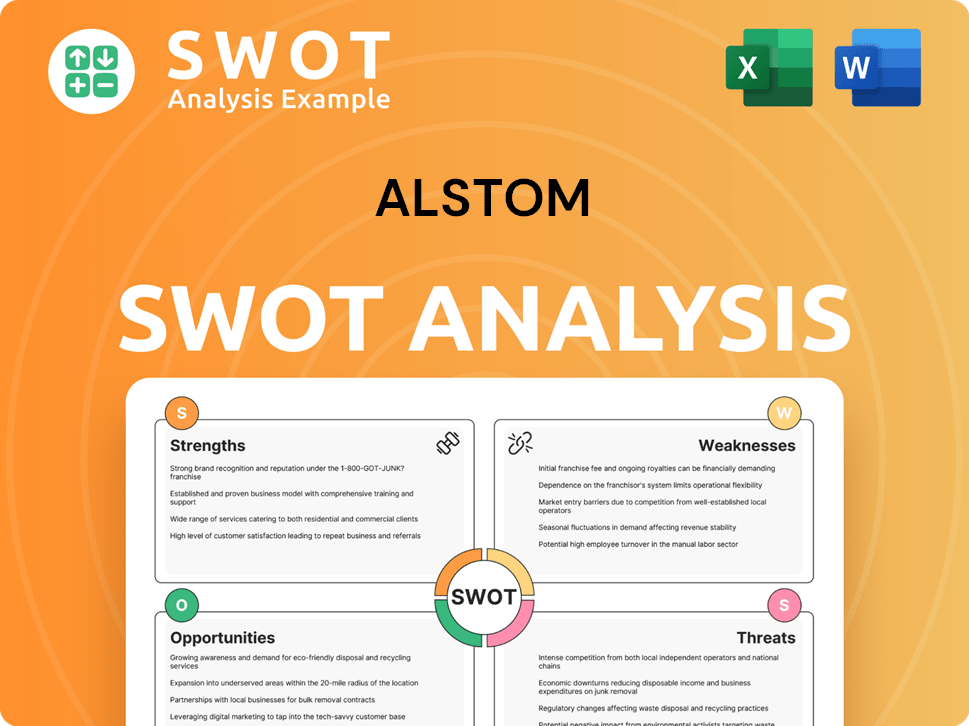
Alstom SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Alstom?
The early growth of the Alstom company, a pivotal chapter in its Alstom history, was marked by significant advancements in the railway sector and expansion into diverse industrial areas. Founded in 1928, Alstom quickly became a key player in supplying electric locomotives, responding to the growing need for efficient rail transport. This period established Alstom's commitment to innovation and high performance, setting the stage for its future endeavors. The company's early successes laid the foundation for its eventual global leadership in transportation and energy.
Alstom's early growth was significantly tied to the electrification of the French railway network. This initiative created a substantial demand for electric locomotives, which Alstom was well-positioned to supply. This focus on rail transport was a cornerstone of Alstom's early business strategy.
A key product launch was the CC 7100 class of locomotives, which set world speed records in the 1950s. These locomotives demonstrated Alstom's early commitment to innovation and high performance. This early success helped to solidify Alstom's reputation in the market.
The initial team expansion involved integrating the workforces and engineering expertise of both SACM and Thomson-Houston. Consolidating manufacturing facilities, particularly in Belfort, France, was a key strategy. This consolidation enhanced Alstom's manufacturing capabilities.
Early diversification included venturing into power generation equipment, such as turbines and alternators. The acquisition of Chantiers de l'Atlantique in 1976 broadened Alstom's industrial base. These strategic moves helped to strengthen Alstom's market position.
Market reception to Alstom's early offerings was generally positive, driven by the reliability and advanced technology of its products. The company distinguished itself through its integrated approach to railway and energy solutions. Strategic shifts during this period were aimed at meeting the infrastructure needs of a post-war Europe. Alstom's early growth laid the groundwork for its emergence as a global leader. Learn more about the company's values and goals by reading the Mission, Vision & Core Values of Alstom.
