Hang Seng Bank Bundle
How Did Hang Seng Bank Rise to Banking Prominence?
Journey back to 1933 and discover the fascinating Hang Seng Bank SWOT Analysis! From its humble beginnings as a small money-changing shop in Hong Kong, Hang Seng Bank has transformed into a financial powerhouse. Explore its remarkable evolution and understand the key milestones that shaped its success.

The story of Hang Seng Bank history is a compelling narrative of growth and resilience within the Hong Kong banking industry. Understanding the brief history of Hang Seng Bank, including its founding date and relationship with HSBC Hong Kong, is crucial for anyone interested in the financial landscape. With a customer base of close to 4 million, Hang Seng Bank's impact on the Hong Kong economy is undeniable, making its journey a vital case study for investors and strategists alike.
What is the Hang Seng Bank Founding Story?
The story of Hang Seng Bank begins on March 3, 1933. It was founded by a group of four partners: Lam Bing-yim, Ho Sin-hang, Leung Chik-wai, and Sheng Chun-lin. Their vision was to create a financial institution focused on gold trading, exchange, and currency conversion, marking the start of a significant chapter in Hang Seng Bank history.
These founders, bringing their experience from the gold and silver industry, saw an opportunity in the evolving Hong Kong banking landscape. With an initial capital of HKD 100,000, they set out to build what would become a cornerstone of the Hong Kong financial system. This early focus on gold and currency exchange was a strategic move, positioning the bank to capitalize on the financial activities of the time.
The first branch, a modest money-changing shop, was established on Wing Lok Street in Sheung Wan, Hong Kong. Lam Bing-yim took on the role of chairman, with Ho Sin-hang and Leung Chik-wai managing the operations. The team started with only 11 staff members, but their diligent approach quickly led to profitability. In its first year, 'Hang Seng Ngan Ho' reported earnings exceeding HKD 10,000, a testament to its early success. The name 'Hang Seng,' which translates to 'ever-growing,' reflected the bank's ambition to expand alongside its customers, setting the stage for its future growth in the Hong Kong banking industry.
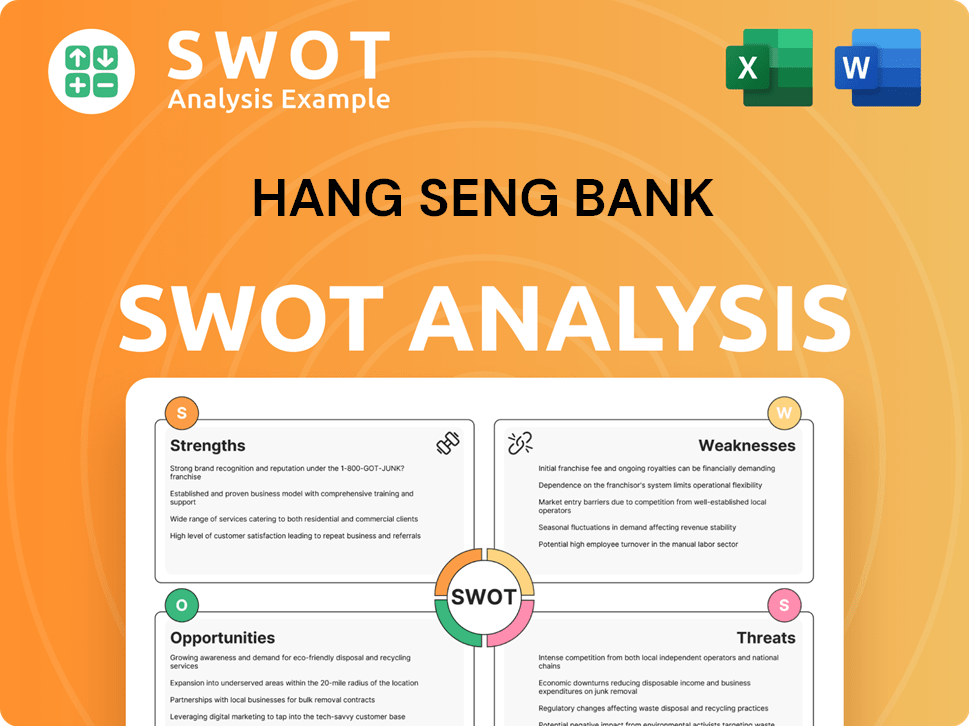
Hang Seng Bank SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Hang Seng Bank?
