Nippon Telegraph & Tel Bundle
How Did Nippon Telegraph & Tel Company Become a Global Giant?
From post-war reconstruction to a global technology leader, the Nippon Telegraph & Tel SWOT Analysis reveals a fascinating story. This Japanese telecommunications giant, known as NTT, has shaped the digital landscape. Let's dive into the remarkable journey of NTT, tracing its evolution and impact on the world.
Founded in 1952, NTT's NTT history is a testament to its strategic vision. Initially focused on building Japan's telecommunications infrastructure, NTT quickly became a cornerstone of the Japanese economy. The company’s evolution from a public corporation to a diversified global player showcases its adaptability and forward-thinking approach to innovation in the field of Japanese telecommunications.
What is the Nippon Telegraph & Tel Founding Story?
The genesis of what is now known as the Nippon Telegraph & Tel Company, or NTT, traces back to August 1, 1952. This pivotal date marked the formal establishment of the Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Public Corporation, the precursor to today's NTT Group. The formation of this entity was a direct response to the imperative need to rebuild and modernize Japan's telecommunications infrastructure following World War II.
Prior to NTT's inception, the Ministry of Communications managed telecommunications services. However, this structure proved insufficient to meet the demands of national reconstruction. The creation of a public corporation was deemed the most effective strategy to consolidate resources, expedite development, and ensure universal access to essential telecommunication services throughout Japan. This was a critical step in the NTT history.
The initial operational model for NTT was that of a state-owned monopoly. Its primary mission was to provide indispensable telecommunications services, including telephone and telegraph, to every part of the nation. Its initial focus was on rapidly deploying telephone lines and modernizing switching systems. While specific individual founders are not cited due to its nature as a public corporation, its establishment was a direct result of government policy and the collective efforts of various ministries and telecommunications experts. The initial funding came primarily from governmental appropriations, reflecting its role as a critical public utility for national development. The immediate challenge was the vast infrastructure deficit and the need to connect a recovering nation. For more details on the company's evolution, you can explore a brief history of NTT.
The establishment of NTT was a crucial step in modernizing Japan's telecommunications infrastructure.
- Established on August 1, 1952, as the Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Public Corporation.
- Created to rebuild and expand Japan's telecommunications network after World War II.
- Operated as a state-owned monopoly, providing essential services nationwide.
- Focused on deploying telephone lines and modernizing switching systems.
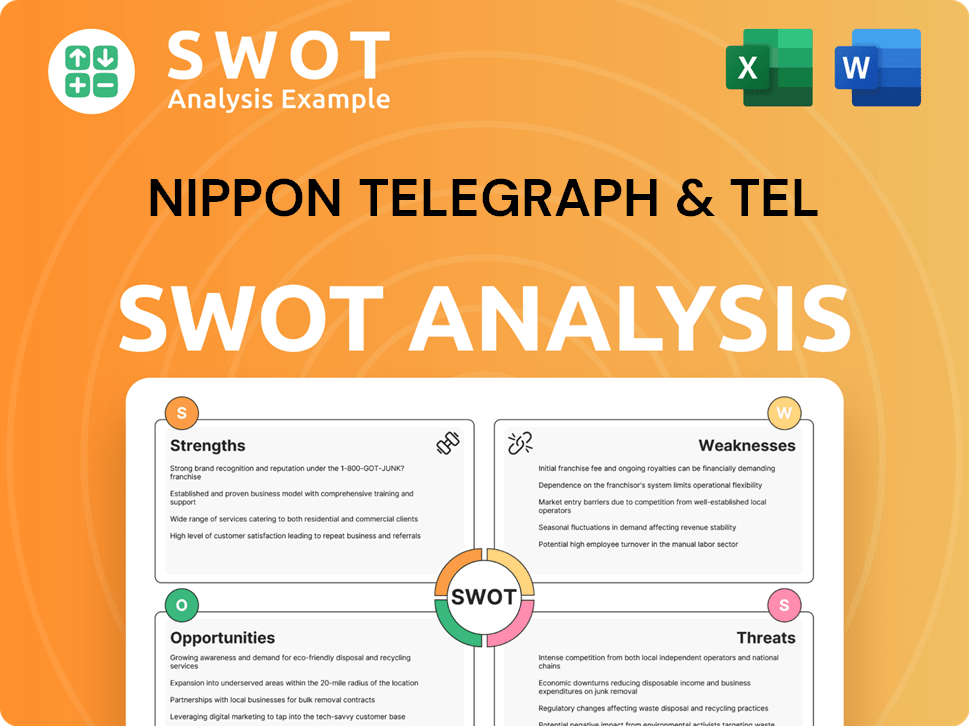
Nippon Telegraph & Tel SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Nippon Telegraph & Tel?
