Spirit Airlines Bundle
What's the Story Behind Spirit Airlines?
Spirit Airlines, a name synonymous with budget travel, has a fascinating past shaped by innovation and financial turbulence. From its humble beginnings in 1983 as Charter One Airlines, the company has dramatically reshaped the Spirit Airlines SWOT Analysis landscape. This journey is a compelling case study of how a low-cost carrier can disrupt the airline industry.
The brief history of Spirit Airlines reveals a strategic evolution, from charter flights to becoming North America's largest ultra-low-cost carrier. Examining the Spirit Airlines company's early years, its business model, and its route expansion offers valuable insights into the competitive world of budget airlines. Understanding Spirit Airlines's journey provides a crucial context for investors and industry watchers alike, especially considering its recent restructuring and shift towards a more premium experience.
What is the Spirit Airlines Founding Story?
The story of Spirit Airlines begins in 1983, when Ned Homfeld established the company in Macomb County, Michigan. Initially, it operated under the name Charter One Airlines. This marked the beginning of what would evolve into a significant player in the airline industry.
Homfeld's vision was to provide affordable travel packages. These were aimed at casino gamblers and tourists looking to visit popular destinations. These destinations included Atlantic City, Las Vegas, and the Bahamas. This initial focus on tour services set the stage for the future.
In 1990, Charter One started leasing its own aircraft. This led to scheduled services from Boston and Providence, Rhode Island, to Atlantic City. The company then underwent a major transformation in May 1992. It changed its name to Spirit Airlines and acquired 13 McDonnell Douglas DC-9 aircraft. This transition marked a shift from charter services to a regular flight operator. The first route operated by its own fleet was between Detroit and Atlantic City.
Spirit Airlines' early focus on cost-effective travel was key.
- The company's business model was built on providing low-cost travel options.
- The economic context of the 1980s and early 1990s influenced the creation of a budget airline.
- The growing demand for leisure travel and increased access to air transportation played a role.
- Spirit Airlines' early focus on affordability laid the foundation for its ultra-low-cost carrier model.
Spirit Airlines SWOT Analysis
- Complete SWOT Breakdown
- Fully Customizable
- Editable in Excel & Word
- Professional Formatting
- Investor-Ready Format
What Drove the Early Growth of Spirit Airlines?
Following its rebranding as Spirit Airlines in 1992, the company experienced substantial early growth and expansion. This period saw the airline establish itself within the competitive airline industry, focusing on a budget-friendly approach. This strategy allowed Spirit to capture a significant portion of the market, evolving into a prominent low-cost carrier.
In April 1993, Spirit Airlines initiated scheduled flights to Florida, marking a key step in its route expansion. Over the next five years, the airline broadened its network, adding major cities like Los Angeles and New York. This strategic growth was crucial for establishing its presence in the airline industry.
By 1993, the airline's annual revenues had reached nearly $21 million, reflecting the early financial success of the Spirit Airlines company. This growth demonstrated the effectiveness of its strategy in the competitive budget airlines market. The expansion and revenue growth set the stage for future developments.
In 1999, Spirit Airlines relocated its headquarters from Detroit, Michigan, to Miami. The airline's fleet initially consisted of McDonnell Douglas MD-80s and DC-9s. The early 2000s saw the incorporation of Airbus A319s and A320s. This transition reflects the airline's adaptation to market demands.
A pivotal strategic shift occurred in 2007 when Spirit Airlines adopted the 'ultra-low-cost carrier' (ULCC) model. This involved eliminating traditional business class and introducing 'Big Front Seat' premium options. This strategic move, as explored in detail in the business model of Spirit Airlines, cemented its focus on unbundled fares and ancillary revenue.
Spirit Airlines PESTLE Analysis
- Covers All 6 PESTLE Categories
- No Research Needed – Save Hours of Work
- Built by Experts, Trusted by Consultants
- Instant Download, Ready to Use
- 100% Editable, Fully Customizable
What are the key Milestones in Spirit Airlines history?