The early phase of Hang Seng Bank, initially known as Hang Seng Ngan Ho, focused on expanding its services beyond basic money changing. In 1952, the company reincorporated as a private limited company, officially launching commercial banking operations. The bank experienced rapid growth in Hong Kong's burgeoning economy. By the late 1950s, its total assets surpassed many older Chinese banks.
In 1960, Hang Seng Ngan Ho rebranded to Hang Seng Bank. While it went public, it wasn't yet listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. A critical turning point occurred in 1965 when HSBC acquired a majority interest following a bank run. This acquisition provided stability for future expansion.
The bank listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange in 1972. Throughout the 1980s, Hang Seng expanded its physical presence, opening branches in Mass Transit Railway stations. International expansion began in 1985 with a representative office in mainland China. A branch office in Shanghai opened in 1997.
By the early 2000s, Hang Seng Bank actively pursued further expansion in mainland China. This included negotiations for an equity stake in Minsheng Bank in 2003. Plans were made to invest HK$200 million to open a branch office in Beijing. This strategic move highlighted the bank's commitment to the Chinese market.
In 2024, HSBC, the parent company of Hang Seng Bank, reported a profit before tax of USD $30.8 billion. Hang Seng Bank continues to be a significant player in the Hong Kong banking industry, with a focus on retail and commercial banking services. The bank's strategic expansions in mainland China have been a key driver of its growth.
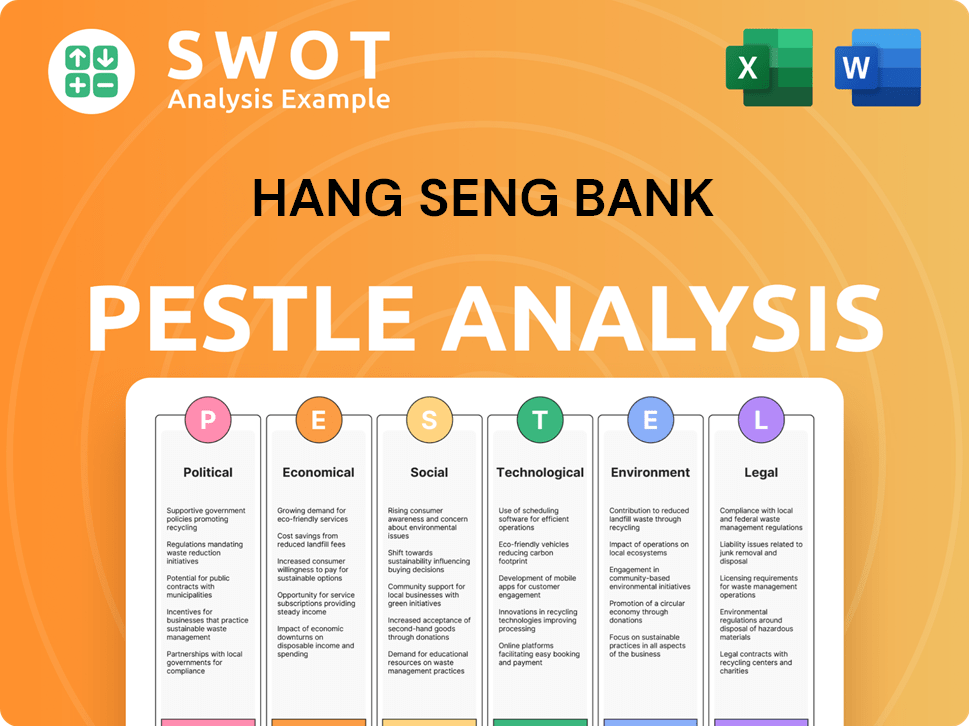
Hang Seng Bank PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Hang Seng Bank history?
