China Evergrande Group Bundle
From Real Estate Titan to Liquidation: What Happened to China Evergrande?
China Evergrande Group, once a symbol of China's booming real estate market, now stands as a stark reminder of the risks associated with rapid expansion. Founded in 1996, Evergrande's journey from a Guangzhou-based developer to a global behemoth is a compelling story of ambition and financial engineering. This China Evergrande Group SWOT Analysis will explore the factors that led to its rise and fall.
Understanding the Evergrande history is crucial for anyone invested in the Chinese property market or global financial stability. The Evergrande crisis serves as a case study in the dangers of high leverage and the interconnectedness of the global economy. Examining Evergrande Group financial troubles provides valuable insights into risk management and the importance of sustainable business practices. From its ambitious beginnings, Evergrande Group founder, Hui Ka Yan, built a real estate empire that ultimately faced a dramatic default timeline.
What is the China Evergrande Group Founding Story?
The story of China Evergrande Group began in 1996. Xu Jiayin (Hui Ka Yan) established the company in Guangzhou, Guangdong province. This was a time of rapid urbanization in China, and Xu saw a major opportunity in the real estate market.
Xu Jiayin, who had a background in construction, aimed to build a leading real estate developer. His initial focus was on high-quality construction and innovative designs. This was meant to attract a loyal customer base. The company's main business was buying land, developing properties, and selling them, mainly residential apartments for middle- and upper-income buyers.
Initially known as Hongda Group, the company quickly gained recognition in Guangdong. The early funding sources aren't detailed like seed rounds. However, its fast growth suggests it used various financing methods common in the developing Chinese market. The cultural and economic conditions of China in the mid-1990s, with rapid urbanization and property sector liberalization, significantly influenced the company's creation and provided a favorable environment for its expansion.
The company was founded in 1996 by Xu Jiayin in Guangzhou, China, capitalizing on the country's rapid urbanization and real estate boom.
- The initial focus was on developing high-quality residential properties.
- The company's early success was fueled by leveraging financing mechanisms common in the emerging Chinese market.
- Rapid urbanization and the liberalization of the property sector were key factors in Evergrande's early growth.
- The company's original business model centered on land acquisition, property development, and sales, targeting middle- and upper-income buyers.
The Owners & Shareholders of China Evergrande Group played a significant role in the company's early trajectory. The company's expansion was rapid, with the number of projects and land acquisitions increasing substantially in the early 2000s. This aggressive growth strategy was fueled by debt, a common practice in the Chinese property market at the time. By the late 2010s, Evergrande had become one of the largest real estate developers in China, with projects across the country.
In 2024, the impact of the Evergrande crisis continues to reverberate through the Chinese property market. The company's debt restructuring plan is ongoing, and the ultimate outcome remains uncertain. The Evergrande Group financial troubles have led to significant losses for investors and bondholders. The Evergrande default timeline is a stark reminder of the risks associated with high leverage and rapid expansion in the real estate sector. The latest news on Evergrande indicates that the company is still navigating complex legal and financial challenges.
China Evergrande Group SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of China Evergrande Group?
The early growth of China Evergrande Group, now known as China Evergrande, saw a rapid expansion beyond its initial base in Guangdong province. This expansion involved diversifying its portfolio to include commercial and retail properties, as well as hotels and resorts. This strategic move capitalized on China's booming real estate market, quickly establishing the company as a leading developer.
A key milestone in Evergrande's early growth was its IPO on the Stock Exchange of Hong Kong (SEHK) in October 2009. The IPO raised approximately $722 million, providing significant capital for further expansion. This funding fueled an aggressive growth strategy, characterized by high debt and leverage.
Evergrande expanded its operations to over 170 cities across mainland China. By 2020, the company had developed more than 1,300 projects. The company diversified into property management, property investment, new energy vehicles, and health and entertainment, transforming into a conglomerate.
By the 2010s, Evergrande became China's second-largest property developer by sales. This strong presence in both residential and commercial real estate markets solidified its position. In 2018, Evergrande was recognized as the most valuable real estate company globally.