The journey of Spirit Airlines, a prominent player in the airline industry, has been marked by significant milestones, innovative strategies, and considerable challenges. From its inception, the company has navigated the complexities of the low-cost carrier model, leaving a notable impact on the budget airlines landscape.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| Early 2000s | Spirit Airlines pioneered the ultra-low-cost carrier (ULCC) model in the United States, focusing on unbundled fares and optional services. |
| 2007 | Introduction of 'Big Front Seat' and the elimination of traditional business class, influencing pricing strategies across the industry. |
| 2024 | Filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection in November, following years of financial losses and failed merger attempts. |
| March 2025 | Emergence from bankruptcy, having reduced debt and secured significant equity investment, marking a strategic shift towards a more premium experience. |
Spirit Airlines has consistently sought to redefine air travel through innovative approaches. A key element of its strategy was the unbundling of fares, allowing for extremely low base prices and generating revenue through ancillary services. This approach, coupled with the introduction of new fare bundles like 'Go Savvy,' 'Go Comfy,' and 'Go Big,' aimed to attract a wider range of travelers and boost revenue.
Spirit Airlines pioneered the ultra-low-cost carrier (ULCC) model in the United States, focusing on unbundled fares and optional services.
The introduction of 'Big Front Seat' and the elimination of traditional business class, influencing pricing strategies across the industry.
New fare bundles like 'Go Savvy,' 'Go Comfy,' and 'Go Big,' aimed to attract a wider range of travelers and boost revenue.
The company has faced a series of significant challenges, particularly in recent years. Spirit Airlines reported losses exceeding $335 million in the first half of 2024, with total losses reaching $1.2 billion by the end of 2024, more than double the previous year's losses. These financial struggles, compounded by rising labor costs and engine recalls, led to the Chapter 11 bankruptcy filing in November 2024.
Spirit Airlines reported losses exceeding $335 million in the first half of 2024, with total losses reaching $1.2 billion by the end of 2024.
Filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection in November 2024, following years of financial losses and failed merger attempts.
A planned $3.8 billion merger with JetBlue Airways was blocked by a federal judge in January 2024 on antitrust grounds.
Increased labor costs in 2023 and 2024, and an expensive engine recall affecting its A320 Neos leading to fleet groundings.
Rising competition from other low-cost operators further intensified the financial strain on the company.
Emerging from bankruptcy in March 2025, having reduced its debt by approximately $795 million through debt-to-equity conversion.
The journey of Spirit Airlines is a testament to the volatile nature of the airline industry. To understand more about the company's core values, you can read this article about Mission, Vision & Core Values of Spirit Airlines.
Spirit Airlines Business Model Canvas
- Complete 9-Block Business Model Canvas
- Effortlessly Communicate Your Business Strategy
- Investor-Ready BMC Format
- 100% Editable and Customizable
- Clear and Structured Layout
What is the Timeline of Key Events for Spirit Airlines?
The Marketing Strategy of Spirit Airlines has evolved significantly since its founding. The
Spirit Airlines
history began in 1983 as Charter One Airlines, later transforming intoSpirit Airlines
in May 1992. Initially, the airline offered travel packages before transitioning to scheduled flights. A key milestone was the shift to an ultra-low-cost carrier (ULCC) model in the 2000s, a strategy that defined its operations. Despite financial struggles, including a net loss of $158 million in Q2 2024 and losses exceeding $335 million in H1 2024, the company emerged from Chapter 11 bankruptcy in March 2025. This restructuring involved reducing debt by $795 million and securing a $350 million equity investment.| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 1983 | Ned Homfeld founded Charter One Airlines, offering travel packages. |
| 1990 | Charter One began scheduled services from Boston and Providence to Atlantic City. |
| May 1992 | Charter One rebranded as Spirit Airlines and began operating flights with its own jet aircraft. |
| 1993 | Scheduled flights to Florida were introduced, and the airline continued to expand its network. |
| 1999 | Spirit Airlines relocated its headquarters to Miami. |
| 2007 | Spirit introduced the 'Big Front Seat' and eliminated traditional business class, solidifying its ULCC strategy. |
| 2019 | Spirit Airlines last reported a full-year profit. |
| Q2 2024 | Spirit Airlines reports a net loss of $158 million. |
| H1 2024 | Spirit reports losses exceeding $335 million. |
| August 2024 | Spirit introduces new fare bundles as part of a transformation strategy. |
| November 2024 | Spirit Airlines files for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection. |
| December 2024 | Spirit Airlines sells 23 Airbus aircraft as part of its restructuring process. |
| January 2025 | Spirit Airlines lays off 200 employees to reduce costs. |
| February 2025 | Spirit's plan of reorganization is confirmed by the U.S. Bankruptcy Court. |
| March 2025 | Spirit Airlines emerges from Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection, having reduced debt by $795 million and receiving a $350 million equity investment. |
| Q1 2025 | Spirit reports a net loss of nearly $143 million. |
Spirit Airlines is implementing a transformational strategy to return to profitability. This involves enhancing the guest experience and attracting a broader customer base. The goal is to increase revenue per passenger by up to 13%.