Throughout its history, Hang Seng Bank has achieved numerous milestones, reflecting its growth and adaptation within the Hong Kong banking industry. These achievements have been pivotal in shaping its presence and influence in the financial sector, demonstrating its commitment to innovation and customer service.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2000 | Launched e-banking services, marking its entry into the digital banking era. |
| 2007 | Received authorization to establish Hang Seng Bank (China) Limited, expanding its footprint in mainland China. |
| 2007 | Opened a new Hong Kong office at MegaBox, Kowloon Bay. |
| 2010 | Became the first bank in Hong Kong to fix the renminbi (RMB) prime rate. |
| 2012 | Introduced the world's first RMB gold exchange-traded fund (ETF). |
| 2018 | Rolled out Hong Kong's first AI chatbots for retail banking services. |
| 2020 | Launched remote account opening services for business banking customers and introduced the 'Future Branch Concept'. |
| 2020 | Included in the Dow Jones Sustainability Asia Pacific Index. |
| 2023 | Unveiled its 'Future Banking' service concept, including the first Smart Teller in Hong Kong. |
| 2024 | Unveiled its newly renovated Hong Kong main branch, featuring the 'Come to You' service concept. |
| 2025 | Jointly launched Hong Kong's first business World Mastercard debit card, the Hang Seng Commercial Multi-Currency Debit Mastercard. |
Hang Seng Bank has consistently embraced innovation to enhance its services and customer experience. These initiatives highlight its forward-thinking approach and dedication to meeting the evolving needs of its customers within the dynamic Hong Kong banking landscape.
In 2000, the bank launched its e-banking services, a pivotal move that embraced the digital era, providing customers with convenient online access to their accounts and financial services. This initiative improved customer service and operational efficiency.
In 2010, the bank became the first in Hong Kong to fix the renminbi (RMB) prime rate, followed by the introduction of the world's first RMB gold exchange-traded fund (ETF) in February 2012, demonstrating its leadership in RMB-related financial products.
In 2018, Hang Seng Bank rolled out Hong Kong's first AI chatbots for retail banking services, enhancing customer service through automated and readily available support. This technological advancement improved customer interaction.
In 2020, the bank launched remote account opening services for business banking customers, streamlining the process and improving accessibility. This initiative was part of the bank's efforts to support business clients.
Also in 2020, the bank unveiled its 'Future Branch Concept' integrating digital innovation and human touch, aiming to provide a seamless banking experience. This concept combined digital tools with personalized customer service.
In 2023, Hang Seng Bank introduced the 'Future Banking' service concept, featuring Hong Kong's first Smart Teller at its Festival Walk Branch. In 2023, the bank also introduced a 'Simple Mode' for its mobile app, enhancing user experience.
Despite its successes, Hang Seng Bank has navigated several challenges, including economic uncertainties. The bank's strategic responses and proactive measures have been critical in maintaining its financial health and market position.
The bank faced a bank run in 1965, and has since dealt with persistent economic uncertainties, including geopolitical and macro uncertainties in 2024. These events tested the bank's resilience and risk management strategies.
In response, Hang Seng Bank adopted a prudent and forward-looking risk management approach. This approach, coupled with a focus on diversifying its revenue streams, has helped the bank navigate challenging economic conditions.
In 2024, the bank saw a 26% increase in non-interest income and a 75% jump in new-to-bank affluent customers. These figures demonstrate the effectiveness of its strategic pivots and its ability to attract new customers.
The bank's strategic adaptations and innovations, such as the 'Come to You' service concept, reflect its commitment to enhancing customer service and operational efficiency. These changes are designed to meet evolving customer expectations.
The recent launch of the Hang Seng Commercial Multi-Currency Debit Mastercard in April 2025, demonstrates support for enterprise digital transformation. This initiative helps businesses manage their finances efficiently.
Hang Seng Bank continues to evolve, as highlighted in this article about the history of HSBC and Hang Seng Bank, adapting to market changes and technological advancements.
