DiDi Global Bundle
Who Really Controls DiDi Global?
Ever wondered who truly steers the ship at DiDi Global, the massive mobility tech giant? Understanding DiDi Global SWOT Analysis is key to unlocking its strategic moves and future potential. From its humble beginnings in Beijing to its global presence, DiDi's ownership story is a complex web of founders, investors, and public markets.
The evolution of DiDi's ownership, from its founders to its current shareholders, offers critical insights for any investor or strategist. Discovering who owns DiDi, including its major shareholders and the impact of its IPO, is essential to understanding the company's direction. Knowing the DiDi company's ownership structure illuminates its governance, strategic priorities, and long-term prospects, making it a critical area of focus for anyone interested in DiDi stock.
Who Founded DiDi Global?
The ride-hailing giant, DiDi Global Inc., was co-founded by Cheng Wei and Jean Liu. They played crucial roles in shaping the company's initial vision and operational strategies. Understanding the founders and early investors is key to grasping the company's trajectory.
Cheng Wei, serving as the founder and CEO, spearheaded the company's inception. Jean Liu joined in 2014 as President, bringing valuable experience from her previous role at Goldman Sachs. While the exact initial equity splits are not publicly available, Cheng Wei held a significant founding stake.
Early backing came from angel investors and venture capital firms recognizing the potential of the ride-hailing market in China. These early investments were pivotal in fueling DiDi's rapid expansion and establishing its market presence. Understanding the influence of these early backers is important when discussing DiDi ownership.
Cheng Wei, as founder and CEO, was the primary visionary behind DiDi Global. He held a significant founding stake.
Jean Liu joined DiDi in 2014 as President, bringing experience from Goldman Sachs. Her strategic insights were crucial to the company's growth.
Tencent Holdings and Alibaba Group (through Ant Financial) were among the early investors. They provided crucial financial and strategic support.
Early backers acquired stakes through various funding rounds. These rounds provided the capital needed for DiDi's expansion.
Early agreements likely included standard venture capital terms. These terms included preferred shares and board representation.
Cheng Wei maintained significant decision-making power. Early investors supported his vision and strategic direction.
Early investors in DiDi Global, including Tencent and Alibaba, played critical roles in the company's initial growth. These strategic investments provided the necessary capital and support for DiDi's expansion in the competitive ride-hailing market. For more details on the company's structure, you can read more about it in this article about DiDi Global.
