PostNL Bundle
How has the PostNL SWOT Analysis shaped the company's journey?
Delve into the fascinating PostNL history, a story of transformation from its roots in the 18th century as the Dutch postal service. Witness the evolution of this Benelux giant, from a government-owned entity to a publicly listed powerhouse, navigating the dynamic world of parcel delivery and mail services.

From its PostNL founding date, the company has consistently adapted to market shifts, including the crucial PostNL rebranding in 2011. This article will provide a detailed PostNL timeline, exploring key PostNL acquisitions, PostNL services overview, and the PostNL financial history, all while examining the PostNL challenges and strategic direction.
What is the PostNL Founding Story?
The story of PostNL, a leading player in the mail and parcel delivery sector, is rooted in the rich history of postal services in the Netherlands. Its beginnings are traced back to the establishment of a national postal system in 1799, which set the stage for what would evolve into PTT Post.
A crucial turning point came with the Postal Act of 1850, which reshaped postal delivery as a public service, moving away from its previous role as a tax collector. This act solidified its domestic monopoly. The Dutch postal service then issued its first postage stamp in 1852, marking its entry into the modern era of postal delivery. While there wasn't a single founder, the vision was to create an efficient public postal service for the nation.
The evolution of PostNL reflects a significant transformation from a state-owned entity to a publicly traded company. It showcases the company's adaptability and growth within the evolving landscape of postal and logistics services.
PostNL's origins are deeply connected to the Dutch postal service's history, starting in 1799 with the establishment of a national postal system. The Postal Act of 1850 was a pivotal moment, re-establishing postal delivery as a public service. The company's journey reflects a significant transition from a state-owned monopoly to a publicly traded entity.
- 1799: National postal system established in the Netherlands.
- 1850: Postal Act redefines postal delivery as a public service.
- 1852: First Dutch postage stamp issued.
- 1886: Postal, telegraph, and telephone services combined to form PTT.
In 1886, the postal system, along with telegraph and telephone services, was integrated under a single ministry, forming PTT. The privatization process began in 1989, with PTT being privatized and the postal service being renamed PTT Post. Further changes occurred in 1998 when PTT Nederland split into two independent companies: Royal KPN and TNT Post Group (TPG). TPG, the direct predecessor to PostNL, was listed on the Amsterdam, Frankfurt, London, and New York stock exchanges. This move marked a shift from a state-owned monopoly to a publicly traded entity, aiming to compete more effectively in a globalizing market. In 2001, the company changed its name to TPG N.V.
PostNL's history reveals a strategic evolution. It began as a national postal service and transformed to meet the demands of a changing market. The company's ability to adapt and expand its services has been key to its success. For more insights into how PostNL targets its audience, you can explore the Target Market of PostNL.
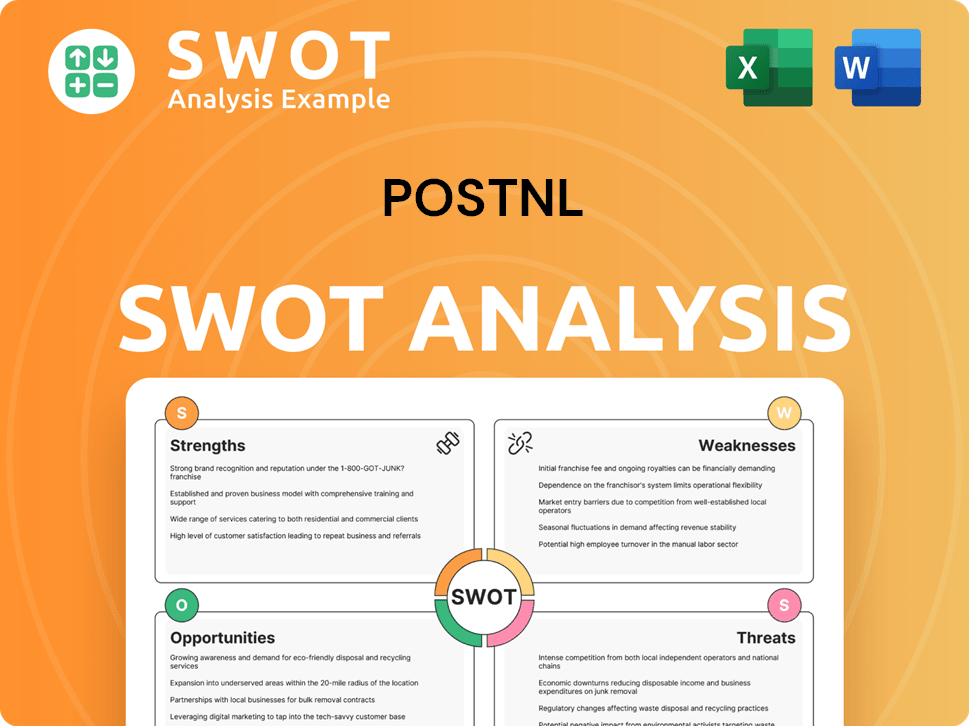
PostNL SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of PostNL?
