Burlington Coat Factory Bundle
How did Burlington Coat Factory become a retail giant?
From its humble beginnings as a coat retailer in 1972, Burlington Coat Factory, now known as Burlington Stores, has transformed the retail landscape. This Burlington Coat Factory SWOT Analysis showcases how the company navigated market challenges and capitalized on opportunities. Discover the fascinating journey of this discount retail pioneer and its impact on the industry.
This brief history of Burlington Coat Factory explores the company's origins and its evolution into a major player in the discount retail sector. Examining the Burlington company's timeline, from its early days to its current status as a national retailer, reveals key milestones and strategic decisions. Understanding Burlington's growth and business model provides valuable insights into its enduring success.
What is the Burlington Coat Factory Founding Story?
The story of Burlington Coat Factory, a significant player in retail history, began in 1972. Henrietta Milstein, with $75,000 from her librarian career, persuaded her husband, Monroe Milstein, to purchase a former factory outlet in Burlington, New Jersey. This marked the inception of what would become a major force in the discount retail sector.
Monroe Milstein, already experienced in the outerwear business since 1946, saw the potential in expanding into retail. The company initially operated under the name Burlington Coat Factory Warehouse Corporation. The early days were marked by a focus on selling coats and jackets at discounted prices, a strategy that quickly resonated with consumers.
The initial investment, primarily from Henrietta's savings, underscored the family-driven nature of the venture. The opening of the first store saw a remarkable response, with approximately 300 people lining up on its first Sunday. This immediate success highlighted the appeal of the off-price model, setting the stage for the company's future growth and evolution.
The foundation of Burlington Coat Factory was laid in 1972 by Henrietta and Monroe Milstein. They acquired a factory outlet in Burlington, New Jersey, marking the beginning of the company's journey.
- The initial investment was $675,050, with Henrietta Milstein contributing $75,000 from her savings.
- Monroe Milstein, with experience in the outerwear business, recognized the retail opportunity.
- The company's original name was Burlington Coat Factory Warehouse Corporation.
- The first store's opening day saw a significant turnout, indicating strong market interest.
To overcome the seasonal nature of coat sales, the Milsteins strategically diversified their product offerings. They expanded beyond outerwear to include a variety of items such as clothing, accessories, linens, and gift items. This diversification, including the addition of a baby department, later known as Baby Depot, and shoes, was crucial for Burlington's long-term success. For more details on the company's business model, check out Revenue Streams & Business Model of Burlington Coat Factory.
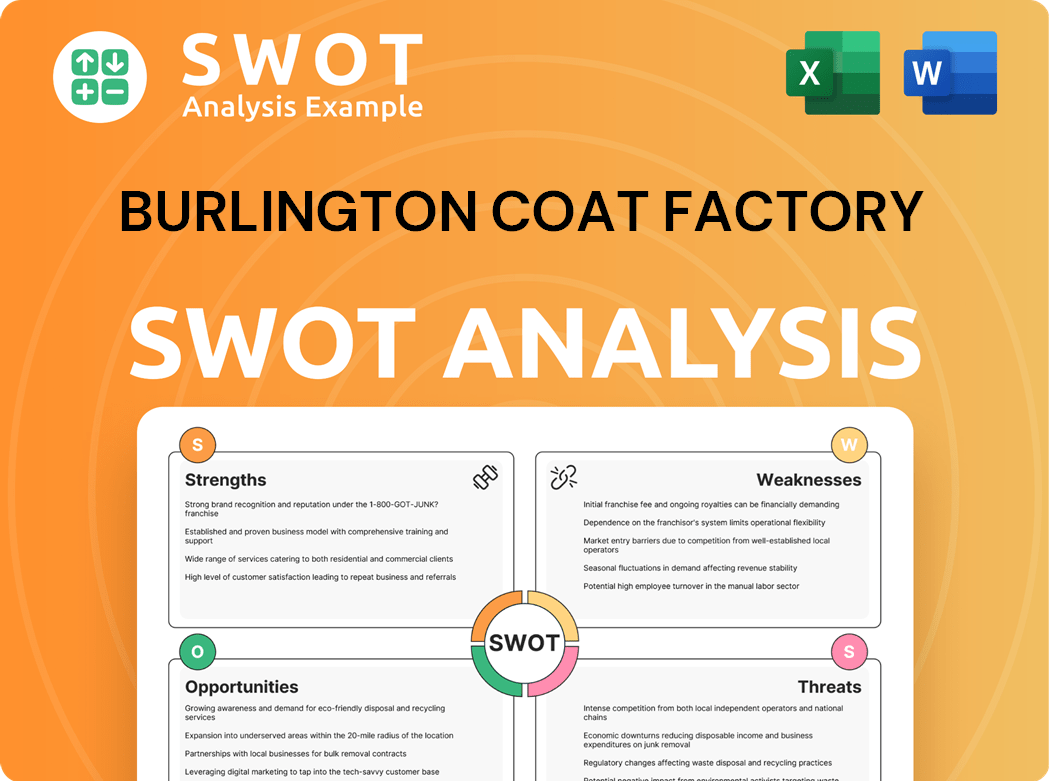
Burlington Coat Factory SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Burlington Coat Factory?