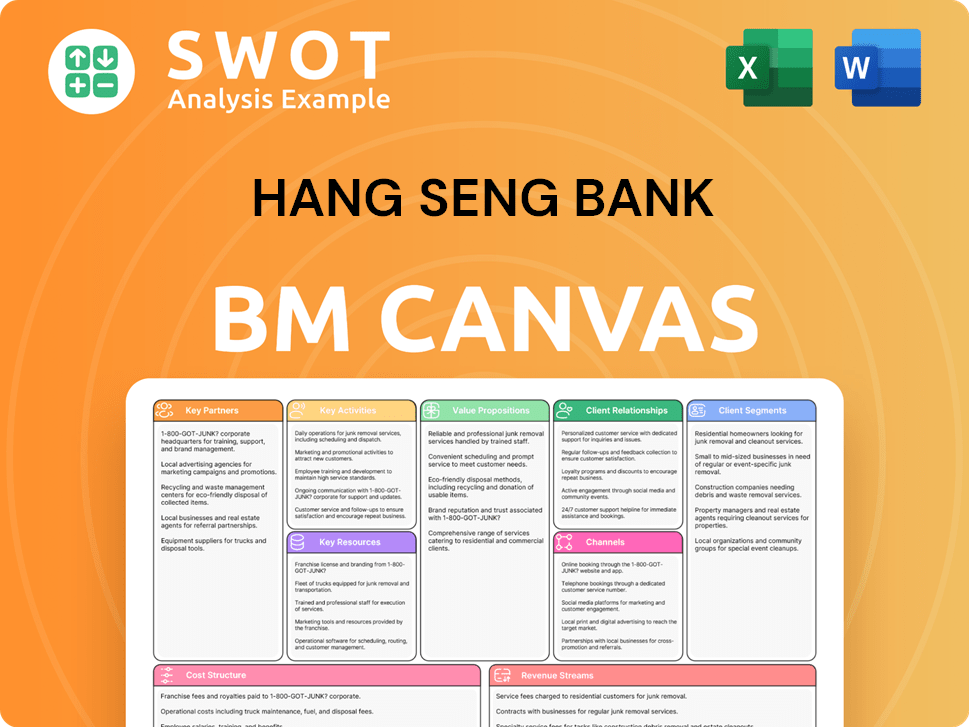
Hang Seng Bank Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Hang Seng Bank?
The brief history of Hang Seng Bank is marked by significant milestones, from its establishment as 'Hang Seng Ngan Ho' in Hong Kong on March 3, 1933, to its transformation and expansion within the Hong Kong banking and financial landscape. The bank's journey includes key moments such as the acquisition of a majority interest by HSBC in 1965, its public listing in 1972, and the introduction of innovative services like e-banking in 2000 and AI chatbots in 2018. More recently, Hang Seng Bank has focused on digital transformation, cross-boundary wealth management, and sustainable growth, with a strong financial performance in 2024, including a 3% increase in profit attributable to shareholders to HKD 18.38 billion and a 26% rise in non-interest income.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1933 | Founded as 'Hang Seng Ngan Ho' in Hong Kong. |
| 1952 | Reincorporated as a private limited company, beginning commercial banking operations. |
| 1960 | Renamed Hang Seng Bank and became a public company. |
| 1965 | HSBC acquired a majority interest in Hang Seng Bank. |
| 1972 | Listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. |
| 1981 | Began opening branches in Mass Transit Railway stations. |
| 1985 | Opened its first representative office in mainland China. |
| 1997 | Opened a branch office in Shanghai. |
| 2000 | Introduced e-banking services. |
| 2007 | Hang Seng Bank (China) Limited was authorized and established; new Hong Kong office opened at MegaBox. |
| 2010 | Became the first bank in Hong Kong to fix the RMB prime rate. |
| 2012 | Introduced the world's first RMB gold ETF. |
| 2018 | Rolled out Hong Kong's first AI chatbots for retail banking services. |
| 2020 | Launched remote account opening for business banking; unveiled 'Future Branch Concept'; included in Dow Jones Sustainability Asia Pacific Index. |
| July 2023 | Unveiled 'Future Banking' service concept with Smart Teller. |
| November 2024 | Unveiled newly renovated Hong Kong main branch with 'Come to You' service concept. |
| February 2025 | Reported strong full-year financial results for 2024, with profit attributable to shareholders increasing by 3% to HKD 18.38 billion and non-interest income up 26%. |
| April 2025 | Launched Hang Seng Commercial Multi-Currency Debit Mastercard with Mastercard. |
| May 8, 2025 | Scheduled Annual General Meeting to consider audited financial statements for 2024 and re-election of directors. |
Hang Seng Bank plans to continue investing in its capabilities. The bank anticipates economic uncertainties to persist in 2025. It will maintain a prudent and forward-looking risk management approach. The renovation of its main branch is expected to be completed by the second quarter of 2025, featuring a new Cross-boundary Wealth Management Centre.