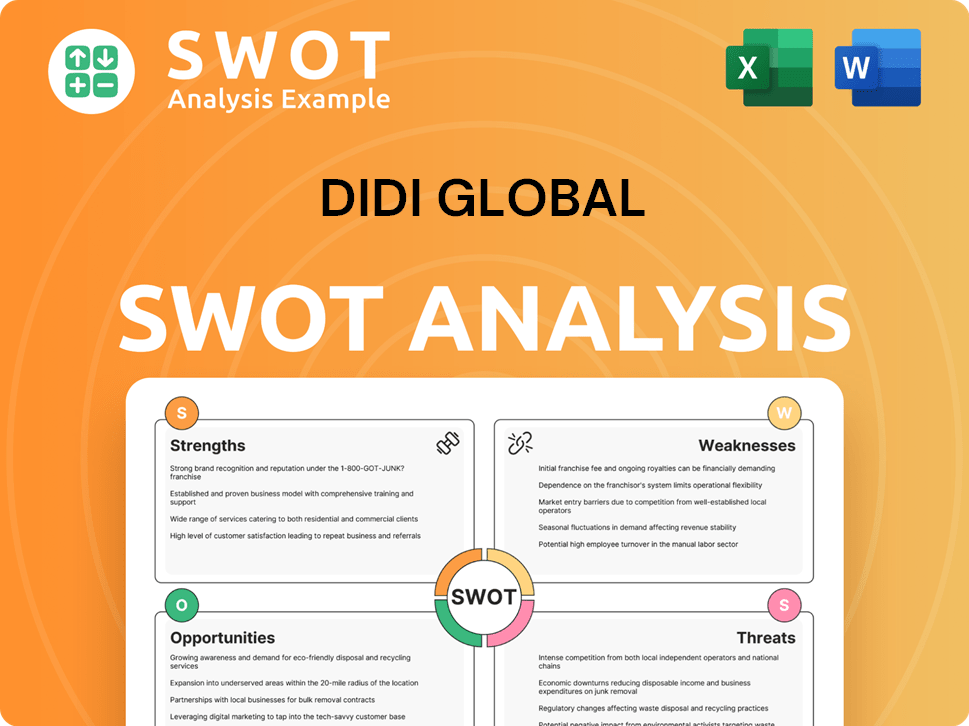
DiDi Global SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has DiDi Global’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The ownership structure of DiDi Global, a prominent player in the ride-hailing industry, has seen significant shifts since its inception. A critical juncture was its initial public offering (IPO) on June 30, 2021, on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) under the ticker 'DIDI'. The IPO raised approximately $4.4 billion, valuing the company at around $68 billion at the time, and introduced a diverse range of investors, including institutional investors and individual shareholders. This event marked a major step in the evolution of DiDi's ownership, transforming it from a privately held entity to a publicly traded company.
Following the IPO, the company faced substantial regulatory scrutiny from Chinese authorities, which led to its delisting from the NYSE in June 2022. This delisting caused a considerable change in its shareholder base, as many institutional investors had to sell their holdings. The regulatory actions and subsequent delisting have reshaped the ownership landscape, emphasizing domestic control and compliance. The evolution of DiDi ownership reflects the dynamic interplay of market forces, regulatory pressures, and strategic decisions that have shaped its trajectory.
| Event | Date | Impact on Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| IPO | June 30, 2021 | Expanded shareholder base, increased institutional ownership. |
| Regulatory Scrutiny | Post-IPO | Led to delisting and shift towards domestic control. |
| Delisting from NYSE | June 2022 | Forced divestment by many foreign investors, concentration of ownership. |
As of recent developments, the ownership structure has become more concentrated. SoftBank, through its Vision Fund, remains a key investor. Uber has also continued to hold a stake in the company. The regulatory crackdown by Chinese authorities has led to a re-evaluation of DiDi's ownership structure, with a greater emphasis on domestic control and compliance. For more insights into the competitive environment, you can explore the Competitors Landscape of DiDi Global.
DiDi Global's ownership has evolved significantly, influenced by its IPO and regulatory pressures.
- SoftBank's Vision Fund and Uber are among the major shareholders.
- The delisting from the NYSE in 2022 led to a shift in the shareholder base.
- The trend indicates a move towards greater domestic Chinese ownership.
- Regulatory compliance is now a key priority for the company.