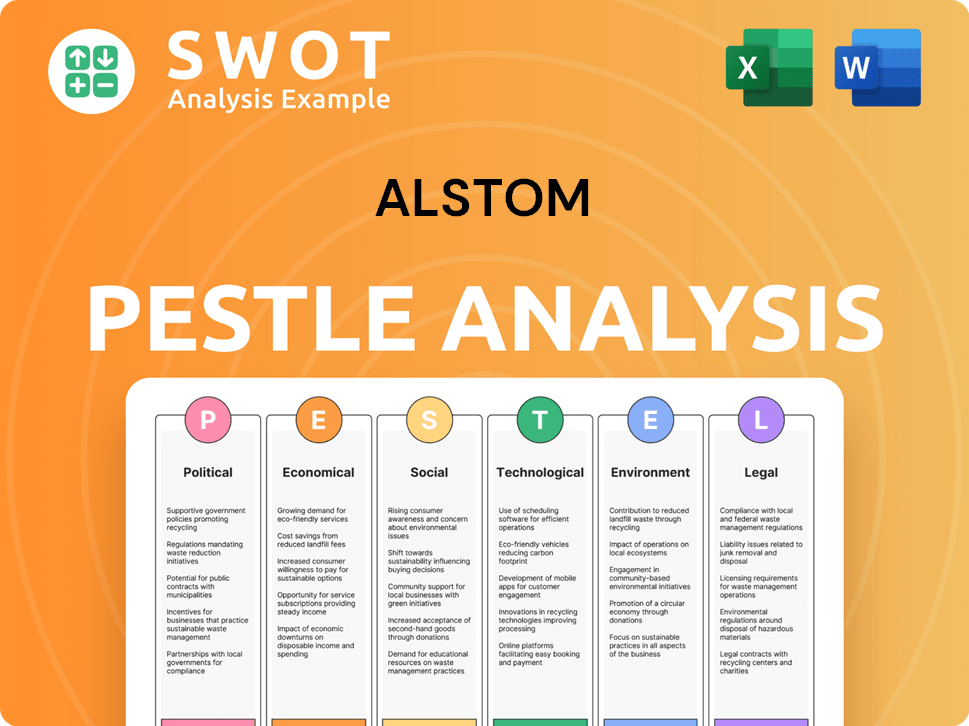
Alstom PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Alstom history?
The Alstom company has a rich history marked by significant milestones in the transportation sector. From its origins to its current status as a global leader, Alstom's journey reflects its adaptability and innovation in a constantly evolving market. The company's Alstom timeline is filled with strategic moves and technological advancements.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1928 | Alstom was founded through the merger of the Société Alsacienne de Constructions Mécaniques and Compagnie Française Thomson-Houston. |
| 1970s-1980s | Development of the TGV (Train à Grande Vitesse) high-speed train, revolutionizing rail travel. |
| 2000s | Navigated financial difficulties and restructuring, leading to the divestment of its power and grid businesses. |
| 2015 | Divested power and grid businesses to General Electric. |
| 2019 | Proposed merger with Siemens Mobility blocked by European regulators. |
| 2021 | Acquired Bombardier Transportation, significantly expanding its global footprint. |
Alstom's innovations have consistently pushed the boundaries of transportation technology. These advancements have not only improved efficiency but also contributed to more sustainable and intelligent mobility solutions.
The TGV revolutionized rail travel with its high speeds and efficiency. This innovation set a new standard for passenger transport.
Advanced signaling systems have enhanced safety and optimized rail operations. These systems are crucial for managing complex rail networks.
Alstom has developed rolling stock that reduces energy consumption and environmental impact. This focus aligns with sustainability goals.
The Mastria multimodal supervision system, launched in 2024, exemplifies Alstom's commitment to digital innovation. These solutions improve operational efficiency.
Alstom's focus on green mobility solutions addresses decarbonization efforts. They are constantly working to reduce the carbon footprint of their products.
The company is developing smart mobility solutions to enhance connectivity and efficiency. These solutions are designed to improve the passenger experience.
Throughout its history, the Alstom company has faced numerous challenges. These challenges have required strategic adjustments and a focus on core competencies.
Alstom has had to navigate periods of economic instability and reduced demand. These downturns have tested the company's resilience.