Evergrande's success was driven by a 'high debt, high leverage, high turnover, and low cost' business model. This strategy, while effective in rapidly expanding the company, later contributed to its financial challenges. The company's rapid growth significantly impacted the Chinese property market.
China Evergrande Group PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in China Evergrande Group history?
The story of China Evergrande Group, a significant player in the Chinese property market, is marked by periods of remarkable growth and, ultimately, severe financial difficulties. Its trajectory reflects the volatile nature of the real estate sector in China and the risks associated with rapid expansion and high leverage. The company's journey provides valuable insights into the dynamics of the Chinese property market and the challenges faced by large-scale developers.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2018 | China Evergrande became the world's most valuable real estate company, showcasing its rapid ascent and market dominance. |
| 2020 | Accumulated approximately $300 billion in total liabilities, highlighting the company's significant debt burden. |
| 2021 | Defaulted on its offshore debt, signaling the beginning of its liquidity crisis. |
| 2022 | Total liabilities reached 2.43 trillion yuan (roughly US$340 billion) as of December 31, 2022, underscoring the extent of its financial troubles. |
| 2023 | Filed for Chapter 15 bankruptcy in the United States as part of its debt restructuring efforts. |
| 2024 | A Hong Kong court ordered the liquidation of China Evergrande Group after it failed to present a concrete restructuring plan. |
China Evergrande Group demonstrated innovation by diversifying into sectors beyond real estate. This included venturing into new energy vehicles, property management, and healthcare, reflecting an ambition for broader market presence. For instance, its subsidiary, Evergrande New Energy Auto, aimed to start making electric cars by 2022, showcasing a forward-looking approach.
Evergrande expanded beyond real estate into areas like new energy vehicles, property management, and healthcare.
Evergrande New Energy Auto aimed to start making electric cars by 2022.
The company ventured into property management to broaden its business scope.
Evergrande also explored opportunities in the healthcare sector.
The company's expansion into various sectors demonstrated its innovative approach.
These ventures were part of Evergrande's strategy to diversify its revenue streams.
The company faced significant challenges, primarily stemming from its aggressive, debt-fueled expansion. The introduction of the 'three red lines' policy by the Chinese government in August 2020, which restricted developers' debt, significantly impacted Evergrande's business model. The company's financial troubles led to a liquidity crisis, culminating in a default on its offshore debt in late 2021.
By 2020, Evergrande had accumulated approximately $300 billion in total liabilities.
The Chinese government's policy capping property developers' debt-to-cash, debt-to-assets, and debt-to-equity ratios significantly impacted Evergrande.
The company faced a liquidity crisis in 2021, leading to its default on offshore debt.
In March 2024, the CSRC alleged that Evergrande overstated its revenue by significant amounts.
The company filed for Chapter 15 bankruptcy in the United States as part of its debt restructuring efforts.
A Hong Kong court ordered the liquidation of China Evergrande Group in January 2024.
China Evergrande Group Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for China Evergrande Group?
The Evergrande history is marked by rapid growth and a dramatic downfall. Founded in 1996, the company quickly rose to become a major player in the Chinese real estate market. However, after years of expansion, the group faced a severe liquidity crisis, leading to a debt default and eventual liquidation. This timeline illustrates the key events that shaped the company's trajectory.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1996 | Evergrande Group is founded by Xu Jiayin (Hui Ka Yan) in Guangzhou. |
| 2009 (October) | The company raises $722 million in its Initial Public Offering (IPO) on the Stock Exchange of Hong Kong. |
| 2010s | Evergrande becomes China's second-largest property developer by sales. |
| 2018 | Evergrande is listed as the world's most valuable real estate company. |
| 2020 (August) | China introduces the 'three red lines' policy to curb developers' debt. |
| 2021 | Evergrande faces a severe liquidity crisis and defaults on offshore debt payments, triggering the Chinese property sector crisis. |
| 2023 (July) | Evergrande publicly reports significant net losses for 2021 (476 billion yuan) and 2022 (105.9 billion yuan). |
| 2023 (August) | Evergrande files for Chapter 15 bankruptcy protection in the U.S. |
| 2024 (January) | A Hong Kong court orders the liquidation of China Evergrande Group. |
| 2024 (March) | China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC) alleges Evergrande overstated revenue in 2019 and 2020. |
| 2024 (August) | Liquidators seek to recover $6 billion from Evergrande executives and initiate legal action against former auditors. |
| 2024 (September) | China imposes a six-month ban on PwC over its Evergrande audit. |
| 2025 (March) | China Evergrande New Energy Vehicle Group Limited delays its 2024 annual results publication, leading to a trading suspension application. |
The China Evergrande Group is currently undergoing liquidation, with assets being sold to repay creditors. This process involves complex legal proceedings, including attempts by liquidators to recover funds from executives. Legal actions are also being pursued against former auditors.