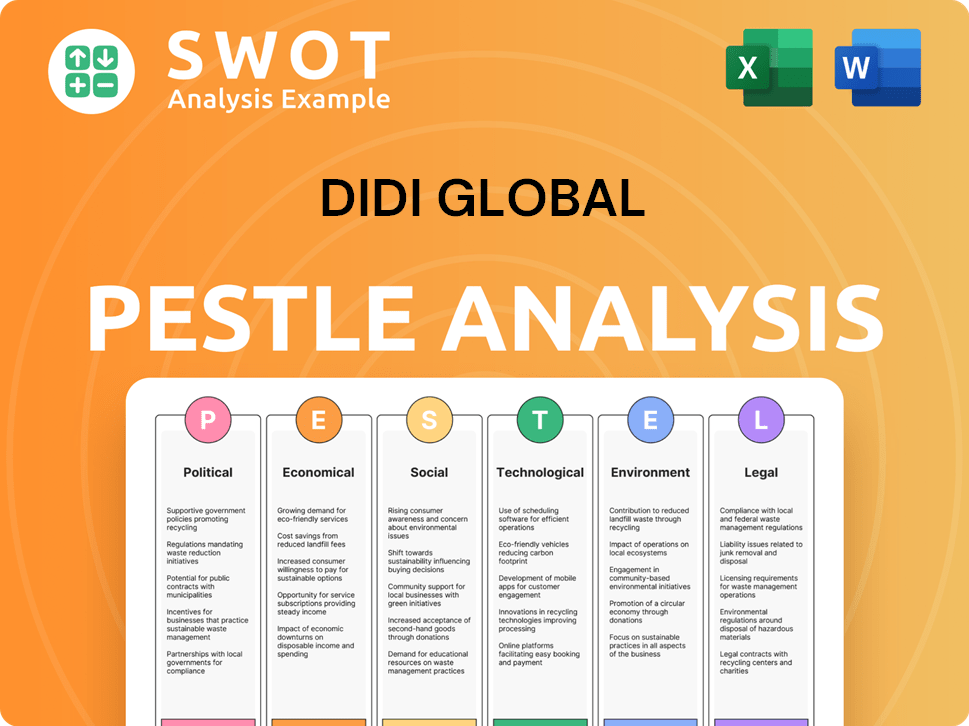
DiDi Global PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on DiDi Global’s Board?
The current board of directors of DiDi Global Inc. plays a crucial role in the company's governance. The board typically includes representatives from major institutional investors, the founding team, and independent directors. For instance, SoftBank, a significant investor, has historically held board representation, ensuring their strategic input and oversight. Cheng Wei, as the founder and CEO, and Jean Liu, as President, maintain prominent positions on the board, representing the founding vision and operational leadership of the company. Independent directors are appointed to provide objective oversight and ensure good corporate governance practices. Knowing who owns DiDi is essential for understanding its strategic direction.
DiDi's board composition and governance structure have been significantly influenced by its delisting from the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and its subsequent focus on domestic operations and regulatory compliance. The board's decisions are now heavily shaped by the need to navigate complex regulatory environments in China and balance shareholder interests with government mandates. This shift underscores the importance of the board's role in ensuring the company's long-term sustainability and strategic alignment with the evolving market dynamics. The Brief History of DiDi Global provides further context on the company's journey and the evolution of its governance.
DiDi's voting structure has historically involved a dual-class share structure. This arrangement grants disproportionate voting power to certain classes of shares, typically held by founders and early investors, compared to ordinary shares held by public investors. This mechanism allows the founding team and key insiders to retain significant control over the company's strategic direction and major decisions, even if their economic ownership (percentage of total equity) is diluted over time. While the specific details of DiDi's dual-class structure are not always publicly highlighted post-delisting, it is a common practice among tech giants to ensure long-term vision and stability. Understanding who controls DiDi Global is key to assessing its strategic direction.
The board of directors includes representatives from major investors, founders, and independent directors, ensuring diverse perspectives and oversight.
- SoftBank has historically held board representation, providing strategic input.
- Cheng Wei and Jean Liu, as founder and CEO/President, maintain key positions.
- DiDi's dual-class share structure gives founders significant voting power.
- Regulatory compliance and domestic focus shape current board decisions.
