CarMax Bundle
How Did CarMax Revolutionize the Used Car Market?
Ever wondered about the CarMax SWOT Analysis and how this used car giant came to be? CarMax, a name synonymous with transparency and choice, didn't just appear overnight. Its journey is a fascinating tale of innovation in the automotive industry, transforming the way people buy and sell cars.
The CarMax company story began in 1993, a pivotal moment for the used car retailer landscape. From its CarMax founding by Circuit City to its current status as the largest in the U.S., the CarMax history is filled with strategic moves and a keen understanding of customer needs. This brief history CarMax showcases its evolution.
What is the CarMax Founding Story?
The story of the CarMax company, a major player in the used car market, began in 1991. Executives at Circuit City Stores, Inc., initiated research into the used car sector under the project name 'Project X'. This marked the genesis of what would become a significant shift in how consumers buy used vehicles. This research was a crucial step in understanding the existing market dynamics and identifying opportunities for improvement.
The primary aim was to address the common frustrations associated with traditional used car dealerships. The traditional model was often criticized for its high-pressure sales tactics and lack of transparency. The leaders of this initiative, Richard Sharp and W. Austin Ligon, envisioned a new approach to the used car market, inspired by the successful big-box retail model of Circuit City.
The founders aimed to create a more transparent and customer-friendly environment. This approach would set the stage for CarMax's distinctive business model. The early years were focused on establishing a reliable and trustworthy brand in a market known for its variability.
CarMax was founded to revolutionize the used car buying experience, moving away from traditional, often untrustworthy dealerships. The company's innovative approach included a 'no-haggle' pricing strategy and a focus on transparency.
- The initial funding for CarMax was approximately $170 million from Circuit City Stores, Inc.
- The first CarMax store opened in Richmond, Virginia, in October 1993.
- The company was incorporated in Virginia in 1996.
- CarMax's early success was a result of its focus on customer satisfaction and a transparent business model.
The initial problem was the fragmented nature of the used car industry. The small annual revenue of the average used car dealer hindered economies of scale and modern management methods. The vision was a 'superstore' model, similar to Circuit City's big-box retail concept, designed to offer a more relaxed and confident buying experience. The first CarMax location, branded as 'CarMax: The Auto Superstore,' opened in Richmond, Virginia, in October 1993. This prototype store showcased around 500 used cars, each no more than five model years old and with under 70,000 miles.
A key innovation from the outset was the 'no-haggling' fixed-price policy. This policy aimed to reduce the adversarial atmosphere and eliminate price negotiations. The initial investment for CarMax came from Circuit City Stores, Inc., which provided approximately $170 million to develop the concept and establish the first few stores. The company was formally incorporated in the Commonwealth of Virginia in 1996. The company's early focus on customer satisfaction and a transparent business model contributed to its initial success.
The Growth Strategy of CarMax shows how the company has expanded over time. This expansion has been marked by strategic decisions and innovations in the used car market. The company's early years were focused on establishing a reliable brand in a market known for its variability.
