Hang Seng Bank Bundle
Who Really Owns Hang Seng Bank?
Understanding the ownership structure of a major financial institution like Hang Seng Bank is crucial for investors and strategists alike. From its humble beginnings in 1933, Hang Seng Bank has evolved into a financial powerhouse. This article unravels the intricate web of Hang Seng Bank SWOT Analysis, exploring its ownership history and the key players who shape its destiny.

Delving into "Hang Seng Bank ownership" reveals a fascinating narrative of strategic acquisitions and market dynamics. The influence of "HSBC" on Hang Seng Bank, particularly after the 1965 bank run, is a critical aspect of understanding its current structure. This analysis provides insights into "Who owns Hang Seng Bank," examining the roles of major stakeholders, public shareholders, and the overall "Hong Kong banking" landscape to illuminate the bank's strategic direction and potential for future growth. Learn about "Hang Seng Bank shareholders" and "Hang Seng Bank major stakeholders" to better understand "Who is the parent company of Hang Seng Bank" and the "Hang Seng Bank and HSBC relationship."
Who Founded Hang Seng Bank?
The story of Hang Seng Bank, now a cornerstone of Hong Kong's financial landscape, began on March 3, 1933. It was originally established as Hang Seng Ngan Ho, marking the start of a journey that would see it become one of the most significant financial institutions in the region. The founders, a group of visionary entrepreneurs, laid the groundwork for what would become a powerhouse in Hong Kong banking.
The founders of Hang Seng Ngan Ho were Lam Bing Yim, Ho Sin Hang, Sheng Tsun Lin, and Leung Chik Wai. These individuals brought together their expertise and resources to create a bank focused on gold trading, exchange, and currency conversion. Their collaboration was a crucial factor in the early success and growth of the bank.
In the early days, the bank operated from a small shop at 70 Wing Lok Street, Sheung Wan, covering about 800 square feet. The initial capital was approximately HKD100,000, and the staff comprised only 11 people. This humble beginning contrasts sharply with the bank's current status as a major player in the financial world.
The founders aimed to create a bank specializing in gold trading and currency exchange. Their combined experience in finance and business laid the foundation for Hang Seng's early success.
Lam Bing Yim served as the first chairman, while Ho Sin Hang took on the role of manager. Leung Chik Wai was the deputy manager, and Sheng Tsun Lin held a director position.
The bank started with a modest capital base of approximately HKD100,000. This initial investment was crucial for starting operations and establishing a presence in the market.
The bank's first branch was a small money-changing shop at 70 Wing Lok Street, Sheung Wan. The limited space and small staff reflected the bank's early stage.
In 1952, Hang Seng Ngan Ho was incorporated as a private limited company, with a registered capital of HKD10 million and a paid-up capital of HKD5 million.
Ho Sin Hang became chairman, Leung Chik Wai was appointed vice chairman, and Ho Tim became general manager.
Understanding the initial ownership of Hang Seng Bank is crucial for appreciating its evolution. The founders, with their diverse backgrounds, pooled their resources to establish the bank. The early focus on gold trading and currency exchange was a strategic move, given the economic environment of the time. The transition to a private limited company in 1952 marked a significant step in the bank's growth. For more insights into the competitive landscape, consider exploring the Competitors Landscape of Hang Seng Bank.
- The founders' collaborative approach and shared vision were critical to the bank's formation.
- The initial capital and the small-scale operations were typical of early banking ventures.
- The incorporation as a private limited company allowed for more structured growth.
- The leadership changes reflected the bank's evolving structure and ambitions.
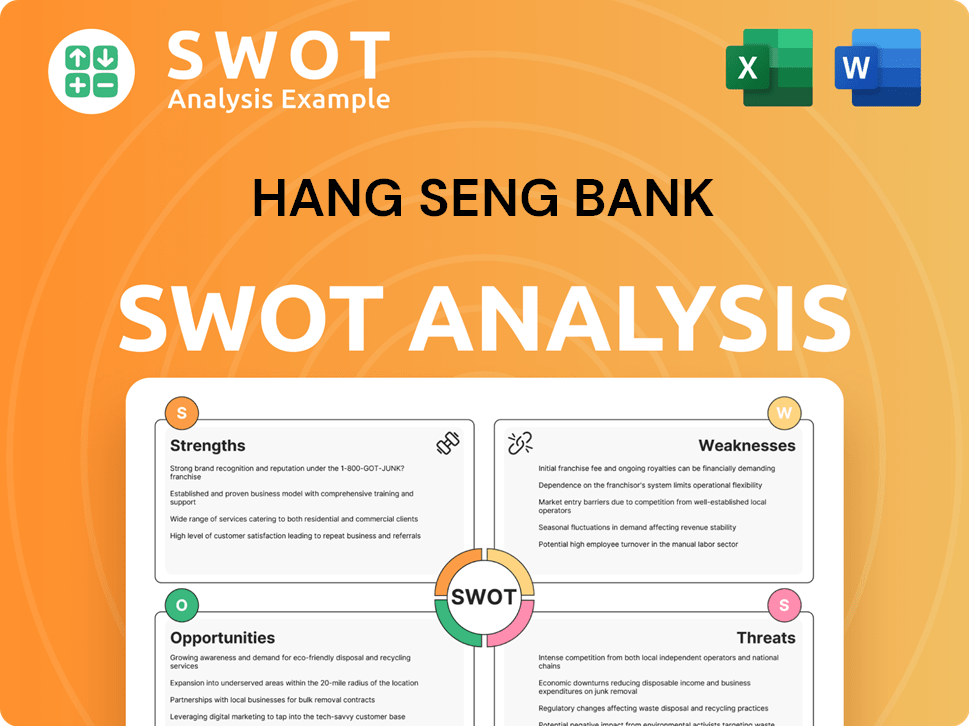
Hang Seng Bank SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
How Has Hang Seng Bank’s Ownership Changed Over Time?
