Kobe Steel Bundle
What's the Story Behind Kobe Steel's Global Success?
From its humble beginnings in 1905, Kobe Steel, originally Kobe Seikosho, has evolved into a global industrial powerhouse. This Japanese steel manufacturer's story is one of relentless innovation and strategic adaptation. Discover how this company, now known as Kobelco, transformed from a local steel producer into a diversified enterprise.
Kobe Steel's Kobe Steel SWOT Analysis reveals the strategies that have shaped its trajectory. Understanding the brief history of Kobe Steel company is crucial for appreciating its current market position. This exploration will chart its course, from its early years supporting the Japanese steel industry to its current status as a major player in the global market, touching upon key figures and significant milestones along the way.
What is the Kobe Steel Founding Story?
The story of the Kobe Steel company begins in September 1905. Suzuki Shoten, a trading company, acquired Kobayashi Seikosho, a steel business owned by Seiichiro Kobayashi, in Wakinohama, Kobe. This acquisition set the stage for the future Kobe Steel Works, Ltd.
In 1911, Suzuki Shoten formally spun off Kobe Seikosho to establish Kobe Steel Works, Ltd. The founders aimed to reduce Japan's dependence on imported industrial goods. Their goal was to foster domestic production and contribute to the 'independence of Japanese industry'.
The initial focus of Kobe Steel was on steel casting and forging, essential for Japan's heavy industry. In 1914, the company produced Japan's first domestically made air compressor. The company's early growth was significantly aided by the Imperial Japanese Navy, which provided technical guidance and orders. This support was part of a broader policy to encourage private factories. Understanding the Target Market of Kobe Steel helps appreciate its early strategic moves.
Here are some key details about the founding of Kobe Steel:
- Founded in 1905 with the acquisition of Kobayashi Seikosho by Suzuki Shoten.
- Officially established as Kobe Steel Works, Ltd. in 1911.
- Focused initially on steel casting and forging.
- Received support from the Imperial Japanese Navy.
- Aimed to reduce Japan's reliance on imported industrial products.
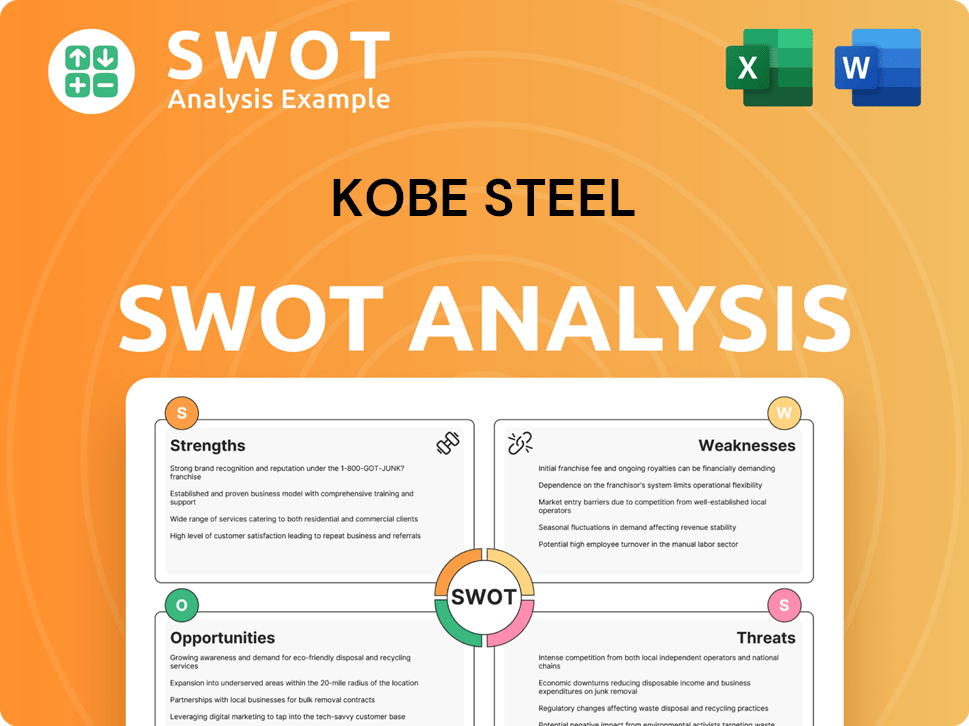
Kobe Steel SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Kobe Steel?
The early growth of the Kobe Steel company was marked by a significant diversification beyond its initial focus on steel casting and forging. This expansion included ventures into machinery, steel products, and copper, showcasing its adaptability and ambition. This period laid the foundation for Kobe Steel's evolution into a diversified industrial group, responding to the changing needs of the Japanese market.