The early growth of Nippon Telegraph & Tel Company (NTT) was marked by an aggressive build-out of telecommunications infrastructure across Japan. During the 1950s and 1960s, the company focused on expanding its telephone network and transitioning to automated exchanges. By 1970, NTT had established a nationwide direct dialing system, significantly improving communication efficiency. Early team expansion was significant, with NTT hiring thousands of engineers and technicians.
NTT's early focus was on establishing a robust telecommunications infrastructure. This involved a shift from manual to automated telephone exchanges. The company invested heavily in expanding its network to cover the entire nation. By the 1970s, a nationwide direct dialing system was in place, enhancing communication efficiency across Japan.
NTT began exploring data communication services in the 1960s, anticipating the shift towards information-centric societies. The company introduced new services like facsimile and video conferencing in the 1980s. This early adoption of technology set the stage for future innovations and growth.
The 1980s were a pivotal period, with the privatization of NTT in 1985. This transition aimed to boost efficiency and competitiveness. Following privatization, NTT expanded its research and development efforts, leading to breakthroughs in fiber optics and mobile communications. The company also began exploring international markets, laying the groundwork for its future global ambitions.
The deregulation of the telecommunications market brought in new players, increasing competition. This prompted NTT to innovate and optimize its operations. The company's focus shifted to market-driven strategies and customer needs. For more insights into the competitive landscape, consider exploring the Competitors Landscape of Nippon Telegraph & Tel.
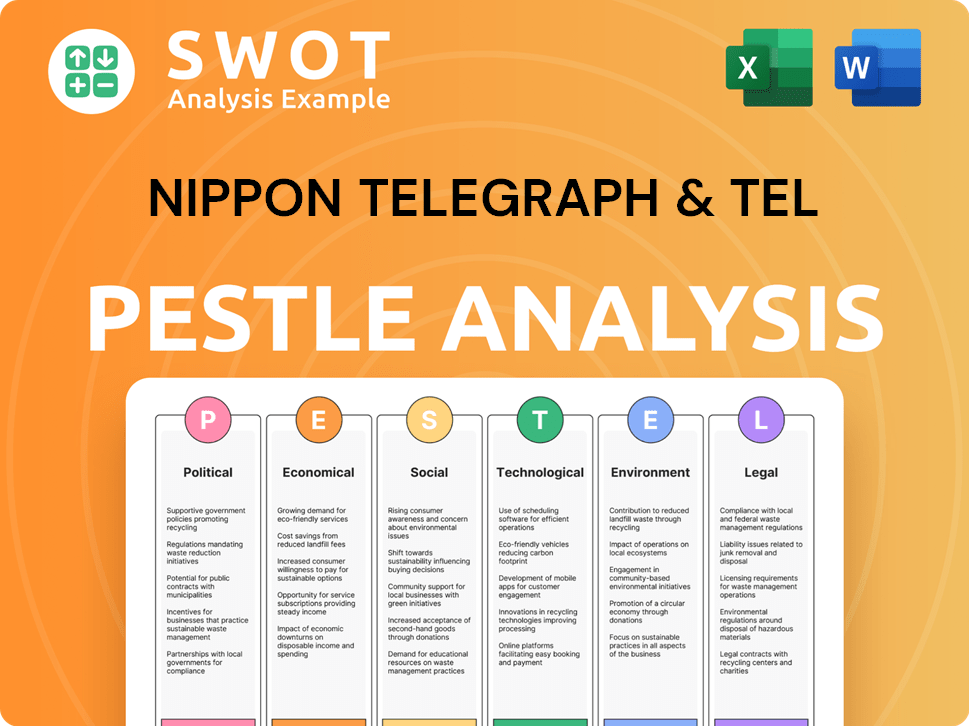
Nippon Telegraph & Tel PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Nippon Telegraph & Tel history?
The Growth Strategy of Nippon Telegraph & Tel, or NTT, has a rich history marked by significant milestones that have shaped the landscape of Japanese telecommunications and its global presence. From its early days as a public entity to its evolution into a global technology leader, NTT's journey reflects the dynamic changes in the telecommunications industry and its impact on Japanese society.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1952 | Established as a public corporation, initially responsible for domestic telecommunications in Japan. |
| 1980s | Pioneered the deployment of fiber optic networks across Japan, laying the groundwork for high-speed internet. |
| 1991 | NTT DoCoMo, a subsidiary, was established, later becoming a leader in mobile communication. |
| 1999 | NTT underwent restructuring, including the creation of a holding company structure to manage its various operating companies. |
| 1999 | NTT DoCoMo launched i-mode, a pioneering mobile internet platform. |
| 2000s-2020s | Expanded globally through various acquisitions and partnerships, solidifying its presence in international markets. |
| 2024-2025 | Heavily invested in IOWN (Innovative Optical and Wireless Network) technology to create next-generation communication infrastructure. |
NTT has consistently been at the forefront of technological advancements in Japanese telecommunications. The company's innovations include the development of fiber optic networks, which significantly improved data transmission speeds and reliability. Moreover, NTT DoCoMo's i-mode platform revolutionized mobile internet services, setting a global standard for mobile communication.