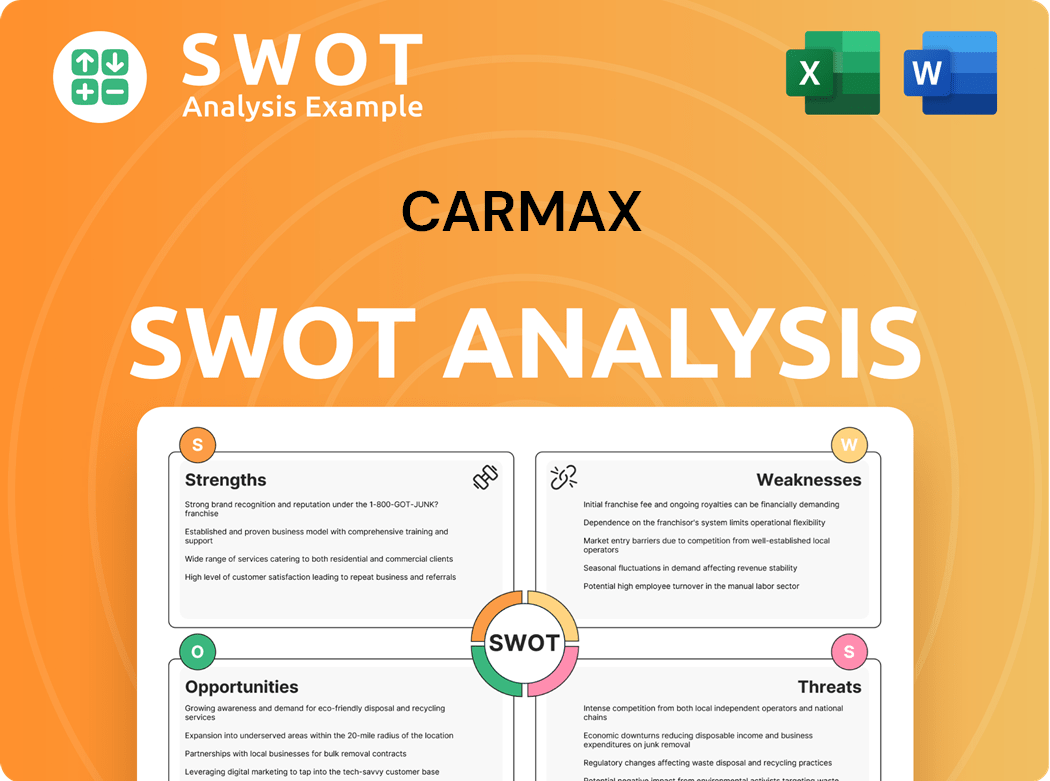
CarMax SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of CarMax?
The early growth of the company, a prominent used car retailer, centered on replicating its successful initial model. The company's expansion was rapid, with new locations opening quickly. This period saw significant revenue increases, although the company initially faced financial losses. This phase set the stage for the company's future in the automotive industry.
By October 1995, just two years after the first store opened, the company had expanded to four locations. These included two superstores in Atlanta and one in Raleigh, North Carolina. Sales figures showed substantial growth, increasing from $77 million in fiscal year 1995 to $304 million. Despite this revenue growth, the company reported losses, including a $7 million loss in fiscal 1995.
To address financial constraints and support expansion, the company announced its intention to sell a portion of its subsidiary to the public in late 1996. The company went public with an Initial Public Offering (IPO) in February 1997, raising $470 million. By the time of the IPO, the company had seven superstores, generating nearly $450 million in revenues. This influx of capital helped fuel further expansion and debt repayment.
By mid-1998, the number of superstores had grown to 23, contributing to $1.47 billion in sales for fiscal 1998. In 1996, the company acquired its first new car franchise, a Chrysler-Plymouth-Jeep store in Atlanta, marking a strategic shift. CarMax Auto Finance (CAF) was established in 1996, becoming a key part of the business model by offering customer financing.
The company achieved full independence on October 1, 2002, when it was spun off from its parent company as a separate publicly traded entity. By fiscal 2002, the company's revenues had increased by 28% to $3.2 billion, and net income nearly doubled to $90.8 million. Understanding who the Owners & Shareholders of CarMax are can provide further insights into the company's financial structure.