The early growth and expansion of the PostNL company, initially operating as TPG N.V. and later TNT N.V., marked a pivotal phase in its development. Following its listing on multiple stock exchanges in 1998 as TNT Post Group (TPG), the company quickly focused on broadening its operational reach. This period was characterized by strategic acquisitions and investments aimed at establishing a strong international presence in the parcel delivery and mail services sectors.
In April 1998, TPG established its European Express Centre at Liège Airport in Belgium, and in October of the same year, it opened an international road hub in Duiven, Netherlands. These moves were key to its PostNL international expansion strategy. The company's focus on cross-border logistics was evident from the start, laying the groundwork for its future global operations.
PostNL expanded its reach by acquiring companies like the French express service company Jet Services in December 1998. In 1999, it acquired Italy's Tecnologistica, strengthening its logistics operations. The acquisition of CTI LOGISTX in 2000, the logistics arm of CSX Corporation, was its largest purchase since becoming independent in 1998, solidifying its position in international logistics. These acquisitions are important to the PostNL history.
In 2003, TNT (then TPG) acquired a 60% stake in Prime Vision, a Dutch company specializing in postal automation. This integration showed a commitment to technological advancements. In April 2005, TNT Post Group was rebranded as TNT, simplifying its corporate identity. These moves demonstrate the company's effort to refine its business model.
The company sold its logistics division to Apollo Global Management in November 2006, later rebranded as CEVA Logistics. In March 2007, TNT entered the Chinese market by acquiring Hoau. These strategic moves, including acquisitions and divestitures, show TNT's focus on core mail and express services. For more information, you can read about the Mission, Vision & Core Values of PostNL.