The early years of the Burlington Coat Factory company were marked by significant expansion and diversification. From its humble beginnings in 1972, the company quickly grew its store count and broadened its product offerings. This strategic approach allowed Burlington to establish itself as a prominent player in the discount retail sector. Understanding the Owners & Shareholders of Burlington Coat Factory is crucial to understanding its growth.
Between 1973 and 1982, Burlington opened an additional 29 stores, demonstrating rapid growth. The initial focus on coats expanded to include ladies sportswear, men's clothing, and children's apparel. By 1982, annual sales exceeded $130 million, reflecting the success of this expansion strategy.
The Initial Public Offering (IPO) in June 1983 marked a significant milestone for Burlington. The company operated 31 stores at the time of its IPO. The capital raised fueled a rapid expansion, doubling the store count to 68 by 1985.
By the end of the 1980s, Burlington had 134 stores across 37 states, with net sales surpassing $600 million. The company entered the West Coast market, opening stores in San Francisco and San Jose. A new distribution center was established in 1990.
Annual sales reached $1.2 billion in 1993, with 185 stores in operation. Burlington expanded internationally, signing an agreement to open a store in Juarez, Mexico. By 2005, the company operated 362 stores in 42 states, with annual sales of $3.2 billion.
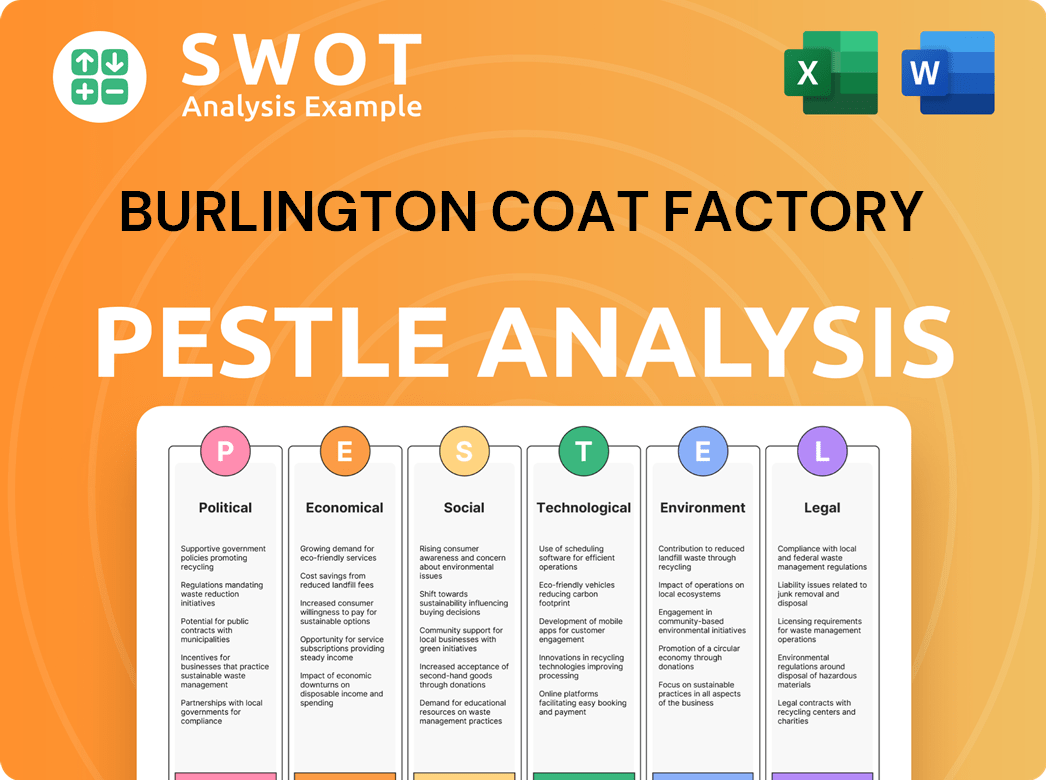
Burlington Coat Factory PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Burlington Coat Factory history?