The transportation industry is highly competitive, with various companies vying for market share. Alstom faces challenges from both established and emerging competitors.
In the early 2000s, Alstom experienced financial difficulties, necessitating a bailout. This period led to significant restructuring.
The company has undergone several restructuring efforts, including the divestment of its power and grid businesses. These moves aimed to streamline operations.
The proposed merger with Siemens Mobility was blocked by regulators in 2019. This presented a setback to Alstom's growth strategy.
The acquisition of Bombardier Transportation, valued at EUR 5.5 billion, presented integration challenges. Successfully integrating new assets is crucial for long-term growth.
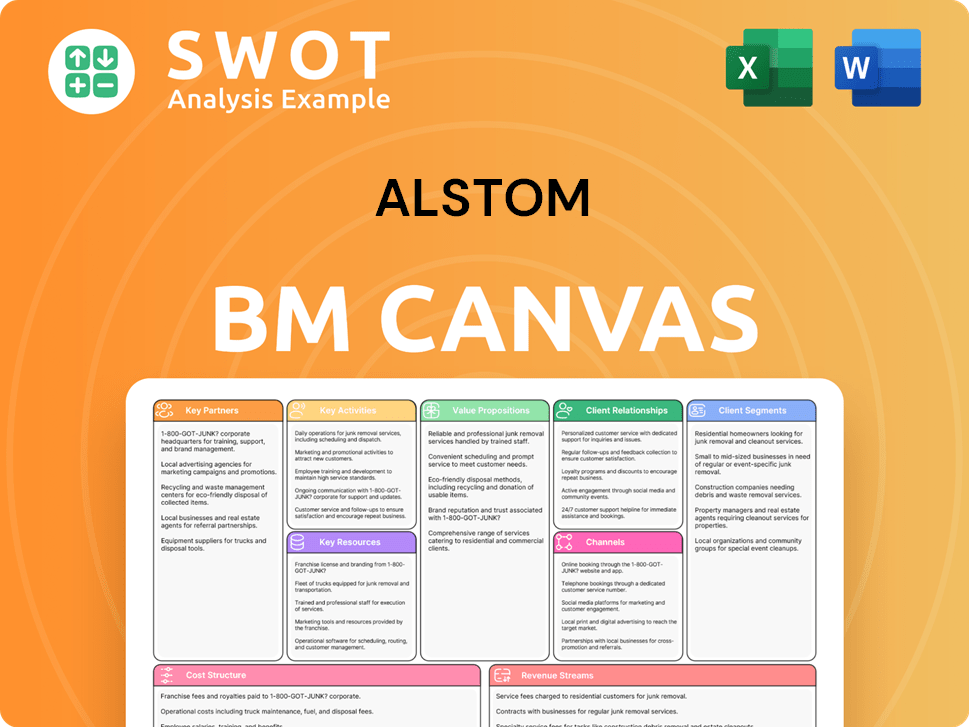
Alstom Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Alstom?
The Alstom company has a rich history, marked by significant technological advancements and strategic shifts. From its origins in 1928, the company has evolved through mergers, acquisitions, and periods of restructuring, becoming a global leader in the transportation sector. Key milestones include the development of high-speed rail technology and major acquisitions like Bombardier Transportation in 2021, significantly expanding its product portfolio and global reach. The company has consistently adapted to market demands and technological advancements, focusing on sustainable mobility solutions.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1928 | Formation of Alsthom through the merger of Société Alsacienne de Constructions Mécaniques (SACM) and Thomson-Houston. |
| 1955 | Alsthom-built CC 7100 locomotive sets a world rail speed record of 331 km/h. |
| 1978 | Introduction of the first TGV prototype, marking a new era in high-speed rail. |
| 1981 | Commercial launch of the TGV on the Paris-Lyon line. |
| 1992 | Acquisition of the transportation division of General Electric Company (GEC) Alsthom, leading to the simplification of the name to Alstom. |
| 1998 | Alstom lists on the Paris Stock Exchange. |
| 2003-2004 | Period of financial difficulties and subsequent restructuring, involving state aid and asset sales. |
| 2015 | Sale of Alstom's power and grid businesses to General Electric, allowing the company to fully focus on transportation. |
| 2019 | Proposed merger with Siemens Mobility blocked by European regulators. |
| 2021 | Acquisition of Bombardier Transportation, significantly expanding Alstom's global presence and product portfolio. |
| 2023 | Alstom secures major contracts, including a significant order for 103 trains for the Barcelona suburban network, valued at nearly 1 billion euros. |
| 2024 | Alstom launches Mastria, a multimodal supervision system, enhancing its digital mobility solutions. |
| March 31, 2024 | Alstom reports an order intake of €16.9 billion for the fiscal year, with a backlog of €92.5 billion, demonstrating strong market confidence. |
Alstom is prioritizing sustainable and smart mobility solutions. They are actively investing in green technologies such as hydrogen-powered trains and battery-electric solutions. This aligns with the growing demand for decarbonized transport, making Alstom a key player in the future of eco-friendly transportation.