The evolution of Hang Seng Bank's ownership has been marked by key events that shaped its current structure. Initially a private entity, Hang Seng Bank transitioned to a public company in 1960. A pivotal moment occurred in 1965 when The Hongkong and Shanghai Banking Corporation (HSBC) acquired a controlling stake, driven by a bank run. This acquisition significantly influenced the bank's trajectory, establishing HSBC as a major shareholder.
HSBC's influence solidified over time, with its stake increasing. The bank's listing on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange in 1972 further broadened its shareholder base. As of 2024-2025, the relationship between Hang Seng Bank and HSBC remains strong, with HSBC holding a substantial majority equity interest, solidifying its position as the primary owner. This ownership structure allows Hang Seng Bank to leverage HSBC's extensive resources and services.
| Year | Event | Impact on Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| 1960 | Conversion to Public Company | Broadened shareholder base |
| 1965 | HSBC Acquisition | HSBC gained controlling interest (51%) |
| 1972 | Listing on Hong Kong Stock Exchange | Further diversification of shareholders |
As of 2024-2025, HSBC Group holds a 62.14% majority equity interest in Hang Seng Bank, making it the controlling shareholder. Other significant institutional investors include BlackRock, Inc., The Vanguard Group, Inc., and State Street Global Advisors, Inc. This ownership structure allows Hang Seng Bank to leverage HSBC Group's infrastructure and services, including information technology and operational services, enabling the bank to maintain high-quality operations and benefit from HSBC Group's advanced capabilities. This relationship is key to understanding the Hang Seng Bank's financial information and overall structure.
HSBC is the primary owner of Hang Seng Bank, holding a majority stake.
- HSBC's acquisition in 1965 was a pivotal moment.
- Other institutional investors also hold significant shares.
- The relationship with HSBC allows Hang Seng Bank to leverage resources.
- Understanding the ownership structure is crucial for analyzing the bank.
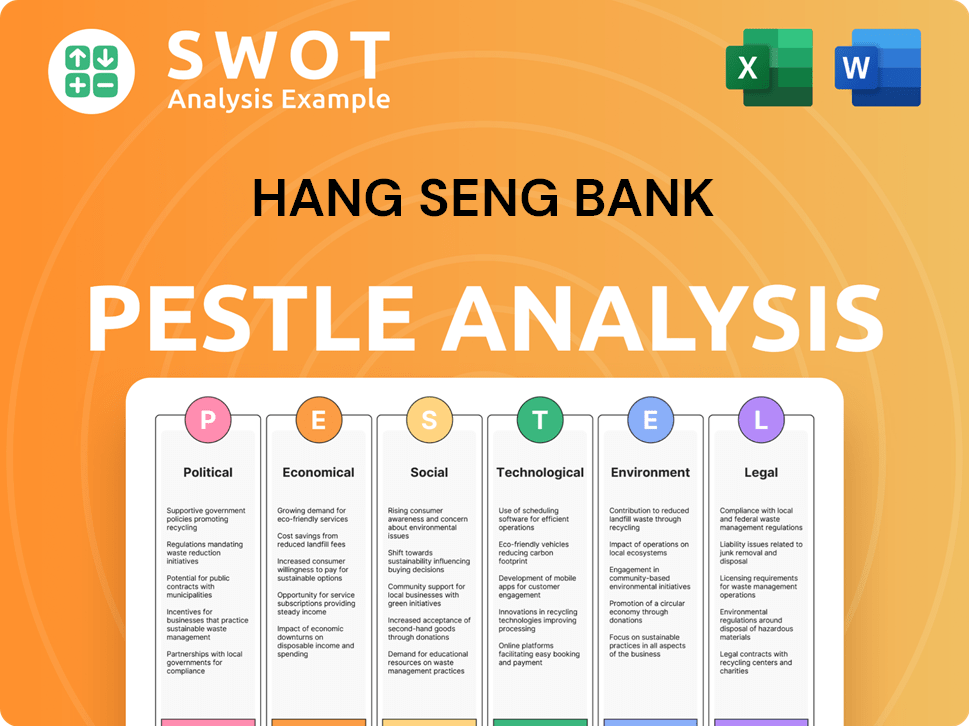
Hang Seng Bank PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
Who Sits on Hang Seng Bank’s Board?