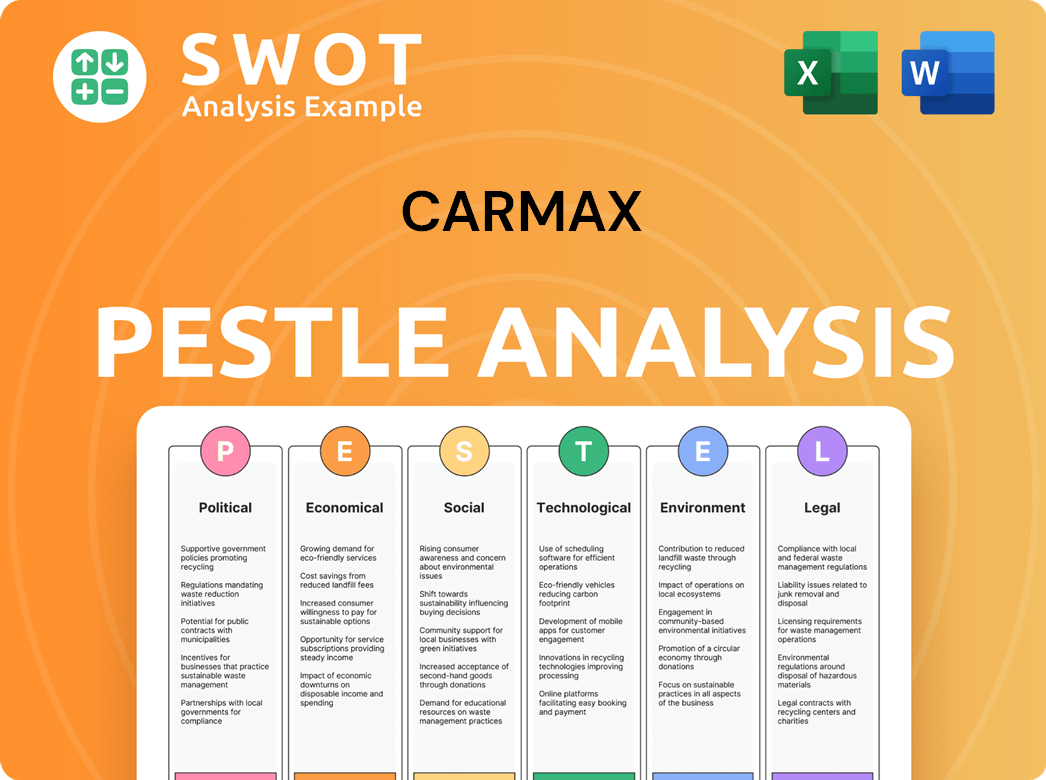
CarMax PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in CarMax history?
The CarMax company has achieved several significant milestones since its founding, shaping the used car market. These achievements include pioneering a customer-centric approach and expanding its services to meet evolving consumer demands, leading to its current position as a leading used car retailer.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1993 | CarMax, a subsidiary of Circuit City, was founded, marking its entry into the used car market. |
| 1996 | CarMax Auto Finance (CAF) was established, providing in-house financing options. |
| 2003 | The first reconditioning center was opened, improving vehicle preparation efficiency. |
| 2015 | CarMax launched its online car-buying experience, adapting to digital consumer preferences. |
| 2024 | CarMax's share of the nationwide age 0-10 year old used vehicle market remained at 3.7%. |
A core innovation of the
This policy offered a transparent and straightforward buying experience, setting CarMax apart from traditional dealerships. This innovation focused on customer satisfaction and trust.
CAF allowed CarMax to provide financing directly to customers. This innovation streamlined the purchase process and contributed significantly to the company's profitability.
Opening reconditioning centers improved efficiency and quality control in vehicle preparation. This ensured that vehicles met high standards before being offered for sale.
The introduction of an online platform expanded CarMax's reach and adapted to evolving consumer preferences. This allowed customers to browse, purchase, and manage their car-buying experience online.
Early on, despite robust sales growth, the
In its early years, CarMax experienced annual losses, raising questions about the viability of its mass-merchandising approach. These financial struggles highlighted the challenges of entering a competitive market.
Intense competition from both traditional dealerships and online retailers like Carvana posed ongoing threats. This competition pressured profit margins and market share.
The gross profit margin compressed in fiscal years 2022 through 2025 due to high acquisition costs for inventory. This impacted the company's financial performance.
The debt-to-equity ratio of 2.84 in early 2025 was significantly higher than the industry average. This raised concerns about financial leverage and risk.