The Burlington Coat Factory's journey is marked by strategic shifts and adaptations. From its early days to its current status, the company has navigated the retail landscape, undergoing significant changes in ownership, branding, and operational strategies to maintain its market position.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2006 | Acquired by Bain Capital Partners for $2.06 billion, transitioning from a publicly traded company to private ownership. |
| 2009 | Underwent a major restructuring, including a rebranding from 'Burlington Coat Factory' to 'Burlington Stores Inc.' to reflect its expanded product offerings. |
| 2020 | Launched 'Burlington 2.0', a strategy focused on accelerating new store openings in smaller footprints and expanding merchandise categories. |
| 2019 | Michael O'Sullivan took over as CEO, succeeding Thomas Kingsbury, marking a leadership transition. |
Burlington's business model is a continuous innovation in off-price retail, procuring branded goods at significant discounts. This approach allows the company to offer a 'treasure-hunt' shopping experience with constantly updated assortments, driving high inventory turnover.
The company buys excess inventory and closeout items to offer branded goods at deep discounts, creating a value proposition for customers. This model relies on a network of vendors, including designers and manufacturers, to source merchandise.
Burlington focuses on high inventory turnover to maximize profitability, ensuring a fresh and dynamic product selection. The constantly changing inventory encourages frequent store visits from customers.
Burlington 2.0 strategy involves opening stores in smaller footprints, which aims to improve customer shopping experience and increase store productivity. This strategy has led to a reduction in average new store size, from 40,000 square feet in 2020 to 28,000 square feet in 2022.
Burlington has faced challenges, including controversies and operational disruptions. The COVID-19 pandemic led to temporary store closures in March 2020, impacting operations.
In 1998, the company faced controversy over the sale of parkas trimmed with dog fur, leading to product relabeling. This incident highlighted the importance of accurate product labeling and sourcing.
The company temporarily closed stores and corporate offices in March 2020 due to the pandemic, impacting its operations. This highlighted the vulnerability of retail businesses to external disruptions.
The company is continually adapting to changing retail trends through strategies like Burlington 2.0, focusing on smaller store formats and expanding product categories. This demonstrates a commitment to evolving with the market.
