DiDi Global Bundle
How Did DiDi Global Conquer the Ride-Hailing World?
DiDi Global, a name now synonymous with mobility, has a fascinating origin story. From its humble beginnings in Beijing, China, in 2012, DiDi quickly recognized the potential of technology to revolutionize transportation. This early focus on ride-hailing blossomed into a comprehensive suite of services, reshaping how millions move daily.
This DiDi Global SWOT Analysis delves into the brief history of DiDi Global, charting its remarkable rise from a startup to a global mobility leader. Understanding the DiDi company's background, including its DiDi IPO and expansion timeline, is crucial for grasping its impact on ride-hailing and its future prospects. Explore the journey of DiDi China and how it became a dominant force in the industry.
What is the DiDi Global Founding Story?
The story of DiDi Global begins with a simple observation and a clear need. Founded on June 6, 2012, by Cheng Wei, the company emerged to solve a common problem in China's rapidly growing cities: the difficulty of finding a taxi.
Cheng Wei, formerly of Alibaba, recognized the inefficiency of existing transportation options. This led to the creation of a mobile application designed to connect passengers with available taxis. This marked the beginning of what would become a major player in the ride-hailing industry.
The initial concept was straightforward: a taxi-hailing app named Didi Dache. The goal was to provide a more efficient and transparent way for passengers to find taxis and for drivers to secure fares. This addressed the issues of empty returns for drivers and long wait times for passengers.
The early days of DiDi were marked by a lean startup approach and a focus on solving a specific problem in the Chinese market.
- The initial product was a basic mobile application.
- Funding came from bootstrapping and angel investors.
- The founding team had expertise in internet technology and operations.
- China's rapid urbanization and increasing smartphone use created a favorable environment for DiDi.
DiDi Global SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of DiDi Global?
The early phase of the DiDi Global journey focused on establishing a strong presence and gaining users within China. This involved expanding rapidly into major cities and refining its platform based on user feedback. This period was crucial for the company's development, setting the stage for its future growth and market dominance in the ride-hailing sector.
Initially, the focus for DiDi was on acquiring users and penetrating the Chinese market. The company quickly moved beyond Beijing, entering key cities across China. Early product iterations were centered on improving the matching algorithm to connect drivers and passengers efficiently. User experience enhancements, including real-time tracking and in-app payments, were also key features.
A significant aspect of DiDi's early expansion was its competition with Kuaidi Dache. Both companies offered substantial ride subsidies to attract and retain users and drivers. This aggressive strategy significantly increased the user base, making ride-hailing a common practice among Chinese consumers. The merger of DiDi Dache and Kuaidi Dache in February 2015, forming DiDi Kuaidi, consolidated the market, reducing competition.
After the merger, the company, rebranded as DiDi Chuxing in September 2015, broadened its services. New offerings included private car services, hitchhiking, and bus services. This expansion attracted significant investments from venture capital firms and strategic investors, fueling further growth and technological advancements. By 2016, DiDi had facilitated over 1.4 billion rides, showcasing its rapid growth and market acceptance.
In 2016, DiDi completed over 1.4 billion rides, demonstrating its rapid growth. The merger with Kuaidi Dache in 2015 was a pivotal strategic move. DiDi's expansion included services beyond taxi-hailing, such as private cars and hitchhiking. These moves significantly impacted the ride-hailing market.
DiDi Global PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in DiDi Global history?