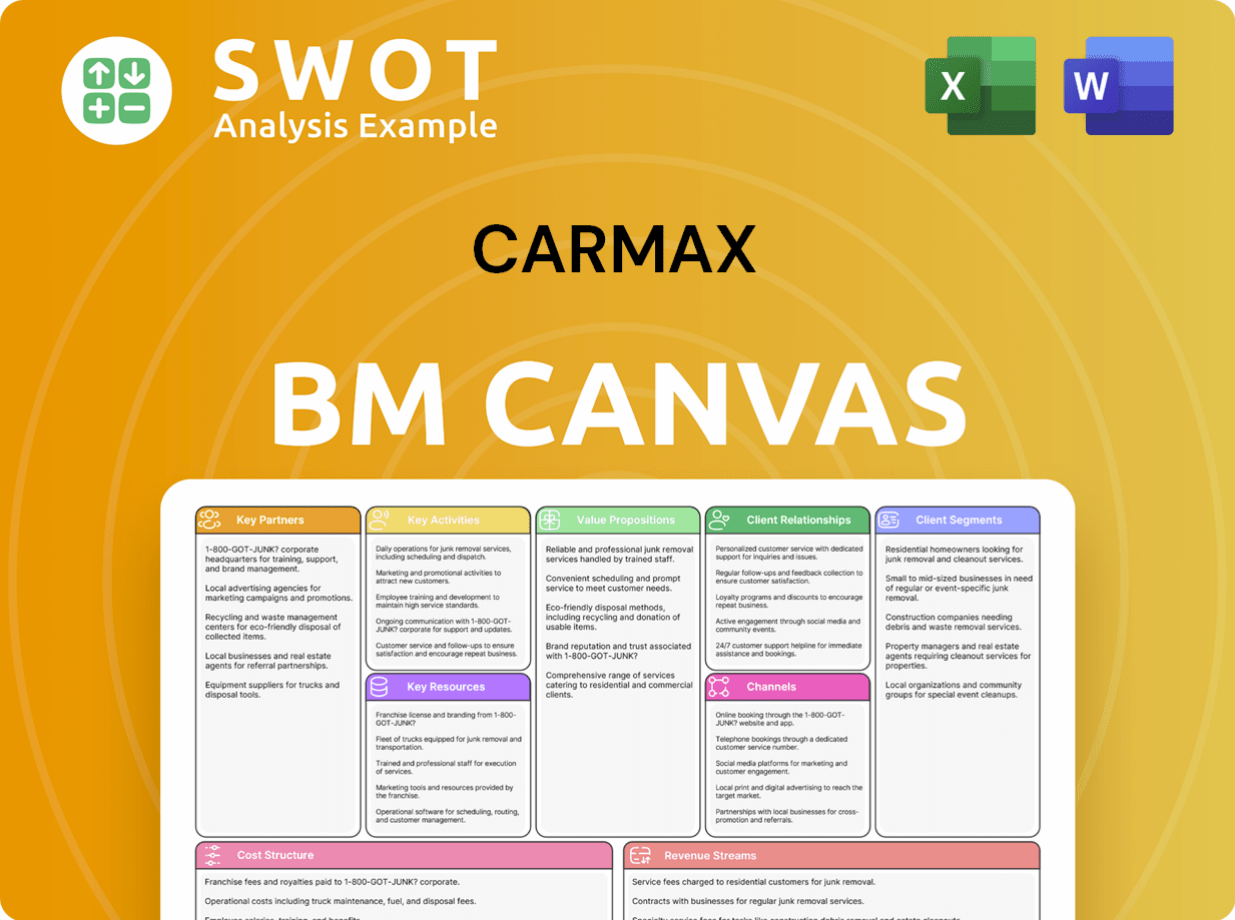
CarMax Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for CarMax?
The CarMax history is marked by significant milestones, starting with research in 1991 by Circuit City executives, who initially codenamed the project 'Project X.' The first used car lot opened in Richmond, Virginia, in September 1993, establishing the foundation for the
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1991 | Circuit City executives begin researching the used car market, codenaming the project 'Project X.' |
| September 1993 | The first CarMax used car lot opens in Richmond, Virginia. |
| 1996 | CarMax Auto Finance (CAF) is established; CarMax acquires its first new car franchise with Chrysler. |
| February 1997 | CarMax goes public with an IPO, raising $470 million. |
| October 1, 2002 | CarMax officially spins off from Circuit City, becoming an independent publicly traded company. |
| 2003 | CarMax opens its first reconditioning center. |
| 2015 | CarMax begins offering an online car-buying experience. |
| Late 2021 | CarMax sells its last new vehicle dealership, focusing solely on used vehicles. |
| Calendar Year 2024 | CarMax's share of the nationwide age 0-10 year old used vehicle market remains at 3.7%. |
| February 28, 2025 | CarMax reports net revenues of $6.0 billion for Q4 FY2025. |
| May 2025 | CarMax releases its 2025 Responsibility Report. |
CarMax is focused on double-digit earnings per share growth, aiming to expand both retail and wholesale unit sales, and increase market share. The company plans to open six new store locations in fiscal year 2026, up from five in FY2025. They are also increasing the number of reconditioning and auction centers.