Hang Seng is focusing on diversifying its revenue streams and growing its target customer base. In 2024, there was a 26% increase in non-interest income and a 75% jump in new-to-bank affluent customers. The bank's long-term strategic initiatives include promoting digital transformation for businesses and enhancing cross-boundary wealth management services, particularly for mainland China customers.
The bank is promoting digital transformation for businesses. They are enhancing cross-boundary wealth management services, particularly for mainland China customers. New account openings surged by 81% year-on-year in 2024. These initiatives reflect the bank's commitment to supporting customer success and Hong Kong's position as a financial center.
Hang Seng Bank plans to continue investing in its capabilities and supporting the community to fuel sustainable growth. The bank's forward-looking approach remains consistent with its founding vision of being an 'ever-growing' institution. This approach supports the success of its customers and contributes to Hong Kong's role as an international financial center.
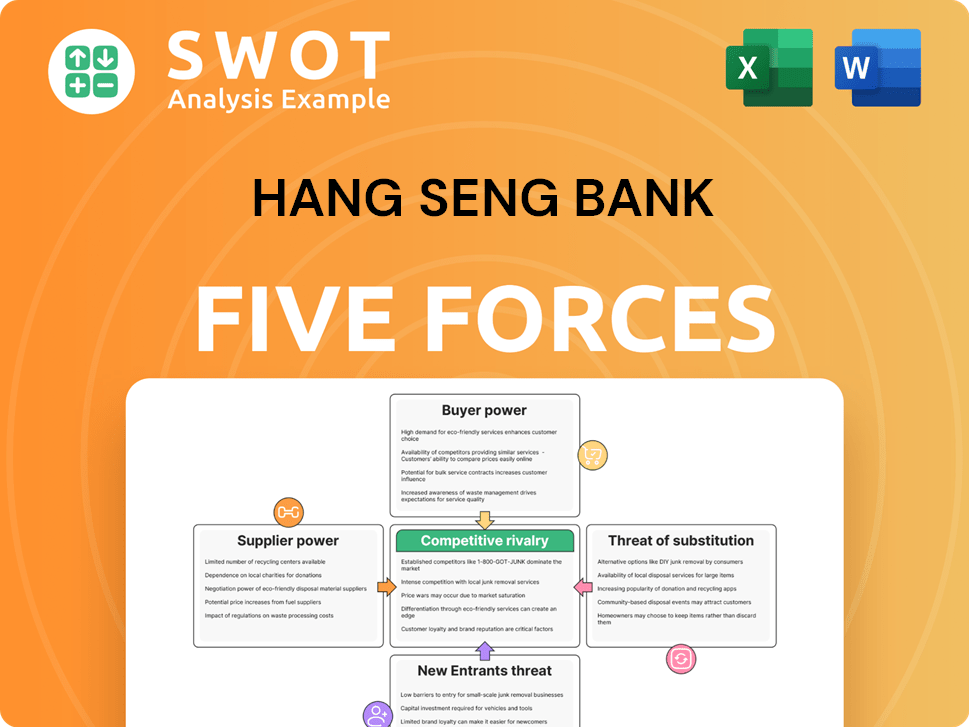
Hang Seng Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Hang Seng Bank Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Hang Seng Bank Company?
- How Does Hang Seng Bank Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Hang Seng Bank Company?
- What is Brief History of Hang Seng Bank Company?
- Who Owns Hang Seng Bank Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Hang Seng Bank Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.