Mattel Bundle
How Did Mattel Conquer the Toy World?
In 1959, a doll changed everything. That doll was Barbie, and the company behind it was Mattel, a name now synonymous with childhood and imagination. But how did this toy titan rise from its humble beginnings to become a global powerhouse? From picture frames to iconic Mattel SWOT Analysis, the story of Mattel is a fascinating journey of innovation and strategic brilliance.
This article delves into the rich Mattel history, exploring the early history of Mattel company and the key moments that shaped its destiny. Discover the impact of Mattel on the toy industry, from the vision of its founders to the evolution of its beloved Mattel brands like Hot Wheels and Fisher-Price. Uncover the strategic decisions and challenges that have defined Mattel's business strategy over time, making it a leader in the global market.
What is the Mattel Founding Story?
The story of the Mattel company began on January 19, 1945. It was founded by Harold 'Matt' Matson, Elliot Handler, and Ruth Handler, marking the start of what would become a global toy empire. The company's name cleverly combined 'Matt' from Matson and 'El' from Elliot Handler, setting the stage for a legacy in the toy industry.
Initially, Mattel operated from a humble garage in Southern California. The primary focus was on manufacturing picture frames. However, the entrepreneurial spirit of Elliot Handler, a talented designer, led to the creation of dollhouse furniture using leftover materials from the picture frame business. Ruth Handler, with her keen eye for market opportunities, recognized the higher profit potential in toys, which led to a pivotal shift in the company's direction.
This strategic pivot was crucial. It moved Mattel away from picture frames and into the burgeoning toy market. The early days of Mattel were characterized by resourcefulness and ingenuity. The founders largely funded the company through personal savings and the profits generated from their initial ventures. This foundation set the stage for Mattel's future growth and dominance in the toy industry, which has since seen significant changes and expansions.
The early days of Mattel were marked by innovation and strategic shifts, leading to its eventual success in the toy industry. The company's founding and initial focus on picture frames were quickly followed by a pivot towards toy manufacturing, driven by the potential for higher profits.
- 1945: Mattel is founded by Harold 'Matt' Matson, Elliot Handler, and Ruth Handler.
- Early Focus: The initial business was picture frames.
- Strategic Shift: Elliot Handler began making dollhouse furniture from scrap materials.
- Market Insight: Ruth Handler recognized the higher profit potential in toys.
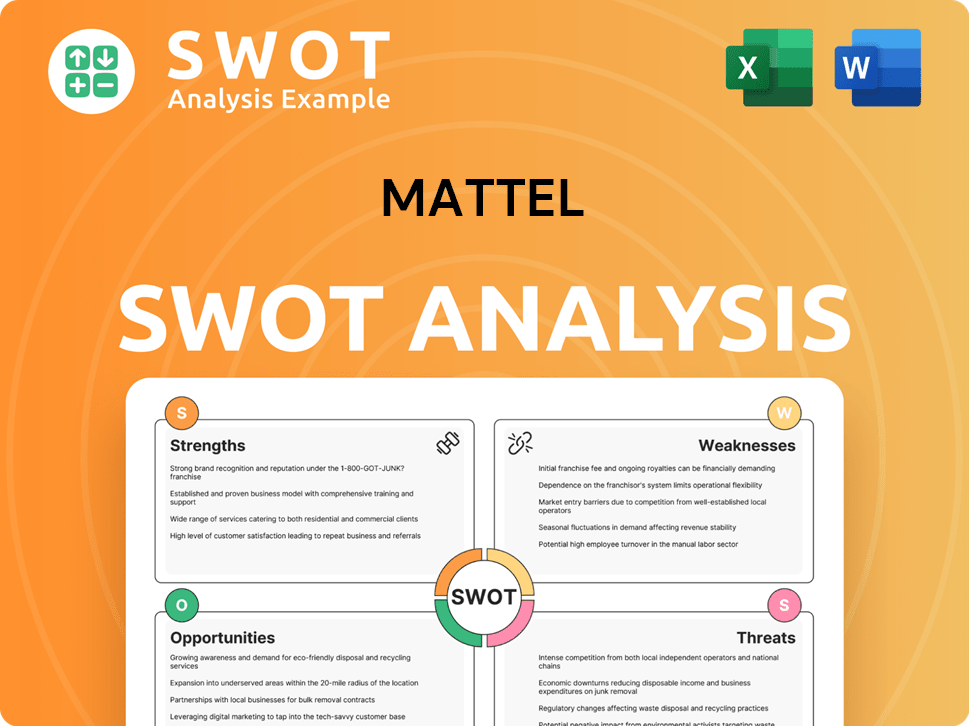
Mattel SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Mattel?