The airline plans to redefine its loyalty program. It is also exploring partnerships with other carriers. This strategic move aims to enhance customer engagement and expand market reach.
Spirit is focused on optimizing its network and adjusting capacity. Operational efficiency is a key priority. These efforts are designed to improve the airline's overall financial performance.
The
airline industry
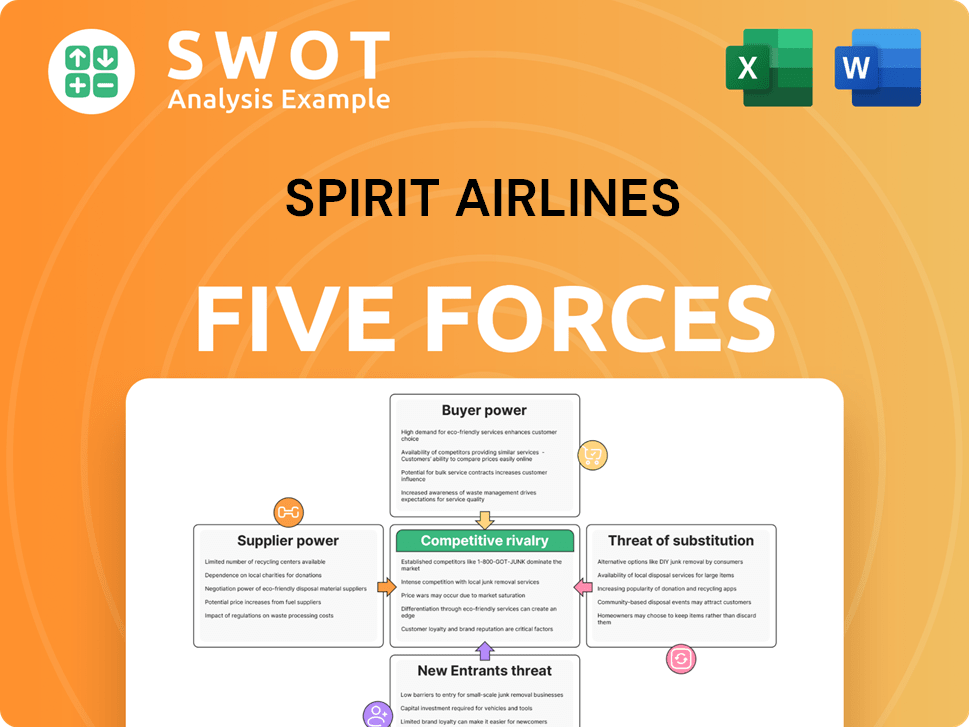
faces significant challenges, including intense competition. Gaining traction as a premium airline may be difficult. Leadership believes the restructuring and strategic initiatives will lead to long-term success.Spirit Airlines Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- Covers All 5 Competitive Forces in Detail
- Structured for Consultants, Students, and Founders
- 100% Editable in Microsoft Word & Excel
- Instant Digital Download – Use Immediately
- Compatible with Mac & PC – Fully Unlocked
Related Blogs
- What is Competitive Landscape of Spirit Airlines Company?
- What is Growth Strategy and Future Prospects of Spirit Airlines Company?
- How Does Spirit Airlines Company Work?
- What is Sales and Marketing Strategy of Spirit Airlines Company?
- What is Brief History of Spirit Airlines Company?
- Who Owns Spirit Airlines Company?
- What is Customer Demographics and Target Market of Spirit Airlines Company?
Disclaimer
All information, articles, and product details provided on this website are for general informational and educational purposes only. We do not claim any ownership over, nor do we intend to infringe upon, any trademarks, copyrights, logos, brand names, or other intellectual property mentioned or depicted on this site. Such intellectual property remains the property of its respective owners, and any references here are made solely for identification or informational purposes, without implying any affiliation, endorsement, or partnership.
We make no representations or warranties, express or implied, regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of any content or products presented. Nothing on this website should be construed as legal, tax, investment, financial, medical, or other professional advice. In addition, no part of this site—including articles or product references—constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any securities, franchises, or other financial instruments, particularly in jurisdictions where such activity would be unlawful.
All content is of a general nature and may not address the specific circumstances of any individual or entity. It is not a substitute for professional advice or services. Any actions you take based on the information provided here are strictly at your own risk. You accept full responsibility for any decisions or outcomes arising from your use of this website and agree to release us from any liability in connection with your use of, or reliance upon, the content or products found herein.