CarMax is committed to becoming a leading retailer of used EVs. This includes expanding capabilities, enhancing infrastructure, and broadening consumer resources to support the growing demand for electric vehicles. The company is adapting to meet evolving consumer needs.
In Q4 FY2025, CarMax reported net revenues of $6.0 billion, up 6.7% year-over-year. Retail used unit sales increased 6.2%, and net earnings per diluted share increased 81.3% to $0.58 from $0.32 a year ago. They sold approximately 790,000 used vehicles and 540,000 wholesale vehicles in fiscal year 2025.
While analysts have a positive long-term outlook, with an average target price of $90.33, CarMax faces macroeconomic uncertainties and strong competition. Their strategic focus on customer experience, leveraging data science, and AI, positions them for future growth. This aligns with their founding vision.
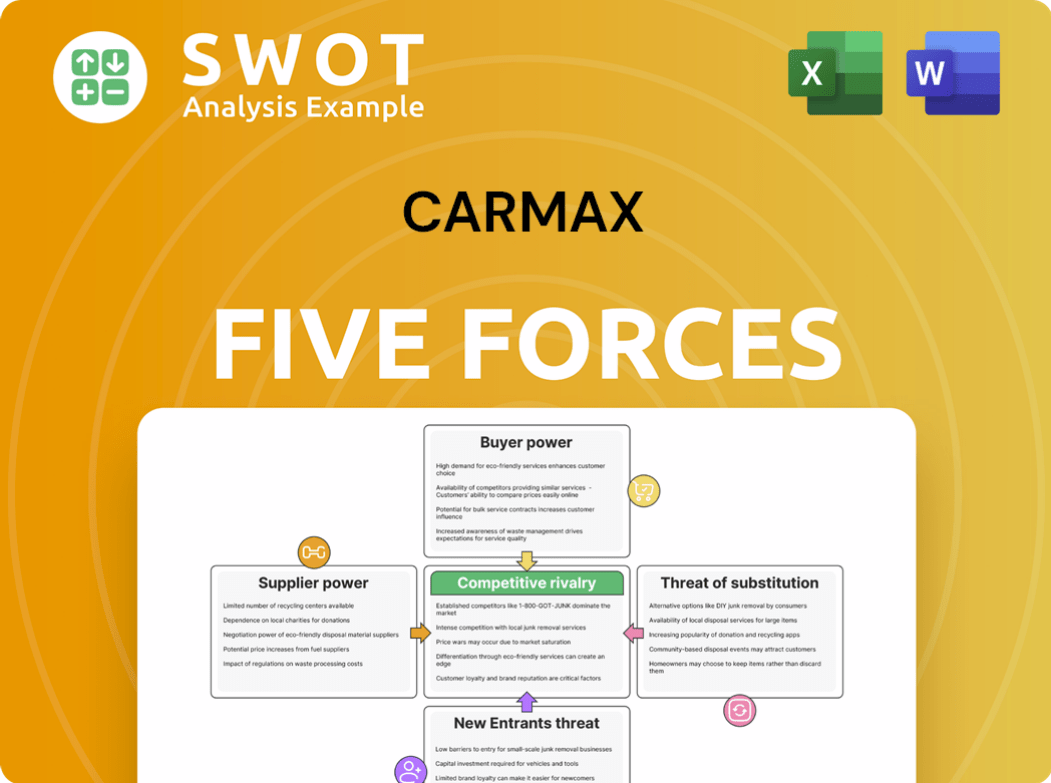
CarMax Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of CarMax Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of CarMax Company?
- How Does CarMax Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of CarMax Company?
- What is Brief History of CarMax Company?
- Who Owns CarMax Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of CarMax Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.