The early growth of the Mattel company was characterized by innovative product launches and strategic expansions. The company's journey began with dollhouse furniture, but it quickly evolved with the introduction of the 'Uke-A-Doodle' toy ukulele in 1947. This was followed by the 'Magic 8-Ball' in 1949, showcasing the company's ability to diversify its offerings.
Mattel toys experienced early success with the 'Uke-A-Doodle' and 'Magic 8-Ball'. These products helped establish Mattel brands in the toy market. These early successes paved the way for future innovations and expansions.
The debut of the Barbie doll in 1959 was a turning point in the Mattel history. Barbie's immediate success propelled Mattel into the global spotlight. This launch revolutionized the toy industry, setting new standards for product innovation.
In the 1960s, Mattel continued its aggressive expansion. Iconic brands like Chatty Cathy (1960) and Hot Wheels (1968) were introduced. The company also began its international expansion, establishing a presence in Europe and other key markets.
By the end of the 1960s, Mattel had become a publicly traded company. It was a dominant force in the toy industry, with annual sales exceeding hundreds of millions of dollars. This growth was fueled by strategic marketing and product development.
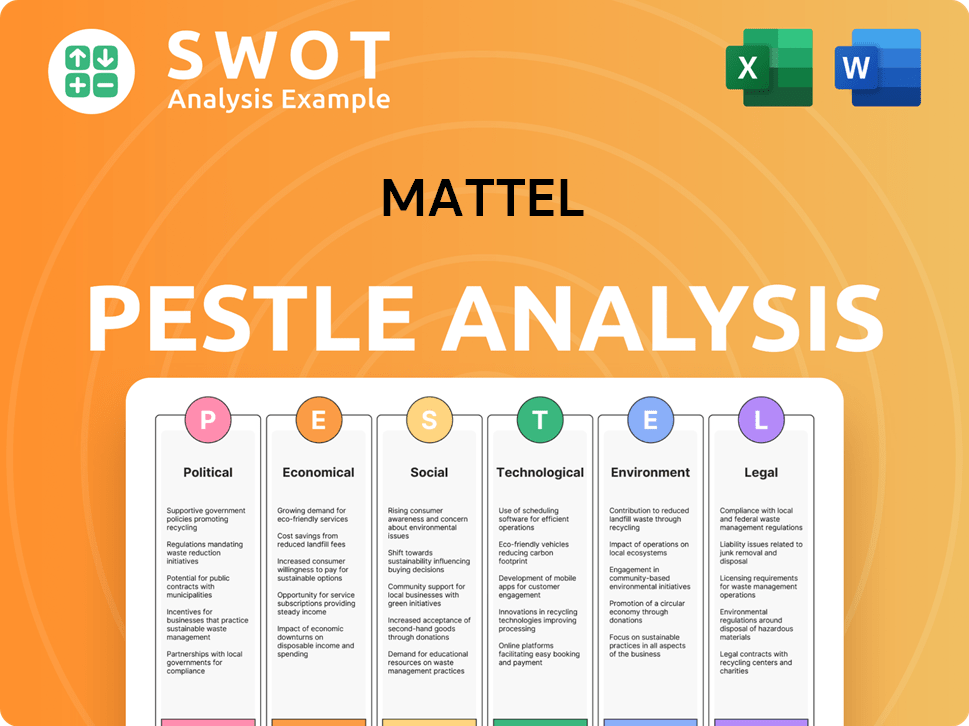
Mattel PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Mattel history?
The Mattel history is marked by significant milestones that have shaped the Mattel company into a global leader in the toy industry. From its humble beginnings to its current status, the company has consistently adapted and innovated, leaving a lasting impact on the world of play. The brief history of Mattel toys is a testament to its enduring appeal and its ability to resonate with consumers across generations.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1945 | Harold Matson and Elliot Handler founded the company, initially focusing on picture frames. |
| 1959 | The introduction of the Barbie doll revolutionized the toy industry, creating a new category of fashion dolls. |
| 1968 | The launch of Hot Wheels brought innovation to the die-cast car market with its unique track systems and designs. |
| 1993 | The acquisition of Fisher-Price expanded the company's reach into the infant and preschool toy market. |
| 1998 | The acquisition of The American Girls Collection further diversified the company's portfolio and brand offerings. |
| 2023 | The success of the Barbie movie, generating over $1.4 billion globally, showcased the company's ability to leverage its brands in entertainment. |
Mattel toys have consistently pushed the boundaries of innovation, introducing new play experiences and technologies. The company's commitment to creativity and design has resulted in iconic products that have captured the imaginations of children worldwide. Ruth Handler, co-founder, played a pivotal role in shaping the company's innovative spirit.