The company is focusing on expanding its presence in emerging markets. They also plan to strengthen their position in existing markets. This strategy includes leveraging their comprehensive portfolio of trains, metros, signaling systems, and related services to meet global demand.
Alstom is heavily investing in digital mobility solutions, predictive maintenance, and autonomous train operations. The launch of Mastria in 2024 showcases their commitment to advanced technologies. This focus ensures they remain at the forefront of innovation in the transportation sector.
With an order intake of €16.9 billion and a backlog of €92.5 billion as of March 31, 2024, Alstom demonstrates strong market confidence. This substantial backlog is expected to drive sustained growth. They are well-positioned to capitalize on industry trends like urbanization and environmental concerns.
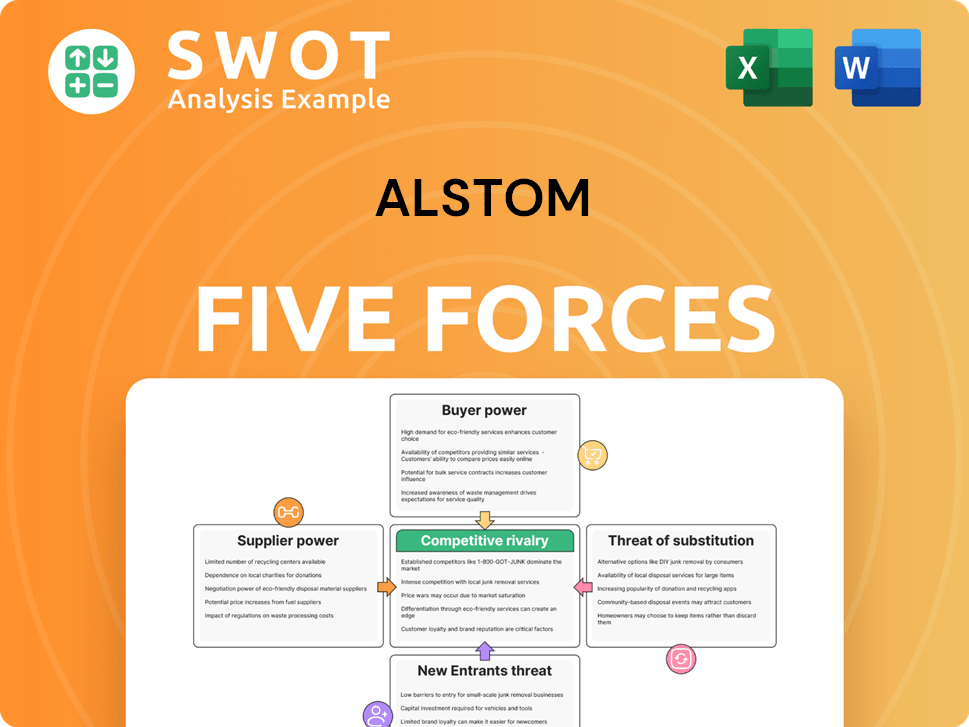
Alstom Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Alstom Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Alstom Company?
- How Does Alstom Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Alstom Company?
- What is Brief History of Alstom Company?
- Who Owns Alstom Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Alstom Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.