Hennes & Mauritz Bundle
How Did H&M Conquer the Fast-Fashion World?
Dive into the captivating Hennes & Mauritz SWOT Analysis and explore the remarkable journey of H&M, a global leader in the fast-fashion industry. From its humble beginnings in Sweden, the company revolutionized retail with its innovative approach to offering trendy, affordable clothing. Discover how a simple vision transformed into a fashion empire, shaping the way we consume fashion today.

This exploration of H&M history will uncover the key milestones and strategies that propelled Hennes & Mauritz from a local brand to a global phenomenon. Learn about the H&M founder, Erling Persson, and his initial vision, which set the stage for the company's remarkable expansion. We'll examine the early days of H&M, its evolution in fashion, and the challenges it overcame to become a household name.
What is the Hennes & Mauritz Founding Story?
The story of Hennes & Mauritz (H&M) began on October 4, 1947, in Västerås, Sweden. Erling Persson, the visionary founder, saw an opportunity to provide stylish yet affordable clothing to women in the post-World War II era. This marked the beginning of what would become a global fashion powerhouse.
Persson's initial focus was clear: to offer ready-to-wear fashion at competitive prices. This approach was relatively new at the time, setting the stage for H&M's future success. The company's early days were centered around women's apparel, establishing its foundation in the fashion industry.
The company's original name, Hennes, which means 'hers' in Swedish, reflected its initial focus on women's fashion. Persson's entrepreneurial drive fueled the company's early growth, as he aimed to make fashion accessible. The cultural and economic climate of post-war Sweden, with a growing middle class, played a significant role in shaping H&M's early success.
Here are some key points about the H&M history and Hennes & Mauritz origin:
- H&M founder Erling Persson established the company in 1947.
- The initial focus was on affordable women's fashion, a novel concept at the time.
- The original name, Hennes, reflected the company's target audience.
- The post-war economic environment in Sweden provided a favorable market for growth.
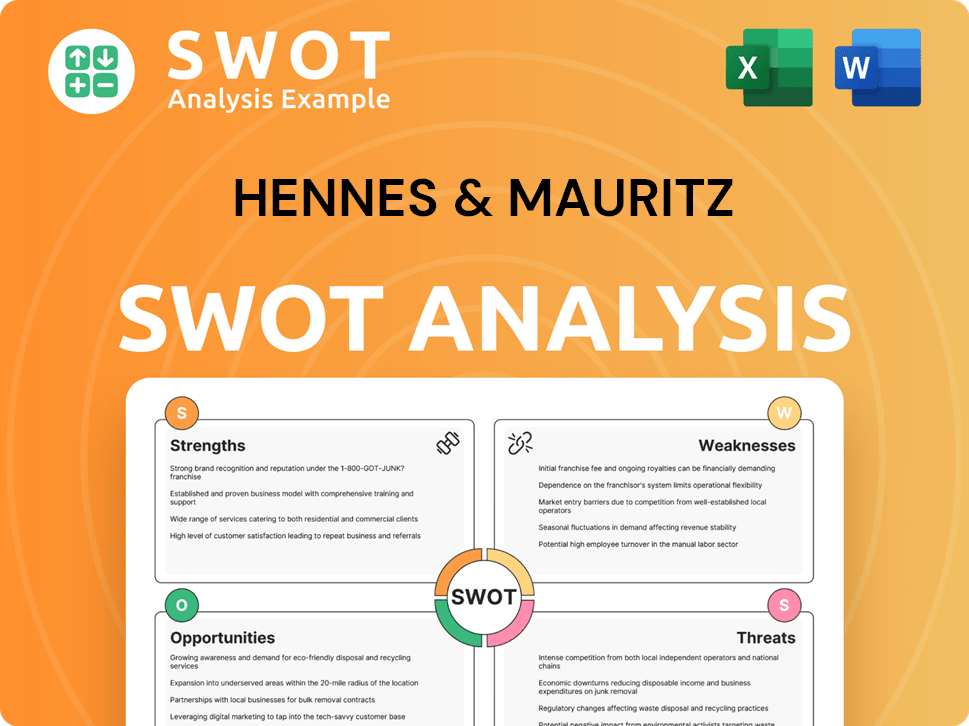
Hennes & Mauritz SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Hennes & Mauritz?
The early growth of Hennes & Mauritz, or H&M, was marked by strategic expansions and key acquisitions. This period saw the company evolve from a Swedish retailer to an international fashion brand. The company's journey included significant milestones that shaped its business model and laid the foundation for its future global dominance.