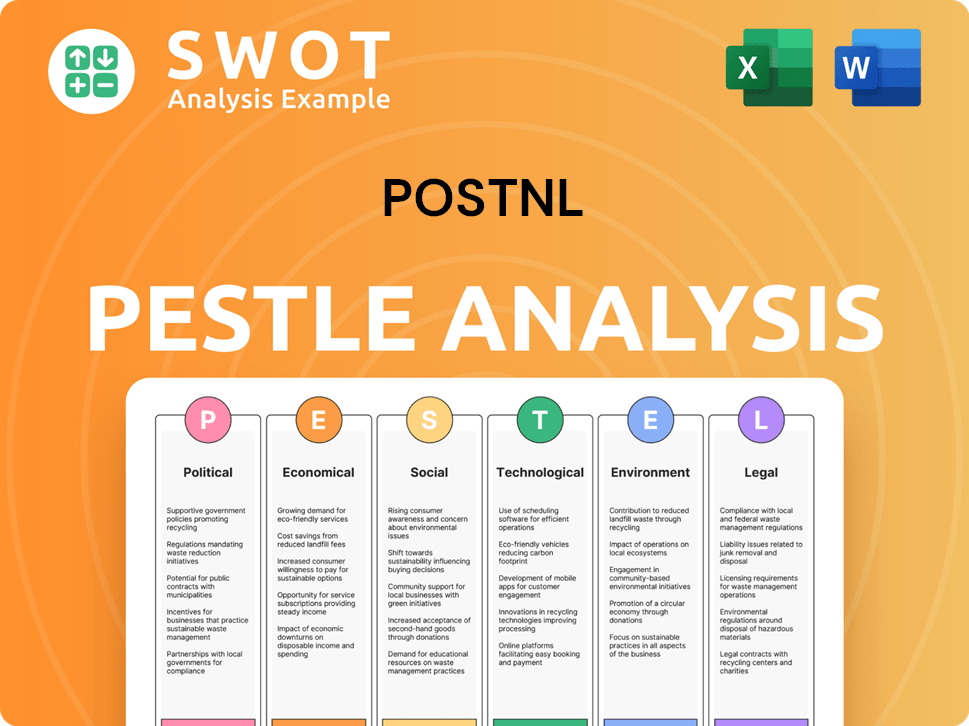
PostNL PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in PostNL history?
The PostNL company has achieved notable milestones throughout its history, evolving from its origins as the Dutch postal service to a significant player in the parcel delivery and mail services sectors. This evolution includes strategic acquisitions, expansions, and adaptations to changing market dynamics, solidifying its position in the competitive logistics landscape. For a deeper dive into the business operations, explore Revenue Streams & Business Model of PostNL.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2024 | Achieved a 6% improvement in average carbon efficiency, demonstrating a commitment to sustainability. |
| Q1 2025 | Reached 30% emission-free last-mile delivery, up from 26% in Q1 2024, through investments in electric vehicles. |
| January 1, 2025 | Transitioned non-USO business mail to a standard service level of 'within 2 days' to adapt to declining volumes. |
| April 2025 | Pim Berendsen succeeded Herna Verhagen as CEO, with Linde Jansen appointed as CFO, marking a leadership transition. |
PostNL has consistently embraced innovation to enhance its services and operational efficiency. A key focus has been on leveraging technology to streamline processes and improve customer experience.
Investing in companies like Prime Vision, which specializes in computer vision systems, has enabled advanced sorting processes. This has led to improvements in the speed and accuracy of mail and parcel handling.
Significant investment in electric vehicles and cleaner fuels has driven the expansion of emission-free last-mile delivery. This initiative aligns with sustainability goals and meets the growing demand for eco-friendly services.
Implementing measures like new electric towing devices and task rotation has been crucial. These efforts are designed to reduce physical strain on employees and improve overall working conditions.
Expanding the Out-of-Home strategy, particularly parcel locker deliveries, has been a key focus. Parcel locker deliveries surged by 150% compared to 2023, showcasing the effectiveness of this approach.
Focusing on yield management improvements has been a strategic response to margin pressures. This approach helps optimize pricing and resource allocation to maintain profitability.
Building on international opportunities, especially within its Spring intra-European activities, is a key focus. This expansion strategy aims to diversify revenue streams and increase market presence.
Despite its achievements, PostNL has faced significant challenges, especially in its mail division, which continues to experience volume declines. The company has had to adapt its strategies to navigate these difficulties and maintain its market position.
Mail volumes were down 8% in 2024 and 6.9% in Q1 2025, significantly impacting the mail division. This decline has put substantial pressure on margins, prompting strategic adjustments.
Accelerating client concentration in the parcel segment has put further pressure on margins. This has led to the implementation of yield management improvements and strategic initiatives.
The company sought government support to cover the costs of the universal postal service obligation (USO), requesting €30 million for 2025 and €38 million for 2026. This plea was rejected by the Dutch Ministry of Economic Affairs.
Considering further stamp price increases to offset rising costs is another challenge. These adjustments are necessary to maintain financial stability in the face of declining mail volumes.