The Barbie doll, introduced in 1959, was a groundbreaking innovation, offering children a doll with adult features and a wide range of careers and fashions. This innovation created a new category in the toy market and established a new standard for doll design.
Hot Wheels, launched in 1968, revolutionized the die-cast car market with its innovative track systems and designs. These cars were designed to be fast and visually appealing, appealing to a broad audience.
The Masters of the Universe franchise, popular in the 1980s, introduced a line of action figures, vehicles, and a related animated series. This franchise expanded Mattel brands into the action figure market.
The acquisition of Fisher-Price in 1993 expanded the company's reach into the infant and preschool toy market. This strategic move broadened the company's product offerings and customer base.
Mattel has invested in digital content and expanded its entertainment division to adapt to changing consumer preferences. The company has leveraged its brands, such as Barbie, in movies, television, and digital platforms.
The 2023 Barbie movie grossed over $1.4 billion globally, demonstrating the company's ability to successfully translate its brands into other forms of media. This success highlighted the company's brand strength.
Despite its successes, Mattel has faced significant challenges over the years, including market downturns and intense competition. The company has navigated shifts in consumer preferences and the rise of digital entertainment, requiring strategic adaptations. For a deeper dive into the company's strategies and history, consider reading this article about Mattel's business strategy over time.
The early 2000s saw a decline in traditional toy sales due to the rise of video games and digital entertainment, impacting Mattel's financial performance. The company had to adapt its product offerings and business strategies to remain competitive.
Mattel faces intense competition from other toy manufacturers and entertainment companies. This competition requires the company to continually innovate and differentiate its products to maintain market share.
Changes in consumer preferences, such as the increasing popularity of digital entertainment, have presented challenges. The company has had to adapt its product lines and marketing strategies to remain relevant.
Mattel has faced supply chain disruptions and increased raw material costs in recent years, impacting its profitability. These factors have required the company to manage its operations efficiently.
The company's financial performance has fluctuated due to market conditions and other factors. In 2023, Mattel reported net sales of approximately $5.44 billion, with a gross profit margin of around 47.8%.
Mattel has undertaken strategic restructuring and rebranding efforts to adapt to the evolving toy landscape. These efforts aim to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and drive sustainable growth.
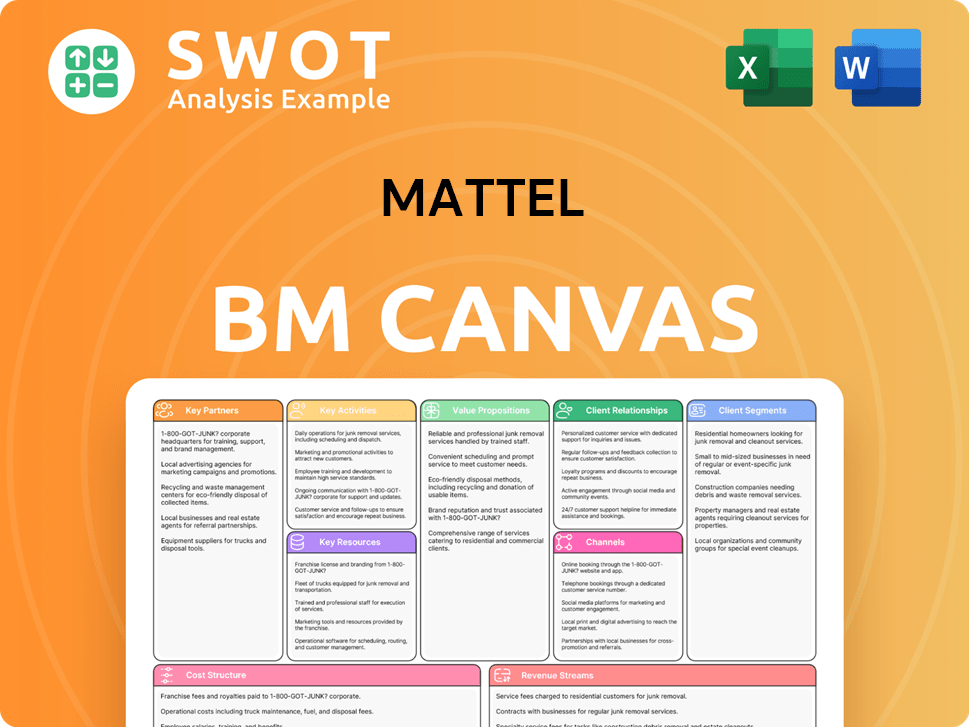
Mattel Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Mattel?
