Quantum Bundle
How Has Quantum Company Evolved Over Time?
From revolutionizing PC storage to leading in unstructured data management, Quantum Company's journey is a testament to adaptability. Founded in 1980, its story is a compelling exploration of technological innovation and strategic pivots. Discover how this pioneer of data storage has navigated the ever-changing landscape of Quantum SWOT Analysis to remain a key player.

The Quantum computing history reveals a fascinating narrative of resilience and foresight. This Brief history will delve into the Quantum Company's early goals, key milestones, and the challenges it overcame. Understanding the Quantum technology and Early quantum computing landscape provides valuable insights into its present-day strategies and future prospects, highlighting the Quantum mechanics that shaped its evolution.
What is the Quantum Founding Story?
The story of the Quantum Company begins in February 1980. It was founded by a team of six individuals with a vision to revolutionize the hard disk drive market. Their goal was to create high-performance drives that were both cost-effective and less complex than existing solutions. This marked the beginning of a journey that would significantly impact the evolution of data storage.
The founders, James Patterson, David A. Brown, Richard Haughton, Barry A. Folsom, C. Norman Harrison, and Ken Medley, brought diverse expertise from companies like Shugart Associates, IBM, and Memorex. They saw an opportunity to innovate in a rapidly growing market. Their initial focus was on designing an 8-inch hard drive that could outperform existing models without the high costs associated with full closed-loop servo systems. This innovative approach set the stage for Quantum's early success.
The company's early business model centered on delivering these innovative hard drives to the market. In June 1980, Quantum secured crucial initial funding, raising $3 million from five venture capital groups. This early investment was pivotal in supporting the company's operations and research and development efforts. The first office was established at 2150 Bering Drive, San Jose, California, which became the company's initial base of operations.
Quantum's early years were marked by strategic partnerships and technological advancements.
- 1980: Quantum is founded with an initial focus on innovative hard disk drives.
- 1980: Secures $3 million in initial funding from venture capital.
- 1984: Forms a partnership with Matsushita Kotobuki Electronics (MKE, now Panasonic) to emphasize process engineering and automation.
- Early Focus: The primary goal was to design an 8-inch hard drive that could achieve high performance without the high cost and complexity of existing systems.
A significant partnership formed in 1984 with Matsushita Kotobuki Electronics (MKE, now Panasonic) highlighted Quantum's commitment to process engineering and automation. This collaboration was crucial for achieving unmatched quality and consistency in their products. This strategic decision allowed Quantum to differentiate itself in a competitive market, setting the stage for future innovations. Understanding the Target Market of Quantum is essential for appreciating its impact.
Quantum SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
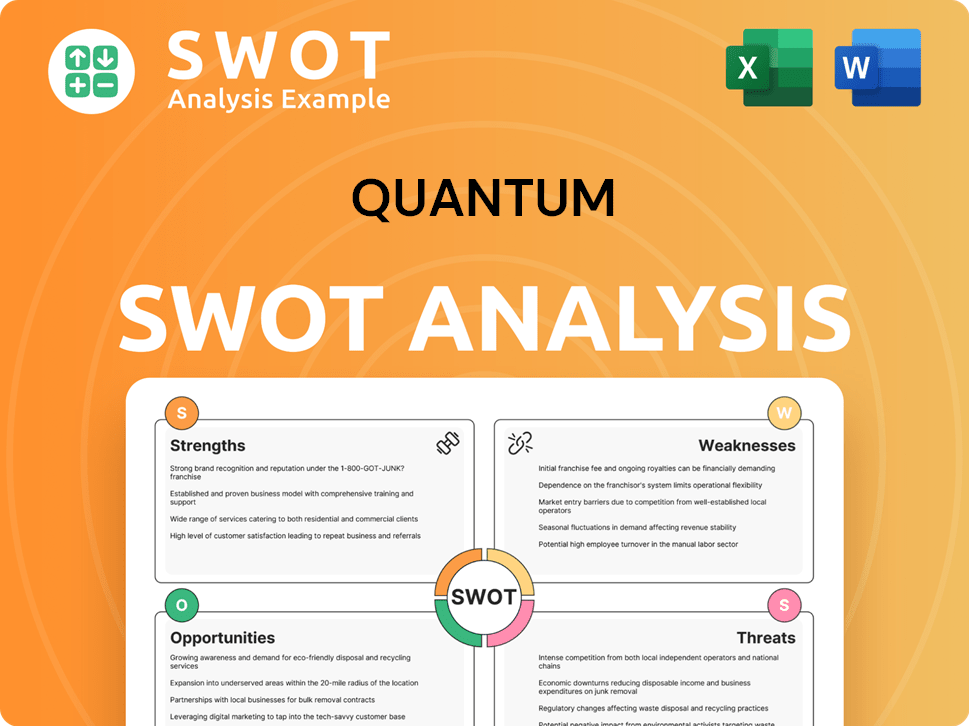
What Drove the Early Growth of Quantum?