NTT's early adoption and deployment of fiber optics provided the backbone for high-speed internet access across Japan, enhancing both residential and business connectivity. This technological leap significantly improved data transmission capabilities.
NTT DoCoMo's i-mode platform, launched in 1999, was a pioneering mobile internet service that offered email, web browsing, and other data services on mobile phones, influencing mobile communication globally. It set a new standard for mobile data services.
NTT has been a leader in optical networking technologies, continuously innovating to improve network speeds, capacity, and efficiency. This has been crucial for supporting the increasing demands of data-intensive applications.
NTT has made significant contributions to wireless communication, including advancements in 5G and beyond. These innovations are essential for supporting the growing number of connected devices and applications.
NTT has developed advanced data processing technologies to manage and analyze vast amounts of data, supporting various services from cloud computing to smart city initiatives. This is key for data-driven decision-making.
NTT is heavily invested in IOWN, a next-generation communication infrastructure that aims to create faster, more secure, and energy-efficient networks. This technology is designed to meet the increasing demands for data and promote sustainable operations.
Despite its successes, NTT has faced several challenges, including intense competition following the deregulation of the Japanese telecommunications market. The company has also navigated the complexities of managing a vast organization, especially during and after privatization. Economic downturns and the need to adapt to technological shifts have also presented hurdles.
The deregulation of the Japanese telecommunications market introduced significant competition, requiring NTT to adapt its strategies to maintain market share and profitability. This led to restructuring and a focus on new services.
NTT faces strong competition from both domestic and international telecommunications companies, forcing it to innovate constantly and offer competitive services. Staying ahead requires continuous investment in new technologies.
Some of NTT's niche services have not gained widespread adoption, leading to financial losses and a need to refocus on more successful ventures. This underscores the importance of market analysis and product development.
Managing a vast and complex organization, particularly after privatization, presented significant restructuring challenges, requiring strategic adjustments to improve efficiency and responsiveness. This includes streamlining operations.
Global financial crises and economic downturns have impacted NTT's financial performance, necessitating cost-cutting measures and a focus on international expansion to diversify revenue streams. This has led to strategic adjustments.
The rapid pace of technological change requires NTT to continually invest in new technologies like 5G and IOWN to remain competitive and meet evolving customer demands. This has led to strategic partnerships.
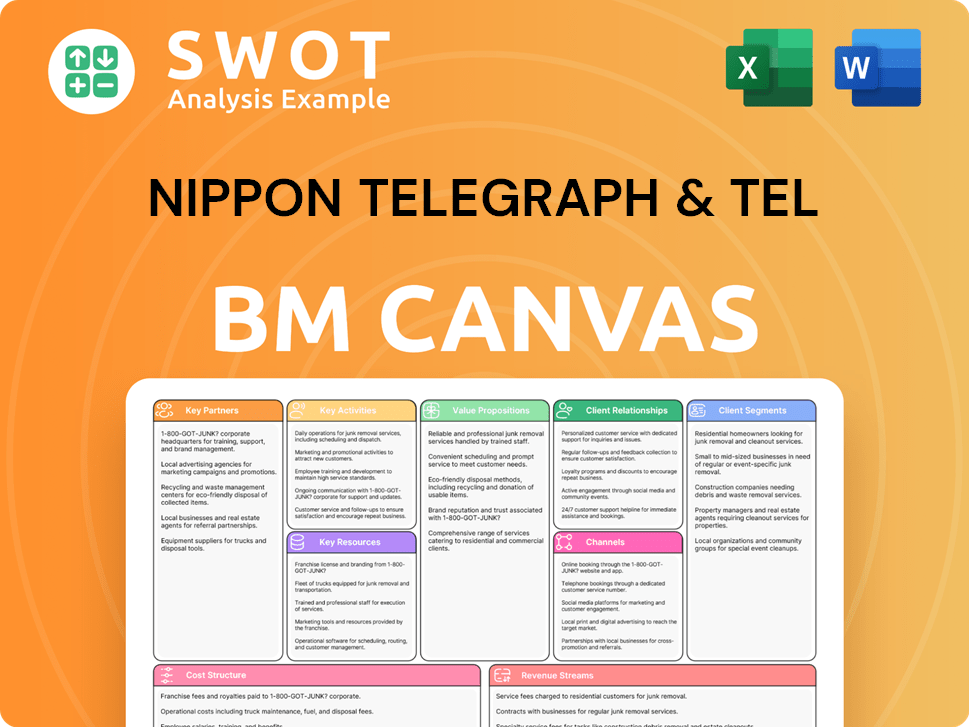
Nippon Telegraph & Tel Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Nippon Telegraph & Tel?