The history of Mattel is a story of innovation and adaptation in the toy industry, marked by iconic products and strategic shifts. Founded in 1945 by Harold Matson, Elliot Handler, and Ruth Handler, the company quickly established itself as a leader. From the introduction of the Barbie doll in 1959 to the global success of the Barbie movie in 2023, Mattel has continuously evolved, navigating financial challenges and embracing new technologies to remain relevant in a dynamic market.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1945 | Mattel is founded by Harold Matson, Elliot Handler, and Ruth Handler, marking the beginning of the |
| 1959 | The introduction of the Barbie doll at the American International Toy Fair revolutionized the toy industry and cemented |
| 1960 | The Chatty Cathy doll was launched, expanding |
| 1968 | Hot Wheels were introduced, quickly becoming a cornerstone of Mattel's product offerings with its innovative die-cast cars. |
| 1970s | Mattel faced financial difficulties and underwent leadership changes, reshaping its strategic direction. |
| 1980s | Masters of the Universe became a major success, showcasing Mattel's ability to create popular franchises. |
| 1993 | Mattel acquired Fisher-Price, broadening its portfolio to include a wider range of toys. |
| 1998 | The acquisition of The American Girls Collection further diversified Mattel's offerings. |
| 2000s | The company navigated challenges from digital entertainment, adapting to evolving consumer preferences. |
| 2015 | Mattel partnered with Google for virtual reality viewers, exploring new technologies. |
| 2023 | The Barbie movie became a global box office hit, grossing over $1.4 billion, highlighting Mattel's brand strength. |
| 2024 | Mattel reported strong Q1 2024 results, with net sales up 1% as reported, or 2% in constant currency, indicating continued financial health. |
Mattel is focused on transforming its iconic brands into entertainment franchises. The success of the Barbie movie demonstrates the potential of this strategy. Further content, including movies and television shows, is planned to expand brand presence and revenue streams.
The company is investing in digital platforms and interactive experiences to engage consumers. This includes integrating digital elements into toys and creating online content. Mattel is also exploring new technologies, such as augmented reality, to enhance product offerings.
Mattel is focused on expanding its presence in emerging markets. This includes adapting products to local preferences and building distribution networks. The company aims to capitalize on the growing demand for toys in these regions.
Mattel is committed to sustainability initiatives, including using eco-friendly materials and reducing waste. The company is also focused on optimizing its supply chain to improve efficiency and reduce costs. The 'Capital Light' strategy aims to streamline operations.
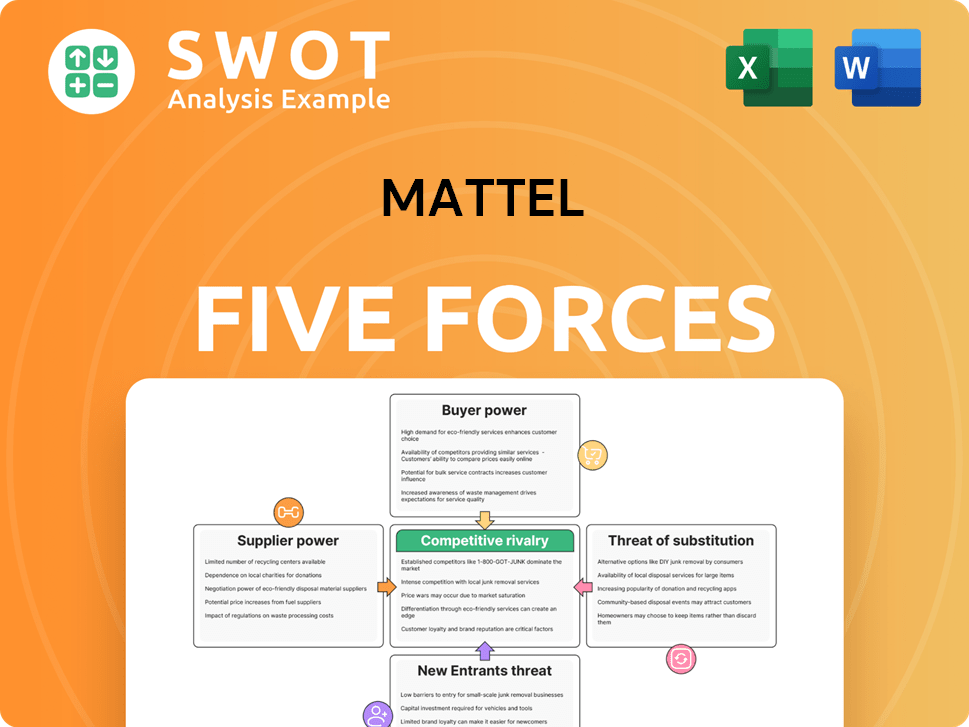
Mattel Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Mattel Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Mattel Company?
- How Does Mattel Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Mattel Company?
- What is Brief History of Mattel Company?
- Who Owns Mattel Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Mattel Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.