The early years of the Quantum Company were marked by significant expansion and strategic shifts in the hard disk drive market. The company rapidly grew, establishing itself as a leader in the mid-capacity 5.25-inch drive market by 1984. This period saw the launch of a subsidiary, Plus Development, which focused on smaller form factors, a move that positioned the company well for future market trends. This Competitors Landscape of Quantum highlights the early strategic decisions.
By 1984, Quantum Company had become a leader in the mid-capacity 5.25-inch drive market. This early success set the stage for further innovation and expansion. The company's focus on smaller form factors, particularly through its subsidiary, Plus Development, proved to be a key strategic advantage.
In the 1990s, Quantum Company diversified beyond hard disk drives, expanding into tape storage solutions. This move was further solidified by the acquisition of Digital Equipment Corp's storage business in 1994, which added tape automation products to its portfolio. This diversification was crucial for adapting to changing market demands.
Quantum Company's financial growth was substantial, with sales increasing from $13.7 million in fiscal year 1982 to over $877.7 million by fiscal year 1990. The company's global footprint expanded, occupying over 2.3 million square feet of real estate worldwide. This growth was fueled by strategic acquisitions and market adaptation.
In 2001, Quantum Company made a pivotal decision to sell its hard disk drive business to concentrate on data protection and archive solutions. This strategic shift allowed the company to focus on emerging market opportunities and adapt to the evolving technological landscape. This transition marked a new phase in its development.
Quantum PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
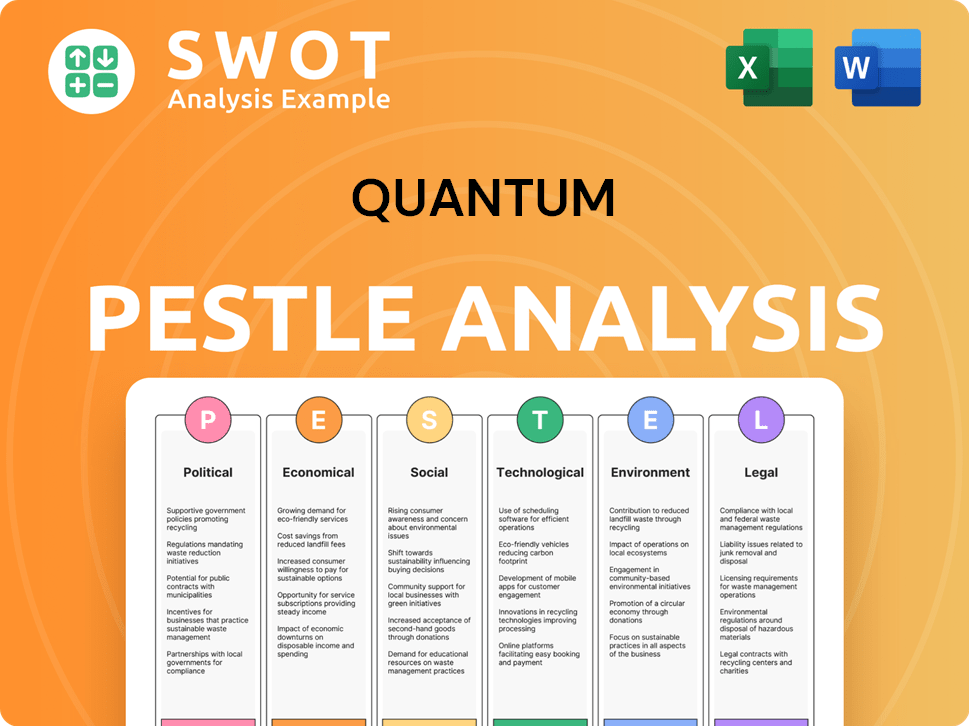
What are the key Milestones in Quantum history?