The current Board of Directors of Hang Seng Bank Limited plays a crucial role in the company's governance. As of May 8, 2025, the Board included Irene Y. L. Lee (Chairman until May 8, 2025), Diana Cesar (Chief Executive), Cordelia Chung, Kathleen C. H. Gan, Clement K. M. Kwok, Patricia S. W. Lam, David Y. C. Liao, Huey Ru Lin, Say Pin Saw, and Wang Xiao Bin. Edward Cheng Wai Sun, an Independent Non-executive Director, was re-designated as the Chairman of the Board and the Nomination Committee after the 2025 Annual General Meeting. Catherine Zhou Rong was appointed as a Non-executive Director with effect from October 25, 2024, and her appointment was subject to shareholder election at the 2025 AGM. She is currently the Global Chief Information Officer, Wealth and Personal Banking of the HSBC Group, highlighting the strong link between Hang Seng Bank and its controlling shareholder.
| Board Member | Role | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Edward Cheng Wai Sun | Chairman of the Board and the Nomination Committee | Re-designated after the 2025 Annual General Meeting |
| Diana Cesar | Chief Executive | |
| Catherine Zhou Rong | Non-executive Director | Appointed October 25, 2024, subject to shareholder election at 2025 AGM |
The voting structure of Hang Seng Bank is generally based on a one-share-one-vote principle. HSBC's 62.14% stake gives it significant control and influence over decision-making processes. This substantial ownership ensures a degree of alignment in strategic direction. For more information on the bank's background, see the Brief History of Hang Seng Bank.
The Board of Directors includes members from major shareholders and independent members, ensuring diverse perspectives. HSBC holds a significant majority stake, giving it substantial control over the bank's strategic direction.
- HSBC's ownership is a key factor in understanding Hang Seng Bank's corporate structure.
- The one-share-one-vote principle ensures fairness in shareholder voting.
- The composition of the board reflects the bank's strong ties to its parent company.
- Catherine Zhou Rong's appointment emphasizes the link between Hang Seng Bank and the HSBC Group.
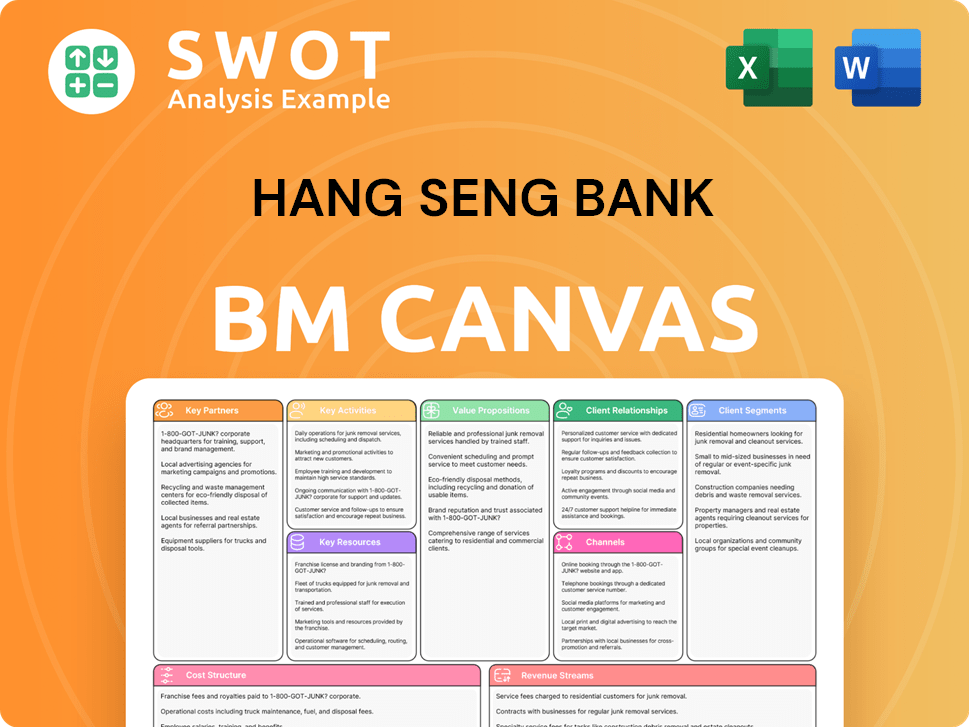
Hang Seng Bank Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What Recent Changes Have Shaped Hang Seng Bank’s Ownership Landscape?