The broader Chinese property market continues to face challenges, although the pace of decline in new home sales has slowed in Q1 2025. The government is implementing stimulus packages, including special loans to complete stalled projects, to stabilize the market. However, deflationary risks and weak consumer demand remain concerns.
The property management services segment, Evergrande Property Services Group Limited, reported operating revenue of approximately RMB12,756.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2024, a year-on-year increase of approximately 2.2%. The company is focusing on cost control and market expansion.
The future of China Evergrande is tied to its liquidation process. The broader Chinese property market faces an uncertain outlook. The market's performance, along with the government's measures, will significantly impact the economy.
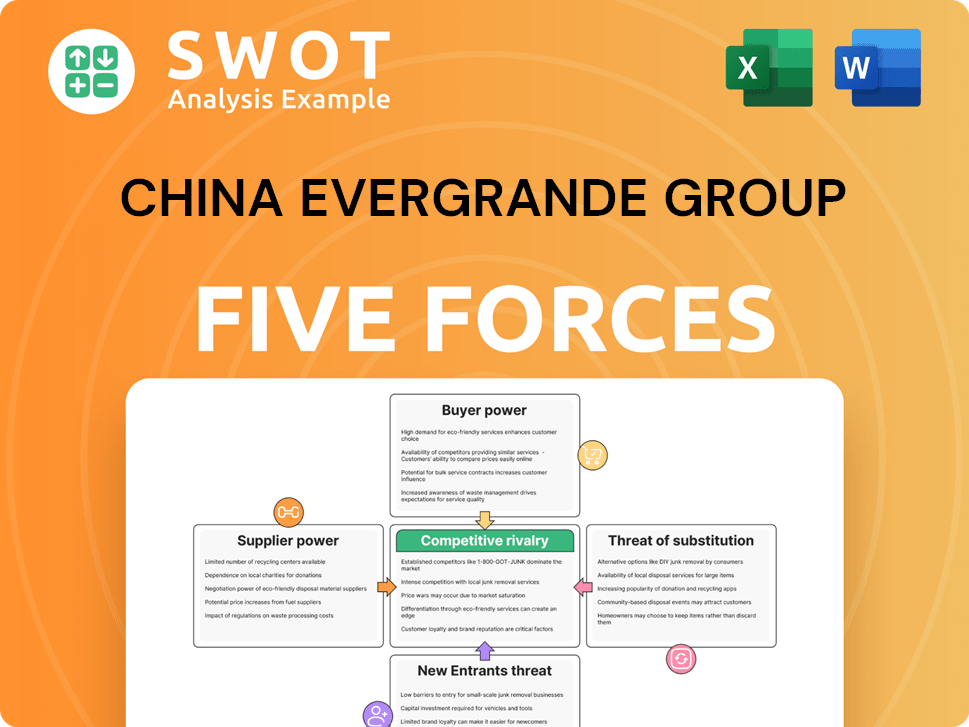
China Evergrande Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of China Evergrande Group Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of China Evergrande Group Company?
- How Does China Evergrande Group Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of China Evergrande Group Company?
- What is Brief History of China Evergrande Group Company?
- Who Owns China Evergrande Group Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of China Evergrande Group Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.