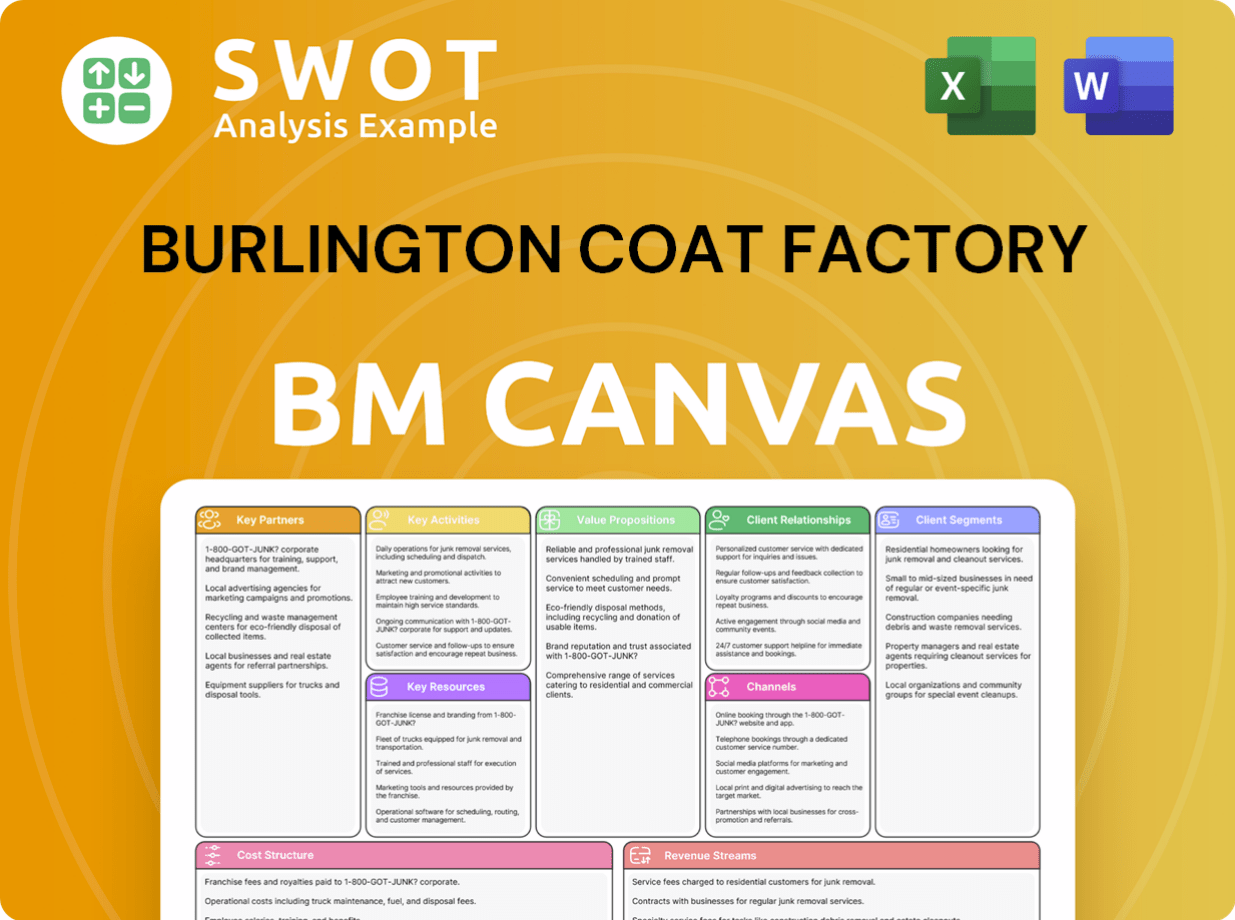
Burlington Coat Factory Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Burlington Coat Factory?
The story of Burlington Coat Factory, now known as Burlington, is a journey through retail evolution. From its humble beginnings in 1972, the company has grown into a major player in the discount retail sector. The Burlington history reflects strategic adaptations and expansions, shaping its current status and future prospects. The Burlington company has navigated significant milestones, from going public to undergoing acquisitions and rebranding, demonstrating its resilience and commitment to delivering value to its customers.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1972 | Henrietta and Monroe Milstein acquired a former factory outlet in Burlington, New Jersey, establishing Burlington Coat Factory. |
| 1975 | A second store opened in Copiague on Long Island. |
| 1983 | Burlington Coat Factory went public with an IPO. |
| 1985 | Store count doubled to 68 locations. |
| 1990 | A 438,000-square-foot national distribution center was established. |
| 1993 | Annual sales surpassed $1 billion. |
| 1999 | Burlington launched its e-commerce website. |
| 2006 | Bain Capital Partners acquired Burlington for $2.06 billion, taking the company private. |
| 2009 | The company underwent restructuring and rebrands from Burlington Coat Factory to Burlington Stores Inc.. |
| 2012 | The 500th Burlington store opened. |
| 2013 | Burlington went public again. |
| 2019 | Michael O'Sullivan became CEO, succeeding Thomas Kingsbury. |
| 2020 | Burlington launched 'Burlington 2.0' strategy, focusing on smaller store formats. |
| 2023 | Burlington acquired leases for over 40 closed Bed Bath & Beyond locations. |
| 2024 | Reported total revenues of approximately $9.7 billion for the fiscal year ending January 28, 2024. |
Burlington is focused on significant store expansion. The company aims to open 130-150 new stores annually, beginning in 2023, while closing or relocating approximately 30 older locations each year. This strategy is designed to increase the store base by 60% or more over the next five years, reflecting confidence in its off-price model.