The H&M history began with steady growth within Sweden. The
H&M founder
Erling Persson focused on expanding the number of stores across the country. This expansion helped solidify its domestic market share and build a strong brand presence.In 1964, Hennes & Mauritz made its first international move by expanding into Norway. This marked a significant step in the
H&M timeline
. Initial international expansion set the stage for future global growth.A pivotal moment in the
H&M origin
story was the acquisition of Mauritz Widforss in 1968. This acquisition included a stock of men's clothing, which prompted the introduction of a men's line. This strategic move led to the renaming of the company to Hennes & Mauritz, or H&M.Following the name change, H&M expanded its product categories and geographical reach. In the 1970s, the company entered new European markets, including Denmark and the United Kingdom. The company also diversified its offerings to include children's clothing and cosmetics.
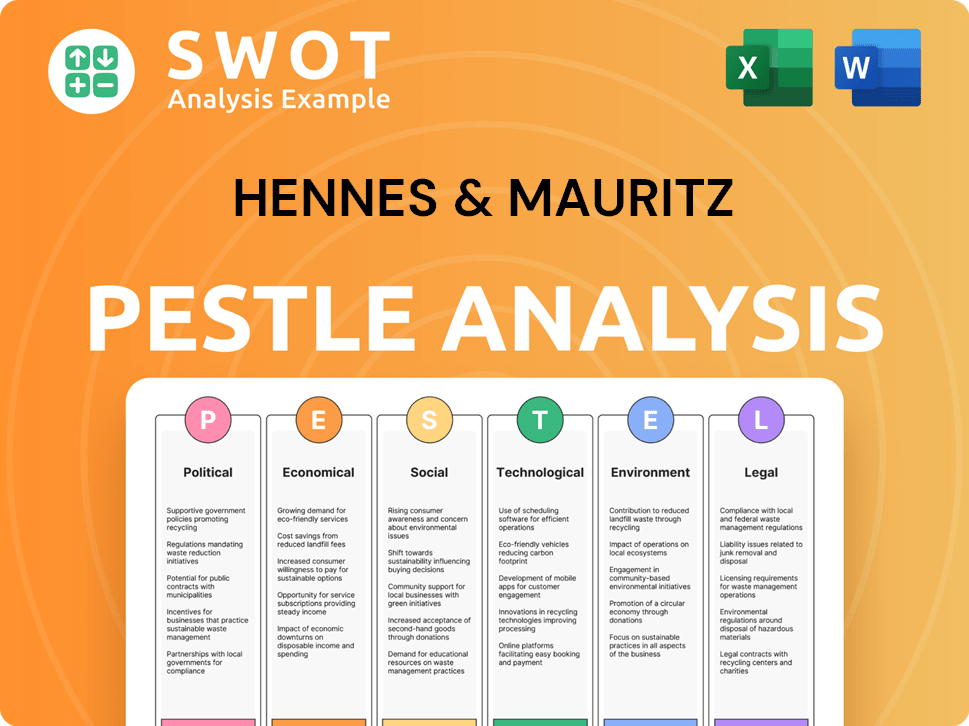
Hennes & Mauritz PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Hennes & Mauritz history?
The H&M history is marked by significant milestones that have shaped its journey from a small Swedish retailer to a global fashion giant. From its H&M origin to its present-day status, the company has consistently adapted and evolved.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1947 | Erling Persson founded Hennes, selling women's clothing in Västerås, Sweden. |
| 1968 | Persson acquired Mauritz Widforss, a hunting and fishing equipment store, and expanded into menswear, renaming the company Hennes & Mauritz. |
| 1974 | H&M was listed on the Stockholm Stock Exchange, marking a significant step in its growth. |
| 1976 | The first store outside of Scandinavia opened in London, marking the beginning of international expansion. |
| 1998 | H&M launched its online store, embracing digital retail. |
| 2000s | The company began its designer collaborations, starting with Karl Lagerfeld in 2004, and expanded its sustainability initiatives. |
| 2013 | H&M launched its garment collecting program, emphasizing its commitment to sustainability. |
H&M has consistently embraced innovation to stay ahead in the fast-paced fashion industry. A key strategy has been its designer collaborations, which have generated excitement and made high fashion accessible to a broader audience. The company has also been a leader in sustainable fashion, investing in eco-friendly materials and production methods.
Collaborations with renowned designers like Karl Lagerfeld, and others, have created buzz and attracted customers. This strategy has allowed H&M to offer exclusive designs at accessible prices.
H&M has invested in sustainable materials and production processes, including the Conscious collection. The company's garment collecting program, launched in 2013, is another key initiative.