By 1914, Kobe Steel entered the machinery business, developing Japan's first air compressors. The company expanded into steel products in 1916 and the copper business in 1917. In 1926, it completed Japan's first cement plant, entering the engineering business, and in 1930, it produced Japan's first electric mining shovel, entering the construction machinery sector.
The shipbuilding boom during World War I boosted Kobe Steel's growth. In 1918, the company acquired rights to manufacture diesel engines from Sulzer of Switzerland. Kobe Steel was listed on the stock market in 1937, the same year it began its aluminum business.
After World War II, Kobe Steel played a crucial role in Japan's reconstruction, resuming wire rod production within three months of the war's end. The company became a pioneer in titanium, beginning research and development in 1949 and industrial production in 1955. Key facilities, like the Nadahama No.1 Blast Furnace in 1959, enabled integrated steel production.
International expansion began in the 1960s, with an office opening in New York City in 1960 and the completion of Japan's first plant export, a fertilizer plant in East Pakistan (now Bangladesh), in 1962. By the 1970s, Kobe Steel's global activities accelerated with the establishment of companies and offices across Southeast Asia, the Middle East, the United States, and China, solidifying 'KOBELCO' as its international mark. This expansion helped to establish Kobe Steel as a globally recognized brand.
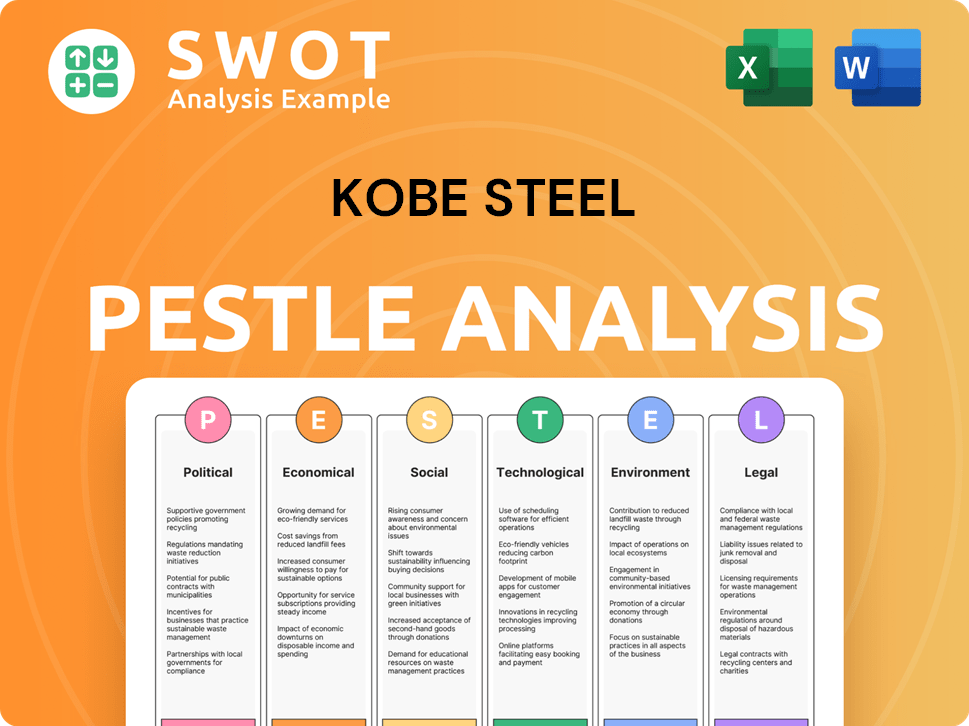
Kobe Steel PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Kobe Steel history?
The Kobe Steel history is marked by significant achievements and pivotal moments that have shaped its trajectory in the steel industry Japan. From its early innovations to its responses to major crises, the company's evolution reflects its resilience and adaptability.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1914 | Introduced Japan's first air compressor, marking an early innovation in industrial equipment. |
| 1926 | Established Japan's first cement plant, expanding its industrial portfolio. |
| 1930 | Launched Japan's first electric mining shovel, enhancing its machinery offerings. |
| 1940 | Introduced Japan's first welding electrodes, contributing to advancements in construction and manufacturing. |
| 1955 | Began industrial production of Japan's first titanium metal, establishing itself as a pioneer in this field. |
| 1959 | The 'blowing-in' of its No. 1 blast furnace at Kobe Works, transitioning to an integrated steelmaker. |
| 1983 | Acquired Midrex Technologies, Inc., significantly developing its direct reduction and ironmaking plant business. |
| 2022 | Launched Japan's first low-CO2 blast furnace steel product, Kobenable Steel, a step towards decarbonization. |
| 2023 | Partnered with Mitsui and Co. to explore developing a Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) facility in Oman. |
Kobe Steel has consistently been at the forefront of technological advancements, introducing groundbreaking products and processes. These innovations have not only enhanced its competitive edge but also contributed significantly to the broader steel industry.