The brief history of DiDi Global is marked by significant milestones, innovations, and challenges that have shaped its trajectory in the ride-hailing industry. From its inception, the company has expanded rapidly, navigating both domestic and international markets while facing intense competition and regulatory scrutiny. Understanding these key events provides crucial context for assessing DiDi's current position and future potential. For more insight into the company's ownership structure, consider reading about Owners & Shareholders of DiDi Global.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2012 | DiDi Dache (formerly Xiaoju Dache) was founded in Beijing, marking the company's initial entry into the ride-hailing market. |
| 2015 | DiDi merged with Kuaidi Dache, its main competitor, creating a dominant force in the Chinese ride-hailing market. |
| 2016 | DiDi acquired Uber China, solidifying its leading position and expanding its market share. |
| 2018 | DiDi launched its services in several international markets, including Australia, Japan, and Mexico, expanding its global footprint. |
| 2021 | DiDi Global went public on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) with its DiDi IPO, raising approximately $4.4 billion. |
| 2022 | DiDi delisted from the NYSE due to regulatory pressures, focusing on restructuring and compliance within the domestic market. |
DiDi's innovations have been central to its growth and market dominance. The integration of various mobility services onto a single platform, moving beyond simple taxi-hailing, has significantly enhanced user convenience.
DiDi created a 'one-stop' mobility solution, integrating ride-hailing, chauffeur services, carpooling, and bike-sharing, enhancing user convenience. This comprehensive platform approach has been a key differentiator in the market. This integration has significantly improved user experience and operational efficiency.
The company implemented advanced AI and big data analytics to optimize dispatching, routing, and pricing, leading to greater efficiency. This technology has enabled personalized user experiences and improved operational performance. These technologies have been pivotal in managing large-scale operations and adapting to real-time demand fluctuations.
DiDi invested heavily in autonomous driving technology, signaling its long-term vision for the future of mobility. This investment indicates a strategic move towards future transportation solutions. The company's commitment to autonomous vehicles underscores its innovative approach to the evolving transportation landscape.
DiDi expanded into smart transportation solutions, including traffic management and smart city initiatives. These initiatives leverage its existing data and technology infrastructure. This diversification reflects a broader strategy to integrate mobility solutions with urban planning.
DiDi adapted its services to local market needs, including language support and payment options. This strategy has been crucial for expanding its global presence. This localized approach has helped the company gain traction in diverse markets.
DiDi has been integrating electric vehicles into its fleet and promoting EV charging infrastructure. This initiative aligns with the global trend towards sustainable transportation. This move supports environmental sustainability and reduces operational costs.
Despite its successes, DiDi has faced significant challenges. Intense competition, particularly during its early years, led to costly subsidy wars. Regulatory scrutiny, especially concerning data security and anti-monopoly practices, has been a recurring issue.
DiDi faced fierce competition from both domestic and international ride-hailing services. This competition led to price wars and increased marketing expenses. The competitive landscape has required DiDi to constantly innovate and adapt its strategies.
Chinese regulators launched a cybersecurity review shortly after DiDi's IPO in the U.S., leading to app removals and a halt in new user registrations. This regulatory crackdown severely impacted its business and stock performance. The ongoing regulatory environment in China continues to pose challenges for the company.
Data security concerns have been a significant challenge, particularly following the cybersecurity review. Ensuring the protection of user data has become a top priority for DiDi. Addressing these concerns is critical for maintaining user trust and regulatory compliance.
The company has experienced market volatility due to regulatory changes and economic fluctuations. These factors have influenced its financial performance and strategic decisions. Adapting to market dynamics remains a key challenge.
DiDi undertook significant restructuring, focusing on compliance and domestic market stability in response to regulatory pressures. This restructuring involved changes to its business model and operational strategies. The company is working to align its operations with regulatory requirements.
Expanding into international markets has presented challenges related to competition and regulatory compliance. DiDi faces the need to adapt to local market conditions and regulations. Successful international expansion requires a nuanced understanding of each market.
DiDi Global Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for DiDi Global?