The Nippon Telegraph & Tel Company (NTT) has a rich history, marked by significant milestones in Japanese telecommunications. From its inception as a public corporation to its privatization and global expansion, NTT has played a pivotal role in shaping Japan's technological landscape.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1952 | NTT was established as a public corporation, succeeding the Ministry of Communications. |
| 1985 | NTT was privatized, marking a significant shift in the Japanese telecommunications sector. |
| 1987 | NTT Data, a major subsidiary, was established to focus on data communications and system integration. |
| 1999 | NTT DoCoMo, the mobile communications arm, was listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange. |
| 2002 | NTT reorganized into a holding company structure, with NTT East and NTT West established to manage regional operations. |
| 2015 | NTT Communications acquired RagingWire Data Centers, expanding its data center business. |
| 2020 | NTT announced its "Business Restructuring Plan" to streamline operations and focus on growth areas. |
| 2024 | NTT continues to invest heavily in 6G research and development, with plans to launch commercial 6G services in the future. |
NTT is at the forefront of technological innovation, particularly in areas like 6G, fiber optic networks, and AI. The company is investing billions in R&D to maintain its competitive edge. NTT's focus is on developing advanced technologies to meet the evolving demands of its customers. They are also exploring innovative solutions for smart cities and IoT.
NTT holds a strong position in the Japanese telecommunications market, but faces competition from both domestic and international players. The company's strategy involves expanding its global presence through acquisitions and partnerships. NTT is also focusing on diversifying its services to include cloud computing, data centers, and consulting.
NTT's financial performance remains robust, driven by its core telecommunications business and expansion into new markets. The company is focused on optimizing its cost structure and improving operational efficiency. NTT aims to achieve sustainable growth by investing in new technologies and services. In fiscal year 2024, NTT's consolidated revenue was approximately $106 billion.
NTT is poised for continued growth, with a focus on global expansion and digital transformation. The company is actively pursuing strategic acquisitions and partnerships to strengthen its market position. NTT is also investing in areas like cybersecurity and digital transformation services. NTT aims to increase its overseas revenue to 30% of total revenue by 2026.
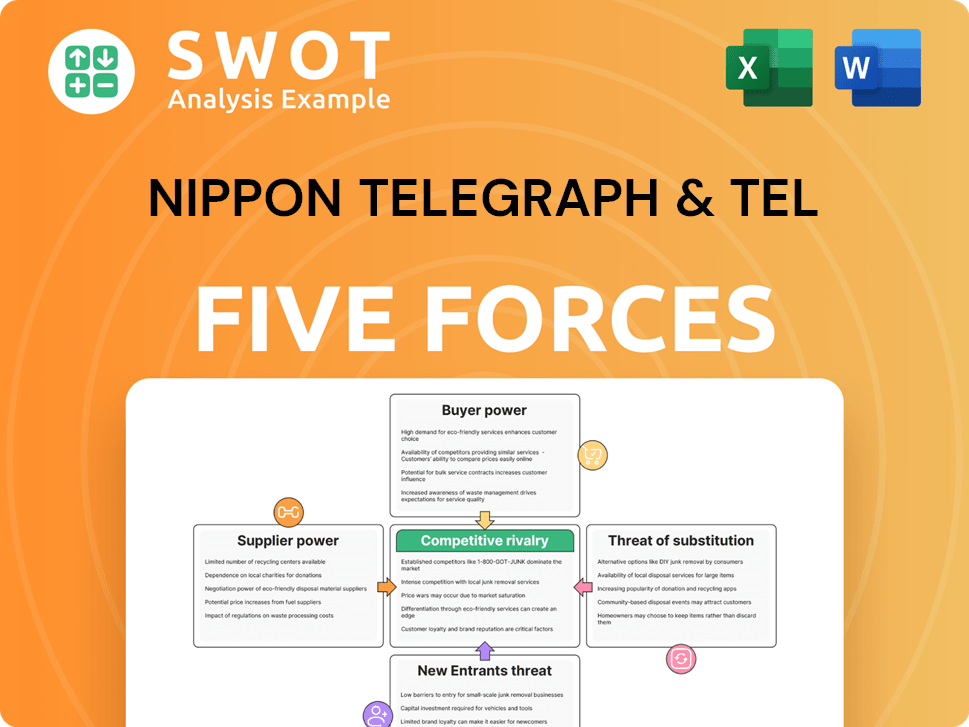
Nippon Telegraph & Tel Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Nippon Telegraph & Tel Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Nippon Telegraph & Tel Company?
- How Does Nippon Telegraph & Tel Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Nippon Telegraph & Tel Company?
- What is Brief History of Nippon Telegraph & Tel Company?
- Who Owns Nippon Telegraph & Tel Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Nippon Telegraph & Tel Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.