In recent years, Hang Seng Bank has seen shifts in its ownership and operational strategies. A key development was the share buyback program conducted in 2024, totaling approximately HK$3 billion, which concluded on September 9, 2024. This move, the first in over two decades, aimed to return surplus capital to shareholders, signaling a strategic focus on shareholder value. The Hang Seng Bank ownership structure is significantly influenced by HSBC, which holds a controlling stake.
HSBC's substantial 63% stake in Hang Seng Bank limits the free float of shares, yet the bank still complies with the Hong Kong Exchange's requirement of a 25% free float. This ownership structure is a critical aspect of understanding the bank’s operational decisions and financial performance. The relationship between Hang Seng Bank and HSBC is a central theme in the bank's history and its current strategic direction. To understand the bank's customer base better, one can read about the Target Market of Hang Seng Bank.
| Metric | 2024 | Change |
|---|---|---|
| Non-interest income | Increased by 26% | |
| Operating profit | HK$21,558 million | Up 8% |
| Profit attributable to shareholders | HK$18,379 million | Up 3% |
| Earnings per share | HK$9.33 | Improved by 4% |
| Return on average ordinary shareholders' equity | 11.3% | Steady |
| Customer deposits | HK$1,267 billion | Up 7% |
| CET1 capital ratio | 17.7% |
The bank's recent initiatives include a focus on cost-effectiveness. In May 2025, Hang Seng Bank announced a restructuring plan involving a 1% reduction in core staff, with departmental cuts ranging from 10% to 50%. Despite this, the bank continues to recruit in growth areas, particularly in wealth management. Who owns Hang Seng Bank is a key consideration when evaluating these strategic moves and the overall financial health of the institution.
HSBC's majority stake significantly influences Hang Seng Bank ownership and strategic decisions.
The share buyback program and restructuring efforts reflect a focus on shareholder value and operational efficiency.
The bank reported strong financial results for 2024, with increases in non-interest income and operating profit.
The Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) capital ratio stood at 17.7% as of December 31, 2024, well above regulatory requirements.
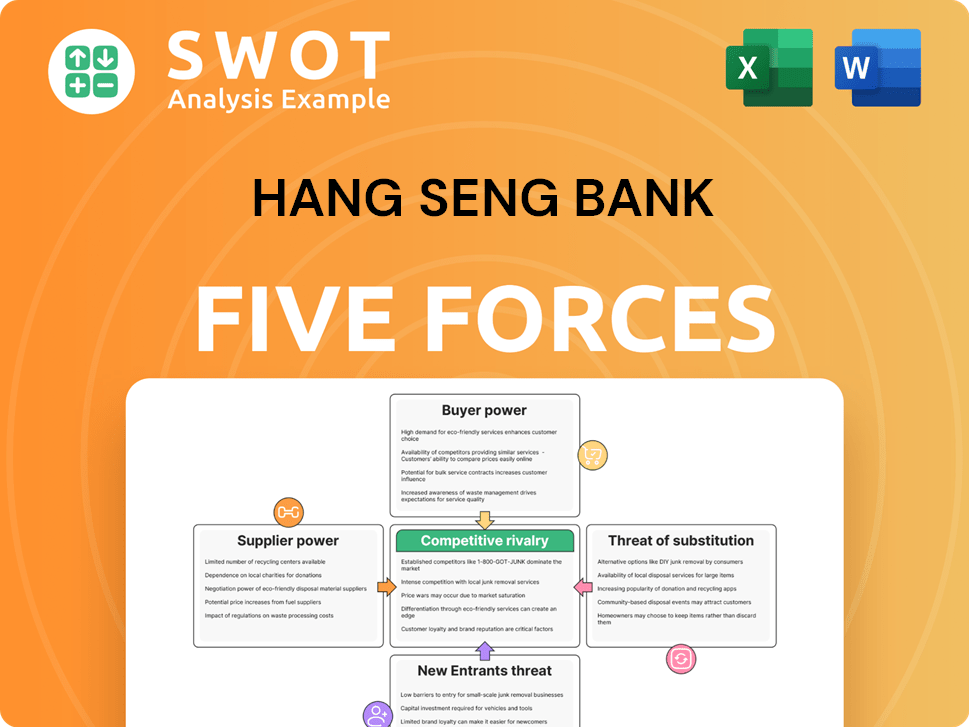
Hang Seng Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What are Mission Vision & Core Values of Hang Seng Bank Company?
- What is Competitive Landscape of Hang Seng Bank Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Hang Seng Bank Company?
- How Does Hang Seng Bank Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Hang Seng Bank Company?
- What is Brief History of Hang Seng Bank Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Hang Seng Bank Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.