The change in CEO, with Pim Berendsen succeeding Herna Verhagen, and the appointment of Linde Jansen as CFO, signals a need to navigate complex market dynamics. This transition aims to steer the company through current challenges.
Emptying mailboxes during the daytime instead of the evening is a strategic adaptation to declining mail volumes. This operational change reflects the need to optimize resources.
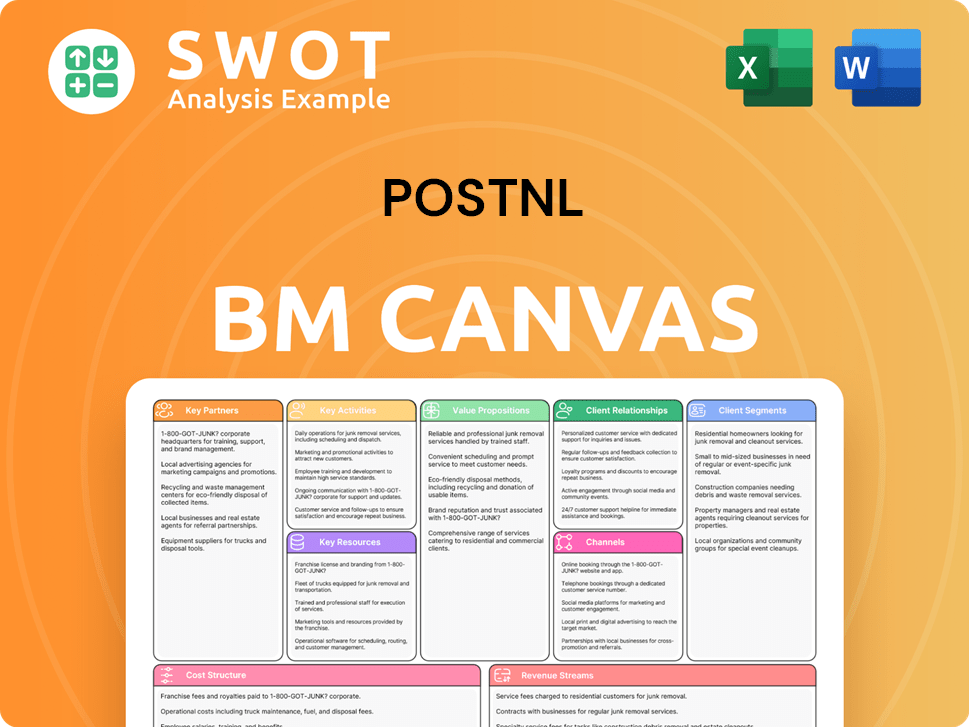
PostNL Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for PostNL?
The PostNL history is a story of evolution, beginning with the establishment of the Dutch postal service in 1799. Over the centuries, it has adapted to technological advancements and market changes, from the introduction of postage stamps in 1852 to the privatization and restructuring in the late 20th and early 21st centuries, culminating in its current form as a leading provider of mail services and parcel delivery.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1799 | Dutch postal services were reformed into a single, national system, marking the beginning of the company's long history. |
| 1850 | The Postal Act was passed, establishing postal delivery as a public service and codifying its domestic monopoly. |
| 1852 | The first postage stamp was issued in the Netherlands, a significant milestone in postal history. |
| 1886 | Postal system, telegraph, and telephone services were combined to form the PTT. |
| 1989 | PTT was privatized, and the postal service was renamed PTT Post. |
| 1998 | PTT Nederland split into Royal KPN and TNT Post Group (TPG), which was listed on multiple stock exchanges. |
| 2001 | TPG N.V. was officially renamed TNT N.V. |
| May 2011 | TNT N.V. was rebranded as PostNL N.V. following the separation of TNT Express. |
| 2024 | PostNL celebrated its 225th anniversary and achieved a 6% improvement in average carbon efficiency; revenue reached €3.25 billion, with normalized EBIT at €53 million. |
| January 1, 2025 | PostNL began transitioning non-USO business mail to a standard service level of 'within 2 days'. |
| February 3, 2025 | PostNL adjusted mailbox collection, emptying street mailboxes during the daytime instead of the evening. |
| April 15, 2025 | Pim Berendsen was appointed CEO of PostNL, succeeding Herna Verhagen, and Linde Jansen was appointed CFO. |
| May 6, 2025 | PostNL reported Q1 2025 results, with parcels revenue up 3.5% and mail volumes down 6.9%. |
PostNL's normalized EBIT is projected to remain in line with 2024 levels. Parcel volume growth is expected between 1% to 3%, while mail volumes are anticipated to decline by 8% to 10%. The company aims to achieve significant cost savings in its mail segment.