Kobe Steel was the first to produce titanium metal in Japan in 1955, which was a significant technological achievement. This innovation positioned the company as a leader in advanced materials.
The acquisition of Midrex Technologies expanded Kobe Steel's expertise in direct reduction ironmaking. This technology is crucial for producing iron with lower environmental impact.
In 2022, Kobe Steel launched Kobenable Steel, a low-CO2 blast furnace steel product. This initiative reflects the company's commitment to sustainability and reducing carbon emissions.
Despite its successes, Kobe Steel, a Japanese steel manufacturer, has faced numerous challenges that have tested its resilience. These events have prompted significant changes within the company, shaping its future direction and strategies.
The oil crisis of 1973 significantly impacted heavy manufacturing, prompting Kobe Steel to streamline its iron and steel division. The company expanded its machinery and engineering divisions.
The Great Hanshin Earthquake in January 1995 caused severe damage to Kobe Steel's facilities. The rapid restoration of the blast furnace was a symbol of resilience.
In July 2017, Kobe Steel was embroiled in a scandal involving falsified quality data. This led to significant damage to the company's reputation and financial performance.
In response to the scandal, Kobe Steel implemented major reforms to its governance and quality assurance systems. These measures included establishing a Quality Management Department.
Kobe Steel has focused on regaining credibility and strengthening compliance. Efforts to enhance supply chain security and integrate cybersecurity tools have been prioritized.
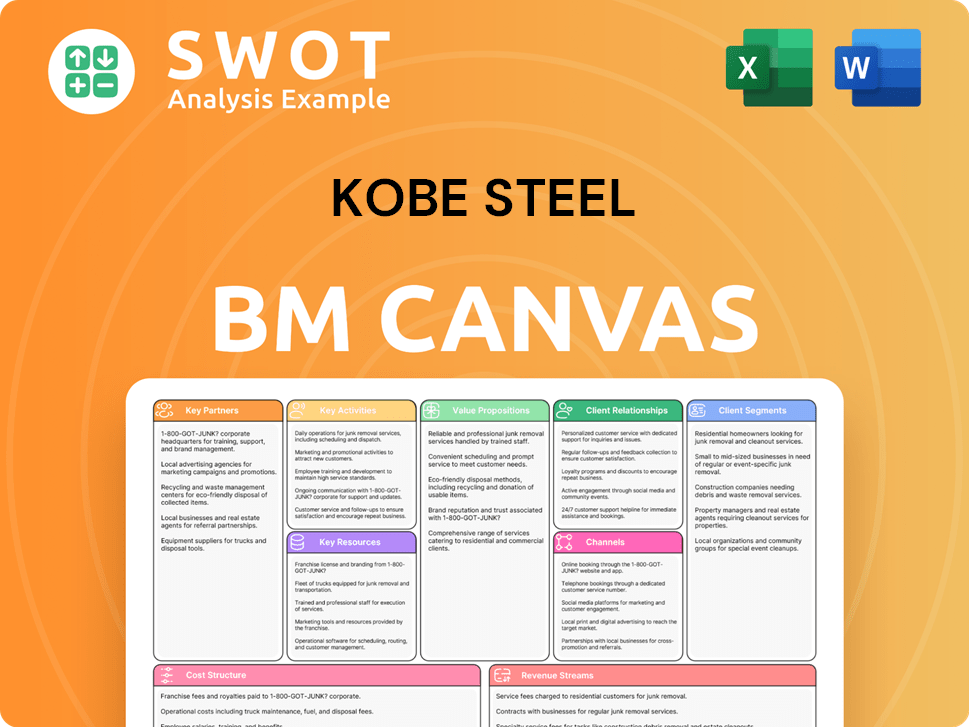
Kobe Steel Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Kobe Steel?