H&M has significantly invested in its online presence and digital platforms to meet evolving consumer preferences. This includes enhancing its e-commerce capabilities and digital marketing strategies.
The company has focused on improving its supply chain to enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact. This involves increased transparency and ethical sourcing practices.
H&M has been strategically optimizing its store portfolio, closing underperforming stores and focusing on prime locations. This includes integrating physical and digital retail experiences.
H&M is increasingly using data analytics to understand consumer behavior, optimize product offerings, and streamline operations. This helps in making informed decisions about design, marketing, and inventory.
Despite its successes, H&M has faced several challenges. Market downturns and economic crises, such as the 2008 financial crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic, have affected sales and store traffic. Intense competition from online retailers and other fast-fashion brands has also increased pressure on pricing and speed to market.
Economic recessions and global crises have impacted consumer spending and store traffic, affecting H&M's sales. The company has had to adapt to changing economic conditions.
The fast-fashion industry is highly competitive, with rivals like Zara and Shein. This competition puts pressure on pricing and the need for rapid innovation.
H&M has faced criticism regarding its supply chain practices, including labor and environmental concerns. The company has responded by increasing transparency and improving sustainability efforts.
Consumer tastes and preferences are always evolving, requiring H&M to stay agile and adapt its product offerings. This includes responding to the growing demand for sustainable and ethical fashion.
Managing inventory effectively is crucial in the fast-fashion industry. Overstocking or incorrect product choices can lead to markdowns and reduced profitability.
Geopolitical events and trade policies can disrupt supply chains and affect market access. H&M must navigate these risks to maintain its global operations.
To address these challenges, H&M has undertaken strategic pivots. This includes a significant investment in its online presence and digital transformation, and a focus on optimizing its store portfolio. The company has also restructured its operations to be more agile and responsive to changing consumer demands. For a deeper dive into the company's financial structure and business model, consider reading about the Revenue Streams & Business Model of Hennes & Mauritz.
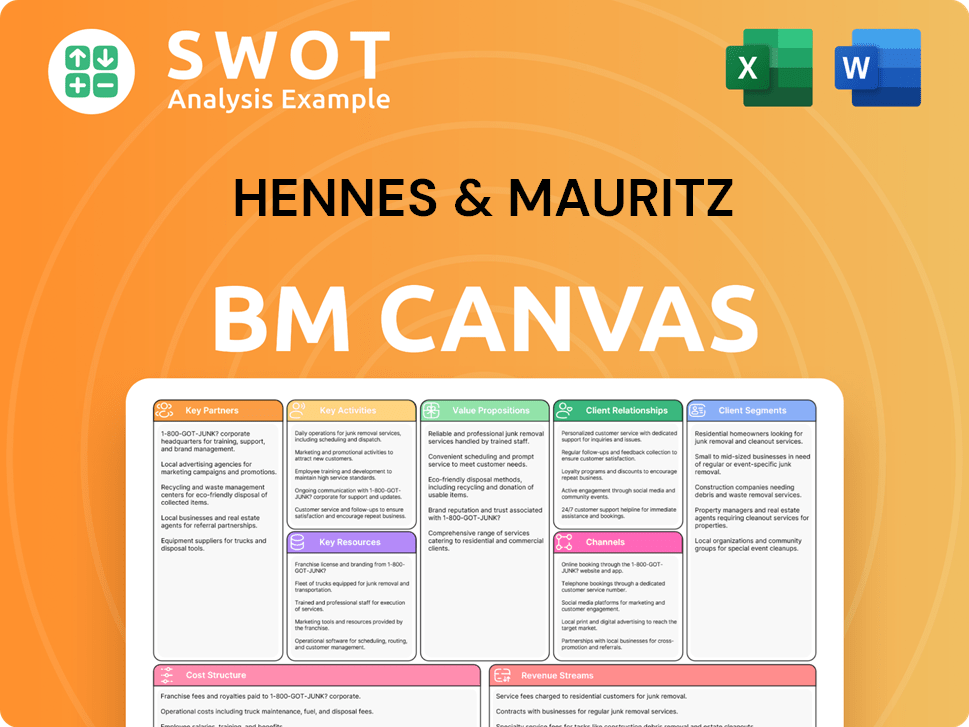
Hennes & Mauritz Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Hennes & Mauritz?