PostNL is focusing on yield management, expanding its European network, and growing its presence in Belgium. They are also accelerating their Out-of-Home delivery strategy, including expanding automated parcel lockers. Investments in sustainability and health and well-being are also a priority.
In early 2025, PostNL implemented changes to its mail service, including transitioning non-USO business mail to a two-day standard and adjusting mailbox collection times. These changes are part of ongoing efforts to optimize operations.
PostNL continues to engage with the Dutch government regarding the USO, seeking financial contributions to cover associated costs. The estimated costs are €30 million for 2025 and €38 million for 2026, highlighting the importance of government support for maintaining postal services.
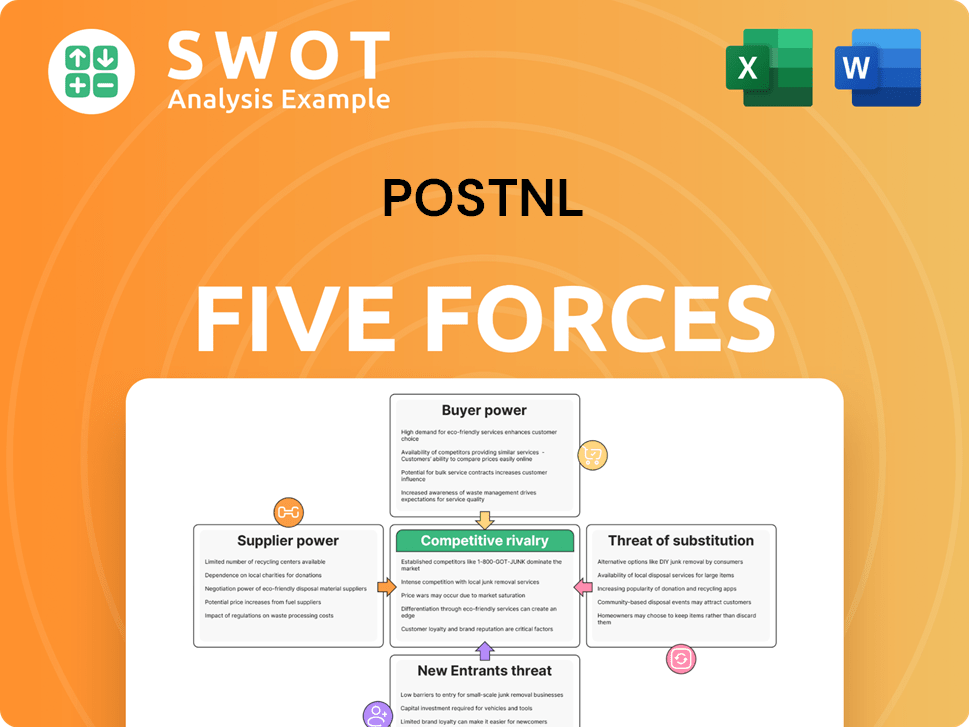
PostNL Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of PostNL Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of PostNL Company?
- How Does PostNL Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of PostNL Company?
- What is Brief History of PostNL Company?
- Who Owns PostNL Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of PostNL Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.