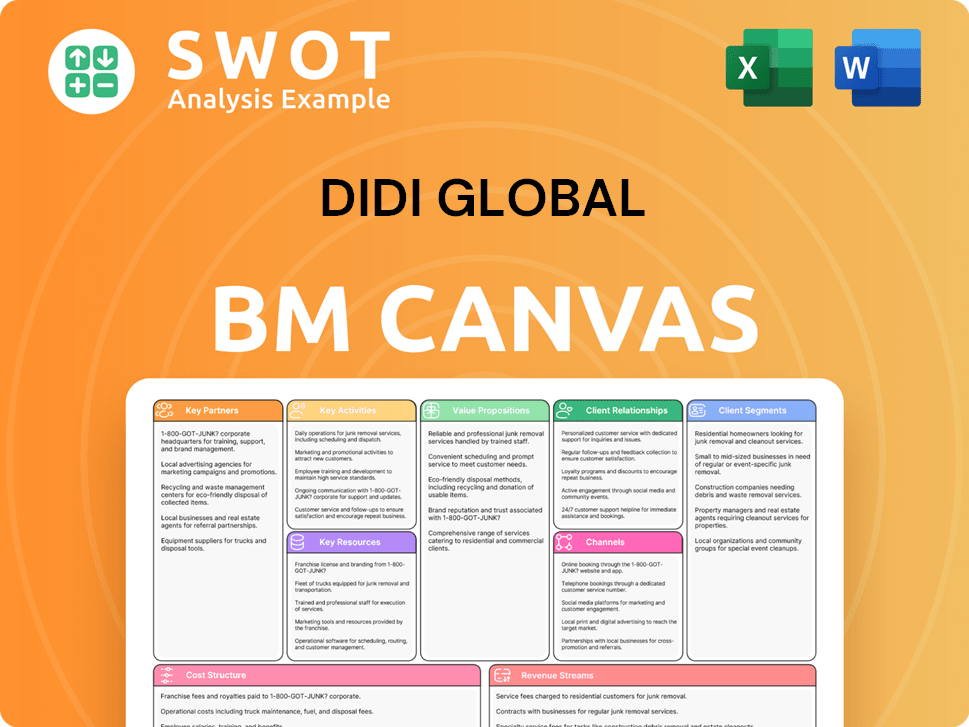
DiDi Global Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped DiDi Global’s Ownership Landscape?
Over the past few years, the ownership structure of DiDi Global has seen considerable shifts, largely influenced by regulatory actions and strategic adjustments. The company's initial public offering (IPO) on the New York Stock Exchange in July 2021 was followed by a cybersecurity review by Chinese authorities. This resulted in the removal of DiDi's apps from Chinese app stores and a halt to new user registrations. Consequently, DiDi was delisted from the NYSE in June 2022 and moved to the OTC market, which led to many institutional investors divesting their holdings.
The trend in DiDi ownership indicates a general de-risking by foreign institutional investors from Chinese tech companies due to increased regulatory uncertainty. While specific details on recent share buybacks or secondary offerings are not widely publicized, the overall trend suggests a potential consolidation of ownership, possibly with increased stakes held by domestic Chinese entities. The potential for a Hong Kong listing could reshape the ownership landscape again, attracting new investors, particularly those focused on the Asian market. For more insights into the company's marketing approaches, you can explore the Marketing Strategy of DiDi Global.
Leadership stability, with figures like Cheng Wei and Jean Liu remaining at the helm, has helped guide the company through these changes. The company has adapted its operational and strategic focus in response to regulatory demands. The industry trend for Chinese tech companies is greater compliance with domestic regulations, often including a re-evaluation of global expansion plans. DiDi's focus is on regaining full operational capacity in China and its long-term strategy for sustainable growth within the regulated environment, which influences its attractiveness to different investor segments.
| Ownership Aspect | Details | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Delisting from NYSE | June 2022 | Forced divestment by many institutional investors |
| Regulatory Scrutiny | Ongoing | Increased uncertainty, affecting investor confidence |
| Potential Hong Kong Listing | Speculative | Could attract new investors, especially from Asia |
The ownership of DiDi has shifted due to regulatory changes and delisting from the NYSE. Domestic Chinese entities may be increasing their stakes.
The DiDi stock is now traded on the OTC market. The company's market capitalization and current stock price are subject to market fluctuations.
DiDi investors have been affected by the regulatory changes and delisting. The company's financial backers and major shareholders are subject to change.
The DiDi company is working to regain operational capacity in China. It is adapting to regulatory demands and focusing on sustainable growth.
DiDi Global Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of DiDi Global Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of DiDi Global Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of DiDi Global Company?
- How Does DiDi Global Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of DiDi Global Company?
- What is Brief History of DiDi Global Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of DiDi Global Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.