The history of Quantum Company is marked by significant milestones, showcasing its evolution and adaptation in the tech industry. From groundbreaking hard drive designs to advancements in data storage and AI solutions, Quantum has consistently pushed technological boundaries. This journey highlights the company's resilience and its commitment to innovation within a competitive market. To understand more about the financial aspects, you can explore Revenue Streams & Business Model of Quantum.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1980 | The founding team designed an 8-inch hard drive with high performance, without a full closed-loop servo system. |
| 2006 | Quantum introduced its DXi-Series products after acquiring Advanced Digital Information Corporation (ADIC), incorporating data deduplication technology. |
| September 2020 | Quantum, IBM, and Hewlett Packard Enterprise released specifications for LTO-9 storage tape technology. |
| April 2023 | Quantum announced Myriad, a new scale-out unstructured data storage platform. |
| May 2025 | Quantum announced LTO-10 support for its Scalar tape library systems, offering 30 TB native capacity per cartridge. |
| June 2025 | Hugues Meyrath was appointed as the new CEO. |
Quantum has consistently introduced innovative solutions throughout its history. A key innovation was the introduction of data deduplication technology with the DXi-Series, which provided significant data reduction ratios. More recently, the company has focused on software-defined storage and cloud solutions, including the Myriad platform for unstructured data.
In 1980, Quantum designed an 8-inch hard drive that achieved high performance without the complexity of a full closed-loop servo system. This innovation set an early standard for efficiency.
Following the acquisition of ADIC in 2006, Quantum introduced its DXi-Series products. These products incorporated data deduplication technology, offering data reduction ratios of approximately 15:1 or 93%.
Quantum has been at the forefront of tape storage advancements. Partnering with IBM and HPE to release specifications for LTO-9, and later LTO-10, demonstrating a commitment to high-capacity data storage solutions.
In April 2023, Quantum announced Myriad, a scale-out unstructured data storage platform. This software-defined platform is designed to run on public cloud infrastructure.
In May 2025, Quantum announced LTO-10 support for its Scalar tape library systems. This offers up to 30 TB native capacity per cartridge and up to 75 TB compressed.
Quantum has formed strategic partnerships to advance its technological capabilities. Collaborations with IBM and HPE on LTO tape technology have been crucial.
Despite its innovations, Quantum has faced several challenges, including market downturns and competitive pressures. The company has experienced revenue declines, with a reported $70.5 million in the fiscal second quarter of 2025, down from $75.7 million a year prior.
Quantum has navigated periods of economic uncertainty that have impacted its financial performance. These downturns have required strategic adjustments.
The company operates in a competitive market, facing challenges from other technology providers. Maintaining a competitive edge requires continuous innovation and adaptation.
Quantum has experienced revenue decreases in recent years, with $70.5 million in the fiscal second quarter of 2025. This is a decrease from $75.7 million a year earlier.
Operational challenges, including supply chain issues, have led to higher-than-anticipated backlogs. Addressing these issues is critical for maintaining operational efficiency.