The H&M history is marked by significant milestones. From its humble beginnings in Sweden to its global presence, the company has consistently adapted to market changes. The brand's evolution reflects its commitment to providing fashion at competitive prices while navigating the complexities of the fast-fashion industry.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1947 | Erling Persson opened the first Hennes store in Västerås, Sweden, selling women's clothing, marking the H&M origin. |
| 1964 | The first international store opened in Norway, expanding the company's reach beyond Sweden. |
| 1968 | Acquisition of Mauritz Widforss led to the introduction of menswear and the renaming to Hennes & Mauritz (H&M). |
| 1974 | H&M was listed on the Stockholm Stock Exchange, increasing its visibility and access to capital. |
| 1976 | The first store opened outside Scandinavia, in London, UK, beginning its global expansion. |
| 1980s | Expansion into Germany and the Netherlands, solidifying its presence in Europe. |
| 2000 | The first U.S. store opened on Fifth Avenue in New York City, entering a major new market. |
| 2004 | The first designer collaboration with Karl Lagerfeld, boosting its fashion credibility. |
| 2013 | Launch of the global garment collecting initiative, highlighting its commitment to sustainability. |
| 2018 | Helena Helmersson appointed CEO, focusing on sustainability and digital transformation. |
| 2020 | Accelerated digital expansion and optimization of the store portfolio in response to the pandemic. |
| 2024 | H&M Group's net sales for the first quarter decreased by 2% in local currencies, reflecting ongoing market challenges. |
H&M aims to drive profitable growth by focusing on efficiency and strategic investments. The company is working to optimize its store portfolio and enhance its online presence. This includes improving the supply chain and customer experience to boost sales.
Accelerating digital transformation is a key focus for H&M. This involves integrating online and physical stores for a seamless customer experience. The company is investing in technology to improve supply chain management and customer engagement.
Sustainability is a central pillar of H&M's future strategy. The company is focused on circular business models and developing new sustainable materials. The goal is to achieve a fully circular fashion system by 2040.
H&M faces competitive pressures but is well-positioned due to its brand recognition and sustainability efforts. Consumer demand for sustainable products and the growth of e-commerce will significantly impact its future. Analyst predictions suggest continued adaptation.
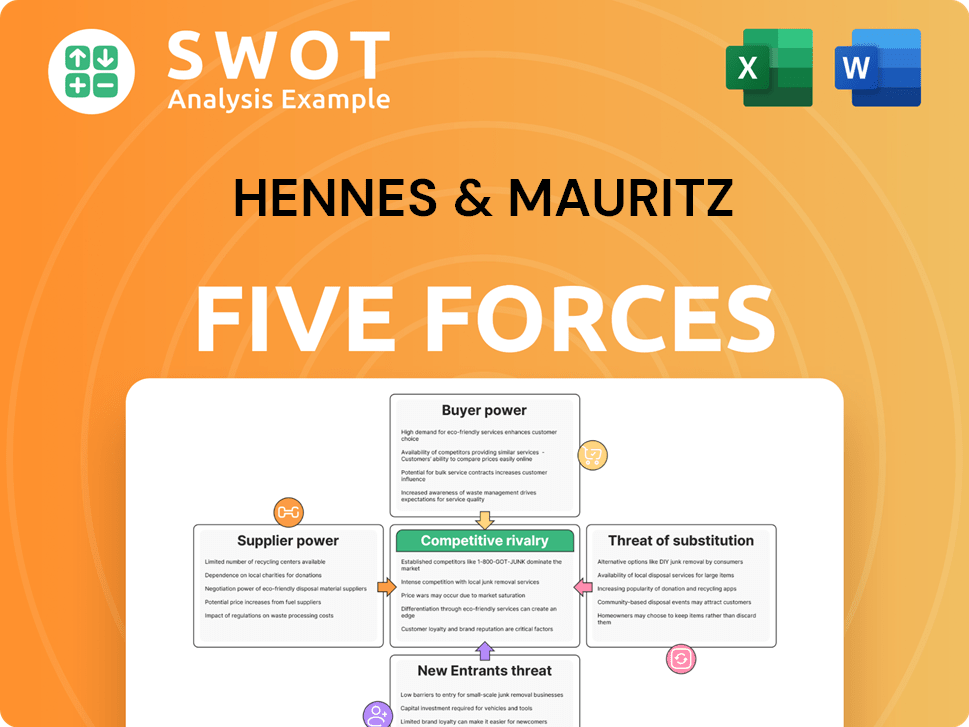
Hennes & Mauritz Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Hennes & Mauritz Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Hennes & Mauritz Company?
- How Does Hennes & Mauritz Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Hennes & Mauritz Company?
- What is Brief History of Hennes & Mauritz Company?
- Who Owns Hennes & Mauritz Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Hennes & Mauritz Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.