The DiDi Global journey began in 2012 with the founding of DiDi Dache, quickly evolving through mergers, acquisitions, and international expansions. This
DiDi history
showcases its rapid growth and adaptation to changing market dynamics, including significant regulatory challenges and strategic shifts.| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 2012 | Cheng Wei founded DiDi Dache in Beijing, marking the beginning of the DiDi Global company . |
| 2015 | DiDi Dache merged with Kuaidi Dache, forming Didi Kuaidi, later rebranded as DiDi Chuxing. |
| 2016 | DiDi acquired Uber China's operations, solidifying its dominant position in the Chinese ride-hailing market. |
| 2017 | DiDi launched DiDi Food, entering the food delivery service sector. |
| 2018 | The company expanded internationally, entering markets like Australia, Japan, and parts of Latin America. |
| 2021 | DiDi conducted its DiDi IPO on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE). |
| 2021 | Chinese regulators initiated a cybersecurity review, which led to the removal of the app and a halt on new user registrations. |
| 2022 | DiDi was delisted from the NYSE, and its applications were reinstated in Chinese app stores. |
| 2023 | DiDi continued to focus on its core mobility business within DiDi China and select international markets, emphasizing compliance and sustainable growth. |
DiDi Global's future is heavily influenced by its ability to adhere to regulatory requirements, particularly within China. The company's operational strategies must prioritize compliance to avoid further penalties or restrictions. This includes data security and user privacy, which are key areas of regulatory focus.
Technological innovation, especially in autonomous driving, is a key area for DiDi. Investments in AI and data analytics will be crucial for improving operational efficiency and user experience. Partnerships with automotive manufacturers could accelerate the integration of self-driving technology into its platform.
International expansion will likely continue, but with a more cautious approach. The company may focus on strengthening its presence in existing markets and exploring new opportunities. This expansion will be carefully managed to mitigate regulatory and market risks.
Analysts anticipate a continued emphasis on profitability within the ride-hailing business. Strategic development of complementary services, such as food delivery and financial technology, is expected to contribute to revenue diversification and growth. The company's financial strategies will aim at sustainable growth and profitability.
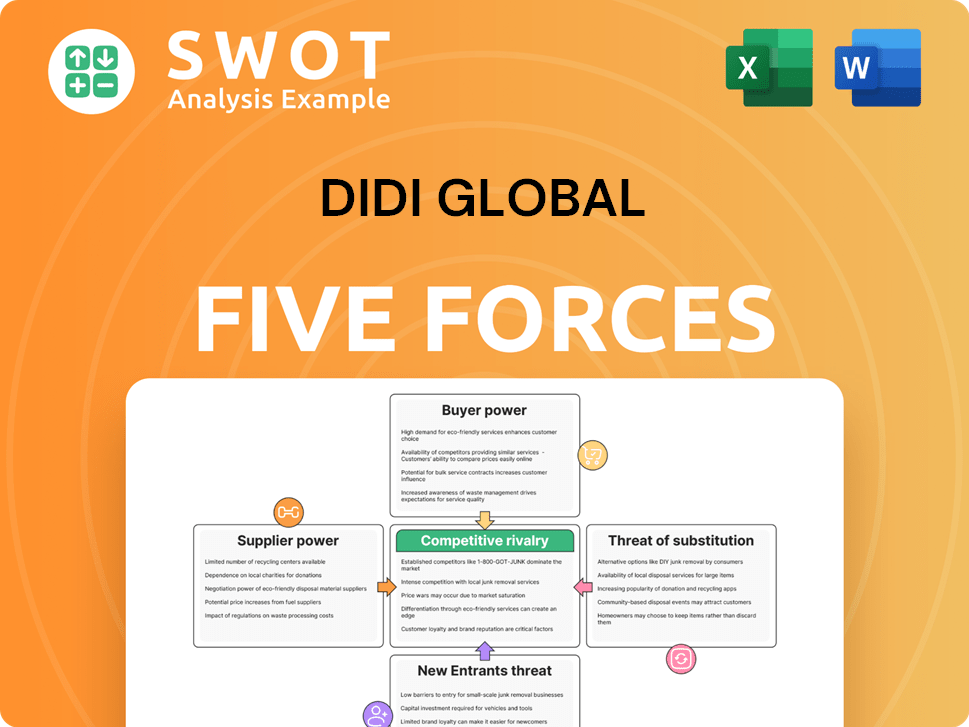
DiDi Global Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of DiDi Global Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of DiDi Global Company?
- How Does DiDi Global Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of DiDi Global Company?
- What is Brief History of DiDi Global Company?
- Who Owns DiDi Global Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of DiDi Global Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.