Quantum has responded to challenges by shifting towards software-defined storage and cloud solutions. These strategic moves aim to align with evolving market demands.
In June 2025, Quantum announced leadership changes, with Hugues Meyrath appointed as the new CEO. This change aims to drive further progress toward growth initiatives.
Quantum Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
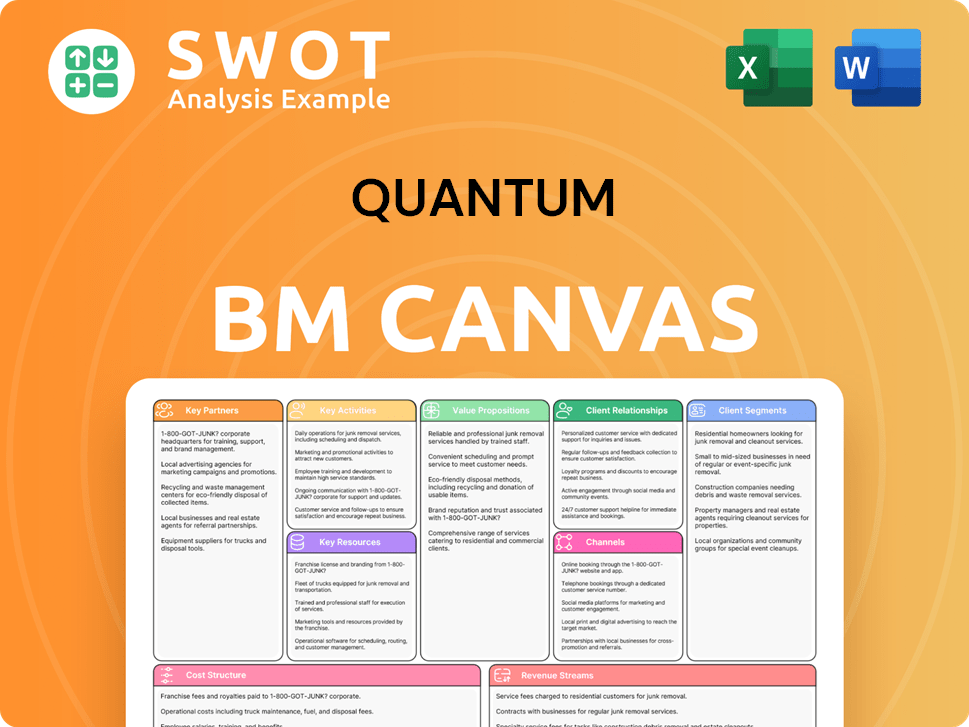
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Quantum?
The Owners & Shareholders of Quantum have witnessed a dynamic evolution since its inception. The company's journey, marked by significant acquisitions, strategic shifts, and technological advancements, showcases its resilience and adaptability in the ever-changing tech landscape.
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1980 | Quantum Corporation is founded in San Jose, California, marking the beginning of its journey in the tech industry. |
| 1982 | The company goes public, a pivotal moment in its early development. |
| 1984 | Quantum leads the market for mid-capacity 5.25-inch drives and launches Plus Development, also changing its name to Quantum Services. |
| 1989 | Quantum leads the compact drive market, solidifying its position in the storage solutions sector. |
| 1994 | Quantum acquires Digital Equipment Corp's storage business, expanding into tape automation. |
| 2001 | Quantum sells its hard disk drive business, focusing on data protection and archive solutions, reflecting a strategic shift. |
| 2006 | Quantum acquires Advanced Digital Information Corporation (ADIC), gaining Scalar tape libraries and other key technologies. |
| 2007 | Quantum discontinues DLT line development in favor of LTO technology. |
| 2017 | Quantum acquires assets of the Western Digital Active Archive business, expanding its object storage portfolio. |
| 2020 | Quantum celebrates its 40-year anniversary and releases LTO-9 specifications with IBM and Hewlett Packard Enterprise. |
| 2021 | Quantum acquires Pivot3 and EnCloudEn, enhancing its hyperconverged infrastructure. |
| 2023 | Quantum introduces the new unified data platform, MyQuantum, and announces Myriad, a new scale-out unstructured data storage platform. |
| April 2023 | Quantum announces Myriad, a new scale-out unstructured data storage platform. |
| February 2025 | Quantum reports fiscal third quarter 2025 revenue of $72.6 million. |
| May 2025 | Quantum announces LTO-10 support for its Scalar tape library systems. |
| June 2025 | Quantum appoints Hugues Meyrath as its new Chief Executive Officer. |
Quantum's future is strongly tied to the growing data volumes and the increasing need for efficient storage, especially for AI and unstructured data. The company is positioning itself to meet the evolving demands of AI-driven organizations.