The 'Burlington 2.0' strategy emphasizes smaller-format stores. This approach is intended to improve productivity and enhance the customer experience. The focus on smaller stores is a key element of Burlington's future trajectory, aligning with evolving consumer preferences and retail trends.
The company anticipates continued growth in comparable store sales. Burlington is focused on securing desirable merchandise at deep discounts. Maintaining rapid inventory turnover is expected to drive sustained profitability, supporting its long-term financial goals.
Burlington's strategy builds on its founding vision of providing exceptional value. This is now enhanced by a disciplined approach to operational efficiency. The company's strategic expansion in the dynamic off-price retail landscape reflects its commitment to long-term success. For more insights, you can find additional details on the Brief history of Burlington Coat Factory.
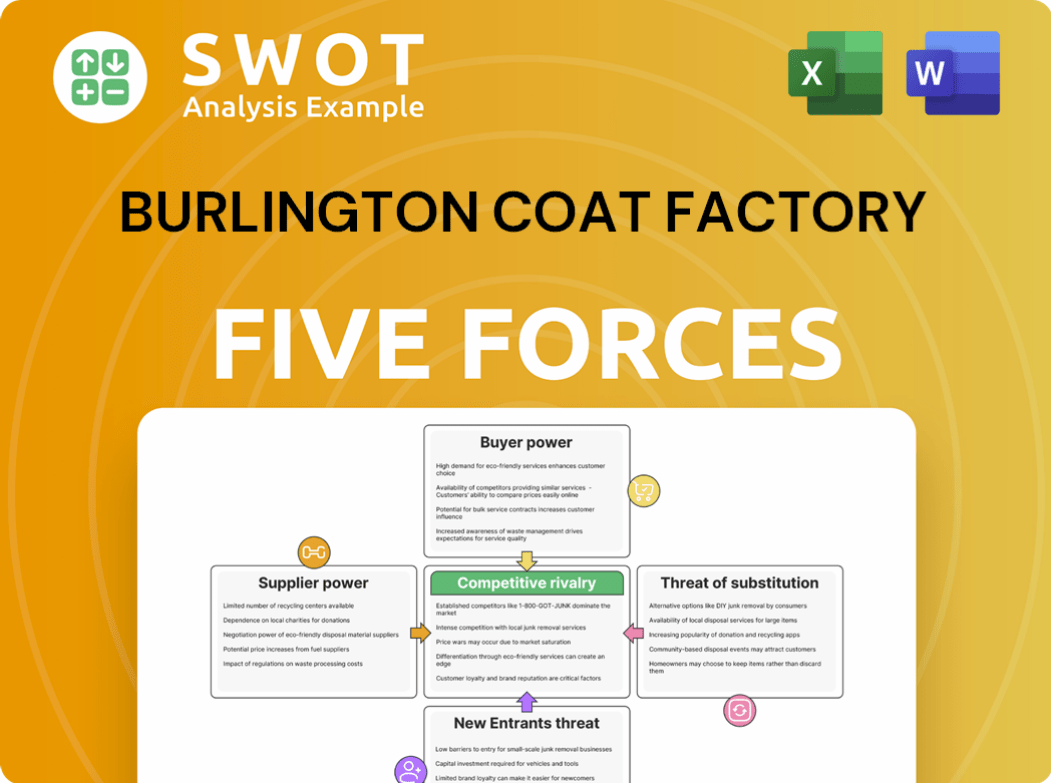
Burlington Coat Factory Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Burlington Coat Factory Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Burlington Coat Factory Company?
- How Does Burlington Coat Factory Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Burlington Coat Factory Company?
- What is Brief History of Burlington Coat Factory Company?
- Who Owns Burlington Coat Factory Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Burlington Coat Factory Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.