The Kobe Steel history is marked by significant milestones, from its inception as Kobe Seikosho in 1905 to its current status as a leading Japanese steel manufacturer. The company has consistently expanded its operations, venturing into various industries and technologies. Kobe Steel company has navigated challenges, including the Great Hanshin Earthquake and a data falsification scandal, while continuously innovating and adapting to market demands.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1905 | Founded as Kobe Seikosho by Suzuki Shoten in Wakinohama, Kobe. |
| 1911 | Spun off to establish Kobe Steel Works, Ltd. |
| 1914 | Began machinery business, developing Japan's first air compressor. |
| 1917 | Began copper business. |
| 1926 | Completed Japan's first cement plant, entering the engineering business. |
| 1930 | Produced Japan's first electric mining shovel, entering construction machinery. |
| 1937 | Listed on the stock market; began aluminum business. |
| 1940 | Began welding business, producing Japan's first welding electrodes. |
| 1955 | Began industrial production of Japan's first titanium metal. |
| 1959 | Nadahama No.1 Blast Furnace inaugurated, establishing integrated steel production. |
| 1960 | Opened first overseas office in New York City. |
| 1970 | Kakogawa Works completed, broadening steel product lineup. |
| 1983 | Acquired Midrex Technologies, Inc., expanding direct reduction ironmaking business. |
| 1995 | Severely damaged by the Great Hanshin Earthquake, but facilities quickly restored. |
| 2002 | Began electric power business. |
| 2017 | Involved in a data falsification scandal, leading to significant reforms. |
| 2022 | Launched Kobenable Steel, a low-CO2 blast furnace steel product. |
| 2025 | Expects net sales revenues of JPY 2.55 trillion for the fiscal year ending March 31, 2026. |
Kobe Steel aims to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050. An interim target is to reduce carbon emissions by 30-40% by 2030 compared to 2013 levels. This involves utilizing innovative electric arc furnaces and ammonia co-combustion technology.
The company plans to increase scrap usage, integrate biomass into blast furnaces, and implement energy-efficient processes. Kobe Steel has revised its decarbonization investment to approximately JPY 150 billion ($1.05 billion) for 2024-2026, prioritizing financial stability.
For fiscal year 2024-2025, Kobe Steel reported a net profit of JPY 120.2 billion ($812.13 million) and net sales revenues of JPY 2.55 trillion ($17.26 billion). The company forecasts crude steel output of 5.90 million metric tons for fiscal year 2025-2026.
Kobe Steel is expanding its technological capabilities, especially in advanced materials and manufacturing. R&D expenditure was around ¥40 billion for fiscal year 2023. Partnerships are key to fostering innovation and developing advanced materials.
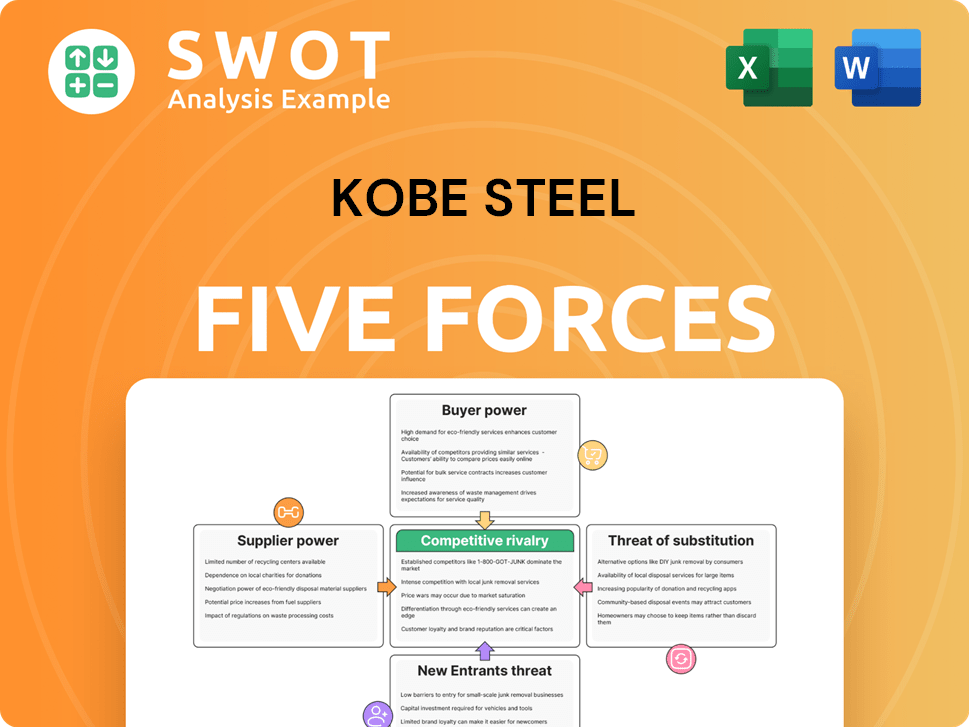
Kobe Steel Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Kobe Steel Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Kobe Steel Company?
- How Does Kobe Steel Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Kobe Steel Company?
- What is Brief History of Kobe Steel Company?
- Who Owns Kobe Steel Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Kobe Steel Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.