The company aims to boost revenue quality and reduce debt to achieve increasing profitability and cash flow in the coming years. The shift to a subscription model is expected to boost recurring revenue and stabilize financial performance.
Quantum is committed to ongoing research and development to create cutting-edge storage technologies. The collaboration on the Myriad product with a leader in AI and quantum computing-inspired algorithms highlights this commitment.
Quantum anticipates revenue for the fiscal fourth quarter of 2025 to be approximately $66 million, plus or minus $2.0 million. Despite challenges such as debt and cash burn, the company's strategic focus aims to secure its future in the dynamic data storage market.
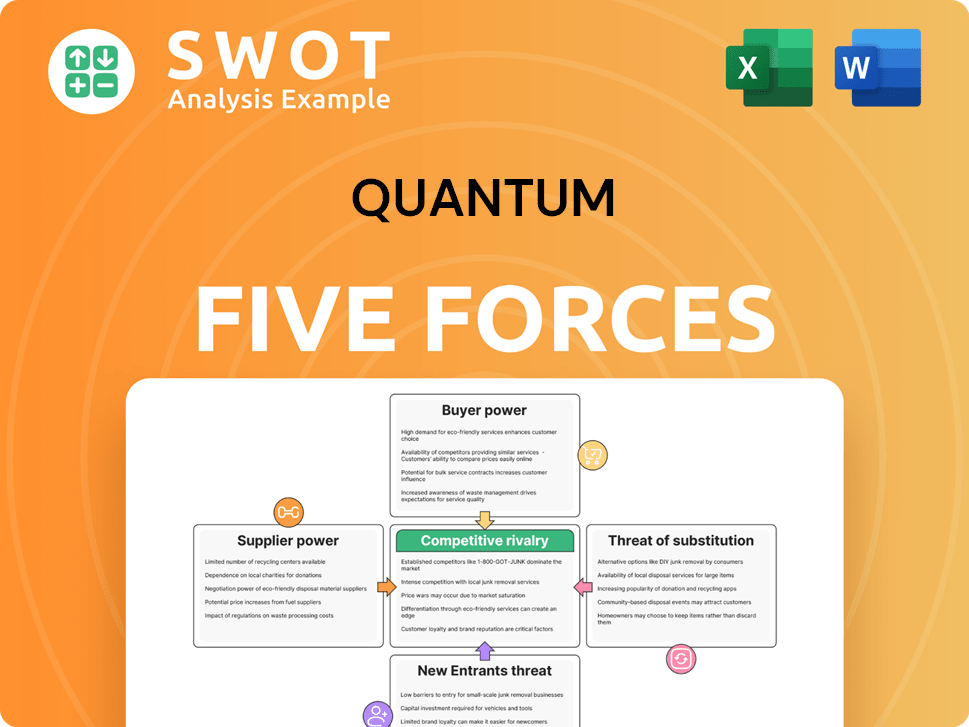
Quantum Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Quantum Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Quantum Company?
- How Does Quantum Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Quantum Company?
- What is Brief History of Quantum Company?
- Who Owns Quantum Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Quantum Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.